【C语言】C语言小项目—贪吃蛇
目录
- 一、ncurse图形库的介绍
- 二、ncurse上下左右键的获取
- 三、地图规划
- 四、显示贪吃蛇身子的第一个节点
- 五、显示贪吃蛇完整身子
- 六、贪吃蛇向右移动
- 七、贪吃蛇撞墙死
- 八、实现贪吃蛇四方向的风骚走位(引入Linux线程)
- 九、贪吃蛇吃饭
- 十、贪吃蛇撞墙和咬死自己代码优化
- 十一、程序全部源码
游戏说明:Linux环境——基于Ncurse图形库的C语言小游戏
一、ncurse图形库的介绍
贪吃蛇最为一款游戏,它使通过人操作键盘控制蛇身走位实现游戏效果的,所以按键响应必然少不了。在我们以前接触过的关于C语言按键响应方面的东西中,我们知道,C语言自带的 s c a n f scanf scanf 、 g e t c h a r getchar getchar 和 g e t s gets gets 等库函数接收键盘输入的话,必须按下相应的键,再按下回车才能完成接收,很显然,这对于一款游戏是很不友好的,所以我们就要通过 n c u r s e ncurse ncurse 库来引入比较实用的按键响应功能,它封装了一个库,不需要按下回车,就能够接收键盘的各种响应。
n c u r s e ncurse ncurse 的应用很广泛,尤其是再Linux内核开发方面,但是由于它图形交互界面不友好,早已淡出舞台,甚至体验感玩爆 n c u r s e ncurse ncurse 的C图形库GTK、C++图形库QT也趋于落伍,如今的嵌入式设备大部分都跑上了安卓系统。
如何使用 n c u r s e ncurse ncurse 呢?我们看下图,这是在Linux环境下的一段代码,解释了 n c u r s e ncurse ncurse 最基本的操作:

编译 n c u r s e ncurse ncurse 程序:( n c u r s e ncurse ncurse 非C自带的库函数,所以编译的时候要加上)

#include当我们运行程序以后,按下 k k k 键,运行结果如图:
由此可见它对于接收键盘响应的强大之处。
二、ncurse上下左右键的获取
在上面我们对于 n c u r s e ncurse ncurse 库有了大致的了解,但是,它如何捕获上下左右键来实现我们贪吃蛇游戏的效果呢?对于 c u r s e curse curse 来说,系统库函数为上下左右键安排了几个值,如下:

由于直接对上下左右键编码会对代码的理解很不友好,所以它的头文件对它们采用了宏定义。下面我们编写代码实现上下左右键的获取:
#include运行程序,当按下上下左右键后,运行结果为:
三、地图规划
- 地图规划:
大小:20X20
地图竖直方向上的边界 : “|”
地图竖直方向上的边界 : “–”
贪吃蛇的身子:“[]”
贪吃蛇的食物:“##”

编程实现:
#include四、显示贪吃蛇身子的第一个节点
在上面,我们通过循环的方式打印出了地图,这种打印类似于扫描,只有通过这种方式,贪吃蛇的身子才可以随时被插到地图中去。那么贪吃蛇身子如何显示呢?为了方便身子的移动和增加,在这里我们使用结构体和链表的形式去定义贪吃蛇身子:
- 贪吃蛇身子的特点:
- 行坐标
- 列坐标
- 下一个节点的位置(地址/指针)
struct Snake
{
int row;
int col;
struct Snake *next;
}
- 贪吃蛇身子的显示:
如何显示蛇身子的一个节点:
设该节点:行坐标为2,列坐标为2
if(row == x.row && col == x.col){
printw("[]");
}
编程实现:
#include
五、显示贪吃蛇完整身子
贪吃蛇身子的显示关键在于多个节点如何构成一条蛇,关键在于节点坐标系的关系,如图:
横坐标不变,纵坐标累加,这样就能显示一条水平的蛇身,我们需要在动态绘制(循环扫描)地图的同时将蛇身打印出来,这里我们采用遍历蛇身链表的方式来实现蛇身的绘制。

将这里的判断条件进行函数的封装:(遍历链表)
int hasSnake(int i, int j)
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
while(p != NULL){
if(i == p->row && j == p->col){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
蛇身初始化函数:(创建链表)
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new = (struct Snake*)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
new->row = tail->row;
new->col = tail->col+1;
new->next = NULL;
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
void initSnake()
{
head = (struct Snake*)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
head->next =NULL;
head->row = 2;
head->col = 2;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
}
相关代码整合后如下:
#include六、贪吃蛇向右移动
上面我们实现了贪吃蛇蛇身的显示,但要实现贪吃蛇向右移动,我们必须对蛇身链表进行增删操作,即向右移动一步,蛇身向右增加一个节点,蛇尾删除一个节点:
void deleteNode()
{
struct Snake *p; //p用来释放删除的节点空间
