源码解析SharedPreferences你不知道的缺点
学习目标:
‘
源码解析SharedPreferences缺点
ps:中文注释很关键!
学习内容:
SharedPreferences,是以键值对的方式存储在xml格式的文件里,通常我们的调用方式如下:
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences = getSharedPreferences("status",MODE_PRIVATE);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = sharedPreferences.edit();
editor.putBoolean("login",true);
editor.commit();
我们这个getSharedPreferences就获得了SharedPreferences 对象,然后就可以操作读写文件了。
我们通过源码的方式来看这个方法
public interface SharedPreferences {
/**
* Interface definition for a callback to be invoked when a shared
* preference is changed.
*/
}
可以看到SharedPreferences 首先是个接口,那肯定有它的实现类来实现操作文件,所以要找到它的实现类。
final class SharedPreferencesImpl implements SharedPreferences {
........
SharedPreferencesImpl(File file, int mode) {
mFile = file;
mBackupFile = makeBackupFile(file);
mMode = mode;
mLoaded = false;
mMap = null;
mThrowable = null;
//从磁盘加载对应file文件的xml文件内容
startLoadFromDisk();
}
private void startLoadFromDisk() {
synchronized (mLock) {
mLoaded = false;
}
new Thread("SharedPreferencesImpl-load") {
public void run() {
loadFromDisk();
}
}.start();
}
private void loadFromDisk() {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mLoaded) {
return;
}
if (mBackupFile.exists()) {
mFile.delete();
mBackupFile.renameTo(mFile);
}
}
// Debugging
if (mFile.exists() && !mFile.canRead()) {
Log.w(TAG, "Attempt to read preferences file " + mFile + " without permission");
}
//看这里,这里就是IO操作了,但一般IO操作就很卡,所以这是它
//慢的一部分原因
Map<String, Object> map = null;
StructStat stat = null;
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath());
if (mFile.canRead()) {
BufferedInputStream str = null;
try {
str = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(mFile), 16 * 1024);
//解析xml,然后在转换成hashmap
map = (Map<String, Object>) XmlUtils.readMapXml(str);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Cannot read " + mFile.getAbsolutePath(), e);
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(str);
}
}
} catch (ErrnoException e) {
// An errno exception means the stat failed. Treat as empty/non-existing by
// ignoring.
} catch (Throwable t) {
thrown = t;
}
synchronized (mLock) {
mLoaded = true;
mThrowable = thrown;
// It's important that we always signal waiters, even if we'll make
// them fail with an exception. The try-finally is pretty wide, but
// better safe than sorry.
try {
if (thrown == null) {
if (map != null) {
mMap = map;
mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtim;
mStatSize = stat.st_size;
} else {
mMap = new HashMap<>();
}
}
// In case of a thrown exception, we retain the old map. That allows
// any open editors to commit and store updates.
} catch (Throwable t) {
mThrowable = t;
} finally {
mLock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
static File makeBackupFile(File prefsFile) {
return new File(prefsFile.getPath() + ".bak");
}
.........
}
所以从上面看出SharedPreferences 首先它使用流的操作读取xml文件,然后需要进行xml解析,现在只是读写,我们再来看它是怎么写入的,我们通过最后调用editor.commit();实现写入文件,所以我们从这里看
@Override
public boolean commit() {
long startTime = 0;
if (DEBUG) {
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory();
//通过线程写入文件
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite(
mcr, null /* sync write on this thread okay */);
try {
mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return false;
} finally {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, mFile.getName() + ":" + mcr.memoryStateGeneration
+ " committed after " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime)
+ " ms");
}
}
notifyListeners(mcr);
return mcr.writeToDiskResult;
}
/**
* Enqueue an already-committed-to-memory result to be written
* to disk.
*
* They will be written to disk one-at-a-time in the order
* that they're enqueued.
*
* @param postWriteRunnable if non-null, we're being called
* from apply() and this is the runnable to run after
* the write proceeds. if null (from a regular commit()),
* then we're allowed to do this disk write on the main
* thread (which in addition to reducing allocations and
* creating a background thread, this has the advantage that
* we catch them in userdebug StrictMode reports to convert
* them where possible to apply() ...)
*/
private void enqueueDiskWrite(final MemoryCommitResult mcr,
final Runnable postWriteRunnable) {
final boolean isFromSyncCommit = (postWriteRunnable == null);
final Runnable writeToDiskRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (mWritingToDiskLock) {
writeToFile(mcr, isFromSyncCommit);
}
synchronized (mLock) {
mDiskWritesInFlight--;
}
if (postWriteRunnable != null) {
postWriteRunnable.run();
}
}
};
// Typical #commit() path with fewer allocations, doing a write on
// the current thread.
if (isFromSyncCommit) {
boolean wasEmpty = false;
synchronized (mLock) {
wasEmpty = mDiskWritesInFlight == 1;
}
if (wasEmpty) {
writeToDiskRunnable.run();
return;
}
}
QueuedWork.queue(writeToDiskRunnable, !isFromSyncCommit);
}
private void writeToFile(MemoryCommitResult mcr, boolean isFromSyncCommit) {
long startTime = 0;
long existsTime = 0;
long backupExistsTime = 0;
long outputStreamCreateTime = 0;
long writeTime = 0;
long fsyncTime = 0;
long setPermTime = 0;
long fstatTime = 0;
long deleteTime = 0;
if (DEBUG) {
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
boolean fileExists = mFile.exists();
if (DEBUG) {
existsTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Might not be set, hence init them to a default value
backupExistsTime = existsTime;
}
// Rename the current file so it may be used as a backup during the next read
if (fileExists) {
boolean needsWrite = false;
// Only need to write if the disk state is older than this commit
if (mDiskStateGeneration < mcr.memoryStateGeneration) {
if (isFromSyncCommit) {
needsWrite = true;
} else {
synchronized (mLock) {
// No need to persist intermediate states. Just wait for the latest state to
// be persisted.
if (mCurrentMemoryStateGeneration == mcr.memoryStateGeneration) {
needsWrite = true;
}
}
}
}
if (!needsWrite) {
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false, true);
return;
}
boolean backupFileExists = mBackupFile.exists();
if (DEBUG) {
backupExistsTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
if (!backupFileExists) {
if (!mFile.renameTo(mBackupFile)) {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't rename file " + mFile
+ " to backup file " + mBackupFile);
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false, false);
return;
}
} else {
mFile.delete();
}
}
// Attempt to write the file, delete the backup and return true as atomically as
// possible. If any exception occurs, delete the new file; next time we will restore
// from the backup.
