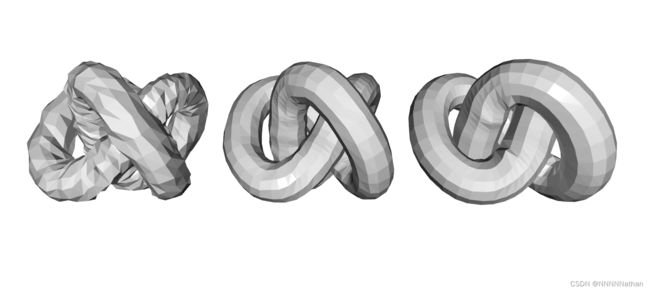『OPEN3D』1.2 mesh处理 python篇
目录
1.mesh IO与可视化
2.mesh表面法线估计
3.mesh裁减与上色
4. open3d中的utility类和函数
5.mesh属性
6.mesh滤波
1 Aerage filter:
2 Laplacian filter
3 Taubin filter
7.mesh采样
8.网格细分(mesh subdivision)
8.1 subdivide_midpoint
8.2 subdivide_loop
9.网格简化(Mesh simplification)
9.1 simplify_vertex_clustering
9.2 simplify_quadric_decimation
10.mesh聚类
1.mesh IO与可视化
mesh的读取比较简单,基本与点云的读取参数设置一直,使用read_triangle_mesh即可读取ply文件的mesh文件,下面介绍以下write_triangle_mesh。
| filename | 保存的mesh的文件名 |
| mesh | 要保存的mesh文件对象-> open3d.geometry.TriangleMesh |
| write_ascii | 是否以ascii的形式保存,默认为二进制保存 |
| compressed | 是否压缩保存的mesh文件,默认为否 |
| write_vertex_normals | 是否写入mesh的法线信息,默认为真 |
| write_vertex_colors | 是否写入mesh中顶点的颜色信息,默认为真 |
| write_triangle_uvs | 是否写入三角面片的uvs坐标,默认为真 |
| print_progress | 是否在控制台输出进度信息,默认为假 |
import open3d as o3d
if __name__ == "__main__":
knot_data = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
print(f"Reading mesh from file: knot.ply stored at {knot_data.path}")
mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(filename=knot_data.path,
enable_post_processing=True,
print_progress=True)
print(mesh)
print("Saving mesh to file: copy_of_knot.ply")
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh])
o3d.io.write_triangle_mesh(filename="copy_of_knot.ply",
mesh=mesh,
write_ascii=False,
compressed=False,
write_vertex_normals=False,
write_vertex_colors=False,
write_triangle_uvs=False,
print_progress=True,
)
TriangleMesh类中的数据项包括vertices、triangles等都可以使用numpy进行直接进行内存访问。
knot_mesh = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh.path)
print('Vertices:')
print(np.asarray(mesh.vertices))
print('Triangles:')
print(np.asarray(mesh.triangles))2.mesh表面法线估计
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
import copy
if __name__ == "__main__":
knot_mesh = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
mesh: o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh.path)
print("Displaying mesh without normals ...")
# Invalidate existing normals.
mesh.triangle_normals = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(np.zeros((1, 3)))
print("normals: \n", np.asarray(mesh.triangle_normals))
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh])
print("Computing normals and rendering it ...")
mesh_normal = copy.deepcopy(mesh)
mesh_normal.compute_vertex_normals()
# mesh.compute_triangle_normals()
print("normals: \n", np.asarray(mesh_normal.triangle_normals))
mesh_normal.translate([200,0,0])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh, mesh_normal])
下图中左边是没有法线的情况,右图是拥有法线的情况;有法线之后,可以使用Phong shading给mesh进行渲染。
3.mesh裁减与上色
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import copy
if __name__ == '__main__':
knot_mesh = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
mesh: o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh.path)
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
print("We make a partial mesh of only the first half triangles.")
