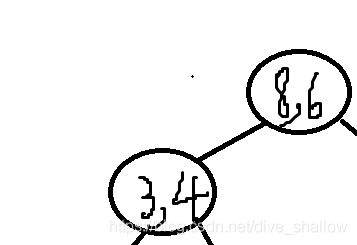Kd树(C++实现建树,插入结点,删除结点,找最邻近点)
Kd树的定义:
Kd树是一棵二叉树,对它的每一个结点(叶结点除外)都设定一个划分,使得它左子树上的点的某一维度(与划分相同的维度)都满足比它的划分小,右子树上的点某一维度(与划分相同的维度)都满足比它的划分大。
Kd树的基本操作(都以二维的为例):
建立Kd树:
思路:
肯定是想建立一棵叶子结点相对均匀(不同的范围差别大,容易找)的二叉树,这样在后面找最邻近点的时候查找的效率会高很多。对于给定的n个点,求出x方向和y方向的方差,比较x方向和y方向方差的大小,如果x方向的方差比y方向的方差大,则本结点在x方向上划分,否则本结点在y方向上划分,这样子建出来的树,点是相对分散的,树就是相对来说较为平衡的。
代码实现:
具体的思路是,先根据方差大小确定划分是在x方向还是y方向,如果是在x方向,就按照点的x坐标对给定的点数组从小到大排序,找到x是中位数的那个点v,然后对于x坐标小于v的所有点,建立在左子树上,对于所有x坐标大于v的所有点,建立在右子树上,如果划分在y方向,就按照点的y坐标对给定的点数组从小到大排序,找到y是中位数的那个点w,然后对于y坐标小于w的所有点建立在左子树上,对于所有y坐标大于w的所有点建立在右子树上。按照这个原则递归建立左子树和右子树直到点数组的左右端点相等即以本结点为根节点的树只有一个结点为止。
void KdTree::BuildTree(Point* pointArray,int l,int r)
{
//这里的方差相当于乘了n,因为只比较大小
//x方向和y方向上的方差 ,和
float sdx,sdy,sumx,sumy;
for(int i = l; i < r; ++i)
{
sumx += pointArray[i].x;
sumy += pointArray[i].y;
}
//得到平均数
float avex = sumx/(r - l),avey = sumy/(r - l);
//计算方差
for(int i = l; i < r; ++i)
{
sdx += pow(pointArray[i].x - avex,2);
sdy += pow(pointArray[i].y - avey,2);
}
int m = (l + r)/2;
if(sdx > sdy)
{
sort(pointArray + l,pointArray + r,XSortFunc);//x排序并找到中间的那个点
splitX = pointArray[m].x;//本结点是在x方向进行了划分
splitY = 0;//y方向没有划分
}
else
{
sort(pointArray + l,pointArray + r,YSortFunc);//y排序并找到中间的那个点
splitY = pointArray[m].y;
splitX = 0;
}
//当前结点设置为中位数
point = pointArray[m];
//[l,r]的区间是左闭右开的
if(m > l)
{
leftTree = new KdTree();
leftTree->BuildTree(pointArray,l,m);//递归构建左子树
}
if(m < r - 1)
{
rightTree = new KdTree();
rightTree->BuildTree(pointArray,m+1 ,r);//递归构建右子树
}
}具体操作一下:
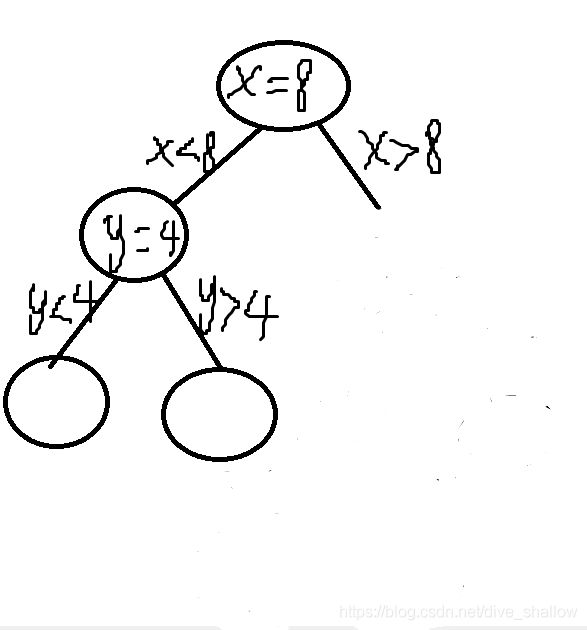
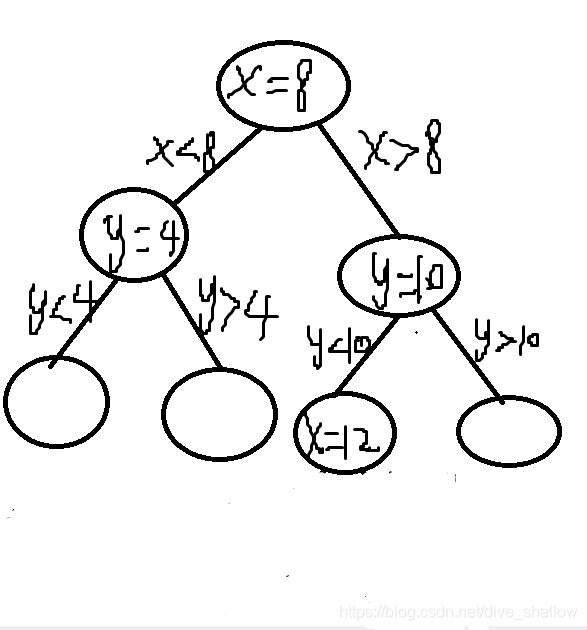
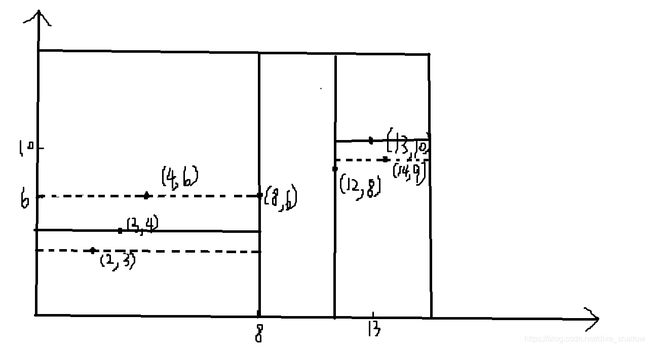
比如要以(2,3),(3,4),(4,6),(8,6),(12,8),(13,10),这六个点为点数组,建立一棵Kd树。
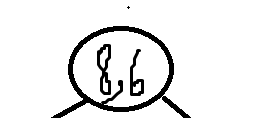
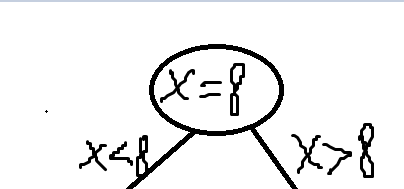
第一轮判断x方向的方差明显比y方向上的方差要大,那肯定是在x方向上划分,且x为中位数的点是(8,6),所以第一轮先建一个(8,6),同时条件树也要画一下,便于理解:
第二轮要用(2,3),(3,4),(4,6)递归建立的是它的左子树,发现左子树上y方向的方差比x方向上更大,于是找到y坐标为中位数的点,建在左子树上,并以4为划分,继续建立它的左子树。
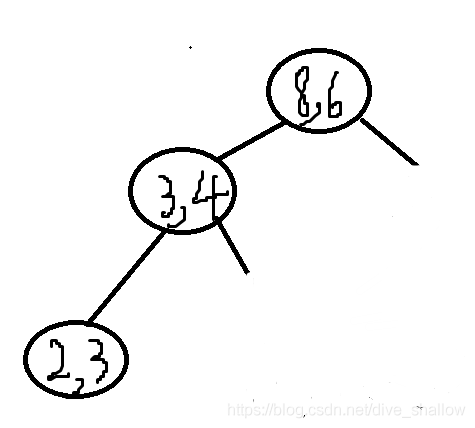
第三轮要用(2,3)建立(3,4)的左子树,只有一个点了,所以建好后就发现数组中l和r之间只有一个元素了,就回退到上一层。
第四轮回退到了(3,4),用(4,6)建立(3,4)的右子树,然后同理回退到上一层。
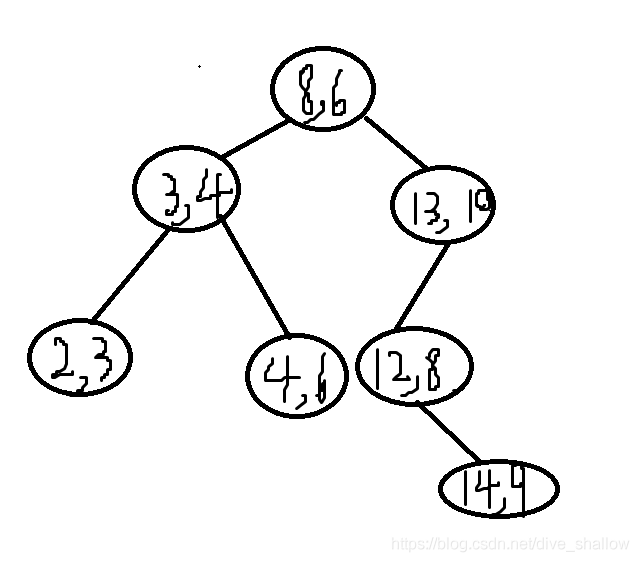
从第五轮开始要建根结点的右子树了,这里不再详细赘述,最终建好的树如图:
插入结点
思路:
就跟二叉搜索树差不多,对于要被插入的结点,先根据x和y方向上的划分确定它在左子树还是在右子树,然后递归插入就可以。
具体实现:
