大数据开发-Flink-数据流DataStream和DataSet
文章目录
- 一、DataStream的三种流处理Api
-
-
- 1.1 DataSource
- 1.2 Transformation
- 1.3 Sink
-
- 二、DataSet的常用Api
-
-
- 2.1 DataSource
- 2.2 Transformation
- 2.3 Sink
-
Flink主要用来处理数据流,所以从抽象上来看就是对数据流的处理,正如前面大数据开发-Flink-体系结构 && 运行架构提到写Flink程序实际上就是在写DataSource、Transformation、Sink.
- DataSource是程序的数据源输入,可以通过StreamExecutionEnvironment.addSource(sourceFuntion)为程序
添加一个数据源 - Transformation是具体的操作,它对一个或多个输入数据源进行计算处理,比如Map、FlatMap和Filter等操作
- Sink是程序的输出,它可以把Transformation处理之后的数据输出到指定的存储介质中
一、DataStream的三种流处理Api
1.1 DataSource
Flink针对DataStream提供了两种实现方式的数据源,可以归纳为以下四种:
- 基于文件
readTextFile(path) 读取文本文件,文件遵循TextInputFormat逐行读取规则并返回
- 基于Socket
socketTextStream 从Socket中读取数据,元素可以通过一个分隔符分开
- 基于集合
fromCollection(Collection) 通过Java的Collection集合创建一个数据流,集合中的所有元素必须是相同类型的,需要注意的是,如果集合里面的元素要识别为POJO,需要满足下面的条件
- 该类有共有的无参构造方法
- 该类是共有且独立的(没有非静态内部类)
- 类(及父类)中所有的不被static、transient修饰的属性要么有公有的(且不被final修饰),要么是包含公有的getter和setter方法,这些方法遵循java bean命名规范
总结:上面的要求其实就是为了让Flink可以方便地序列化和反序列化这些对象为数据流
- 自定义Source
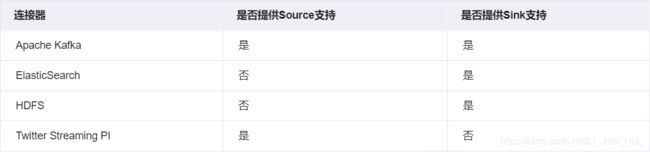
使用StreamExecutionEnvironment.addSource(sourceFunction) 将一个流式数据源加到程序中,具体这个sourceFunction 是为非并行源implements SourceFunction,或者为并行源 implements ParallelSourceFunction接口,或者extends RichParallelSourceFunction,对于自定义Source,Sink, Flink内置了下面几种Connector
对于Source的使用,其实较简单,这里给一个较常用的自定义Source的KafaSource的使用例子。更多相关源码可以查看:
package com.hoult.stream;
public class SourceFromKafka {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
String topic = "animalN";
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "linux121:9092");
FlinkKafkaConsumer<String> consumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer<>(topic, new SimpleStringSchema(), props);
DataStreamSource<String> data = env.addSource(consumer);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<Long, Long>> maped = data.map(new MapFunction<String, Tuple2<Long, Long>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<Long, Long> map(String value) throws Exception {
System.out.println(value);
Tuple2<Long,Long> t = new Tuple2<Long,Long>(0l,0l);
String[] split = value.split(",");
try{
t = new Tuple2<Long, Long>(Long.valueOf(split[0]), Long.valueOf(split[1]));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return t;
}
});
KeyedStream<Tuple2<Long,Long>, Long> keyed = maped.keyBy(value -> value.f0);
//按照key分组策略,对流式数据调用状态化处理
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<Long, Long>> flatMaped = keyed.flatMap(new RichFlatMapFunction<Tuple2<Long, Long>, Tuple2<Long, Long>>() {
ValueState<Tuple2<Long, Long>> sumState;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
//在open方法中做出State
ValueStateDescriptor<Tuple2<Long, Long>> descriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor<>(
"average",
TypeInformation.of(new TypeHint<Tuple2<Long, Long>>() {
}),
Tuple2.of(0L, 0L)
);
sumState = getRuntimeContext().getState(descriptor);
// super.open(parameters);
}
@Override
public void flatMap(Tuple2<Long, Long> value, Collector<Tuple2<Long, Long>> out) throws Exception {
