springboot的web服务器
我们知道,springboot是spring-mvc的整合,其中一项优点是内嵌服务器。但是,他并非一定要使用内嵌服务器,springboot也提供了外部部署的选项。
springboot启动
-
-
- 内嵌服务器
- 外部服务器
-
内嵌服务器
首先摘入官网的一段话:
Under the hood, Spring Boot uses a different type of ApplicationContext for embedded servlet container support. The ServletWebServerApplicationContext is a special type of WebApplicationContext that bootstraps itself by searching for a single ServletWebServerFactory bean. Usually a TomcatServletWebServerFactory, JettyServletWebServerFactory, or UndertowServletWebServerFactory has been auto-configured.
使用ServletWebServerApplicationContext 可以发现服务器。
那么这些服务器在哪里配置呢?按照springboot的套路,一定是在自动配置类中:
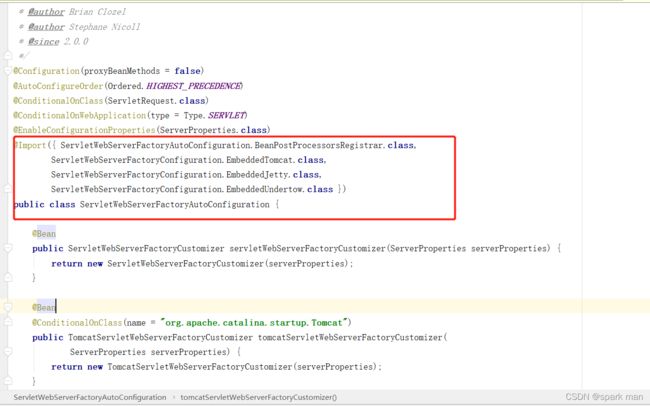
他这里有tomcat,jetty,undertow几个选项。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
所以自带tomcat的包。
所以我们的容器中就会有TomcatServletWebServerFactory。
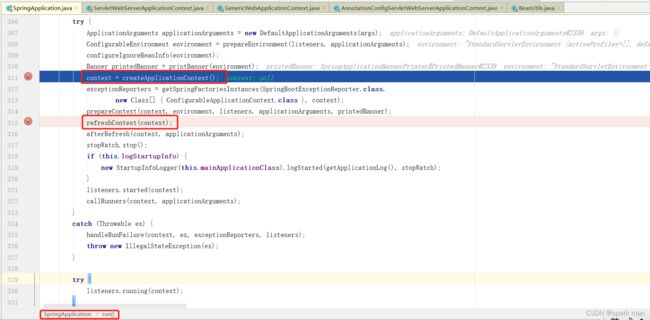
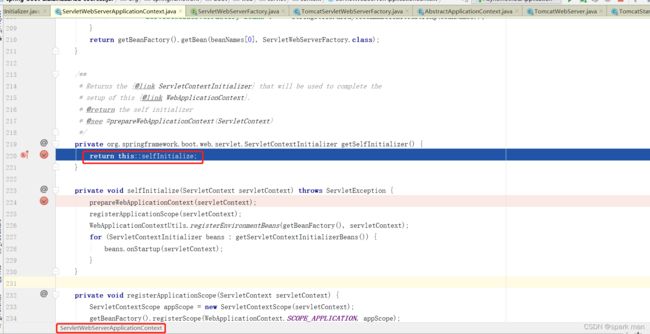
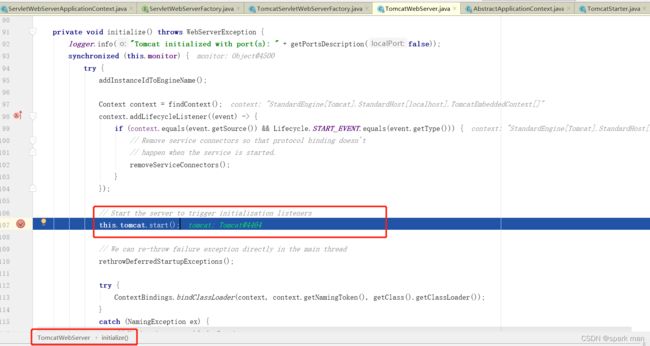
那么,内嵌tomcat是如何启动的呢?我这里截几张图表示重要的点:
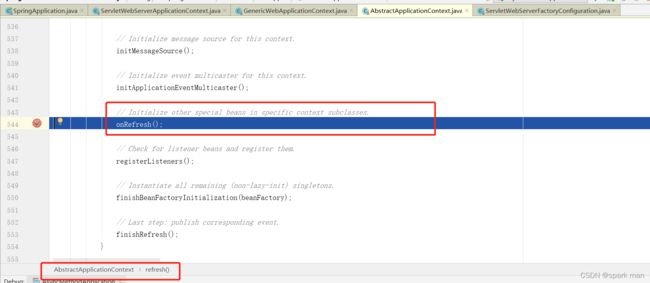
创建容器和刷新容器。我们进入refreshContext方法。