//可以看我们这里又使用了IO流,又是耗时操作。
try {
FileOutputStream str = createFileOutputStream(mFile);
if (DEBUG) {
outputStreamCreateTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
if (str == null) {
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false, false);
return;
}
//这里还要通过xml工具类,转化成xml文件语法,又一段耗时
XmlUtils.writeMapXml(mcr.mapToWriteToDisk, str);
writeTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileUtils.sync(str);
fsyncTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
str.close();
ContextImpl.setFilePermissionsFromMode(mFile.getPath(), mMode, 0);
if (DEBUG) {
setPermTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
try {
final StructStat stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath());
synchronized (mLock) {
mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtim;
mStatSize = stat.st_size;
}
} catch (ErrnoException e) {
// Do nothing
}
if (DEBUG) {
fstatTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
// Writing was successful, delete the backup file if there is one.
mBackupFile.delete();
if (DEBUG) {
deleteTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
mDiskStateGeneration = mcr.memoryStateGeneration;
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(true, true);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "write: " + (existsTime - startTime) + "/"
+ (backupExistsTime - startTime) + "/"
+ (outputStreamCreateTime - startTime) + "/"
+ (writeTime - startTime) + "/"
+ (fsyncTime - startTime) + "/"
+ (setPermTime - startTime) + "/"
+ (fstatTime - startTime) + "/"
+ (deleteTime - startTime));
}
long fsyncDuration = fsyncTime - writeTime;
mSyncTimes.add((int) fsyncDuration);
mNumSync++;
if (DEBUG || mNumSync % 1024 == 0 || fsyncDuration > MAX_FSYNC_DURATION_MILLIS) {
mSyncTimes.log(TAG, "Time required to fsync " + mFile + ": ");
}
return;
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "writeToFile: Got exception:", e);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "writeToFile: Got exception:", e);
}
// Clean up an unsuccessfully written file
if (mFile.exists()) {
if (!mFile.delete()) {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't clean up partially-written file " + mFile);
}
}
mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false, false);
}
从上面看出写入xml写入的时候打开IO流,又要把内容转换成xml语法,所以这里又耗时。
我们在IO流里看到的都是FileOutputStream,所以耗时的元凶也是它,我们一般通过这段代码fileOutputStream.write();写文件,我们来看一下这个方法的源码
/**
* Writes the specified byte to this file output stream. Implements
* the write method of OutputStream.
*
* @param b the byte to be written.
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.
*/
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
// Android-changed: Write methods delegate to write(byte[],int,int) to share Android logic.
write(new byte[] { (byte) b }, 0, 1);
}
/**
* Writes b.length bytes from the specified byte array
* to this file output stream.
*
* @param b the data.
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.
*/
public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException {
// Android-changed: Write methods delegate to write(byte[],int,int) to share Android logic.
write(b, 0, b.length);
}
/**
* Writes len bytes from the specified byte array
* starting at offset off to this file output stream.
*
* @param b the data.
* @param off the start offset in the data.
* @param len the number of bytes to write.
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.
*/
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
// Android-added: close() check before I/O.
if (closed && len > 0) {
throw new IOException("Stream Closed");
}
// Android-added: Tracking of unbuffered I/O.
tracker.trackIo(len);
// Android-changed: Use IoBridge instead of calling native method.
//这里我们看到这个方法IoBridge,这就是最后写入数据的方法,我们理解了这个就好办了
IoBridge.write(fd, b, off, len);
}
我们这里发现发现了一个IoBridge,我们来画一张图方便理解这个类。
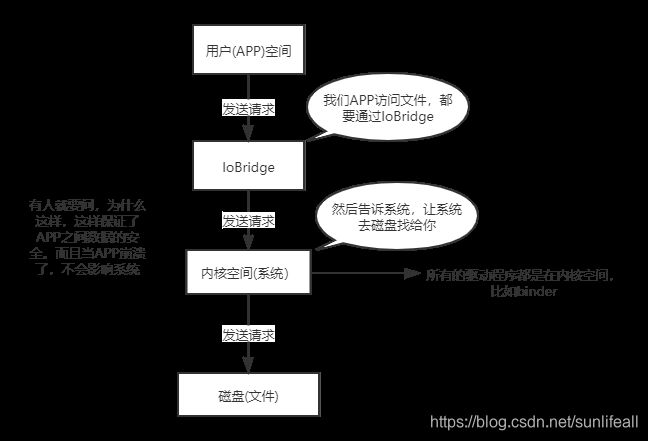
从图中可以看出我们要从用户空间转到内核空间,需要通过系统调用来完成。比如,当我们查看文件内容时,就需要多次系统调用来完成:首先调用 open() 打开文件,然后调用 read() 读取文件内容,并调用 write() 将内容写到标准输出,最后再调用 close() 关闭文件,过程中cpu会发生两次中断,底层帮我们实现了太多,这也就是为什么sharedPreferences卡顿的主要原因。