团队协作中如何处理ConflictingBeanDefinitionException异常
前言
当使用Spring框架进行Java应用程序开发时,可能会遇到ConflictingBeanDefinitionException异常。
如:
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConflictingBeanDefinitionException: Annotation-specified bean name ‘xxxBean’ for bean class [xxxBean] conflicts with existing, non-compatible bean definition of same name and class [xxxBean]
这个异常通常发生在以下情况下:在应用程序上下文中存在多个相同名称的Bean定义,导致Spring无法确定应该使用哪一个Bean。这个问题可能出现在团队协作开发中,特别是当不同的开发者在不同的模块中定义了相同名称的Bean时。在本文中,我们将探讨这个异常出现的原因、解决方案以及在团队协作开发中的编码建议。
原因:
ConflictingBeanDefinitionException异常的主要原因是多个Bean定义拥有相同的名称或类型,这导致了Spring容器无法决定应该使用哪一个Bean。这可能发生在以下情况:
- 相同名称的Bean定义:不同的模块或类中定义了具有相同名称的Bean,例如,两个不同的模块都定义了名为 “ABean” 的Bean。
- 相互依赖Model中Bean定义冲突:在微服务项目中,ModelA中定义了ABean,ModelB中定义了ABean,现由于业务原因,ModelA的pom文件中引入ModelB的坐标,也会引发此异常。
- 当父子容器之间存在冲突的Bean定义: 存在继承关系的Bean中出现相同的Bean定义。
@Override
public String generateBeanName(BeanDefinition definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (definition instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedBeanDefinition) {
String beanName = determineBeanNameFromAnnotation(annotatedBeanDefinition);
if (StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
// Explicit bean name found.
return beanName;
}
}
// Fallback: generate a unique default bean name.
return buildDefaultBeanName(definition, registry);
}
在Spring的源码中探究原因
在Spring中,AnnotationBeanNameGenerator定义了如何加载@Component、@RestController、@Service等注解标注的Bean。
@Override
public String generateBeanName(BeanDefinition definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (definition instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedBeanDefinition) {
String beanName = determineBeanNameFromAnnotation(annotatedBeanDefinition);
if (StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
// Explicit bean name found.
return beanName;
}
}
// Fallback: generate a unique default bean name.
return buildDefaultBeanName(definition, registry);
}
/**
* Derive a bean name from one of the annotations on the class.
* @param annotatedDef the annotation-aware bean definition
* @return the bean name, or {@code null} if none is found
*/
@Nullable
protected String determineBeanNameFromAnnotation(AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedDef) {
//获取元数据对象
AnnotationMetadata amd = annotatedDef.getMetadata();
//获取元数据对象类型
Set<String> types = amd.getAnnotationTypes();
//定义Bean名称
String beanName = null;
for (String type : types) {
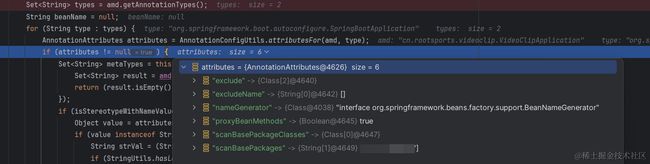
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(amd, type);
if (attributes != null) {
//判断该元数据是否已加载
Set<String> metaTypes = this.metaAnnotationTypesCache.computeIfAbsent(type, key -> {
Set<String> result = amd.getMetaAnnotationTypes(key);
return (result.isEmpty() ? Collections.emptySet() : result);
});
//检查给定类型的注解已通过注解的value属性定义名称
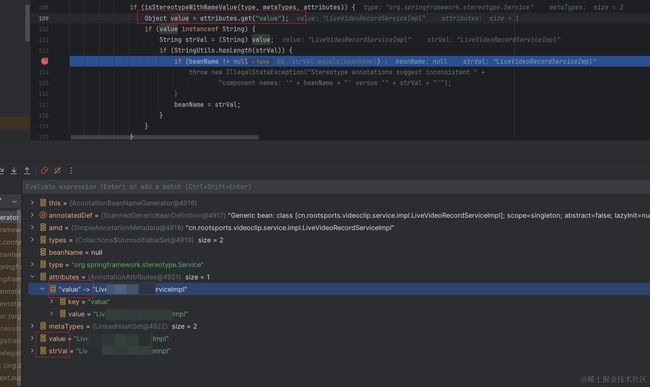
if (isStereotypeWithNameValue(type, metaTypes, attributes)) {
Object value = attributes.get("value");
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = (String) value;
if (StringUtils.hasLength(strVal)) {
//如果beanName不是空,且元数据中解析到定义的Bean名称于当前BeanName不一致,则抛出异常
if (beanName != null && !strVal.equals(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stereotype annotations suggest inconsistent " +
"component names: '" + beanName + "' versus '" + strVal + "'");
}
//给当前Bean的名称赋值
beanName = strVal;
}
}
}
}
}
return beanName;
}
/**
* Check whether the given annotation is a stereotype that is allowed
* to suggest a component name through its annotation {@code value()}.