mesh_crop = copy.deepcopy(mesh)
"""
将原mesh转换成numpy对象后进行截取,
并通过o3d中的工具函数与numpy数据进行交互转换成
TriangleMesh对应的类型
"""
mesh_crop.triangles = o3d.utility.Vector3iVector(
np.asarray(mesh_crop.triangles)[:len(mesh_crop.triangles) // 2, :])
mesh_crop.triangle_normals = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(
np.asarray(mesh_crop.triangle_normals)[:len(mesh_crop.triangle_normals) // 2, :])
print(mesh_crop.triangles)
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh1])
print("Painting the mesh")
mesh_color = copy.deepcopy(mesh_crop)
mesh_color.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 1])
mesh_crop.translate([200,0,0])
mesh_color.translate([400,0,0])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh, mesh_color, mesh_crop])4. open3d中的utility类和函数
| DoubleVector |
Convert float64 numpy array of shape 将形状(n,)的float64 numpy数组转换为Open3D格式。 |
| IntVector |
Convert int32 numpy array of shape 将形状(n,)的int32 numpy数组转换为Open3D格式。 |
| Matrix3dVector |
Convert float64 numpy array of shape 将形状(n,3,3)的float64 numpy数组转换为Open3D格式。 |
| Matrix4dVector |
Convert float64 numpy array of shape 将形状(n,4,4)的float64 numpy数组转换为Open3D格式。 |
| Vector2dVector |
Convert float64 numpy array of shape 将形状(n,2)的float64 numpy数组转换为Open3D格式。 |
| Vector2iVector |
Convert int32 numpy array of shape 将形状(n,2)的int32 numpy数组转换为Open3D格式。 |
| Vector3dVector |
Convert float64 numpy array of shape 将形状(n,3)的float64 numpy数组转换为Open3D格式。 |
| Vector3iVector |
Convert int32 numpy array of shape 将形状(n,3)的int32 numpy数组转换为Open3D格式。 |
| Vector4iVector |
Convert int numpy array of shape 将形状(n,4)的int numpy数组转换为Open3D格式。 |
| VerbosityContextManager |
A context manager to temporally change the verbosity level of Open3D 临时更改Open3D详细级别的上下文管理器,1.1中已经讲过。 |
| VerbosityLevel |
Enum class for VerbosityLevel. VerboseLevel的枚举类,1.1中已经讲过。 |
| append | 添加元素到列表中 |
| clear | 清空整个列表 |
| count | 统计列表中x出现的次数 |
| extend | 同python list的extend,扩展list |
| insert | 在列表中指定的位置插入元素 |
| pop | 1 默认移除并返回列表中最后一个元素;2 移除指定位置的元素,并返回该元素 |
| remove | 移除列表中第一个值为x的元素,若无则报错 |
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
import copy
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""vector在open3d中的四种初始化方式"""
# 无参构造
vi_none = o3d.utility.IntVector()
# 拷贝构造
vi = o3d.utility.IntVector([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) # made from python list
# 从numpy中构造
vi1 = o3d.utility.IntVector(np.asarray(
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype=np.int32)) # made from numpy array
# 从对象中构造
vi2 = o3d.utility.IntVector(vi1)
print(vi2)
vi2.append(5)
print(f"vi2.append(6) = {vi2}")
print(f"count 5 in vi2 = {vi2.count(5)}")
vi2.extend([6,7,8])
print(f"vi2.extend([6,7,8]) = {vi2}")
vi2.insert(i=1, x=100)
print(f"vi2.insert(i=1, x=100) = {vi2}")
print(f"vi2.pop() = {vi2.pop()}, ---> {vi2}")
print(f"vi2.pop(1) = {vi2.pop(1)}, ---> {vi2}")
print(f"vi2.remove(1) = {vi2.remove(1)}, ---> {vi2}")
print(np.asarray(vi2))
print(f"vi2.clear = {vi2.clear()}, ---> {vi2}")| get_verbosity_level() |
Get global verbosity level of Open3D 打印当前open3d中的日志输出等级 |
| reset_print_function() |
重制日志输出函数 |
| set_verbosity_level(verbosity_level) |
Set global verbosity level of Open3D 设置open3d的日志输出等级 |
5.mesh属性
在open3d中一个triangle mesh有几种属性,分别是manifold property和self-intersection和orientable这三种属性。
manifold property分别包含mesh中顶点(vertex)和边(edge)两个属性的manifold判断,分别使用is_vertex_manifold和is_edge_manifold。
如果一个triangle mesh是edge manifold,那么它的边都被一个或者两个三角形的共享。
如果一个triangle mesh是vertex manifold,那么它的点都被者两个或多个三角形三角形的共享。
is_edge_manifold方法包含参数allow_boundary_edges,默认为真,只有该边仅与两个三角形共享时,才为edge manifold
6.mesh滤波
open3d中对于mesh的滤波包含三种方式:
1 Aerage filter:
对于一个顶点Vi,通过与它相邻的N个点对其进行滤波:
def average_filtering():
