代码随想录 Day13 二叉树 LeetCode T104 二叉树的最大深度 T111 二叉树的最小深度 T222完全二叉树的节点个数
以下题解的更详细思路来自于:代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)
前言
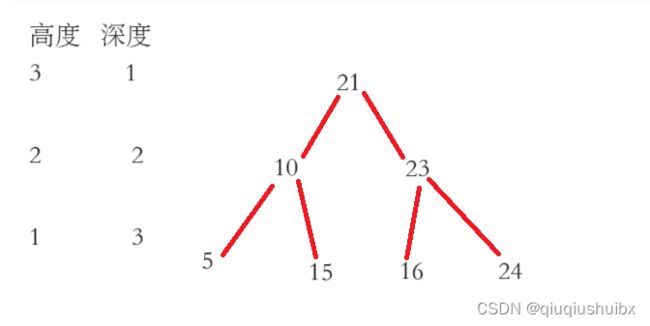
二叉树的高度与深度
这里先补充一下二叉树深度和高度的概念
高度:二叉树中任意一个节点到叶子结点的距离
深度:二叉树中任意一个节点到根节点的距离
下面给出一个图便于理解
获取高度与深度的遍历方式
高度:后序遍历
深度:前序遍历
那么为什么是这两种方式呢?
高度:(从下往上计数)后序遍历可以获取左右子树的高度最后返回给父节点
深度:(从上往下计数)往下遍历一个我们就加1,也符合求深度的过程,前序遍历刚好可以满足需求
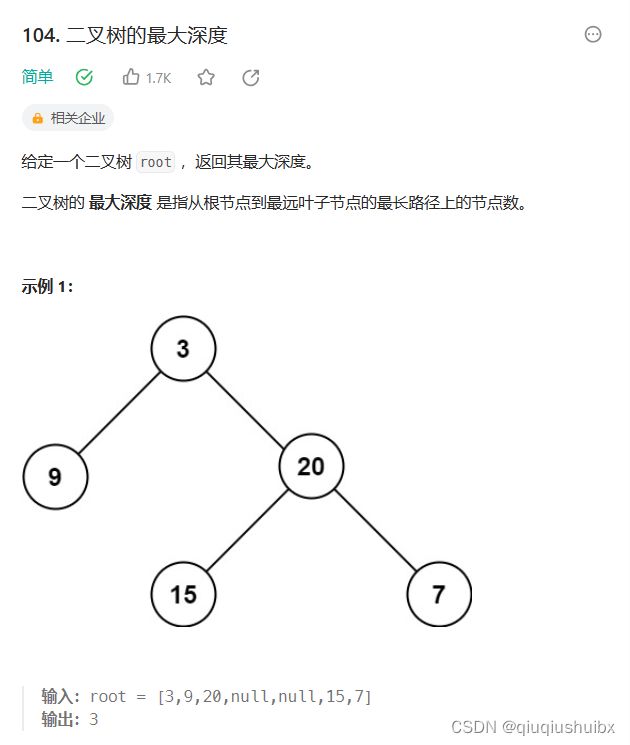
LeetCode T104 二叉树的最大深度
题目链接:104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目思路:
首先我要说的是,这道题虽然是求最大深度,但是前序遍历和后序遍历都可以解决问题,这里我们选择使用后序遍历解决问题,有人会问,刚刚不是说前序遍历更好解决深度问题吗,为什么使用后序遍历呢?这是因为最大深度就是二叉树的根节点的高度, 这里我们将最大深度转化为了根节点 的高度来求解,我们仍然采用递归去求解,分三步.
