Spring源码:Aop中@Aspect切面的解析代理过程
目录
1. 再谈AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator自动代理创建类
2. ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory切面工厂类
2.1 ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory创建Advisor的过程
2.1.1 InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl的构造
2.2 增强方法Advice的排序策略
3. BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilderAdapter 切面builder类
前面分析了Spring源码:Aop源码分析 以及Spring源码:声明式事务@Transaction源码分析,根本上来说都是采用aop的思想来实现的,本篇主要详细分析一下@Aspect注解式切面的解析和代理过程;
1. 再谈AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator自动代理创建类
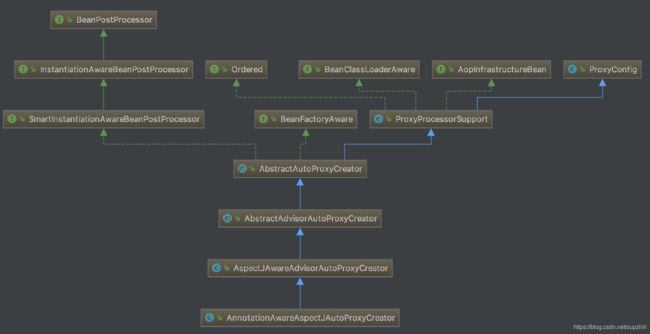
实际上在分析Aop源码的过程中,自动代理创建类为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,它是一个BeanPostProcessor,继承类图如下:
从图中可以看出该自动代理创建类实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,其生命周期方法setBeanFactory是在AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator中实现的,实现代码如下:
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
if (!(beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"AdvisorAutoProxyCreator requires a ConfigurableListableBeanFactory: " + beanFactory);
}
initBeanFactory((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) beanFactory);
}这里主要看initBeanFactory的实现逻辑,具体实现在AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator内:
@Override
protected void initBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.initBeanFactory(beanFactory);
if (this.aspectJAdvisorFactory == null) {
this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = new ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory(beanFactory);
}
this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder =
new BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilderAdapter(beanFactory, this.aspectJAdvisorFactory);
}这里主要初始化了一个aop切面工厂类,AspectJAdvisorFactory,具体实现为ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory,同时构造了BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilderAdapter类,其中:
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory主要用来解析@Aspect注解切面类,获取所有的切面(标注@Before、@After等等的增强方法),进而通过反射调用相应的增强方法;
BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilderAdapter类封装了ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory类和BeanFactory,共同完成Aop切面的build,下面分别对这两个类进行分析;
2. ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory切面工厂类
了解一个实现类,首先要看一下它的继承结构,通过接口可以窥探出实现的功能大概有哪些,对具体实现的细节有很大的指导意义;下面看一下ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory的继承结构:
接口定义这里不做展开,主要的功能就是解析@Aspect注解的切面类,提供创建Advisor和Advice的功能;下面主要通过几点实现来解析ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory的作用:
- 创建Advisor的过程
- 各个不同切面的执行顺序
2.1 ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory创建Advisor的过程
看一下接口方法getAdvisors的实现,然后分后面几点进行说明:
@Override
public List getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
Class aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List advisors = new LinkedList();
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// Find introduction fields.
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
return advisors;
} - AspectMetadata是Aspect切面元数据类,主要包含了aspectName、aspectClass(即标注@Aspect注解的类)等信息;
- LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator采用装饰器模式,使得aspectInstance只会实例化一次,里面采用双重检查加锁实现单例模式;
- getAdvisorMethods方法获取所有的增强方法,实现如下,可以看出这里实际上获取了非切点方法,然后进行方法的排序,具体的排序策略后面再单独分析;
private List getAdvisorMethods(Class aspectClass) {
final List methods = new LinkedList();
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException {
// Exclude pointcuts
if (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) {
methods.add(method);
}
}
});
Collections.sort(methods, METHOD_COMPARATOR);
return methods;
} - getAdvisor方法构造了实际的切面类,实现如下:
@Override
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}该构造切面的过程,首先1)构造了切点AspectJExpressionPointcut ,然后2)构造了切面类InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
关于切点的分析后面再单独分析,这里分析下切面InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl的实现;
2.1.1 InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl的构造
构造函数源码如下:
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
this.declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut;
this.declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass();
this.methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName();
this.parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes();
this.aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod;
this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory;
this.aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory;
this.declarationOrder = declarationOrder;
this.aspectName = aspectName;
// A singleton aspect.
this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;
this.lazy = false;
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
}
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pcut) {
return this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pcut,
this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);
}其中构造Advice过程又调用了aspectJAdvisorFactory的getAdvice方法,下面对该方法进行分析;
2.1.2 ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice()获取Advice方法
getAdvice方法的具体实现如下,这里就看到了各个不同增强注解构造Advice的过程:
@Override
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
Class candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// If we get here, we know we have an AspectJ method.