# Create noisy mesh.
knot_mesh = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
mesh_in = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh.path)
# 去除mesh中所有的顶点
vertices = np.asarray(mesh_in.vertices)
noise = 5
# 给顶点随机添加0-5均匀分布的噪音
vertices += np.random.uniform(0, noise, size=vertices.shape)
# 使用utility函数将numpy对象转为open3d中的Vector
mesh_in.vertices = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(vertices)
# 重新计算mesh中顶点的法向量
mesh_in.compute_vertex_normals()
print("Displaying input mesh ...")
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in])
print("Displaying output of average mesh filter after 1 iteration ...")
# number_of_iterations 代表滤波迭代的次数w
mesh_out1 = mesh_in.filter_smooth_simple(number_of_iterations=1)
mesh_out1.compute_vertex_normals()
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_out1])
print("Displaying output of average mesh filter after 5 iteration ...")
mesh_out2 = mesh_in.filter_smooth_simple(number_of_iterations=5)
mesh_out2.compute_vertex_normals()
mesh_out1.translate([200,0,0])
mesh_out2.translate([400,0,0])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in, mesh_out1,mesh_out2])
if __name__ == "__main__":
average_filtering()2 Laplacian filter
laplacian 滤波器定义如下:
其中,lamda代表滤波的强度,Wn是与相邻顶点的距离相关的归一化权重。
def laplace_filtering():
# Create noisy mesh.
knot_mesh = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
mesh_in = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh.path)
vertices = np.asarray(mesh_in.vertices)
noise = 5
vertices += np.random.uniform(0, noise, size=vertices.shape)
mesh_in.vertices = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(vertices)
mesh_in.compute_vertex_normals()
print("Displaying input mesh ...")
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in])
print("Displaying output of Laplace mesh filter after 10 iteration ...")
mesh_out1 = mesh_in.filter_smooth_laplacian(number_of_iterations=10)
mesh_out1.compute_vertex_normals()
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_out1])
print("Displaying output of Laplace mesh filter after 50 iteration ...")
mesh_out2 = mesh_in.filter_smooth_laplacian(number_of_iterations=50)
mesh_out2.compute_vertex_normals()
mesh_out1.translate([200, 0, 0])
mesh_out2.translate([400, 0, 0])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in, mesh_out1, mesh_out2])
if __name__ == "__main__":
laplace_filtering()3 Taubin filter
上面介绍的Laplacian和average滤波方式都会导致triangle mesh在形状上的收缩,因此Taubin的提出用于解决上述的问题,原文Taubin: Curve and surface smoothing without shrinkage, ICCV, 1995. 提出了使用两个Laplacian算子和不同的lamda参数来避免triangle mesh的收缩问题。
def taubin_filtering():
# Create noisy mesh.
knot_mesh = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
mesh_in = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh.path)
vertices = np.asarray(mesh_in.vertices)
noise = 5
vertices += np.random.uniform(0, noise, size=vertices.shape)
mesh_in.vertices = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(vertices)
mesh_in.compute_vertex_normals()
print("Displaying input mesh ...")
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in])
print("Displaying output of Taubin mesh filter after 10 iteration ...")
mesh_out1 = mesh_in.filter_smooth_taubin(number_of_iterations=10)
mesh_out1.compute_vertex_normals()
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_out1])
print("Displaying output of Taubin mesh filter after 100 iteration ...")
