Leetcode——岛屿问题
1.前置
-
先明确一下岛屿问题中的网格结构是如何定义的,网格问题是由 m×n 个小方格组成一个网格,每个小方格与其上下左右四个方格认为是相邻的,要在这样的网格上进行某种搜索。
-
岛屿问题是一类典型的网格问题。每个格子中的数字可能是 0 或者 1。我们把数字为 0 的格子看成海洋格子,数字为 1 的格子看成陆地格子,这样相邻的陆地格子就连接成一个岛屿。
- 网格结构要比二叉树结构稍微复杂一些,它其实是一种简化版的图结构。要写好网格上的 DFS 遍历,我们首先要理解二叉树上的 DFS 遍历方法,再类比写出网格结构上的 DFS 遍历。我们写的二叉树 DFS 遍历一般是这样的:
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
// 判断 base case
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 访问两个相邻结点:左子结点、右子结点
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
}
可以看到,二叉树的 DFS 有两个要素:「访问相邻结点」和「判断 base case」。
对于网格上的 DFS,我们完全可以参考二叉树的 DFS,写出网格 DFS 的两个要素:
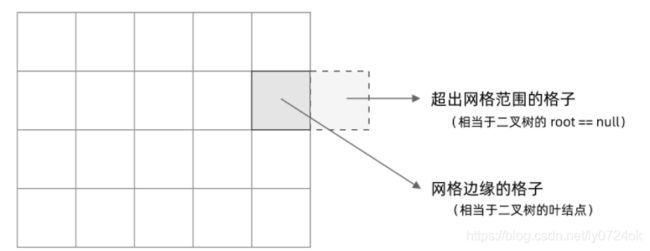
- 首先,网格结构中的格子有多少相邻结点?答案是上下左右四个
- 其次,网格 DFS 中的 base case 是什么?从二叉树的 base case 对应过来,应该是网格中不需要继续遍历、grid[r][c] 会出现数组下标越界异常的格子,也就是那些超出网格范围的格子。
void dfs(int[][] grid, int r, int c) {
// 判断 base case
// 如果坐标 (r, c) 超出了网格范围,直接返回
if (!inArea(grid, r, c)) {
return;
}
// 访问上、下、左、右四个相邻结点
dfs(grid, r - 1, c);
dfs(grid, r + 1, c);
dfs(grid, r, c - 1);
dfs(grid, r, c + 1);
}
// 判断坐标 (r, c) 是否在网格中
boolean inArea(int[][] grid, int r, int c) {
return r >= 0&& r < grid.length
&& c >= 0 && c < grid[0].length;
}
如何避免重复遍历:
- 网格结构的 DFS 与二叉树的 DFS 最大的不同之处在于,遍历中可能遇到遍历过的结点。这是因为,网格结构本质上是一个「图」,我们可以把每个格子看成图中的结点,每个结点有向上下左右的四条边。在图中遍历时,自然可能遇到重复遍历结点。
- 如何避免这样的重复遍历呢?答案是标记已经遍历过的格子。以岛屿问题为例,我们需要在所有值为 1 的陆地格子上做 DFS 遍历。每走过一个陆地格子,就把格子的值改为 2,这样当我们遇到 2 的时候,就知道这是遍历过的格子了。也就是说,每个格子可能取三个值:
- 0 —— 海洋格子
- 1 —— 陆地格子(未遍历过)
- 2 —— 陆地格子(已遍历过)
在框架代码中加入避免重复遍历的语句:
void dfs(int[][] grid, int r, int c) {
// 判断 base case
if (!inArea(grid, r, c)) {
return;
}
// 如果这个格子不是岛屿,直接返回
if (grid[r][c] != 1) {
return;
}
grid[r][c] = 2; // 将格子标记为「已遍历过」
// 访问上、下、左、右四个相邻结点
dfs(grid, r - 1, c);
dfs(grid, r + 1, c);
dfs(grid, r, c - 1);
dfs(grid, r, c + 1);
}
// 判断坐标 (r, c) 是否在网格中
boolean inArea(int[][] grid, int r, int c) {
return 0 <= r && r < grid.length
&& 0 <= c && c < grid[0].length;
}
这样,我们就得到了一个岛屿问题、乃至各种网格问题的通用 DFS 遍历方法。以下所讲的几个例题,其实都只需要在 DFS 遍历框架上稍加修改而已。
PS:
- 在一些题解中,可能会把「已遍历过的陆地格子」标记为和海洋格子一样的 0,美其名曰「陆地沉没方法」,即遍历完一个陆地格子就让陆地「沉没」为海洋。这种方法看似很巧妙,但实际上有很大隐患,因为这样我们就无法区分「海洋格子」和「已遍历过的陆地格子」了。如果题目更复杂一点,这很容易出 bug。
2. 岛屿数量
(1)DFS
class Solution {
private int res;
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j ++) {
//每次dfs会将所有相邻的岛屿标记为2,所有每次遍历到1就代表新的岛屿
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
dfs(grid, i, j);
res ++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int row, int col) {
//终止条件
if (row >= grid.length || col >= grid[0].length || row < 0 || col < 0) {
return;
}
//避免重复遍历
if (grid[row][col] != '1') {
return;
}
//标记已遍历过节点
grid[row][col] = '2';
//继续遍历上下左右四个方向
dfs(grid, row - 1, col);
dfs(grid, row + 1, col);
dfs(grid, row, col - 1);
dfs(grid, row, col + 1);
