代码随想录算法训练营第三天 | LeetCode 203. 移除链表元素、707. 设计链表、206. 反转链表
代码随想录算法训练营第三天 | LeetCode 203. 移除链表元素、707. 设计链表、206. 反转链表
文章链接:代码随想录移除链表元素 代码随想录设计链表 代码随想录反转链表
视频链接:代码随想录移除链表元素 代码随想录设计链表 代码随想录反转链表
目录
代码随想录算法训练营第三天 | LeetCode 203. 移除链表元素、707. 设计链表、206. 反转链表
1. 链表基础
1.1 定义
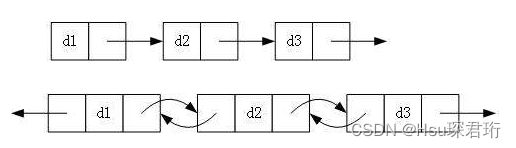
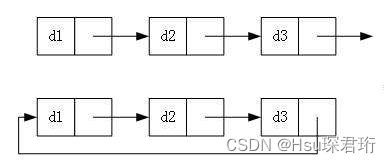
1.2 链表结构示意图
1.3 链表分类
1.3.1 单向/双向
1.3.2 带头/不带头
1.3.3 循环/非循环
1.3.4 常用的链表
1.4 单链表的实现
1.5 双向链表的实现
2. LeetCode 203. 移除链表元素
2.1 自己的思路
2.2 代码
2.3 虚拟头节点思路
2.4 代码
2.5 不用虚拟头节点思路
2.6 代码
3. LeetCode 707. 设计链表
3.1 思路:(含有虚拟头节点,方便增删改的操作)
3.2 代码
4. LeetCode 206. 反转链表
4.1 双指针思路
4.2 代码
1. 链表基础
1.1 定义
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
1.2 链表结构示意图
1.3 链表分类
1.3.1 单向/双向
1.3.2 带头/不带头
1.3.3 循环/非循环
1.3.4 常用的链表
-
无头单向非循环链表
-
无头双向链表
1.4 单链表的实现
public class MySingleList {
class ListNode {//节点
public int val;
public ListNode next;//默认不设置值
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
//不定义在节点里,是因为这是链表的属性而不是节点的属性
public ListNode head;//永远指向我的头节点,这是个假头,跟那些真正带头的节点不是一个意思
//创造链表
public void createList() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(56);//这里5个节点,到这里还没有联系
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;//这5个节点建立联系,node5是最后的就不用了
this.head = node1;//node1就是头了
}
//遍历单链表
public void show() {
ListNode cur = head;//这里不是定义了一个节点,只是头节点的一个引用
while (cur != null) {//cur==null时就是走到最后了
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
//this.head=this.head.next;//这么写head变了,不好
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size() {//即链表的节点个数
ListNode cur = head;//这里不是定义了一个节点,只是头节点的一个引用
int size = 0;
while (cur != null) {//如果想把链表遍历完,那么cur应该是为null的时候
cur = cur.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
//通过遍历链表的方式把key找到
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {//如果val是引用数据类型,那要用equals来比较!!!
