More types: structs, slices, and maps Part2
1.Slices are like references to arrays
A slice does not store any data, it just describes a section of an underlying array.
Changing the elements of a slice modifies the corresponding elements of its underlying array.
Other slices that share the same underlying array will see those changes.
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
names := [4]string{
"John",
"Paul",
"George",
"Ringo",
}
fmt.Println(names)
a := names[0:2]
b := names[1:3]
fmt.Println(a, b)
b[0] = "XXX"
fmt.Println(a, b)
fmt.Println(names)
}
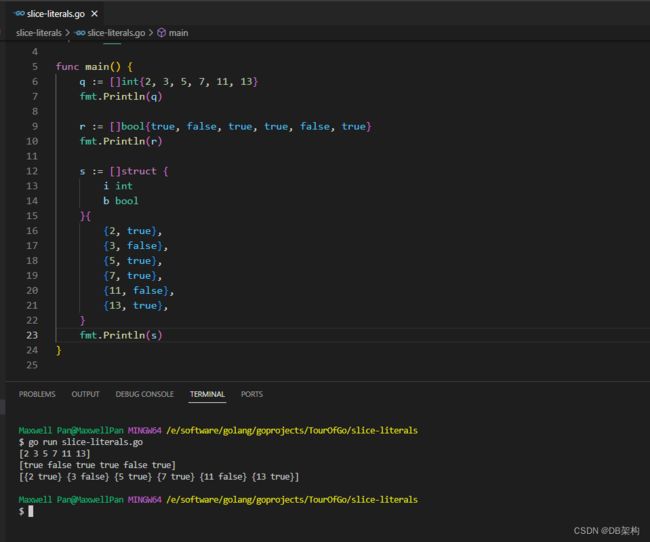
2.Slice literals
A slice literal is like an array literal without the length.
This is an array literal:
[3]bool{true, true, false}
And this creates the same array as above, then builds a slice that references it:
[]bool{true, true, false}
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
q := []int{2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13}
fmt.Println(q)
r := []bool{true, false, true, true, false, true}
fmt.Println(r)
s := []struct {
i int
b bool
}{
{2, true},
{3, false},
{5, true},
{7, true},
{11, false},
{13, true},
}
fmt.Println(s)
}
3.Slice defaults
When slicing, you may omit the high or low bounds to use their defaults instead.
The default is zero for the low bound and the length of the slice for the high bound.
For the array
var a [10]int
these slice expressions are equivalent:
a[0:10] a[:10] a[0:] a[:]
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s := []int{2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13}
s = s[1:4]
fmt.Println(s)
s = s[:2]
fmt.Println(s)
s = s[1:]
fmt.Println(s)
}
4.Slice length and capacity
A slice has both a length and a capacity.
The length of a slice is the number of elements it contains.
The capacity of a slice is the number of elements in the underlying array, counting from the first element in the slice.
The length and capacity of a slice s can be obtained using the expressions len(s) and cap(s).
You can extend a slice's length by re-slicing it, provided it has sufficient capacity. Try changing one of the slice operations in the example program to extend it beyond its capacity and see what happens.
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s := []int{2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13}
printSlice(s)
// Slice the slice to give it zero length.
s = s[:0]
printSlice(s)
//Extend its length
s = s[:4]
printSlice(s)
// Drop its first two values.
s = s[2:]
printSlice(s)
}
func printSlice(s []int) {
fmt.Printf("len=%d cap=%d %v\n", len(s), cap(s), s)
}
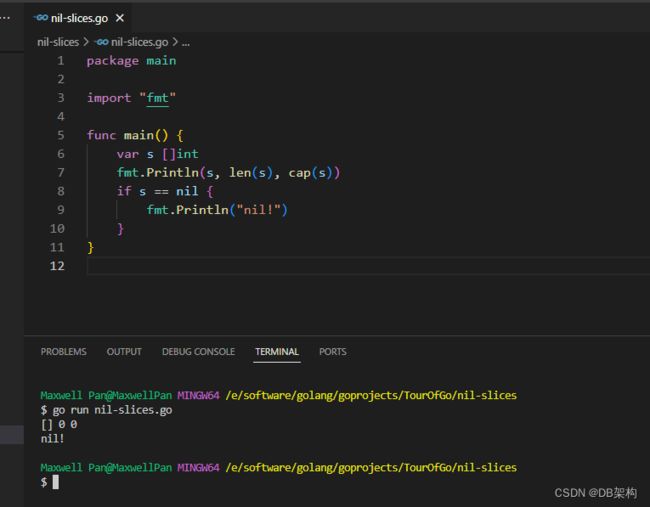
5.Nil slices
The zero value of a slice is nil.
A nil slice has a length and capacity of 0 and has no underlying array.
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var s []int
fmt.Println(s, len(s), cap(s))
if s == nil {
fmt.Println("nil!")
}
}
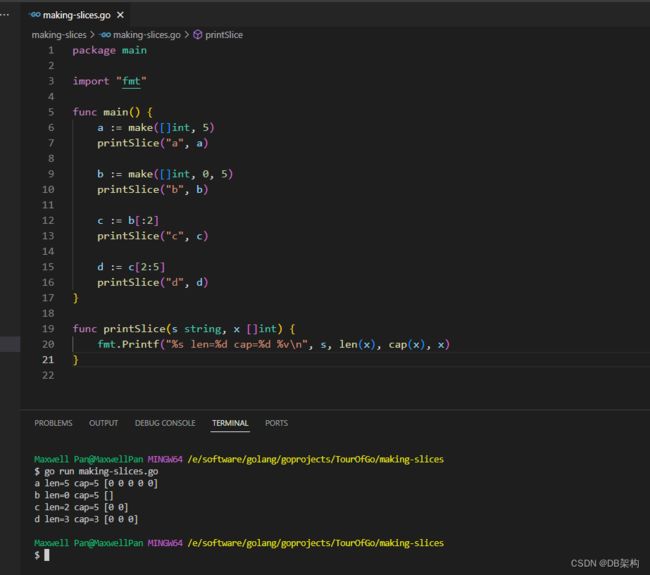
6.Creating a slice with make
Slices can be created with the built-in make function; this is how you create dynamically-sized arrays.
The make function allocates a zeroed array and returns a slice that refers to that array:
a := make([]int, 5) // len(a)=5
To specify a capacity, pass a third argument to make:
b := make([]int, 0, 5) // len(b)=0, cap(b)=5 b = b[:cap(b)] // len(b)=5, cap(b)=5 b = b[1:] // len(b)=4, cap(b)=4
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
a := make([]int, 5)
printSlice("a", a)
b := make([]int, 0, 5)
printSlice("b", b)
c := b[:2]
printSlice("c", c)
d := c[2:5]
printSlice("d", d)
}
func printSlice(s string, x []int) {
fmt.Printf("%s len=%d cap=%d %v\n", s, len(x), cap(x), x)
}