深度学习基础知识数据 数据预处理transforms流程讲解
深度学习基础知识数据 数据预处理transforms流程讲解
- 1、数据预处理
- 2、使用节点
- 2、transform.RandomResizedCrop 随机尺寸裁剪缩放
- 3、水平翻转 与 垂直翻转
- 4、ColorJitter变换
- 5、ToTensor
- 6、Normalization 归一化
- 7、transforms.Compose
- 8、重写transforms
-
- 1、分类任务
- 2、目标检测任务
- 3、分割任务
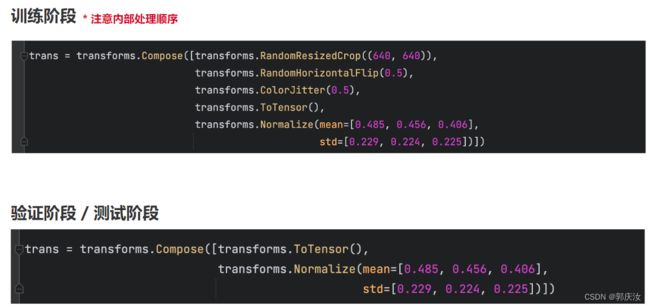
数据增强可以增加训练集的样本数量,缓解过拟合,并提高模型的泛化能力,从而有效提升算法的性能
1、数据预处理
2、使用节点
2、transform.RandomResizedCrop 随机尺寸裁剪缩放
3、水平翻转 与 垂直翻转
4、ColorJitter变换
5、ToTensor
6、Normalization 归一化
7、transforms.Compose
8、重写transforms
1、分类任务
2、目标检测任务
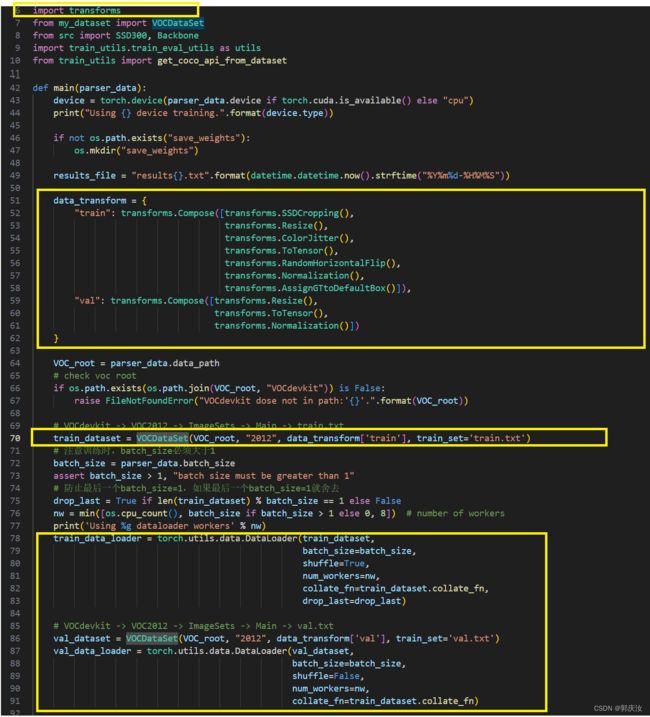
重写 transforms 的目的,接受多个参数,并对图像 和 标注做同步处理
下面以SSD目标检测项目中的重写transforms方法为例:
重写transforms.py代码文件
import random
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as t
from torchvision.transforms import functional as F
from src import dboxes300_coco, calc_iou_tensor, Encoder
class Compose(object):
"""组合多个transform函数"""
def __init__(self, transforms):
self.transforms = transforms
def __call__(self, image, target=None):
for trans in self.transforms:
image, target = trans(image, target)
return image, target
class ToTensor(object):
"""将PIL图像转为Tensor"""
def __call__(self, image, target):
image = F.to_tensor(image).contiguous()
return image, target
class RandomHorizontalFlip(object):
"""随机水平翻转图像以及bboxes,该方法应放在ToTensor后"""
def __init__(self, prob=0.5):
self.prob = prob
def __call__(self, image, target):
if random.random() < self.prob:
# height, width = image.shape[-2:]
image = image.flip(-1) # 水平翻转图片
bbox = target["boxes"]
