spring 事务源码阅读
开启事务
使用@EnableTransactionManagement注解开启事务
该注解会引入TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector类,然后该类导入两个类AutoProxyRegistrar和ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration。
1、添加bean后置处理器
AutoProxyRegistrar类的作用是注册InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类,InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator是Spring中实现AOP代理的关键组件,它会扫描所有的Advisor(通知器),并将其与BeanFactory中的Bean进行匹配,以决定是否需要为该Bean创建AOP代理。
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 继承AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 继承AbstractAutoProxyCreator,实现SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryAware接口。
是一个bean后置处理器
public class InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator extends AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator {
@Nullable
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
protected void initBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.initBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
protected boolean isEligibleAdvisorBean(String beanName) {
return (this.beanFactory != null && this.beanFactory.containsBeanDefinition(beanName) &&
this.beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName).getRole() == BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
}
}
代理的创建在上一篇AOP源码阅读中有说过就是在后置处理器的after方法寻找合适的advisor进行创建代理。上面的源码看到InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator只是重写了initBeanFactory方法用来获取beanfacotry和isEligibleAdvisorBean方法用来判断是否是合适的bean。
2、引入Advisor
TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector引入的另一个类是ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration,该类代码也不多,如下
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource, TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor) {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor(TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource) {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration类主要引入BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor通知类。并为其TransactionAttributeSource和TransactionInterceptor两个属性赋值。该类实现了Advisor接口,是一个PointcutAdvisor类型的Advisor,用来匹配@Transaction注解。具体如何匹配下面结合源码说。
代理创建
1、获取所有Advisor
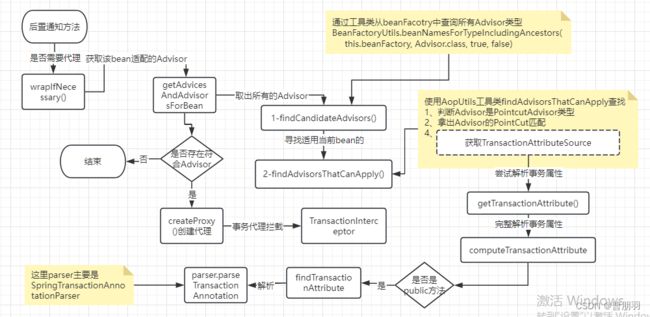
在AbstractAutoProxyCreator的后置出来器afater方法里还是会调用wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey)来判断当前bean是否需要包装代理。然后会调用getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName)方法尝试获取适用于该bean的advice。这个方法在AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 中实现
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
//获取符合条件的advisor
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//获取候选的所有advisor
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
//获取适用于当前bean的advisor
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
findCandidateAdvisors()方法还是在该类中实现,使用了一个BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper工具类进行获取Advisor
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findCandidateAdvisors
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans();
}
BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper#findAdvisorBeans
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;
if (advisorNames == null) {
//从beanfacotry总获取所有的Advisor
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
if (advisorNames.length == 0) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : advisorNames) {
if (isEligibleBean(name)) {//调用isEligibleBean判断bean是否满足基本条件
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
}
}
return advisors;
}
这里看到Advisor的获取是直接从beanFacotry中查找Advisor.class类型的beanDef,这样就能找到我们最开始通过import导入的BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor。这和上一篇说的AOP的Aspect方式有一些区别(扫描所有的bean,反射解析@Aspect注解)。
2、寻找匹配的Advisor
找到所有的Advisor后下一步就是逐个判断是否适用于当前bean
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);
try {
return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);
}
finally {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);
}
}
AopUtils#findAdvisorsThatCanApply
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
//这里不是IntroductionAdvisor类型的不会进入循环
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
//进入canApply方法判断
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
AopUtils#canApply
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {//走这里
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
最开始说过我们引入的advisor是一个PointcutAdvisor类型。所以会进入第二个if分支。拿出pointcut进行匹配。这里的advisor是BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例,器pointcut是TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut类型实例。下一个重载canApply方法主要匹配逻辑是下面代码
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
//...
//这里返回的matcher还是TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut本身
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
//拿出class所有方法与matcher进行匹配
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
主要的匹配逻辑是methodMatcher.matches,也就是
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut#matches
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
//获取TransactionAttributeSource,这是最开始在引入Advisor设置的
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
这里TransactionAttributeSource是最开始引入由ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration类内部设置的,其实例类型是AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource ,该类继承 AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource。getTransactionAttribute()方法在其父类中
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#getTransactionAttribute
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {//Object类方法跳过
return null;
}
// First, see if we have a cached value.
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
TransactionAttribute cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {//先从缓存获取,如果没有解析
// Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute,
// or an actual transaction attribute.
if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) {
return null;
}
else {
return cached;
}
}
else {
// 解析当前方法事务属性
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
// Put it in the cache.
if (txAttr == null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE);
}
else {
String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass);
if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) {
DefaultTransactionAttribute dta = (DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr;
dta.setDescriptor(methodIdentification);
dta.resolveAttributeStrings(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr);
}
return txAttr;
}
}
解析实际方法是computeTransactionAttribute()
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
//step1 判断方法必须是public方法
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
// The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class.
// If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged.
Method specificMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
//step2 解析方法事务属性
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Second try is the transaction attribute on the target class.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
if (specificMethod != method) {
// Fallback is to look at the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// Last fallback is the class of the original method.
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
}
return null;
}
step2处findTransactionAttribute()方法解析事务属性,该方法是AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource类实现,其调用determineTransactionAttribute(method)方法。
AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource#determineTransactionAttribute
protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement element) {
for (TransactionAnnotationParser parser : this.annotationParsers) {
TransactionAttribute attr = parser.parseTransactionAnnotation(element);
if (attr != null) {
return attr;
}
}
return null;
}
这里拿出所有的annotationParsers进行解析方法是否定义事务。annotationParsers是在AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource的构造方法初始化,这里有两个SpringTransactionAnnotationParser和JtaTransactionAnnotationParser。我们主要看SpringTransactionAnnotationParser。
SpringTransactionAnnotationParser#parseTransactionAnnotation
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement element) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotationAttributes(
element, Transactional.class, false, false);
if (attributes != null) {
return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
终于看到熟悉的Transactional注解了,也不往方法里面看了。这里就是解析@Transactional注解配置的事务属性。
3、事务管理
代理创建和AOP过程一致,这里还是以JDK代理类为例。代理对象是JdkDynamicAopProxy。原方法的执行会首先进入JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke方法。
这里还是从invoke的获取拦截器链开始
List chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
最后会调到
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(3);
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {//会走这里
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
}
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {//这是Aspect的情况
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
}
return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[0]);
}
这里要回到开始ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration引入Advisor引入的地方
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor(
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource, TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor) {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
//设置的advisor是TransactionInterceptor类型
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
if (this.enableTx != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
所以最后会调用TransactionInterceptor的invoke方法
TransactionInterceptor#invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new CoroutinesInvocationCallback() {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
return invocation.getThis();
}
@Override
public Object[] getArguments() {
return invocation.getArguments();
}
});
}
最后事务的控制在invokeWithinTransaction方法完成。
总结
开启事务为我们引入了两个重要的
1、BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor事务Advisor。设置两个属性TransactionInterceptor用来代理管理事务,TransactionAttributeSource用来匹配事务方法。
1、InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator是bean后置处理器,用来判断当前bean是否需要代理。会拿出第一步引入的事务Advisor,与当前bean的所有方法进行匹配看是否有@Transaction注解。有就创建代理,最后使用BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor中设置的TransactionInterceptor拦截器进行事务管理。