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {//不管开始有无节点,这段代码都没问题
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);//新创建一个节点,放入data
node.next = head;//把这个新节点放到头位置,下一个位置是原来的头节点
head = node;//把head指向这个新节点,让新节点作为头节点
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);新创建一个节点,放入data
if (head == null) {//这里是为了应对这个链表一个节点都没有的情况,直接head就是这个新节点就行了
head = node;
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {//如果写成cur!=null,那cur直接掉到一个head为null的节点了,就是没有
//只是这么写,如果这个链表一个节点都没有就会报错了,所以前面那个是为了应对这种情况
cur = cur.next;
}//走到原来的最后一个节点
cur.next = node;//让原来的最后一个节点的next指向新节点
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
//0.判断index位置的合法性,不能大于链表长度,也不能为负数,为0就头插法,为长度就尾插法
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBounds("任意位置插入数据的时候,index位置不合法: " + index);
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);//头插
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);//尾插
return;
}
/*
//1.先找到index-1位置的节点
int count=0;
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
if(count==index-1){
//2.进行插入操作
node.next=cur.next;
cur.next=node;
return;
}
count++;
}//这段自己写的
*/
//1.先找到index-1位置的节点
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
//2.进行插入操作
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);//创建新节点
node.next = cur.next;//新节点的next是index-1位置的节点的next
cur.next = node;//ndex-1位置的节点的next变为新节点
}
/*
找到index-1位置的节点
*/
private ListNode findIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (index - 1 != 0) {//index是几就进入几次这个循环
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;//index-1位置的节点
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
if (head.val == key) {
head = head.next;//头往后移一位
return;
}
ListNode prev = searchPrev(key);
if (prev == null) {
System.out.println("没有这个key的数据!");
return;
}
ListNode del = prev.next;//del是个局部变量,就是key所在的节点,方法调用完后就会被JVM回收
prev.next = del.next;//直接让key所在节点的前一个节点的next等于key所在节点的下一个节点
//prev.next=prev.next.next;上面两行换成这行也行
}
private ListNode searchPrev(int key) {//找到key的前一个节点
ListNode prev = head;
while (prev.next != null) {//prev.next是指尾巴那个节点,如果那里为null,
//就说明你找到尾了都没找到key,就可以终止循环了
if (prev.next.val == key) {
return prev;
} else {
prev = prev.next;
}
}
return null;
}
//删除所有值为key的节点。(面试题:要求只遍历一次就删除所有值为key的节点)(或者说时间复杂度为O(n))力扣的203题
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
//双指针
ListNode prev = head;//prev表示当前节点的前驱节点
ListNode cur = head.next;//cur表示当前要删除的节点
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
prev = cur;//只有cur节点的值不为key时prev才可以移动
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//前面while循环把后面出现的key都删除了,但此时如果head那里也有就没有删除head那里的
//所以放到最后单独把head那里的val判断一下
if (head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
}
}
public void clear() {
//this.head = null; // 清空链表,让头节点为null
//头没有了,就没有节点指向下一个节点,以此类推,所有节点都清空了
while (head != null) {
ListNode headNext = head.next;
head.next = null;
head = headNext;
}
}
//反转链表
public ListNode reverseList() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
if (head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (cur != null) {
//记录当前需要反转节点的下一个节点
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
return head;
}
}1.5 双向链表的实现
public class MyLinkedList {
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;//方便头插
public ListNode last;//方便尾插
//无头双向链表实现
//得到双向链表的长度,这里写法跟双向无关
public int size() {
int len = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {//遍历链表
cur = cur.next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
//这里写法跟双向无关
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {//遍历链表
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在双向链表当中,这里写法跟双向无关
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {//遍历链表
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