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p); //释放删除的节点
}
接下来封装蛇身向右移动函数:
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
deleteNode();
}
主函数中需要不断检测按键输入,检测到右方向键输入以后需要调用蛇身移动函数并不断更新:
注意:这里需要在地图绘制函数中加上move(0,0),作用是让光标始终定位在起始位置,实现画面更新的覆盖:

主函数:
int main()
{
int con;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamePic();
while(1){ //不断检测键盘输入
con = getch();
if(con == KEY_RIGHT){
moveSnake();
gamePic(); //每移动一次,画面刷新,实现蛇身动态行走
}
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
以上代码整合以后如下:
#include七、贪吃蛇撞墙死
贪吃蛇小游戏规定,蛇头撞墙蛇死,游戏重新开始。在我们绘制的蛇身中,蛇头作为链表尾,自然需要我们去判断蛇头是否于上下左右四个边界重合,当发生重合的时候,我们则需要重新初始化蛇身,游戏重新开始,编程如下:(代码中的 $tail$ 指的是链表尾,链表尾作为蛇头,链表头作为蛇尾)
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
deleteNode();
if(tail->row == 0 || tail->col == 0 || tail->row == 20 || tail->col == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
当重新初始化蛇身的时候,势必会产生旧蛇身产生的内存垃圾,这时候就需要我们把旧蛇身所占用的内存空间释放掉,相关代码如下:
void initSnake()
{
struct Snake *p = head;
while(head != NULL){ //遍历旧蛇身,释放所有内存
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
head = (struct Snake*)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
head->next =NULL;
head->row = 1;
head->col = 1;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
}
以上代码全部整合以后如下:
#include运行结果:
八、实现贪吃蛇四方向的风骚走位(引入Linux线程)
以上我们实现了贪吃蛇键盘控制移动并且撞墙复活,但是需要我们考虑的是贪吃蛇必须自己游走并且键盘控制转向,接下来我们一起来探讨以下这个问题:
首先我们考虑以下贪吃蛇的自由行走,这就需要我们在主函数中更改贪吃蛇按键检测相关代码:
int main()
{
int con;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamePic();
while(1){
moveSnake();
gamePic();
refresh(); //不断刷新界面
usleep(100000); //给100ms延迟
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
接下来我们考虑一下贪吃蛇不断游走,键盘不断检测按键输入改变贪吃蛇走向,这无非是在上面代码的基础上加入我们首先介绍的键盘检测输入的代码,相关代码可以这样写:
int main()
{
int con;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamePic();
while(1){
moveSnake();
gamePic();
refresh(); //不断刷新界面
usleep(100000); //给100ms延迟
}
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_DOWN:
printw("DOWN\n");
break;
case KEY_UP:
printw("UP\n");
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
printw("LEFT\n");
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
printw("RIGHT\n");
break;
}
}
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
很容易看出,代码中出现了两个 w h i l e while while 循环,按照C程序逻辑,这个程序运行的结果只能是卡在其中一个 w h i l e while while 循环中不能跳出,所以这就阻碍了游戏效果的实现。在这里我们引入线程的概念。(线程在之后的Linux系统编程中有详细讲解,在这里不做深入讨论,只将其用法)
线程(英语:thread)是操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位。线程是独立调度和分派的基本单位。
既然这样,我们就有思路让这两个循环一起循环,就是创建两个线程,让着两个线程一起执行两个 w h i l e while while 循环。在这里,我们将这两个循环进行函数封装,再分别传给两个线程,现在让我们看一下代码:
刷新界面函数:
void* refreshInterface()
{
while(1){
moveSnake();
gamePic();
refresh();
usleep(100000);
}
}
改变方向函数:
void* changeDir()
{
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_DOWN:
printw("DOWN\n");
break;
case KEY_UP:
printw("UP\n");
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
printw("LEFT\n");
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
printw("RIGHT\n");
break;
}
}
}
主函数:
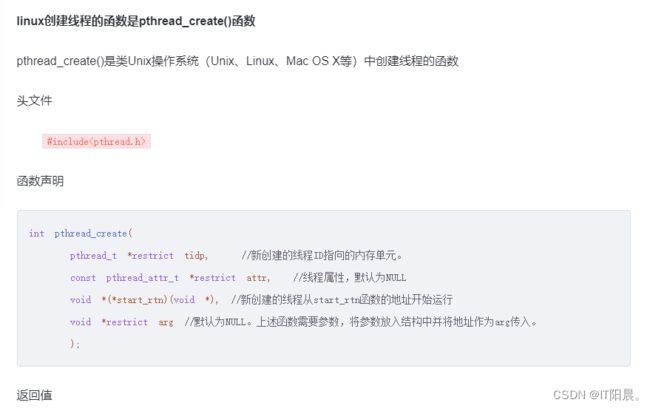
int main()
{
pthread_t t1; //线程描述符
pthread_t t2;
initNcurse();
initSnake();
gamePic();
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, refreshInterface, NULL); //创建线程t1,链接刷新界面函数
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, changeDir, NULL); //创建线程t2,链接改变方向函数
while(1); //卡住程序不退出
getch();
endwin();
return 0;
}
接下来我们将方向改变和界面刷新结合在一起,这样的话我们就需要定义一个变量 d i r dir dir 去记录方向的改变,借助方向的状态去实现转向。
定义方向变量 d i r dir dir ,用来存储方向状态:(采用宏定义的形式使代码更易读)
#define UP 1
#define DOWN 2
#define LEFT 3
#define RIGHT 4
int dir; //全局变量,方便检测方向状态
键盘接收方向,改变状态变量:
void* changeDir()
{
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_DOWN:
dir = DOWN;
printw("DOWN\n");
break;
case KEY_UP:
dir = UP;
printw("UP\n");
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
dir = LEFT;
printw("LEFT\n");
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
dir = RIGHT;
printw("RIGHT\n");
break;
}
}
}
捕获方向的状态,改变节点增加方向:
void addNode()
{
struct Snake *new = (struct Snake*)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
switch(dir){
case UP:
new->row = tail->row-1;
new->col = tail->col;
new->next = NULL;
break;
case DOWN:
new->row = tail->row+1;
new->col = tail->col;
new->next = NULL;
break;
case LEFT:
new->row = tail->row;
new->col = tail->col-1;
new->next = NULL;
break;
case RIGHT:
new->row = tail->row;
new->col = tail->col+1;
new->next = NULL;
break;
}
tail->next = new;
tail = new;
}
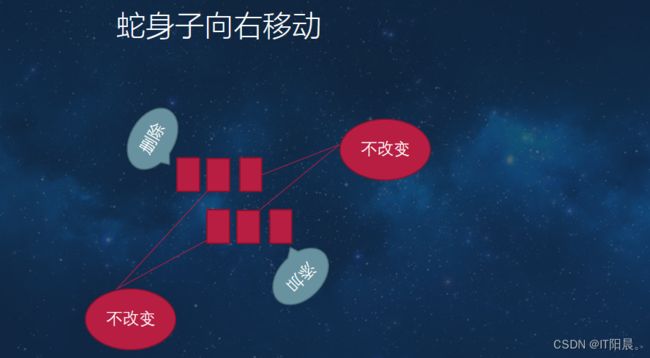
以上的代码基本上实现了贪吃蛇四个方向的走位,但是经过运行以后还存在一些问题,就是当贪吃蛇向右游走时,我们按下左方向键,贪吃蛇会向左走,这样与游戏的规则可能会发生一些冲突,因为蛇会咬死自己,所以我们对以上的代码进行以下优化,利用绝对值的方式避免相反方向的改变:
首先改一下宏定义:
#define UP 1
#define DOWN -1
#define LEFT 2
#define RIGHT -2
封装一个判断贪吃蛇是否反向游走的函数:
void turnDir(int direction)
{
if(abs(dir) != abs(direction)){
dir = direction;
}
}
更改一下方向改变的机制:
void* changeDir()
{
while(1){
key = getch();
switch(key){
case KEY_DOWN:
turnDir(DOWN);
printw("DOWN\n");
break;
case KEY_UP:
turnDir(UP);
printw("UP\n");
break;
case KEY_LEFT:
turnDir(LEFT);
printw("LEFT\n");
break;
case KEY_RIGHT:
turnDir(RIGHT);
printw("RIGHT\n");
break;
}
}
}