对于要被插入的结点v,先找到当前根节点的划分是x还是y,如果是以x为划分,v的x坐标小于当前根节点的x坐标,那么v应该位于当前根结点的左子树,否则,v应该位于当前根结点的右子树,如果是以y为划分,v的坐标小于当前根节点的y坐标,那么v应该位于当前根结点的左子树,否则,v应该位于当前根结点的右子树,
如果v位于当前根结点的左子树,并且当前根节点的左子树为空,那么当前根结点的左孩子直接设置为v并且回退,如果v位于当前根结点的右子树,并且当前根结点的右子树为空,那么当前根结点右孩子直接设置为v并且回退。
void KdTree::Insert(Point point)
{
//只有一个孩子
if(!leftTree && rightTree)
{
if(isLeftTreeNode(point))
{
//cout<point<point<point.x) > abs(point.y - this->point.y))
{
//因为这里我默认用y划分,所以是叶结点要重新比较xy进行划分
splitY = 0;
splitX = this->point.x;
if(point.x > this->point.x)
{
rightTree = new KdTree(point,NULL,NULL,0,point.y);
}
else
{
leftTree = new KdTree(point,NULL,NULL,0,point.y);
}
}
else
{
splitX = 0;
splitY = this->point.y;
if(point.y > this->point.y)
{
rightTree = new KdTree(point,NULL,NULL,0,point.y);
}
else
{
leftTree = new KdTree(point,NULL,NULL,0,point.y);
}
}
return;
}
//只有一个孩子并且往孩子结点走或者是有两个孩子
if(splitX)
{
if(point.x < splitX)
{
leftTree->Insert(point);
}
else
{
rightTree->Insert(point);
}
}
if(splitY)
{
if(point.y < splitY)
{
leftTree->Insert(point);
}
else
{
rightTree->Insert(point);
}
}
}
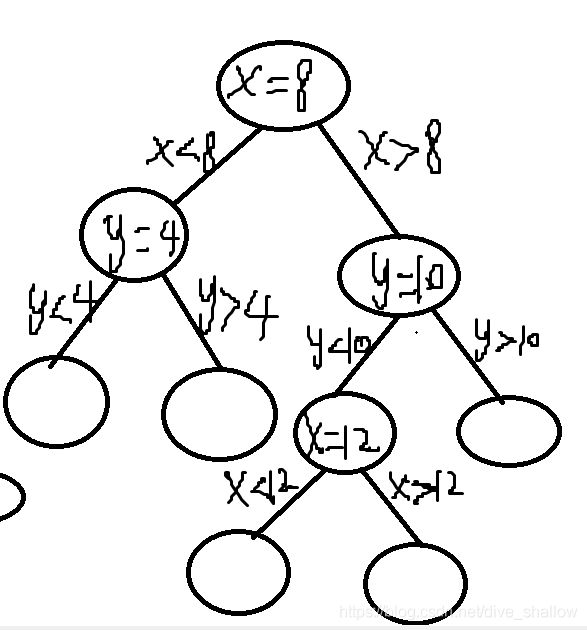
比如要在
6
2 3
3 4
4 6
8 6
12 8
13 10
这组测试数据下,插入一个(14,9)的结点,操作完成后树如下:
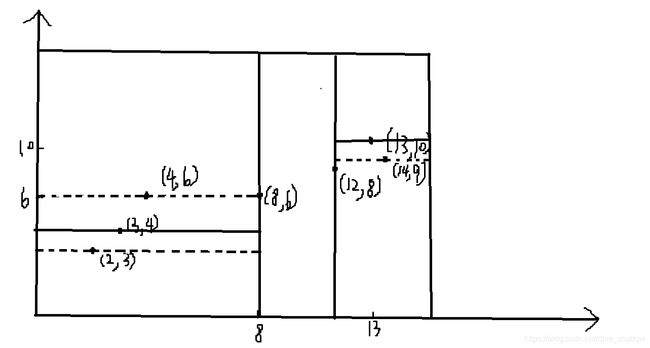
它其实把平面划分后图形也比较有特色:
删除结点:
思路:
如果要被删除的结点是叶结点,直接删。如果要被删除的结点有左孩子,找到左子树上x或y最大的结点lmaxNode(具体是x还是y要看当前的划分),以点值取代当前结点,并且把当前结点的划分方向不变,大小设置为lmaxNode对应点的大小,并且在左子树递归删除lmaxNode。如果要被删除的结点有右孩子,那就找到右子树上x或y最小的结点rminNode,以点值取代当前结点,并且把当前结点划分的方向不变,大小设置为rminNode对应点的大小,并且在右子树上递归删除rminNode。
具体实现:
void KdTree::Delete(KdTree* parent,Point point)
{
//找到了要被删除的结点
if(this->point == point)
{
//要被删除的结点是叶子结点,直接删
if(!leftTree&&!rightTree)
{
if(parent->leftTree&&parent->leftTree->point == this->point)
{
parent->leftTree = NULL;
delete this;
return;
}
else
{
parent->rightTree = NULL;
delete this;
return;
}
}
//要被删除的结点有左子树
else if(leftTree)
{
KdTree* tmpTree;
if(splitX)
{
//找到左子树x最大的点
tmpTree = leftTree->GetMaxXTreeNode();
//调整划分大小
this->splitX = tmpTree->point.x;
}
else
{
//找到左子树y最大的点
tmpTree = leftTree->GetMaxYTreeNode();
//调整划分大小
this->splitY = tmpTree->point.y;
}
//设置点
this->point = tmpTree->point;
//从左子树上递归删除x或y最大的结点
leftTree->Delete(this,tmpTree->point);
}
//要被删除的结点有右子树
else if(!leftTree&&rightTree)
{
KdTree* tmpTree;
if(splitX)
{
//找到右子树上x最小的点
tmpTree = rightTree->GetMinXTreeNode();
//调整划分大小