mesh_out2 = mesh_in.filter_smooth_taubin(number_of_iterations=100)
mesh_out2.compute_vertex_normals()
mesh_out1.translate([200, 0, 0])
mesh_out2.translate([400, 0, 0])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in, mesh_out1, mesh_out2])
if __name__ == "__main__":
taubin_filtering()7.mesh采样
如果要对mesh进行采样的化,在open3d中包含了几种对mesh进行采样的方法:
1 sample_points_uniformly:基于triangle 表面的面积进行均匀的采样;参数number_of_points设定采样生成的点数。
2 sample_points_poisson_disk:均匀采样会因为采用选取面积作为参数,会导致一个表面中出现一堆点的情况,所以sample_points_poisson_disk可以均匀的把点分配到每个表面上;该方法包含参数init_factor和number_of_points;第一步先使用sample_points_uniformly采样init_factor*number_of_points个点,然后使用这些点进行elimination;或者可以自行通过参数pcl(open3d.geometry.PointCloud)自行设定已经采样的点来进行elimination到指定number_of_points。
import open3d as o3d
if __name__ == "__main__":
bunny = o3d.data.BunnyMesh()
mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(bunny.path)
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
print("Displaying input mesh ...")
o3d.visualization.draw([mesh])
print("Displaying pointcloud using uniform sampling ...")
pcd = mesh.sample_points_uniformly(number_of_points=10000)
o3d.visualization.draw([pcd], point_size=5)
print("Displaying pointcloud using Poisson disk sampling ...")
#使用number_of_points*init_factor根据sample_points_uniformly来计算用于elimination的点
# pcd = mesh.sample_points_poisson_disk(number_of_points=1000, init_factor=5)
# 自行通过pcl参数来提供待elimination的点
pcd = mesh.sample_points_poisson_disk(number_of_points=1000, pcl = pcd)
o3d.visualization.draw([pcd], point_size=5)8.网格细分(mesh subdivision)
8.1 subdivide_midpoint
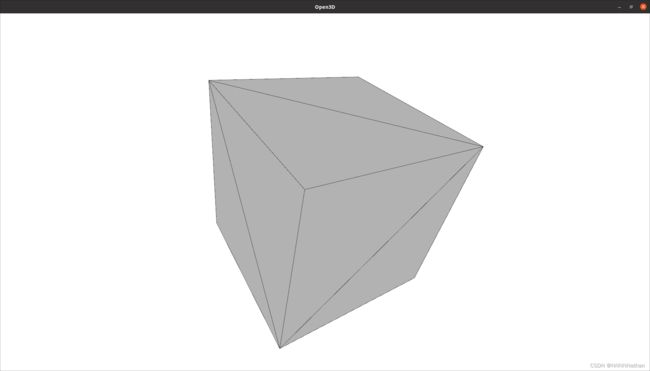
mesh subdivision将每一个triangle mesh变成更多个更小的triangle mesh;简例:一个triangle mesh中,计算每个边的中点,并进行切分,可以得到4个更小的triangle mesh。在Open3D中通过subdivide_midpoint方法来实现,使得3D 物体表面和面积保持不变,但是mesh数量和vertices增加,该方法包含参数number_of_iterations来指定分割迭代的次数。
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import copy
if __name__ == '__main__':
mesh = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_box()
#计算mesh表面的法线信息用于phong shading渲染
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
print(
f'The mesh has {len(mesh.vertices)} vertices and {len(mesh.triangles)} triangles'
)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh], mesh_show_wireframe=True,
mesh_show_back_face = True,
)
mesh = mesh.subdivide_midpoint(number_of_iterations=1)
print(
f'After subdivision it has {len(mesh.vertices)} vertices and {len(mesh.triangles)} triangles'
)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh], mesh_show_wireframe=True)
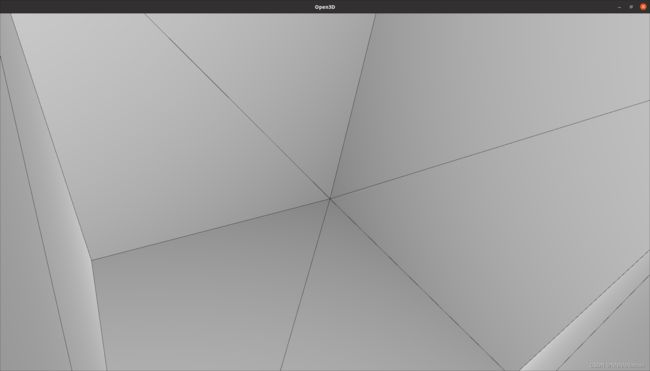
经过一次迭代后一个triangle mesh变成4个triangle mesh(打开了phong shading)
 经过两次迭代后一个triangle mesh变成4*4个triangle mesh (关闭了 phong shading)
经过两次迭代后一个triangle mesh变成4*4个triangle mesh (关闭了 phong shading)
注意:在已经计算点云或mesh的法线信息后可以按L来打开或关闭phong shading渲染
8.2 subdivide_loop