}
}
(2)BFS
主循环和思路一类似,不同点是在于搜索某岛屿边界的方法不同。
- 借用一个队列 queue,判断队列首部节点 (i, j) 是否未越界且为 1:
- 若是则置零(删除岛屿节点),并将此节点上下左右节点 (i+1,j),(i-1,j),(i,j+1),(i,j-1) 加入队列;
- 若不是则跳过此节点;
- 循环 pop 队列首节点,直到整个队列为空,此时已经遍历完此岛屿。
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
//每次bfs会将所有相邻的岛屿标记为2,所有每次遍历到1就代表新的岛屿
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
bfs(grid, i, j);
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void bfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j){
Queue<int[]> list = new LinkedList<>();
//将每个节点坐标加入到list中
list.add(new int[] { i, j });
while(!list.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = list.remove();
i = cur[0]; j = cur[1];
//未遍历过且为陆地节点,将所有相邻的岛屿标记为2,所有每次遍历到1就代表新的岛屿
if(i >= 0 && i < grid.length && j >= 0 && j < grid[0].length && grid[i][j] == '1') {
//标记已遍历过节点
grid[i][j] = '2';
list.add(new int[] { i + 1, j });
list.add(new int[] { i - 1, j });
list.add(new int[] { i, j + 1 });
list.add(new int[] { i, j - 1 });
}
}
}
}
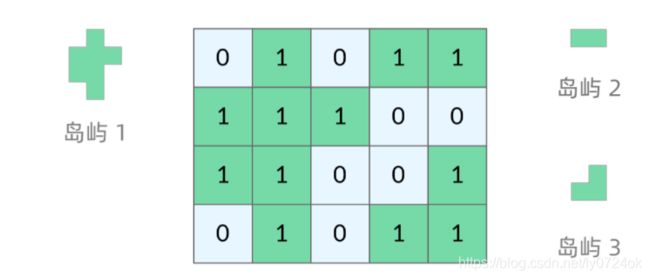
3. 不同岛屿的数量
(1)DFS
- 去重:遍历过的节点都置为2
- 四个方向进行深度搜索
- 每一个坐标都减去第一个坐标的值,相当于的岛屿都移动到以原点(0,0)为起点,得到了岛屿的相对位置,存入list中
- 用set存入每一个岛屿的位置List。相同位置的岛屿存入set中会自动去重
- set的size就是岛屿的个数
class Solution {
private int[][] directions = new int[][]{{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0},{1,0}};
public int numDistinctIslands(int[][] grid) {
Set<List<Integer>> set = new HashSet<>();
if (null == grid|| grid.length == 0){
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(grid, result, i, j, i, j);
if (!result.isEmpty()) {
set.add(result);
}
}
}
}
return set.size();
}
private void dfs(int[][] grid,List<Integer> result,int x,int y,int gapX,int gapY) {
if (x < 0 || x >= grid.length || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].length || grid[x][y] != 1) {
return;
}
//遍历过的点都置为2
grid[x][y] = 2;
//每一个坐标都减去第一个坐标的值,相当于的岛屿都移动到以原点(0,0)为起点,得到了岛屿的相对位置,存入list中
result.add(x - gapX);
result.add(y - gapY);
//四个方向, DFS
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int newX = x + dir[0];
int newY = y + dir[1];
dfs(grid, result, newX, newY, gapX, gapY);
}
}
}
(2)BFS
class Solution {
private int[][] directions = new int[][]{{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0},{1,0}};
public int numDistinctIslands(int[][] grid) {
Set<List<Integer>> set = new HashSet<>();
if (null == grid|| grid.length == 0){
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
bfs(grid, result, i, j, i, j);
if (!result.isEmpty()) {
set.add(result);
}
}
}
}
return set.size();
}
public void bfs(int[][] grid, List<Integer> result, int x, int y, int gapX, int gapY) {
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//将每个节点坐标加入到list中
queue.offer(new int[] {x, y});