* @param annotationType the name of the annotation class to check
* @param metaAnnotationTypes the names of meta-annotations on the given annotation
* @param attributes the map of attributes for the given annotation
* @return whether the annotation qualifies as a stereotype with component name
*/
protected boolean isStereotypeWithNameValue(String annotationType,
Set<String> metaAnnotationTypes, @Nullable Map<String, Object> attributes) {
boolean isStereotype = annotationType.equals(COMPONENT_ANNOTATION_CLASSNAME) ||
metaAnnotationTypes.contains(COMPONENT_ANNOTATION_CLASSNAME) ||
annotationType.equals("javax.annotation.ManagedBean") ||
annotationType.equals("javax.inject.Named");
return (isStereotype && attributes != null && attributes.containsKey("value"));
}
例如,我给被@Service注解标注的AService类手动定义了一个Bean名称,在启动SpringBoot项目时,该Bean会注入Spring容器池中,此时在AnnotationBeanNameGenerator类打个断点,我们可以看到已经从注解的元数据中拿到了对应的Bean名称,而后把Bean的信息放入容器池中,当再次解析到相同的Bean名称时,便会报错ConflictingBeanDefinitionException。
解决方案:
要解决ConflictingBeanDefinitionException异常,可以采取以下解决方案:
@Component指定组件名称
当如此命名时,启动时一定会报错ConflictingBeanDefinitionException。解决方案就是:
使用@Component注解的value属性,给Bean配置组件名称。
@Component(value = "testBeanA")
public class TestBean {
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
@Component(value = "TestBeanA")
public class TestBean {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
团队中的命名规范的一些思考:
命名规范:在团队协作开发中,制定命名规范以避免不同开发者定义相同名称的Bean。避免作用不同Bean使用相同的名称,关于命名规范,可以采用模块名前缀或其他约定来命名Bean,以确保它们在整个应用程序中是唯一的。
处理冲突的Bean:
修改/删除冲突的Bean定义: 如果有多个相同名称的Bean定义,需要查看团队代码、知识库文档等信息,进行适当的文档和沟通,了解冲突Bean的功能和创建该Bean的背景,根据该Bean当前是否正在被使用或者是被废弃、以及自己创建同名Bean的需求,判断对该Bean的修改,确保只有一个Bean定义存在,并加以适当的注释、文档说明,以避免未来的混淆和冲突。
以下是一个反例:
使用@Primary注解:
@Primary注解可以用于标记主要的候选Bean,当存在多个候选Bean时,Spring会优先选择标记为主要的Bean。
团队开发中的一些思考及编码建议:
在团队协作开发中,以下是一些建议,可帮助减少ConflictingBeanDefinitionException异常的发生:
- 命名约定:制定明确的命名约定,以避免不同开发者定义相同名称的Bean。可以使用模块名、功能前缀等来命名Bean。
- 合并Bean定义:如果可能,考虑合并具有相同名称的Bean定义,以简化项目配置。确保合并后的Bean仍然满足应用程序的需求。
- 明确指定依赖:在依赖注入时,使用@Component(value= “xxx”)、@Qualifier注解来明确指定要注入的Bean,以解决自动装配的歧义性。
- 代码质量和维护性:确保编写的Bean具有良好的代码质量和可维护性,以便项目的其他成员容易理解和使用。
- 代码审查:进行代码审查,确保团队成员了解已定义的Bean,并遵循统一的命名和规范。
总结:
ConflictingBeanDefinitionException异常可能在团队协作开发中出现,但通过明确的命名约定、合理的Bean定义和文档沟通,可以有效地减少这种异常的发生,保持项目的可维护性和稳定性。很多萌新遇到类似的问题时,感觉无从下手,首先不要慌,问题的原因都在你IDEA的Console框中,要仔细观察。问题的答案在自己的脑子和搜索引擎中,要善用搜索引擎,要相信自己遇到过的大多数问题,别人也都遇到过,并且有标准答案。
雷军:遇到不懂的问题,要第一时间找个懂的人问问。