【torch】parameters与named_parameters的区别
【torch】parameters与named_parameters的区别
前言
为了详细的查看网络的结构参数等,因此本文研究一下 parameters()与 named_parameters 的区别。
此示例属于从
nn.Module中继承的成员函数。函数位于:[python环境路径]/lib/python3.8/site-packages/torch/nn/modules/module.py文件中。
简要解释说明
从名称上看,named_parameters 比 parameters 多了个 named ,已经能够显示出本质区别来了。
从返回的对象类型来看,parameters 返回的参数类型,named_parameters 返回的是元组,长度为2。其中第一维度为名称, 第二维度为参数类型。
parameters() 和 named_parameters() 都是 PyTorch 中用于获取模型参数的函数,但它们有一些区别:
parameters()返回一个生成器,用于迭代模型中的所有参数,每个参数都是一个torch.nn.Parameter类型对象;named_parameters()也返回一个生成器,用于迭代模型中的所有参数,但是每个参数都是一个元组,包含参数名称和torch.nn.Parameter类型对象。
完整代码示例
为了方便阐述,现提供完整的代码示例以增加读者对本质差异的深刻理解。该示例代码已在本地环境下进行了测试验证,如有任何问题,请在评论区留言并提供错误说明,以供改进。
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.init as init
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.nn.modules.batchnorm import _BatchNorm
class BaseClassifier(nn.Module):
def fresh_params(self, bn_wd):
if bn_wd:
return self.parameters()
else:
return self.named_parameters()
class MyClassifier(BaseClassifier):
def __init__(self):
super(MyClassifier, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(4, 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc1(x)
return x
model = MyClassifier()
# 返回模型的所有参数
params = model.fresh_params(True)
# 返回模型的所有命名 和 参数
named_params = model.fresh_params(False)
print(f"params: {params}, named_params: {named_params}")
for n in params:
print(f"type(n): {type(n)}, n.shape: {n.shape}")
for n in named_params:
print(f"type(n): {type(n)}, len(n): {len(n)}, n[0]: {n[0]}, n[1].shape: {n[1].shape}")
输出:
params: <generator object Module.parameters at 0x7f4f93399e40>, named_params: <generator object Module.named_parameters at 0x7f4f93399eb0>
type(n): <class 'torch.nn.parameter.Parameter'>, n.shape: torch.Size([16, 3, 3, 3])
type(n): <class 'torch.nn.parameter.Parameter'>, n.shape: torch.Size([16])
type(n): <class 'torch.nn.parameter.Parameter'>, n.shape: torch.Size([16])
type(n): <class 'torch.nn.parameter.Parameter'>, n.shape: torch.Size([16])
type(n): <class 'torch.nn.parameter.Parameter'>, n.shape: torch.Size([2, 4])
type(n): <class 'torch.nn.parameter.Parameter'>, n.shape: torch.Size([2])
type(n): <class 'tuple'>, len(n): 2, n[0]: conv1.weight, n[1].shape: torch.Size([16, 3, 3, 3])
type(n): <class 'tuple'>, len(n): 2, n[0]: conv1.bias, n[1].shape: torch.Size([16])
type(n): <class 'tuple'>, len(n): 2, n[0]: bn1.weight, n[1].shape: torch.Size([16])
type(n): <class 'tuple'>, len(n): 2, n[0]: bn1.bias, n[1].shape: torch.Size([16])
type(n): <class 'tuple'>, len(n): 2, n[0]: fc1.weight, n[1].shape: torch.Size([2, 4])
type(n): <class 'tuple'>, len(n): 2, n[0]: fc1.bias, n[1].shape: torch.Size([2])
截图:
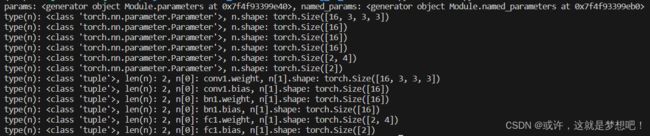
可以看到,named_parameters() 函数返回的不仅是参数本身,还包含了参数的名称。若需要获取参数的名称,建议使用 named_parameters() 函数。否则,可以使用 parameters() 函数。
参考文献
示例中的代码部分参考论文:
[1] JIA J, HUANG H, CHEN X, 等. Rethinking of Pedestrian Attribute Recognition: A Reliable Evaluation under Zero-Shot Pedestrian Identity Setting[M/OL]. arXiv, 2021[2023-06-30]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2107.03576. DOI:10.48550/arXiv.2107.03576.
代码位于:
@misc{BibEntry2023Oct,
title = {{Rethinking{ _ \_ _}of{ _ \_ _}PAR}},
year = {2023},
month = oct,
urldate = {2023-10-05},
language = {english},
note = {[Online; accessed 5. Oct. 2023]},
url = {https://github.com/valencebond/Rethinking_of_PAR}
}