//遍历过的点都置为2
grid[x][y] = 2;
result.add(x - gapX);
result.add(y - gapY);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = queue.poll();
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int newX = cur[0] + dir[0];
int newY = cur[1] + dir[1];
if (newX >= 0 && newX < grid.length && newY >= 0 && newY < grid[0].length && grid[newX][newY] == 1) {
grid[newX][newY] = 2;
result.add(newX - gapX);
result.add(newY - gapY);
queue.offer(new int[] {newX, newY});
}
}
}
}
private void dfs(int[][] grid,List<Integer> result,int x,int y,int gapX,int gapY)
{
if (x < 0 || x >= grid.length || y < 0 || y >= grid[0].length || grid[x][y] != 1) {
return;
}
//遍历过的点都置为2
grid[x][y]=2;
//每一个坐标都减去第一个坐标的值,相当于的岛屿都移动到以原点(0,0)为起点,得到了岛屿的相对位置,存入list中
result.add(x - gapX);
result.add(y - gapY);
//四个方向, DFS
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int newX = x + dir[0];
int newY = y + dir[1];
dfs(grid, result, newX, newY, gapX, gapY);
}
}
}
4. 岛屿的最大面积
(1)DFS
class Solution {
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
//每次dfs会将所有相邻的岛屿标记为2,并且加上相邻节点,计算岛屿面积
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
int a = dfs(grid, i, j);
res = Math.max(res, a);
}
}
}
return res;
}
public int dfs(int[][] grid, int r, int c) {
//终止条件
if (r < 0 || r >= grid.length || c < 0 || c >= grid[0].length) {
return 0;
}
//避免重复遍历
if (grid[r][c] != 1) {
return 0;
}
//标记已遍历过节点
grid[r][c] = 2;
//继续遍历上下左右四个方向,并加上相邻的他们,求最大面积
return 1
+ dfs(grid, r - 1, c)
+ dfs(grid, r + 1, c)
+ dfs(grid, r, c - 1)
+ dfs(grid, r, c + 1);
}
}
(2)BFS
class Solution {
private int[][] directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
//每次bfs会将所有相邻的岛屿标记为2,所有每次遍历到1就代表新的岛屿
if(grid[i][j] == 1){
res = Math.max(res, bfs(grid, i, j));
}
}
}
return res;
}
public int bfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j) {
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//将每个节点坐标加入到list中
queue.offer(new int[] { i, j });
grid[i][j] = 2;
int ans = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = queue.poll();
//未遍历过且为陆地节点,将所有相邻的岛屿标记为2,所有每次遍历到1就代表新的岛屿
//需要加上 上下左右每个节点的有效值,所以需要每个点都判断
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int newX = cur[0] + dir[0];
int newY = cur[1] + dir[1];
if (newX >= 0 && newX < grid.length && newY >= 0 && newY < grid[0].length && grid[newX][newY] == 1) {
grid[newX][newY] = 2;
ans++;
queue.offer(new int[] {newX, newY});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
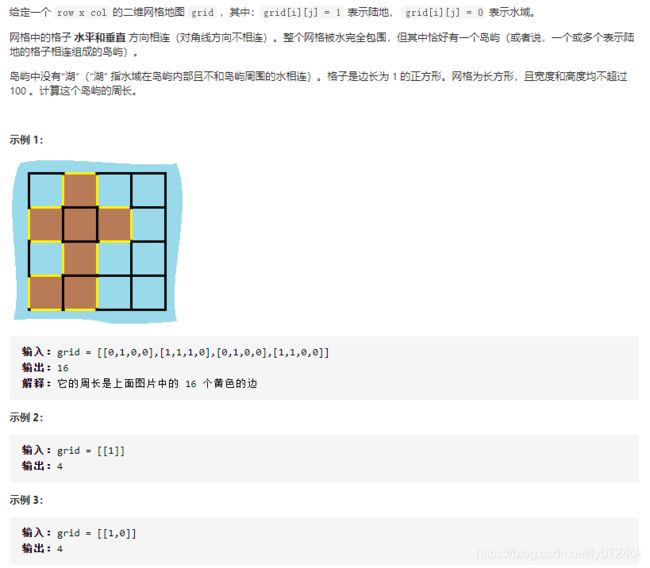
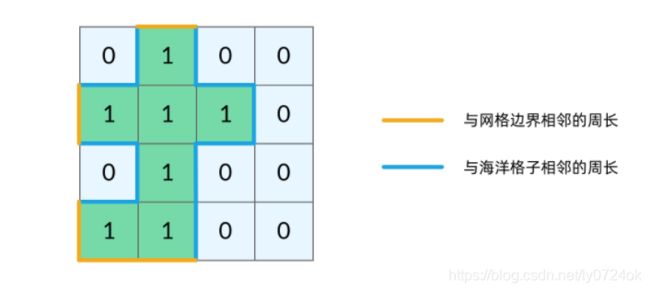
5. 岛屿的周长
(1)DFS
- 以边界条件做判断
- 坐标 (r, c) 超出网格范围」返回,对应一条黄色的边
- 当前格子是海洋格子返回,对应一条蓝色的边
- 遍历的新的陆地格子,加入队列,标记该点已遍历,无需多余操作
- 遇到已遍历的陆地格子,直接continue返回,和周长没关系
class Solution {