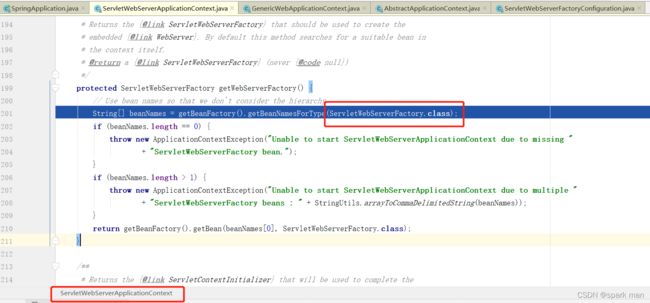
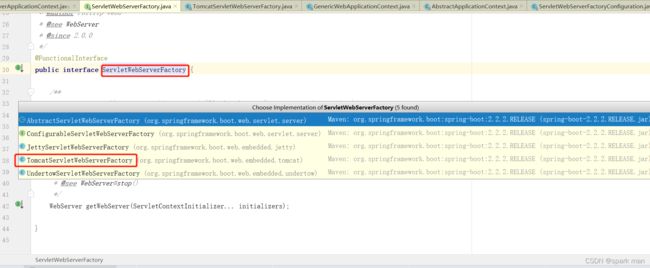
他是按类型去容器拿的,当然,我们容器里有TomcatServletWebServerFactory,他就是个ServletWebServerFactory。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ServletContextInitializer {
/**
* Configure the given {@link ServletContext} with any servlets, filters, listeners
* context-params and attributes necessary for initialization.
* @param servletContext the {@code ServletContext} to initialize
* @throws ServletException if any call against the given {@code ServletContext}
* throws a {@code ServletException}
*/
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}
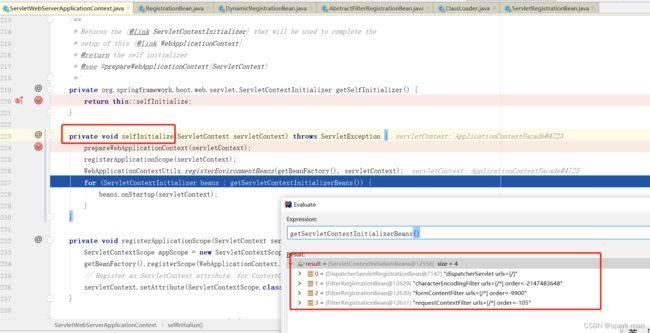
他接受一个参数,不返回值,像Consumer一样。这时是不会调用的,要等到调用ServletContextInitializer 类型的onStartup方法才会将ServletContext 传进来,传给selfInitialize使用。
ServletContextInitializer 这个东西相当于是spring自己来接管servlet的。

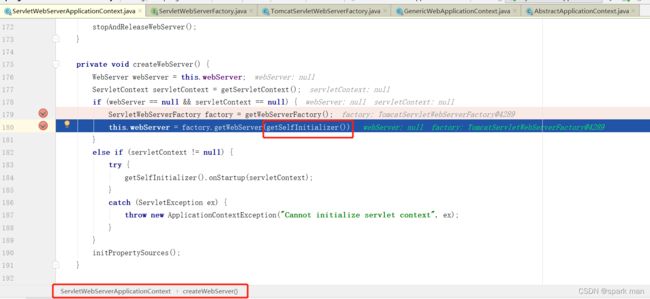
getWebServer这里我们把tomcat给new出来了。
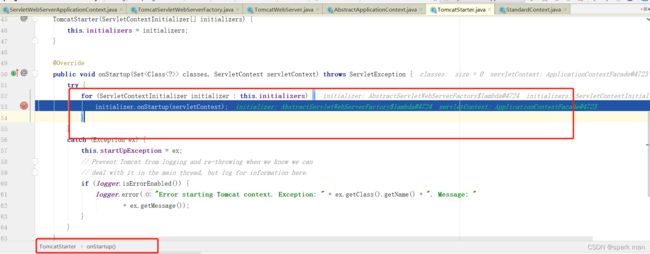
然后把初始化器丢进去,走ServletContextInitializer的onStartup方法。
外部服务器
使用外部服务器,比如tomcat,该怎么做呢?