// Check that it's an AspectJ-annotated class
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {
throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +
"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +
candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
- 上面switch语句根据注解的具体类型,分别创建了不同的Advice
- 完成Advice参数的绑定,具体参数绑定的过程不再展开分析
下面是各个Advice的继承类图:
2.2 增强方法Advice的排序策略
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory中用于Advice的排序器代码如下:
private static final Comparator METHOD_COMPARATOR;
static {
CompoundComparator comparator = new CompoundComparator();
comparator.addComparator(new ConvertingComparator(
new InstanceComparator(
Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class),
new Converter() {
@Override
public Annotation convert(Method method) {
AspectJAnnotation annotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(method);
return (annotation != null ? annotation.getAnnotation() : null);
}
}));
comparator.addComparator(new ConvertingComparator(
new Converter() {
@Override
public String convert(Method method) {
return method.getName();
}
}));
METHOD_COMPARATOR = comparator;
} 具体不做展开,这里主要说明一下排序策略:
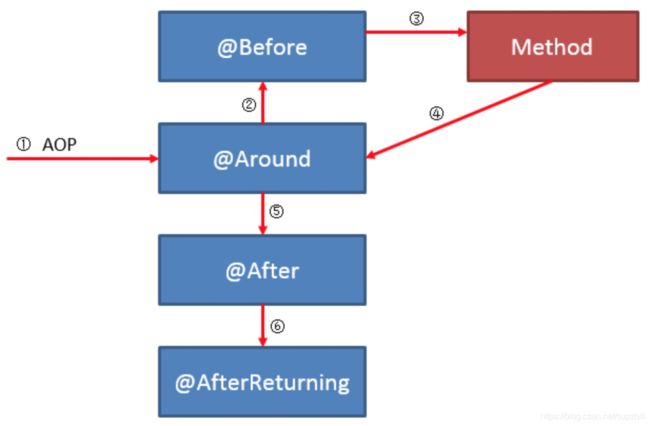
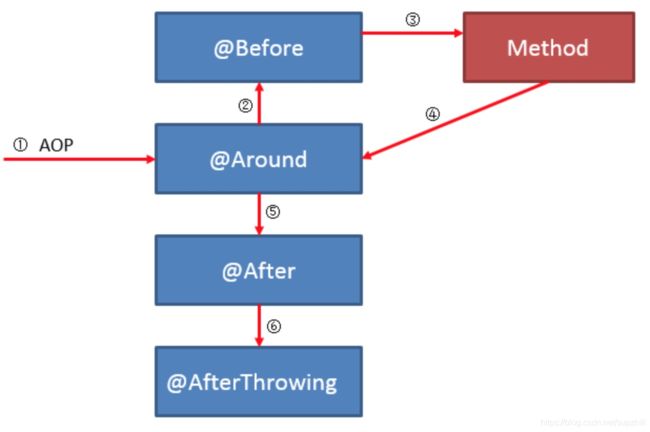
1)根据数组[Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class]的下标索引排序,也及从前往后的顺序,优先级依次降低;
2)对于相同的Advice方法,根据方法名字符串自然序排序;
这样就可以得出各个不同Advice的执行顺序,也即对不同增强方法的执行顺序做出了原理性的解释:
- 正常情况
- 异常情况
3. BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilderAdapter 切面builder类
这里,BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilderAdapter的作用类似于Aop源码中获取Advisor实现类的helper类BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelperAdapter,这里主要封装了获取@Aspect注解类切面的方法,构造切面的具体源码如下:
/**
* Look for AspectJ-annotated aspect beans in the current bean factory,
* and return to a list of Spring AOP Advisors representing them.
* Creates a Spring Advisor for each AspectJ advice method.
* @return the list of {@link org.springframework.aop.Advisor} beans
* @see #isEligibleBean
*/
public List buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List advisors = new LinkedList();
aspectNames = new LinkedList();
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
Class beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
List classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List advisors = new LinkedList();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
List cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}
这里主要包含如下几步:
- 从beanFactory中获取所有的bean
- 判断该bean是否为@Aspect标注的切面类
- 调用advisorFactory获取Advisor列表(具体过程前面已经分析)
- 返回所有@Aspect注解标注的bean解析到的Advisor列表
这样,最终在findCandidateAdvisors方法中,即获得了所有实现Advisor接口的切面类(如声明式事务切面),又获得了所有@Aspect注解的切面类解析得到的所有切面,完美收官!!
@Override
protected List findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
List advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
return advisors;
}