this->splitX = tmpTree->point.x;
}
else
{
tmpTree = rightTree->GetMinYTreeNode();
this->splitY = tmpTree->point.y;
}
//设置点
this->point = tmpTree->point;
//从右子树上递归删除x或y最小的结点
rightTree->Delete(this,tmpTree->point);
}
}
//没有找到目标点,需要先递归寻找
if(leftTree && ((splitX && point.x < splitX)||(splitY && point.y < splitY)))
{
leftTree->Delete(this,point);
}
if(rightTree && ((splitX && point.x > splitX)||(splitY && point.y > splitY)))
{
rightTree->Delete(this,point);
}
}寻找最邻近点
思路:
其实就是找Kd树中哪个点和给定的点距离最小。对于给定的一个点p,从根结点先找到最有可能和p构成最邻近点的叶子结点,以p为圆心,二者的距离为半径画个圆,如果兄弟结点或另一个孩子结点在圆内,就递归地寻找以在圆内点满足条件的子树,寻找最邻近点。
具体实现:
对于给定的点p,先与根结点比较,如果根结点以x方向划分并且p的x比根节点的小,或者根节点以y方向划分,并且p的y比根结点的小,这时需要在左子树上寻找最邻近点,这样递归下去,一直找到某一个最可能的叶子结点或者只有一个孩子结点但p无法走到孩子结点的结点,在这个过程中不断更新最小距离minDis和目标点tarPoint,到叶子结点的时候以p为圆心,p与tarPoint之间的距离为半径画一个圆,此时如果是叶子结点需要回退到上一层,并且找到在圆内且没有走过的兄弟结点或孩子结点 q,递归地寻找以q为根结点的Kd树中p的最邻近点。
其实就是分了两种情况,在找到最有可能的叶结点的情况下,先回退到上一层比较它另一个叶结点(如果有的话)是否在以给定的点p为圆心minDis为半径(也就是p和tarPoint之间的距离)的圆内,如果在,就递归地寻找这个在圆内的叶结点的子树。还有一种情况是找到了只带有一个孩子结点的结点,但是孩子结点因为分割问题走不到,但其实这个孩子结点可能在圆内,有可能成为一个最近点,详情看我最后的举例。
void GetNearestPoint(KdTree* root,KdTree* parent,Point point,float& minDis,Point& tarPoint)
{
//找到了叶子结点的孩子结点
if(root == NULL)
return;
//当前结点已经访问过
root->isVisited = true;
//计算当前结点和point的距离
float dis = pow(point.x-root->point.x,2) + pow(point.y-root->point.y,2);
//如果当前结点和point之间的距离比最小距离小,则更新目标点和最小距离
if(minDis < 0 || dis < minDis)
{
tarPoint = root->point;
minDis = dis;
}
if((root->splitX && point.x < root->point.x) || (root->splitY && point.y < root->point.y))
{
//左子树不为空并且point偏向左子树就从左子树上递归地寻找最邻近点
if(root->leftTree&&!root->leftTree->isVisited)
GetNearestPoint(root->leftTree,root,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
else
{
//右子树不为空并且point偏向右子树就从右子树上递归地寻找最邻近点
if(root->rightTree&&!root->rightTree->isVisited)
GetNearestPoint(root->rightTree,root,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
//走到这里肯定有两种情况,要么到了叶子结点并且回退到了上一层,要么到了只有一个孩子的结点是本层,在这两种情况下:
//1.走到了叶子结点并且回退到了上一层,这时候需要找当前结点的另一个叶子结点(如果有的话)以及兄弟结点
//2.到了只有一个孩子的结点并且在本层,这时候需要找它的兄弟结点以及它的孩子结点,因为在这种情况下仅靠比较分割大小是走不到它孩子结点所在的子树的
//定义当前结点的兄弟结点和孩子结点与目标结点的距离
float rL = minDis + 1,rR = minDis + 1,childrL = minDis + 1,childrR = minDis + 1;
//这里有问题是因为回退到这里不一定是叶子结点,所以需要找它的兄弟以及另一个孩子结点,下面四个递归顶多会走两个
if(parent->leftTree)