//自己写的
/*// 创建新节点
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
// 将新节点的next指针指向原链表的头结点
node.next=head;
if(head!=null){// 如果链表非空,则将原链表头结点的prev指针指向新节点
head.prev=node;
}
// 将链表的头指针指向新节点
head=node;*/
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {//一个节点都没有
head = node;
last = node;
return;
}
node.next = head;//这个新节点的next置为原来的头节点
head.prev = node;//头节点的前驱置为新节点,如果链表为空,则会空指针异常,所以上面写了一个节点都没有的情况
head = node;//将这个新节点作为头节点
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (last == null) {//一个节点都没有
last = node;
head = node;
return;
}
last.next = node;//原来的尾节点的next置为新节点,如果链表为空,则会空指针异常,所以上面写了一个节点都没有的情况
node.prev = last;//这个新节点的前驱置为原来的尾节点
last = node;//将这个新节点作为尾节点
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBounds("双向链表index不合法!");
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);//头插
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);//尾插
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (index != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
//要修改四个地方,一定要先改插入的节点的前后驱,再改前后节点的后驱和前驱(其实也可以稍微改动,但这样不容易乱)
//这两行是改插入的节点
node.next = cur;//改插入节点的后驱
node.prev = cur.prev;//改插入节点的前驱
//这两行是改插入位置的前后节点
cur.prev.next = node;//插入节点的后驱节点改为node
cur.prev = node;//插入节点的前驱节点改为node
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
//cur.prev.next = cur.next;
//cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
//这两行是关键的删除逻辑,但如果是删除头节点第一行就要判断,如果是删除尾节点第二行就要判断,留意一下
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {//遍历链表
if (cur.val == key) {
//开始删除
if (cur == head) {
//删除头节点
head = head.next;
if(head!=null){//这个判断是应对只有一个节点的情况
head.prev = null;//如果这个链表只有一个节点,那么这一行就空指针异常了,所以要判断头是否为null
//只有一个节点的时候,上面的head = head.next就已经删完了,这里是为了防止空指针异常
}else {
last=null;//如果是一个节点,上面把head置为null了,last也要置为null,可以画图检查一下
}
} else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;//删除节点的前驱节点的next置为删除节点的next
if (cur.next != null) {
//不是尾节点
//cur.prev.next = cur.next;共有代码
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;//删除节点的后驱节点的prev置为删除节点的prev
} else {
//删除尾节点
//cur.prev.next = cur.next;共有代码
last = last.prev;
}
}
return;
} else {
cur = cur.next;//cur后移来遍历
}
}
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
//开始删除
if (cur == head) {
//删除头节点
head = head.next;
if(head!=null){//这个判断是应对只有一个节点的情况,但进入if就说明不是一个节点
head.prev = null;//如果这个链表只有一个节点,那么这一行就空指针异常了,所以要判断头是否为null
//只有一个节点的时候,上面的head = head.next就已经删完了,这里是为了防止空指针异常
}else {
last=null;//如果是一个节点,上面把head置为null了,last也要只为null,可以画图检查一下
}
} else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
//不是尾节点
//cur.prev.next = cur.next;共有代码
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
} else {
//删除尾节点
//cur.prev.next = cur.next;共有代码
last = last.prev;
}
}
//return; 不要return了
} /*else {
cur = cur.next;
}*///这几行注释是跟上面方法的区别
cur=cur.next;//if找到了就删,删完就往后走,直到删完为止
}
}
public void clear() {
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){//遍历链表
ListNode curNext=cur.next;//不这么写那下面置空以后就找不到下一个节点了
cur.prev=null;
cur.next=null;
//如果val是引用类型就要写个cur.val=null;
cur=curNext;//cur后移
}
head=null;
last=null;//这两行也要加,不然还有这两个节点
//只这么写也行,但没有每个逐一释放,所以最好上面那么写
/*head = null;
last = null;*/
}
}2. LeetCode 203. 移除链表元素
2.1 自己的思路
- 遍历找到要删除的节点的前一个节点
- 找到这个节点的next置为要删除节点的next
2.2 代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode prev=head;//要删除节点的前一个节点
ListNode cur=head.next;//要删除节点的位置
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==val){//找到要删除的节点
prev.next=cur.next;//prev的next指向cur的next
cur=cur.next;//cur后移
}else{//只有找到要删除的节点prev才后移
prev=cur;//prev移动到cur的位置
cur=cur.next;//cur后移
}
}
//上面的处理方式没有考虑到头节点也是要删除的节点的情况
//另外把当前节点删除
if(head.val==val){
head=head.next;
}
return head;
}
}2.3 虚拟头节点思路
- 定义一个虚拟头节点 dummyhead,并且实例化new出来,让dummyhead.next=head
