杂记一:rocksdb架构及其java读写api
1、架构
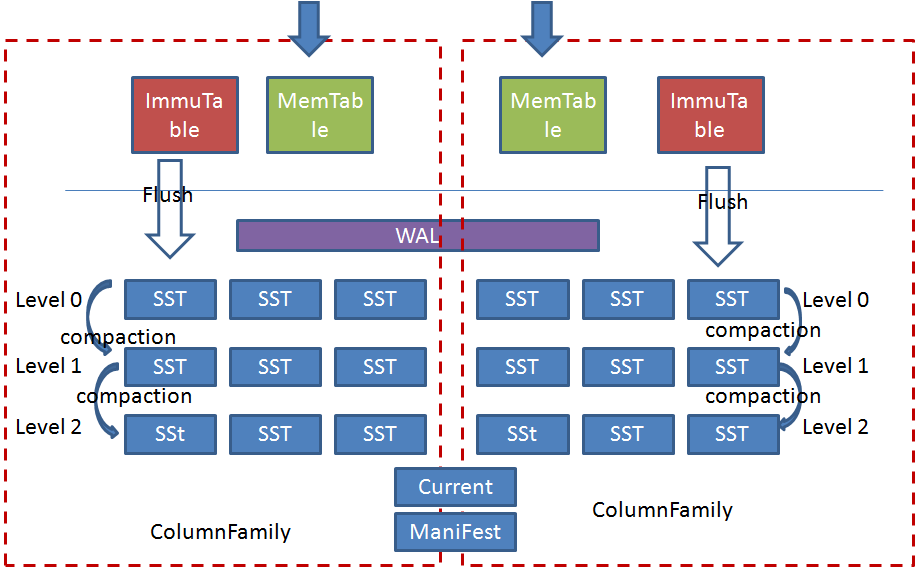
Rocksdb中引入了ColumnFamily(列族, CF)的概念,所谓列族也就是一系列kv组成的数据集。所有的读写操作都需要先指定列族。
写操作先预写日志(Write-Ahead Logging(WAL)),再写memtable,memtable达到一定阈值后切换为Immutable Memtable,只能读不能写。
后台Flush线程负责按照时间顺序将Immutable Memtable刷盘,生成level0层的有序文件(SST)。后台合并线程负责将上层的SST合并生成下层的SST。
Manifest负责记录系统某个时刻SST文件的视图,Current文件记录当前最新的Manifest文件名。
每个ColumnFamily有自己的Memtable,SST文件,所有ColumnFamily共享WAL、Current、Manifest文件。
架构分析
整个系统的设计思路很好理解,这种设计的优势很明显,主要有以下几点:
1.所有的刷盘操作都采用append方式,这种方式对磁盘和SSD是相当有诱惑力的;
2.写操作写完WAL和Memtable就立即返回,写效率非常高。
3.由于最终的数据是存储在离散的SST中,SST文件的大小可以根据kv的大小自由配置,因此很适合做变长存储。
但是这种设计也带来了很多其他的问题:
1.为了支持批量和事务以及上电恢复操作,WAL是多个CF共享的,导致了WAL的单线程写模式,不能充分发挥高速设备的性能优势(这是相对介质讲,相对B树等其他结构还是有优势);
2.读写操作都需要对Memtable进行互斥访问,在多线程并发写及读写混合的场景下容易形成瓶颈。
3.由于Level0层的文件是按照时间顺序刷盘的,而不是根据key的范围做划分,所以导致各个文件之间范围有重叠,再加上文件自上向下的合并,读的时候有可能需要查找level0层的多个文件及其他层的文件,这也造成了很大的读放大。尤其是当纯随机写入后,读几乎是要查询level0层的所有文件,导致了读操作的低效。
4.针对第三点问题,Rocksdb中依据level0层文件的个数来做前台写流控及后台合并触发,以此来平衡读写的性能。这又导致了性能抖动及不能发挥高速介质性能的问题。
5.合并流程难以控制,容易造成性能抖动及写放大。尤其是写放大问题,在笔者的使用过程中实际测试的写放大经常达到二十倍左右。这是不可接受的,当前我们也没有找到合适的解决办法,只是暂时采用大value分离存储的方式来将写放大尽量控制在小数据。
适用场景
1.对写性能要求很高,同时有较大内存来缓存SST块以提供快速读的场景;
2.SSD等对写放大比较敏感以及磁盘等对随机写比较敏感的场景;
3.需要变长kv存储的场景;
4.小规模元数据的存取;
不适合场景
1.大value的场景,需要做kv分离;
2.大规模数据的存取
2、rockdb的java读写api
package com.kk;
import org.rocksdb.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class RocksDBTest {
private static final String dbPath = "E:\\defaultCF";
private static final String cfdbPath = "E:\\CertainCF";
public static void main(String[] args) throws RocksDBException {
RocksDBTest t=new RocksDBTest();
t.testDefaultColumnFamily();
t.testCertainColumnFamily();
}
static {
RocksDB.loadLibrary();
}
// RocksDB.DEFAULT_COLUMN_FAMILY 默认列族
public void testDefaultColumnFamily() throws RocksDBException {
System.out.println("testDefaultColumnFamily begin...");
// 文件不存在,则先创建文件
final Options options = new Options().setCreateIfMissing(true);
final RocksDB rocksDB = RocksDB.open(options, dbPath);
// 简单key-value
byte[] key = "FirstKey".getBytes();
rocksDB.put(key, "FirstValue".getBytes());
System.out.println(new String(rocksDB.get(key)));
rocksDB.put("SecondKey".getBytes(), "SecondValue".getBytes());
// 通过List做主键查询
List<byte[]> keys = Arrays.asList(key, "SecondKey".getBytes(), "missKey".getBytes());
Map<byte[], byte[]> values = rocksDB.multiGet(keys);
for (int i = 0; i < keys.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("multiGet " + new String(keys.get(i)) + ":" + (values.get(keys.get(i)) != null ? new String(values.get(keys.get(i))) : null));
}
// 打印全部[key - value]
RocksIterator iter = rocksDB.newIterator();