//在flatMap方法中,更新State
Tuple2<Long, Long> currentSum = sumState.value();
currentSum.f0 += 1;
currentSum.f1 += value.f1;
sumState.update(currentSum);
out.collect(currentSum);
/*if (currentSum.f0 == 2) {
long avarage = currentSum.f1 / currentSum.f0;
out.collect(new Tuple2<>(value.f0, avarage));
sumState.clear();
}*/
}
});
flatMaped.print();
env.execute();
}
}
1.2 Transformation
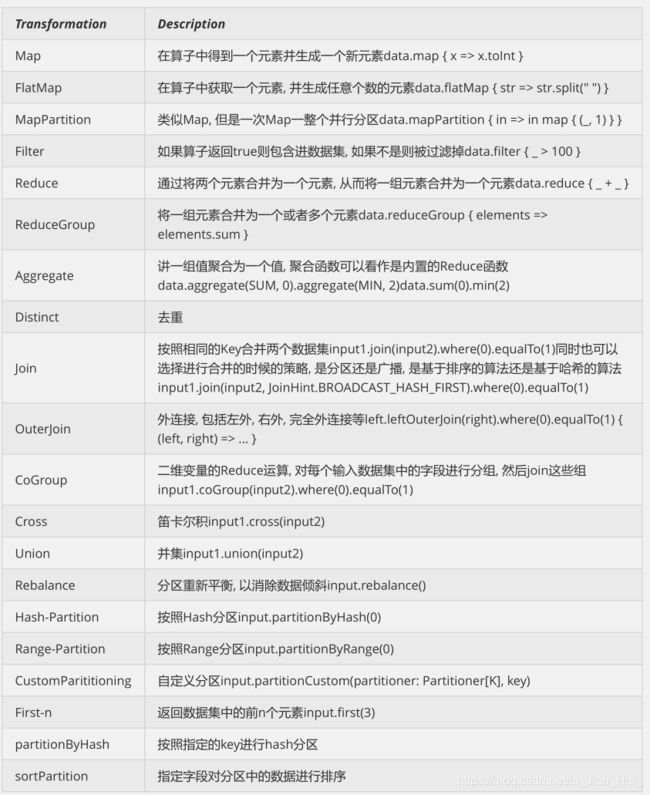
对于Transformation ,Flink提供了很多的算子.
- map
DataStream → DataStream Takes one element and produces one element. A map function that doubles the values of the input stream:
DataStream<Integer> dataStream = //...
dataStream.map(new MapFunction<Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer map(Integer value) throws Exception {
return 2 * value;
}
});
- flatMap
DataStream → DataStream Takes one element and produces zero, one, or more elements. A flatmap function that splits sentences to words:
dataStream.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() {
@Override
public void flatMap(String value, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
for(String word: value.split(" ")){
out.collect(word);
}
}
});
- filter
DataStream → DataStream Evaluates a boolean function for each element and retains those for which the function returns true. A filter that filters out zero values:
dataStream.filter(new FilterFunction<Integer>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(Integer value) throws Exception {
return value != 0;
}
});
更多算子操作可以查看官网,官网写的很好:https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.13/docs/dev/datastream/operators/overview/
1.3 Sink
Flink针对DataStream提供了大量的已经实现的数据目的地(Sink),具体如下所示
-
writeAsText():讲元素以字符串形式逐行写入,这些字符串通过调用每个元素的toString()方法来获取
-
print()/printToErr():打印每个元素的toString()方法的值到标准输出或者标准错误输出流中
-
自定义输出:addSink可以实现把数据输出到第三方存储介质中, Flink提供了一批内置的Connector,其中有的Connector会提供对应的Sink支持
这里举一个常见的例子,下层到Kafka
import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.SimpleStringSchema;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.kafka.FlinkKafkaProducer;
public class StreamToKafka {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStreamSource<String> data = env.socketTextStream("teacher2", 7777);
String brokerList = "teacher2:9092";
String topic = "mytopic2";
FlinkKafkaProducer producer = new FlinkKafkaProducer(brokerList, topic, new SimpleStringSchema());
data.addSink(producer);
env.execute();
}
}
二、DataSet的常用Api
2.1 DataSource
对DataSet批处理而言,较为频繁的操作是读取HDFS中的文件数据,因为这里主要介绍两个DataSource组件
-
基于集合 ,用来测试和DataStream类似
-
基于文件 readTextFile…
2.2 Transformation
更多算子可以查看官网:https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.13/docs/dev/dataset/overview/
2.3 Sink
Flink针对DataStream提供了大量的已经实现的数据目的地(Sink),具体如下所示
-
writeAsText():将元素以字符串形式逐行写入,这些字符串通过调用每个元素的toString()方法来获取
-
writeAsCsv():将元组以逗号分隔写入文件中,行及字段之间的分隔是可配置的,每个字段的值来自对象的
-
toString()方法
-
print()/pringToErr():打印每个元素的toString()方法的值到标准输出或者标准错误输出流中
Flink提供了一批内置的Connector,其中有的Connector会提供对应的Sink支持,如1.1节中表所示