- 然后cur=dummyhead,不定义成dummyhead.next是因为按照我们的想法是找到要删除的节点,让删除的节点前一个节点的next指向要删除节点的next,我们这里是让cur指向要删除节点的前一个节点,然后删掉cur.next
- 因为我们删除的节点是cur.next,所以while(cur.next!=null),if(cur.next==val)就删除,否则就cur后移
- return dummyhead.next;为什么不return head呢,因为head很可能被删除了,dummyhead.next才是链表的新节点
- 虚拟头节点的好处就统一了链表的操作,增删节点都统一了
2.4 代码
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 因为删除可能涉及到头节点,所以设置dummy节点,统一操作
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}2.5 不用虚拟头节点思路
- 判断头节点不为空并且头节点的值是要删的值
- 删除方法就是head=head.next
- 但由于移除头节点的方式是一个持续移除,比如:1,1,1,...这样子,所以判断条件前面写while
- 然后是其他节点,cur=head,为什么从头开始呢?因为按照我们的想法是找到要删除的节点,让删除的节点前一个节点的next指向要删除节点的next,我们这里是让cur指向要删除节点的前一个节点,这里while(cur!=null&&cur.next!=null)条件这么写,因为cur.next的值是我们要判断的,不能为空;如果我们定义cur=head.next,那找到当前节点后由于是单链表,没有前一个节点的记录,就没法找到前一个节点了
- 删除操作:符合cur.next=cur.next.next;否则就cur后移
- 最后return head。头节点一直没变
2.6 代码
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
while (head != null && head.val == val) {
head = head.next;
}
// 已经为null,提前退出
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 已确定当前head.val != val
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}3. LeetCode 707. 设计链表
3.1 思路:(含有虚拟头节点,方便增删改的操作)
- 定义虚拟头节点dummyhead,第0个节点就是head节点
- 获取第n个节点:判断n的合法性(n<0||n>size-1),cur=dummyhead.next,遍历让cur移动n个位置,return cur.val
- 头部插入节点:定义新节点node,node.next=dummyhead.next,先让新节点的next指向原来dummyhead的next,然后再让dummyhead的next指向新节点node
- 尾部插入节点:定义新节点node,定义cur=dummyhead,while(cur.next!=null)cur的next不为空前就一直遍历,cur.next为空说明cur指向尾部节点,cur.next=node就行
- 第n个节点前插入:用cur指向第n个节点的前一个节点,这样才能插入,cur=dummyhead,while(n!=0){cur=cur.next;n--},保证第n个节点是cur.next,然后node.next=cur.next;cur.next=node;size++
- 删除第n个节点:cur=dummyhead,然后让cur遍历后移,我们要让cur指向第n个节点的前一个节点,cur.next指向第n个节点,这样才方便删除,让cur.next=cur.next.next;size--
- 总结:我们要明白比如我要操作第n个节点,这第n个点一定是cur.next,这样才能用cur去操作这个点,而且我们要插入一个点时一定是先更新要插入节点的next,然后才是前一个点的next指向插入的节点
3.2 代码
//单链表
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(){}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val=val;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
//size存储链表元素的个数
int size;
//虚拟头结点
ListNode head;
//初始化链表
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
}
//获取第index个节点的数值,注意index是从0开始的,第0个节点就是头结点
public int get(int index) {
//如果index非法,返回-1
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return -1;
}
ListNode currentNode = head;
//包含一个虚拟头节点,所以查找第 index+1 个节点
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return currentNode.val;
}
//在链表最前面插入一个节点,等价于在第0个元素前添加
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0, val);
}
//在链表的最后插入一个节点,等价于在(末尾+1)个元素前添加
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size, val);
}
// 在第 index 个节点之前插入一个新节点,例如index为0,那么新插入的节点为链表的新头节点。
// 如果 index 等于链表的长度,则说明是新插入的节点为链表的尾结点
// 如果 index 大于链表的长度,则返回空
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index > size) {
return;
}
if (index < 0) {
index = 0;
}
size++;
//找到要插入节点的前驱
ListNode pred = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
pred = pred.next;
}
ListNode toAdd = new ListNode(val);
toAdd.next = pred.next;
pred.next = toAdd;
}
//删除第index个节点
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
return;
}
size--;
if (index == 0) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode pred = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index ; i++) {
pred = pred.next;
}
pred.next = pred.next.next;
}
}4. LeetCode 206. 反转链表
4.1 双指针思路
- 第一个指针cur=head,第二个指针prev指向cur的前一个节点,最开始初始化为null,因为翻转后原来的head要指向null
- 什么时候遍历结束?(cur!=null),当cur指向null时就证明不需要翻转了,遍历就结束了
- 在循环里需要一个临时指针,temp指向cur.next,通过这样保存下来
- 然后cur.next=prev;prev=cur;cur=temp
- 最后return pre就可以了
4.2 代码
// 双指针
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;// 保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return prev;
}
}