首先,改造我们的代码:
<packaging>warpackaging>
<artifactId>springboot-contextartifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcatartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
<version>3.1.0version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-pluginartifactId>
<version>3.0.0version>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
首先要求打成war包,然后去掉自带的tomcat,加入javax包,以及一个打包工具。
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyStarter extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(MyStarter.class);
}
}
主配置类去掉main方法(那是走内嵌服务器的逻辑),继承SpringBootServletInitializer,重写configure方法,把主配置类丢进去。
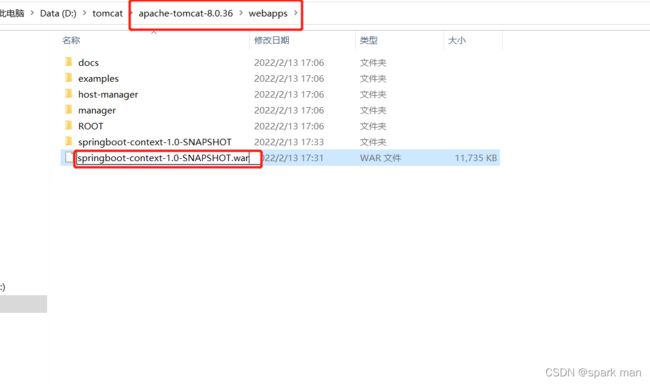
打成war包后丢到webapp目录,运行tomcat就能启动程序了。
关键是,为什么?
我们问的其实是:tomcat怎么发现我们的程序入口的(这里是MyStarter)?
MyStarter继承了一个SpringBootServletInitializer,这又是什么?
public abstract class SpringBootServletInitializer
implements WebApplicationInitializer
他是一个WebApplicationInitializer。
那WebApplicationInitializer又是被谁发现的(或者说调用的)?
有这么一个重要的类:
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer
implements ServletContainerInitializer
他的注释很多。
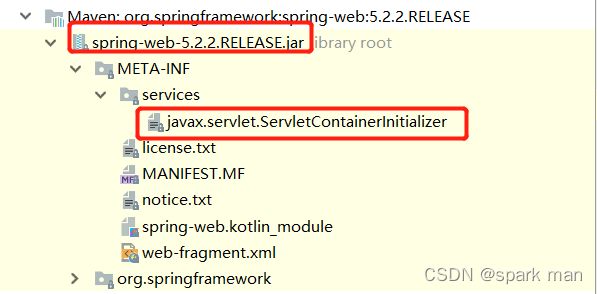
大意是,实现了servlet3.0规范的服务器(我用的是tomcat8,那是实现了的)会去META-INF/services/ 下面找一个ServletContainerInitializer(SPI机制)。
我们有吗?有的。
文件的内容是:
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
服务器看你注解里传的什么:
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
是WebApplicationInitializer。然后他把所有的WebApplicationInitializer给你整来,连着ServletContext一起丢给你:
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>>
webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException

然后循环调用WebApplicationInitializer的onStartup方法。
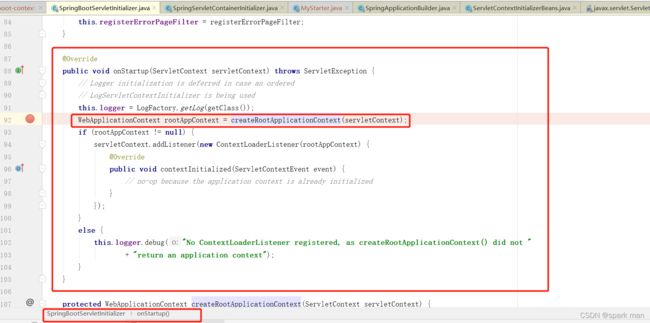
于是就会走到SpringBootServletInitializer的onStartup方法,springboot由此便可以启动了。
关于servlet3.0以及注解化的spring-mvc,可以参考这个