rL = pow(point.x - parent->leftTree->point.x,2) + pow(point.y - parent->leftTree->point.y,2);
if(parent->rightTree)
rR = pow(point.x - parent->rightTree->point.x,2) + pow(point.y - parent->rightTree->point.y,2);
if(root->leftTree)
childrL = pow(point.x - root->leftTree->point.x,2) + pow(point.y - root->leftTree->point.y,2);
if(root->rightTree)
childrR = pow(point.x - root->rightTree->point.x,2) + pow(point.y - root->rightTree->point.y,2);
//左兄弟结点在圆内就递归地寻找以左兄弟结点为根节点子树的point的最邻近点
if(parent->leftTree && !parent->leftTree->isVisited && rL < minDis)
{
GetNearestPoint(parent->leftTree,parent,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
//右兄弟结点在圆内就递归寻找以右兄弟结点为根节点子树的point的最邻近点
if(parent->rightTree && !parent->rightTree->isVisited && rR < minDis)
{
GetNearestPoint(parent->rightTree,parent,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
//左孩子结点在圆内就递归寻找以左孩子结点为根结点子树的point的最邻近点
if(root->leftTree && !root->leftTree->isVisited && childrL < minDis)
{
GetNearestPoint(root->leftTree,root,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
//右孩子结点在圆内就递归寻找以右孩子结点为根结点子树的point的最邻近点
if(root->rightTree && !root->rightTree->isVisited && childrR < minDis)
{
GetNearestPoint(root->rightTree,root,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
}完整的代码:
#include
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
Point(){}
float x;
float y;
friend bool XSortFunc(Point& a,Point& b);
friend bool YSortFunc(Point& a,Point& b);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& output,Point point);
Point operator=(const Point& other);
bool operator==(const Point& other);
bool operator!=(const Point& other);
};
class KdTree
{
public:
KdTree(){splitX = 0,splitY = 0;leftTree = NULL,rightTree = NULL;isVisited = false;}
KdTree(Point point,KdTree* leftTree,KdTree* rightTree,float splitX,float splitY)
{
this->point = point;
this->leftTree = leftTree;
this->rightTree = rightTree;
this->splitX = splitX;
this->splitY = splitY;
isVisited = false;
}
Point point;
//0表示没有划分,例 splitX = 1表示在x轴方向上针对 x=1 对平面进行了划分
float splitX;
float splitY;
int depth;
bool isVisited;
KdTree* leftTree;
KdTree* rightTree;
bool isLeftTreeNode(Point point);
bool isRightTreeNode(Point point);
void BuildTree(Point* pointArray,int l,int r);
void Insert(Point point);
void Delete(KdTree*parent,Point point);
void Bfs();