1.确定返回值和参数类型
int getHeight(TreeNode node)2.确定递归结束条件
if(node == null) { return 0; }3.确定单层递归的代码
int leftHeight = getHeight(node.left); int rightHeight = getHeight(node.right); int height = leftHeight>rightHeight?leftHeight+1:rightHeight+1; return height;
题目代码:
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root);
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode node)
{
if(node == null)
{
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(node.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(node.right);
int height = leftHeight>rightHeight?leftHeight+1:rightHeight+1;
return height;
}
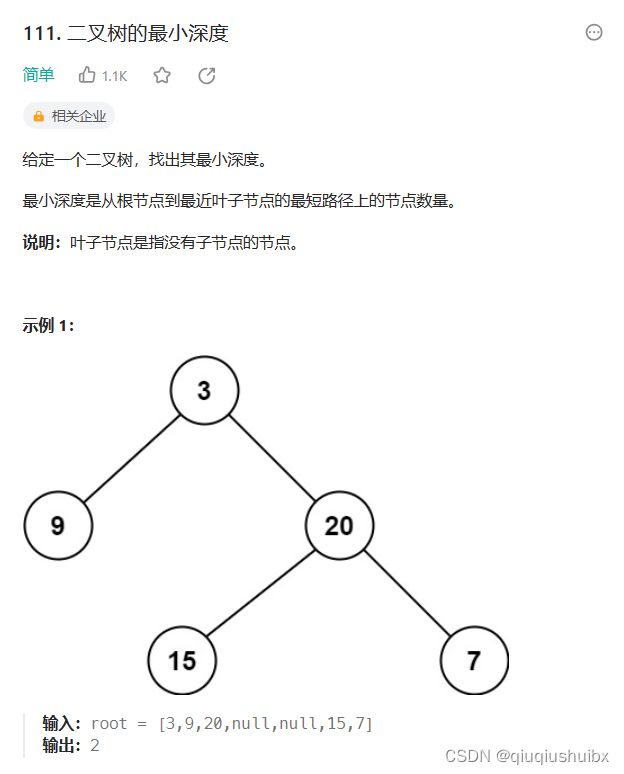
}LeetCode T111 二叉树的最小深度
题目链接:111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目思路:
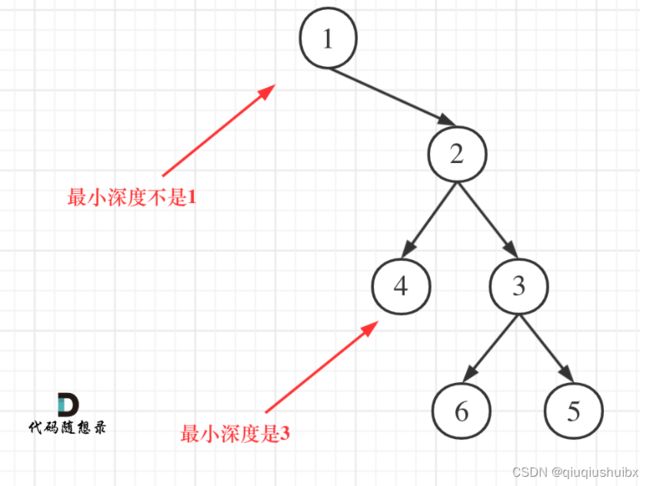
这题我们也能延续上题的思想,不过需要做特殊的处理,我们这里同样使用后序遍历来解决问题,但是要注意不是在上题的基础上把最大值改成最小值即可,因为这里我们是从叶子节点到根节点的距离,这里假设我们左子树为空,用上题的求最大深度的思路解决问题就会发现不成立,如果依据上题的思路这里的最小深度就为1,而实际上这题的最小深度是3,这里我们开始递归三部曲
1.确定参数和返回值
public int getHeight(TreeNode node)2.确定递归结束条件
if(node == null) { return 0; }3.确定单层递归逻辑
int rightHeight = getHeight(node.right); int leftHeight = getHeight(node.left); if(node.left == null && node.right != null) { return rightHeight+1; } if(node.left != null && node.right == null) { return leftHeight+1; } return leftHeight>rightHeight?rightHeight+1:leftHeight+1;这里我们要考虑某个子树为空而另一个子树不为空的情况,我们去返回不为空的子树+1
题目代码:
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root);
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode node)
{
if(node == null)
{
return 0;
}
int rightHeight = getHeight(node.right);
int leftHeight = getHeight(node.left);
if(node.left == null && node.right != null)
{
return rightHeight+1;
}
if(node.left != null && node.right == null)
{
return leftHeight+1;
}
return leftHeight>rightHeight?rightHeight+1:leftHeight+1;
}
}LeetCode T222 完全二叉树的节点个数
题目链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
题目思路:
这里我们知道对于满二叉树,我们的节点数是2^(深度-1)次方,由此我们可以判断如果左边递归到底的深度等于右边递归到底的深度,那么就可以使用这个公式计算,这样也减少了对中间节点的遍历.我们继续进行递归三部曲(后序遍历)
1.返回值和形参列表
public int getNum(TreeNode node)2.终止条件
if(node == null) { return 0; } int leftDepth=0,rightDepth = 0; TreeNode left = node.left; TreeNode right = node.right; while(right != null) { right = right.right; leftDepth++; } while(left != null) { left = left.left; leftDepth++; } if(leftDepth == rightDepth) { return (2>>leftDepth)-1; }3.一层递归逻辑
int leftnum= getNum(node.left); int rightnum = getNum(node.right); int result = leftnum + rightnum+1; return result;
题目代码:
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
return getNum(root);
}
public int getNum(TreeNode node)
{
//终止条件
if(node == null)
{
return 0;
}
int leftDepth=0,rightDepth = 0;
TreeNode left = node.left;
TreeNode right = node.right;
while(right != null)
{
right = right.right;
leftDepth++;
}
while(left != null)
{
left = left.left;
leftDepth++;
}
if(leftDepth == rightDepth)
{
return (2>>leftDepth)-1;
}
int leftnum= getNum(node.left);
int rightnum = getNum(node.right);
int result = leftnum + rightnum+1;
return result;
}
}