for (iter.seekToFirst(); iter.isValid(); iter.next()) {
System.out.println(new String(iter.key()) + ":" + new String(iter.value()));
}
// 删除一个key
rocksDB.delete(key);
System.out.println("after remove key:" + new String(key));
iter = rocksDB.newIterator();
for (iter.seekToFirst(); iter.isValid(); iter.next()) {
System.out.println(new String(iter.key()) + ":" + new String(iter.value()));
}
}
// 使用特定的列族打开数据库,可以把列族理解为关系型数据库中的表(table)
public void testCertainColumnFamily() throws RocksDBException {
System.out.println("\ntestCertainColumnFamily begin...");
final ColumnFamilyOptions cfOpts = new ColumnFamilyOptions().optimizeUniversalStyleCompaction();
String cfName = "my-first-columnfamily";
// list of column family descriptors, first entry must always be default column family
final List<ColumnFamilyDescriptor> cfDescriptors = Arrays.asList(
new ColumnFamilyDescriptor(RocksDB.DEFAULT_COLUMN_FAMILY, cfOpts),
new ColumnFamilyDescriptor(cfName.getBytes(), cfOpts));
List<ColumnFamilyHandle> cfHandles = new ArrayList<>();
final DBOptions dbOptions = new DBOptions().setCreateIfMissing(true).setCreateMissingColumnFamilies(true);
final RocksDB rocksDB = RocksDB.open(dbOptions, cfdbPath, cfDescriptors, cfHandles);
ColumnFamilyHandle cfHandle = cfHandles.stream().filter(x -> {
try {
return (new String(x.getName())).equals(cfName);
} catch (RocksDBException e) {
return false;
}
}).collect(Collectors.toList()).get(0);
// 写入key/value
String key = "FirstKey";
rocksDB.put(cfHandle, key.getBytes(), "FirstValue".getBytes());
// 查询单key
byte[] getValue = rocksDB.get(cfHandle, key.getBytes());
System.out.println(new String(getValue));
// 写入第2个key/value
rocksDB.put(cfHandle, "SecondKey".getBytes(), "SecondValue".getBytes());
List<byte[]> keys = Arrays.asList(key.getBytes(), "SecondKey".getBytes());
List<ColumnFamilyHandle> cfHandleList = Arrays.asList(cfHandle, cfHandle);
// 查询多个key
Map<byte[], byte[]> values = rocksDB.multiGet(cfHandleList, keys);
for (int i = 0; i < keys.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("multiGet:" + new String(keys.get(i)) + ":" + (values.get(keys.get(i)) == null ? null : new String(values.get(keys.get(i)))));
}
// 删除单key
rocksDB.delete(cfHandle, key.getBytes());
RocksIterator iter = rocksDB.newIterator(cfHandle);
for (iter.seekToFirst(); iter.isValid(); iter.next()) {
System.out.println(new String(iter.key()) + ":" + new String(iter.value()));
}
for (final ColumnFamilyHandle columnFamilyHandle : cfHandles) {
columnFamilyHandle.close();
}
}
}
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/cobbliu/articles/9553271.html