KdTree* GetMaxXTreeNode();
KdTree* GetMinXTreeNode();
KdTree* GetMaxYTreeNode();
KdTree* GetMinYTreeNode();
friend void GetNearestPoint(KdTree* root,KdTree* parent,Point point,float& minDis,Point& tarPoint);
};
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
Point pointArray[100];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cin>>pointArray[i].x>>pointArray[i].y;
}
KdTree* root = new KdTree();
root->BuildTree(pointArray,0,n);
Point p;
p.x = 14;
p.y = 9;
root->Insert(p);
Point test,test2;
test.x = 13;
test.y = 10;
test2.x = 13;
test2.y = 10;
root->Delete(root,test2);
cout<rightTree->leftTree->point<Bfs();
return 0;
}
Point Point::operator=(const Point& other)
{
this->x = other.x;
this->y = other.y;
return *this;
}
bool Point::operator==(const Point& other)
{
return abs(x - other.x) < 1e-9 && abs(y - other.y) < 1e-9;
}
bool Point::operator!=(const Point& other)
{
return abs(x - other.x) > 1e-9 || abs(y - other.y) > 1e-9;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& output,Point point)
{
output< leftTree->point.x?this:leftTree;
}
if(rightTree && !leftTree)
{
return point.x > rightTree->point.x?this:rightTree;
}
KdTree* leftMaxNode = leftTree->GetMaxXTreeNode();
KdTree* rightMaxNode = rightTree->GetMaxXTreeNode();
return leftMaxNode->point.x > rightMaxNode->point.x? leftMaxNode:rightMaxNode;
}
KdTree* KdTree::GetMinXTreeNode()
{
if(!leftTree && !rightTree)
return this;
if(leftTree && !rightTree)
{
return point.x < leftTree->point.x? this:leftTree;
}
if(rightTree && !leftTree)
{
return point.x < rightTree->point.x? this:rightTree;
}
KdTree* leftMinNode = leftTree->GetMinXTreeNode();
KdTree* rightMinNode = rightTree->GetMinXTreeNode();
return leftMinNode->point.x < rightMinNode->point.x? leftMinNode:rightMinNode;
}
KdTree* KdTree::GetMaxYTreeNode()
{
if(!leftTree && !rightTree)
return this;
if(leftTree && !rightTree)
{
return point.y > leftTree->point.y?this:leftTree;
}
if(rightTree && !leftTree)
{
return point.y > rightTree->point.y?this:rightTree;
}
KdTree* leftMaxNode = leftTree->GetMaxYTreeNode();
KdTree* rightMaxNode = rightTree->GetMaxYTreeNode();
return leftMaxNode->point.y > rightMaxNode->point.y? leftMaxNode:rightMaxNode;
}
KdTree* KdTree::GetMinYTreeNode()
{
if(!leftTree && !rightTree)
return this;