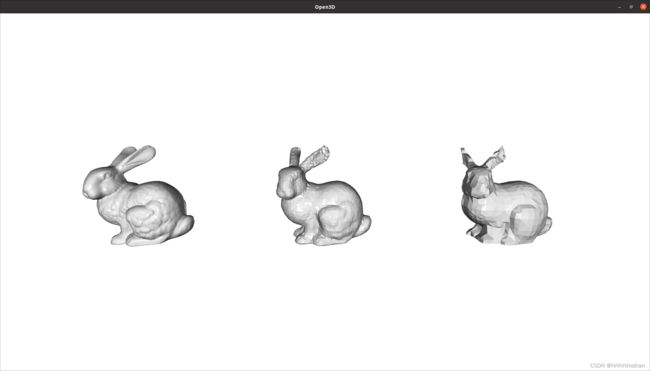
Open3D提供了另外一种subdivision的方法,方法为subdivide_loop,该方法基于Loop: Smooth Subdivision Surfaces Based on Triangles, M.S. Mathematics thesis, University of Utah, 1987 ,该方法quartic box spline;可以使得物体拐角处更加平滑。
import open3d as o3d
if __name__ == "__main__":
knot_mesh = o3d.data.KnotMesh()
mesh:o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(knot_mesh.path)
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
print("Before Subdivision: ", mesh)
print("Displaying input mesh ...")
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh], mesh_show_wireframe=True)
mesh_mid_point = mesh.subdivide_midpoint(number_of_iterations=3)
mesh_loop = mesh.subdivide_loop(number_of_iterations=3)
print("After Subdivision: ", mesh)
print("Displaying subdivided mesh ...")
mesh_mid_point.translate([200,0,0])
mesh_loop.translate([400,0,0])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh, mesh_mid_point, mesh_loop], mesh_show_wireframe=True)可以看到,使用subdivide_loop 细化得到的结果更加的平滑
注:这里解释一下可视化参数mesh_show_back_face
可视化当前物体,当前视角在物体外面
当前视角在物体内部,且 mesh_show_back_face为假,所有的mesh内表面均不显示
当前视角在物体内部,且 mesh_show_back_face为真,所有的mesh内表面均显示
9.网格简化(Mesh simplification)
Mesh simplification可以看成是mesh subdivision的逆过程,把高分辨率的mesh使用更少的Vertices和mesh表示出来,在Open3D中体虫了两种方法实现该功能。
9.1 simplify_vertex_clustering
vertex clustering方法首先对mesh中的vertex进行voxel化,然后对落在一个voxel中所有vertex进行融合得到一个新的vertex;因此simplify_vertex_clustering方法包含两个参数:
voxel_size设置voxel的大小
contraction参数设置vertex融合的方式:
1. o3d.geometry.SimplificationContraction.Average,对voxel中的vertex求平均得到新的点
2 . o3d.geometry.Quadric 最小化点到每个相邻平面的距离
import open3d as o3d
if __name__ == "__main__":
bunny = o3d.data.BunnyMesh()
mesh_in = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(bunny.path)
mesh_in.compute_vertex_normals()
print("Before Simplification: ", mesh_in)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in])
#根据物体的大小来确定voxel的大小
voxel_size = max(mesh_in.get_max_bound() - mesh_in.get_min_bound()) / 32
mesh_smp = mesh_in.simplify_vertex_clustering(
voxel_size=voxel_size,
contraction=o3d.geometry.SimplificationContraction.Average
# contraction = o3d.geometry.Quadric
)
print("After Simplification with voxel size =", voxel_size, ":\n", mesh_smp)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_smp])
voxel_size = max(mesh_in.get_max_bound() - mesh_in.get_min_bound()) / 16
mesh_smp = mesh_in.simplify_vertex_clustering(
voxel_size=voxel_size,
contraction=o3d.geometry.SimplificationContraction.Average)
print("After Simplification with voxel size =", voxel_size, ":\n", mesh_smp)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_smp])
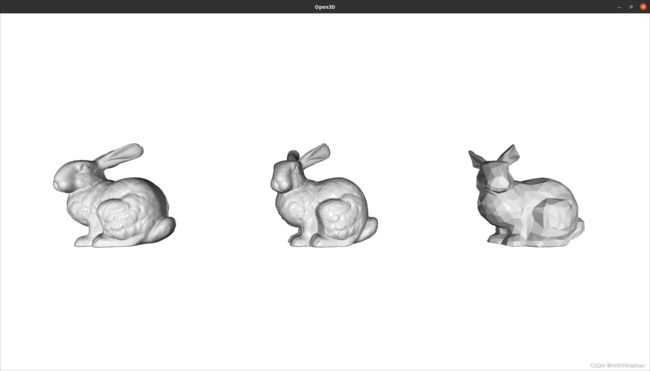
9.2 simplify_quadric_decimation
simplify_quadric_decimation方法是基于Quadric Error Metric Decimation 的方法,这是一种增量式的方法,首先先选择一个triangle mesh,并最小化它到其他平面的误差,并删除它,重复该过程即可。该方法包含参数:
target_number_of_triangles:简化后的mesh应有多少个mesh,算法不保证一定达到该数量
maximum_error:一个vertex可以被合并的最大容忍误差
boundary_weight:边顶点的边界保留权重
import open3d as o3d
if __name__ == "__main__":
bunny = o3d.data.BunnyMesh()
mesh_in = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(bunny.path)
mesh_in.compute_vertex_normals()
print("Before Simplification: ", mesh_in)
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in])
mesh_smp_6500 = mesh_in.simplify_quadric_decimation(
target_number_of_triangles=6500)
print("After Simplification target number of triangles = 6500:\n", mesh_smp_6500)
# o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_smp_6500])
mesh_smp_1000 = mesh_in.simplify_quadric_decimation(
target_number_of_triangles=1000)
print("After Simplification target number of triangles = 1700:\n", mesh_smp_1000)
mesh_smp_6500.translate([0.3, 0, 0])
mesh_smp_1000.translate([0.6, 0, 0])
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_in, mesh_smp_6500, mesh_smp_1000])10.mesh聚类
在进行重建的时候,会因为采集设备噪音等等因素,会引入不连续的mesh;因此Open3D中实现了算法cluster_connected_triangles指定了每一个triangle属于哪一个相连的cluster中;该方法返回了,
1 每个triangle mesh在triangle_clusters中的索引和每个
2 每个cluster中triangle mesh的数量
3 计算每个clsuter的表面积
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
import copy
if __name__ == "__main__":
bunny = o3d.data.BunnyMesh()
mesh = o3d.io.read_triangle_mesh(bunny.path)
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
# 对mesh进行取曲面细分,迭代两次
mesh = mesh.subdivide_midpoint(number_of_iterations=2)
# 取出mesh中所有的vertex,用于创造噪音数据
vert = np.asarray(mesh.vertices)
min_vert, max_vert = vert.min(axis=0), vert.max(axis=0)
for _ in range(30):
# 生成立方体数据当成噪音的
cube = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_box()
# mesh的尺度缩放操作,并将缩放后的mesh中心点设置为cube.get_center()
cube.scale(0.005, center=cube.get_center())
# 移动生成的cube
cube.translate(
(
np.random.uniform(min_vert[0], max_vert[0]),
np.random.uniform(min_vert[1], max_vert[1]),
np.random.uniform(min_vert[2], max_vert[2]),
),
relative=False,
)
mesh += cube
mesh.compute_vertex_normals()
print("Displaying input mesh ...")
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh])
print("Clustering connected triangles ...")
with o3d.utility.VerbosityContextManager(
o3d.utility.VerbosityLevel.Debug) as cm:
triangle_clusters, cluster_n_triangles, cluster_area = (
mesh.cluster_connected_triangles())
triangle_clusters = np.asarray(triangle_clusters)
cluster_n_triangles = np.asarray(cluster_n_triangles)
cluster_area = np.asarray(cluster_area)
print("Displaying mesh with small clusters removed ...")
mesh_0 = copy.deepcopy(mesh)
# 移除triangle_clusters中mesh数量少于100个的cluster的triangle mesh
triangles_to_remove = cluster_n_triangles[triangle_clusters] < 100
# 真值代表该triangle mesh需要被移除
mesh_0.remove_triangles_by_mask(triangles_to_remove)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([mesh_0])