public int islandPerimeter(int[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
// 题目限制只有一个岛屿,计算一个即可
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
return dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
public int dfs(int[][] grid, int r, int c) {
//坐标 (r, c) 超出网格范围」返回,对应一条黄色的边
if (r < 0 || r >= grid.length || c < 0 || c >= grid[0].length) {
return 1;
}
//当前格子是海洋格子返回,对应一条蓝色的边
if (grid[r][c] == 0) {
return 1;
}
//当前格子是已遍历的陆地格子返回,和周长没关系
if (grid[r][c] == 2) {
return 0;
}
//标记已遍历过节点
grid[r][c] = 2;
//继续遍历上下左右四个方向,并加上相邻的他们,求最大面积
return dfs(grid, r - 1, c)
+ dfs(grid, r + 1, c)
+ dfs(grid, r, c - 1)
+ dfs(grid, r, c + 1);
}
}
(2)BFS
- 以边界条件做判断
- 坐标 (r, c) 超出网格范围」返回,对应一条黄色的边
- 当前格子是海洋格子返回,对应一条蓝色的边
- 遍历的新的陆地格子,加入队列,标记该点已遍历,无需多余操作
- 遇到已遍历的陆地格子,直接continue返回,和周长没关系
class Solution {
private int[][] directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
public int islandPerimeter(int[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
// 题目限制只有一个岛屿,计算一个即可
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
return bfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
public int bfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j) {
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//将每个节点坐标加入到list中
queue.offer(new int[] {i, j });
grid[i][j] = 2;
int ans = 0; //先默认边长为4,接着搜索其周边的四个方向:
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = queue.poll();
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int newX = cur[0] + dir[0];
int newY = cur[1] + dir[1];
//坐标 (r, c) 超出网格范围」返回,对应一条黄色的边
if (newX < 0 || newX >= grid.length || newY < 0 || newY >= grid[0].length) {
ans++;
}
//当前格子是海洋格子返回,对应一条蓝色的边
else if (newX >= 0 && newX < grid.length && newY >= 0 && newY < grid[0].length && grid[newX][newY] == 0) {
ans++;
}
//遍历的新的陆地格子,加入队列
if (newX >= 0 && newX < grid.length && newY >= 0 && newY < grid[0].length && grid[newX][newY] == 1) {
grid[newX][newY] = 2;
queue.offer(new int[] {newX, newY});
} else {
//当前格子是已遍历的陆地格子返回,和周长没关系
continue;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
(3)常规思路
- 看每个岛能对总周长贡献几条边。例如一个岛四周都没有岛,自然是贡献4条边。如果一个岛周围有一个岛,那么它就只能贡献3条边,以此类推。
- 因此,其实就是遍历整个矩阵,每遍历到一个岛,则去看这个岛的上下左右有没有岛。可以发现如果一个岛附近每有一个岛,则这个岛贡献的周长会-1。最后返回贡献和即可。
class Solution {
public int islandPerimeter(int[][] grid) {
int[][] directions = new int[][]{{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0},{1,0}};
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == 1) {
int lines = 4;
//判断这个岛旁边连接了多少个岛
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int newX = i + dir[0];
int newY = j + dir[1];
if (newX >= 0 && newX < grid.length && newY >= 0 && newY < grid[0].length && grid[newX][newY] == 1)
lines--;
}
sum += lines;
}
}
}
return sum;
}
}