if(leftTree && !rightTree)
{
return point.y < leftTree->point.y? this:leftTree;
}
if(rightTree && !leftTree)
{
return point.y < rightTree->point.y?this:rightTree;
}
KdTree* leftMinNode = leftTree->GetMinYTreeNode();
KdTree* rightMinNode = rightTree->GetMinYTreeNode();
return leftMinNode->point.y < rightMinNode->point.y? leftMinNode:rightMinNode;
}
bool KdTree::isLeftTreeNode(Point point)
{
if((splitX && point.x < this->point.x)||(splitY && point.y < this->point.y))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool KdTree::isRightTreeNode(Point point)
{
if((splitX && point.x > this->point.x)||(splitY && point.y > this->point.y))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void KdTree::BuildTree(Point* pointArray,int l,int r)
{
//这里的方差相当于乘了n,因为只比较大小
//x方向和y方向上的方差 ,和
float sdx,sdy,sumx,sumy;
for(int i = l; i < r; ++i)
{
sumx += pointArray[i].x;
sumy += pointArray[i].y;
}
//得到平均数
float avex = sumx/(r - l),avey = sumy/(r - l);
//计算方差
for(int i = l; i < r; ++i)
{
sdx += pow(pointArray[i].x - avex,2);
sdy += pow(pointArray[i].y - avey,2);
}
int m = (l + r)/2;
if(sdx > sdy)
{
sort(pointArray + l,pointArray + r,XSortFunc);//x排序并找到中间的那个点
splitX = pointArray[m].x;//本结点是在x方向进行了划分
splitY = 0;//y方向没有划分
}
else
{
sort(pointArray + l,pointArray + r,YSortFunc);//y排序并找到中间的那个点
splitY = pointArray[m].y;
splitX = 0;
}
//当前结点设置为中位数
point = pointArray[m];
//[l,r]的区间是左闭右开的
if(m > l)
{
leftTree = new KdTree();
leftTree->BuildTree(pointArray,l,m);//递归构建左子树
}
if(m < r - 1)
{
rightTree = new KdTree();
rightTree->BuildTree(pointArray,m+1 ,r);//递归构建右子树
}
}
//这里不考虑影响其他层的方差,因为取方差大的方向分割是为了在当时的情况下让这颗树尽可能平衡
void KdTree::Insert(Point point)
{
//只有一个孩子
if(!leftTree && rightTree)
{
if(isLeftTreeNode(point))
{
//cout<point<point<point.x) > abs(point.y - this->point.y))
{
//因为这里我默认用y划分,所以是叶结点要重新比较xy进行划分
splitY = 0;
splitX = this->point.x;
if(point.x > this->point.x)
{
rightTree = new KdTree(point,NULL,NULL,0,point.y);
}
else
{
leftTree = new KdTree(point,NULL,NULL,0,point.y);
}
}
else
{
splitX = 0;
splitY = this->point.y;
if(point.y > this->point.y)
{
rightTree = new KdTree(point,NULL,NULL,0,point.y);
}
else
{
leftTree = new KdTree(point,NULL,NULL,0,point.y);
}
}
return;
}
//只有一个孩子并且往孩子结点走或者是有两个孩子
if(splitX)
{
if(point.x < splitX)
{
leftTree->Insert(point);
}
else