由于考虑到这样优化后可能会出现程序崩溃,所以我们在 n c u r s e ncurse ncurse 初始化的时候添加 n o e c h o ( ) noecho() noecho() 函数来避免按键等无关信息的显示,使程序更健壮:
void initNcurse()
{
initscr();
keypad(stdscr,1); //keyboard acception
noecho();
}
这样我们的代码就全部优化完毕,我们整合以下全部代码:
#include运行结果:
初始状态:
按下向下键:
按下向左键:
按下向上键:
九、贪吃蛇吃饭
关于贪吃蛇的食物,食物关心的是位置及符号,位置同样可以使用贪吃蛇节点结构体,食物我们使用 ‘##’ 去显示。
用贪吃蛇节点结构体定义食物结构体,食物初始化函数,食物坐标采用随机数取余的方式取地图坐标框内的坐标:
struct Snake food;
void initFood()
{
int x = rand()%20; //随机取20以内的数
int y = rand()%20; //随机取20以内的数
food.row = x;
food.col = y;
}
初始化蛇身的同时,初始化食物:
void initSnake()
{
dir = RIGHT;
struct Snake *p = head;
while(head != NULL){
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
initFood(); //食物在这里初始化
head = (struct Snake*)malloc(sizeof(struct Snake));
head->next =NULL;
head->row = 1;
head->col = 1;
tail = head;
addNode();
addNode();
}
定义食物检测函数,方便在地图刷新绘制过程中打印食物位置:
int hasFood(int i, int j)
{
if(i == food.row && j == food.col){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
在蛇身移动函数中增加蛇头碰到食物以后蛇身增长的条件,这里我们采用不删除蛇尾的的方式去实现这个功能:(代码中的 $tail$ 指的是链表尾,链表尾作为蛇头,链表头作为蛇尾)
蛇头和食物坐标重合,食物消失初始化并且不删除蛇尾(等同于增加蛇长),不重合则按平时运行。
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
if(hasFood(tail->row, tail->col)){
initFood();
}else
{
deleteNode();
}
if(tail->row == 0 || tail->col == 0 || tail->row == 20 || tail->col == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
整合以上代码,实现贪吃蛇吃食物的功能:
#include运行结果:
吃食物前:
吃食物后:
十、贪吃蛇撞墙和咬死自己代码优化
直到现在,我们要实现的功能基本都已经实现,但是还存在一些小问题,第一个问题就是蛇无法走到第一行边界,第二个问题就是蛇无法自己咬死自己,下面我们针对这两个问题进行解决:
首先,蛇无法走到上边界是因为我们定义的地图的第一行两行符号,一行是上边界,第二行就是第一对竖线,所以我们可以针对蛇撞墙复活的代码可以这样优化:
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
if(hasFood(tail->row, tail->col)){
initFood();
}else
{
deleteNode();
}
if(tail->row < 0 || tail->col == 0 || tail->row == 20 || tail->col == 20){
initSnake();
}
}
将蛇撞到上边界的条件缩小为tail->row < 0,这样蛇就可以走进上边界。
其次关于蛇咬死自己,我们可以封装一个判断蛇是否死亡的函数,将撞墙和咬死自己两种情况整合在一起判断蛇是否死亡:
int ifSnakeDie()
{
struct Snake *p;
p = head;
if(tail->row < 0 || tail->col == 0 || tail->row == 20 || tail->col == 20){
return 1;
}
while(p->next != NULL){
if(p->row == tail->row && p->col == tail->col){
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
这里采用遍历链表的形式判断蛇头是否和蛇身重合从而判断是否死亡。(代码中的 $tail$ 指的是链表尾,链表尾作为蛇头,链表头作为蛇尾)
更改蛇身初始化函数:
void moveSnake()
{
addNode();
if(hasFood(tail->row, tail->col)){
initFood();
}else
{
deleteNode();
}
if(ifSnakeDie()){
initSnake();
}
}
相关代码整合如下:
#include运行结果:
咬死自己:
复活:
撞上边界:
复活:
十一、程序全部源码
#include
以上就是关于Linux环境下的C语言贪吃蛇小游戏的全部学习流程,多多交流多多分享。
一辈子很短,努力的做好两件事就好;第一件事是热爱生活,好好的去爱身边的人;第二件事是努力学习,在工作中取得不一样的成绩,实现自己的价值,而不是仅仅为了赚钱;