{
rightTree->Insert(point);
}
}
if(splitY)
{
if(point.y < splitY)
{
leftTree->Insert(point);
}
else
{
rightTree->Insert(point);
}
}
}
void KdTree::Delete(KdTree* parent,Point point)
{
//找到了要被删除的结点
if(this->point == point)
{
//要被删除的结点是叶子结点,直接删
if(!leftTree&&!rightTree)
{
if(parent->leftTree&&parent->leftTree->point == this->point)
{
parent->leftTree = NULL;
delete this;
return;
}
else
{
parent->rightTree = NULL;
delete this;
return;
}
}
//要被删除的结点有左子树
else if(leftTree)
{
KdTree* tmpTree;
if(splitX)
{
//找到左子树x最大的点
tmpTree = leftTree->GetMaxXTreeNode();
//调整划分大小
this->splitX = tmpTree->point.x;
}
else
{
//找到左子树y最大的点
tmpTree = leftTree->GetMaxYTreeNode();
//调整划分大小
this->splitY = tmpTree->point.y;
}
//设置点
this->point = tmpTree->point;
//从左子树上递归删除x或y最大的结点
leftTree->Delete(this,tmpTree->point);
}
//要被删除的结点有右子树
else if(!leftTree&&rightTree)
{
KdTree* tmpTree;
if(splitX)
{
//找到右子树上x最小的点
tmpTree = rightTree->GetMinXTreeNode();
//调整划分大小
this->splitX = tmpTree->point.x;
}
else
{
tmpTree = rightTree->GetMinYTreeNode();
this->splitY = tmpTree->point.y;
}
//设置点
this->point = tmpTree->point;
//从右子树上递归删除x或y最小的结点
rightTree->Delete(this,tmpTree->point);
}
}
//没有找到目标点,需要先递归寻找
if(leftTree && ((splitX && point.x < splitX)||(splitY && point.y < splitY)))
{
leftTree->Delete(this,point);
}
if(rightTree && ((splitX && point.x > splitX)||(splitY && point.y > splitY)))
{
rightTree->Delete(this,point);
}
}
void GetNearestPoint(KdTree* root,KdTree* parent,Point point,float& minDis,Point& tarPoint)
{
//找到了叶子结点的孩子结点
if(root == NULL)
return;
//当前结点已经访问过
root->isVisited = true;
//计算当前结点和point的距离
float dis = pow(point.x-root->point.x,2) + pow(point.y-root->point.y,2);
//如果当前结点和point之间的距离比最小距离小,则更新目标点和最小距离
if(minDis < 0 || dis < minDis)
{
tarPoint = root->point;
minDis = dis;
}
if((root->splitX && point.x < root->point.x) || (root->splitY && point.y < root->point.y))
{
//左子树不为空并且point偏向左子树就从左子树上递归地寻找最邻近点
if(root->leftTree&&!root->leftTree->isVisited)
GetNearestPoint(root->leftTree,root,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
else
{
//右子树不为空并且point偏向右子树就从右子树上递归地寻找最邻近点
if(root->rightTree&&!root->rightTree->isVisited)
GetNearestPoint(root->rightTree,root,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
//走到这里肯定有两种情况,要么到了叶子结点并且回退到了上一层,要么到了只有一个孩子的结点是本层,在这两种情况下:
//1.走到了叶子结点并且回退到了上一层,这时候需要找当前结点的另一个叶子结点(如果有的话)以及兄弟结点
//2.到了只有一个孩子的结点并且在本层,这时候需要找它的兄弟结点以及它的孩子结点,因为在这种情况下仅靠比较分割大小是走不到它孩子结点所在的子树的
//定义当前结点的兄弟结点和孩子结点与目标结点的距离
float rL = minDis + 1,rR = minDis + 1,childrL = minDis + 1,childrR = minDis + 1;
//这里有问题是因为回退到这里不一定是叶子结点,所以需要找它的兄弟以及另一个孩子结点,下面四个递归顶多会走两个
if(parent->leftTree)
rL = pow(point.x - parent->leftTree->point.x,2) + pow(point.y - parent->leftTree->point.y,2);
if(parent->rightTree)
rR = pow(point.x - parent->rightTree->point.x,2) + pow(point.y - parent->rightTree->point.y,2);
if(root->leftTree)
childrL = pow(point.x - root->leftTree->point.x,2) + pow(point.y - root->leftTree->point.y,2);
if(root->rightTree)
childrR = pow(point.x - root->rightTree->point.x,2) + pow(point.y - root->rightTree->point.y,2);
//左兄弟结点在圆内就递归地寻找以左兄弟结点为根节点子树的point的最邻近点
if(parent->leftTree && !parent->leftTree->isVisited && rL < minDis)
{
GetNearestPoint(parent->leftTree,parent,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
//右兄弟结点在圆内就递归寻找以右兄弟结点为根节点子树的point的最邻近点
if(parent->rightTree && !parent->rightTree->isVisited && rR < minDis)
{
GetNearestPoint(parent->rightTree,parent,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
//左孩子结点在圆内就递归寻找以左孩子结点为根结点子树的point的最邻近点
if(root->leftTree && !root->leftTree->isVisited && childrL < minDis)
{
GetNearestPoint(root->leftTree,root,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
//右孩子结点在圆内就递归寻找以右孩子结点为根结点子树的point的最邻近点
if(root->rightTree && !root->rightTree->isVisited && childrR < minDis)
{
GetNearestPoint(root->rightTree,root,point,minDis,tarPoint);
}
}
//层序遍历只是为了debug写的
void KdTree::Bfs()
{
KdTree* tree = this;
tree->depth = 1;
queue q;
q.push(tree);
while(!q.empty())
{
KdTree* h = q.front();
q.pop();
cout<point<<" "<depth<<" "<splitX<<" "<splitY<leftTree)
{
h->leftTree->depth = h->depth + 1;
q.push(h->leftTree);
}
if(h->rightTree)
{
h->rightTree->depth = h->depth + 1;
q.push(h->rightTree);
}
}
} 因为叶子结点不一定是最邻近的,这个好想,但是还有一种只有一个孩子却走不到的情况,我再举例说明一下,为什么会有走到只有一个孩子的结点,但走不到它的孩子的情况:
比如:要找(10.1,10.1),根据上述逻辑,10.1>8先走到(8,6)的右子树,之后发现10.1>10,那肯定要走(13,10)的右子树,但(13,10)的右子树是空的,如果在这种情况下回退的时候无操作,输出的结果就是(13,10),但其实(10.1,10.1)到(12,8)的距离才是最小的,因此在找到(13,10)的时候,我需要以(10.1,10.1)为圆心,以(10.1,10.1)和(13,10)之间的距离为半径画一个圆,这时候我判断(12,8)是在圆内的,就需要找(12,8)所在子树中(10.1,10.1)的最邻近点,这样子最后得出来的结果就是(12,8)了。