# bbox: xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
# bbox[:, [0, 2]] = width - bbox[:, [2, 0]] # 翻转对应bbox坐标信息
bbox[:, [0, 2]] = 1.0 - bbox[:, [2, 0]] # 翻转对应bbox坐标信息
target["boxes"] = bbox
return image, target
# This function is from https://github.com/chauhan-utk/ssd.DomainAdaptation.
class SSDCropping(object):
"""
根据原文,对图像进行裁剪,该方法应放在ToTensor前
Cropping for SSD, according to original paper
Choose between following 3 conditions:
1. Preserve the original image
2. Random crop minimum IoU is among 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9
3. Random crop
Reference to https://github.com/chauhan-utk/src.DomainAdaptation
"""
def __init__(self):
self.sample_options = (
# Do nothing
None,
# min IoU, max IoU
(0.1, None),
(0.3, None),
(0.5, None),
(0.7, None),
(0.9, None),
# no IoU requirements
(None, None),
)
self.dboxes = dboxes300_coco()
def __call__(self, image, target):
# Ensure always return cropped image
while True:
mode = random.choice(self.sample_options)
if mode is None: # 不做随机裁剪处理
return image, target
htot, wtot = target['height_width']
min_iou, max_iou = mode
min_iou = float('-inf') if min_iou is None else min_iou
max_iou = float('+inf') if max_iou is None else max_iou
# Implementation use 5 iteration to find possible candidate
for _ in range(5):
# 0.3*0.3 approx. 0.1
w = random.uniform(0.3, 1.0)
h = random.uniform(0.3, 1.0)
if w/h < 0.5 or w/h > 2: # 保证宽高比例在0.5-2之间
continue
# left 0 ~ wtot - w, top 0 ~ htot - h
left = random.uniform(0, 1.0 - w)
top = random.uniform(0, 1.0 - h)
right = left + w
bottom = top + h
# boxes的坐标是在0-1之间的
bboxes = target["boxes"]
ious = calc_iou_tensor(bboxes, torch.tensor([[left, top, right, bottom]]))
# tailor all the bboxes and return
# all(): Returns True if all elements in the tensor are True, False otherwise.
if not ((ious > min_iou) & (ious < max_iou)).all():
continue
# discard any bboxes whose center not in the cropped image
xc = 0.5 * (bboxes[:, 0] + bboxes[:, 2])
yc = 0.5 * (bboxes[:, 1] + bboxes[:, 3])
# 查找所有的gt box的中心点有没有在采样patch中的
masks = (xc > left) & (xc < right) & (yc > top) & (yc < bottom)
# if no such boxes, continue searching again
# 如果所有的gt box的中心点都不在采样的patch中,则重新找
if not masks.any():
continue
# 修改采样patch中的所有gt box的坐标(防止出现越界的情况)
bboxes[bboxes[:, 0] < left, 0] = left
bboxes[bboxes[:, 1] < top, 1] = top
bboxes[bboxes[:, 2] > right, 2] = right
bboxes[bboxes[:, 3] > bottom, 3] = bottom
# 虑除不在采样patch中的gt box
bboxes = bboxes[masks, :]
# 获取在采样patch中的gt box的标签
labels = target['labels']
labels = labels[masks]
# 裁剪patch
left_idx = int(left * wtot)
top_idx = int(top * htot)
right_idx = int(right * wtot)
bottom_idx = int(bottom * htot)
image = image.crop((left_idx, top_idx, right_idx, bottom_idx))
# 调整裁剪后的bboxes坐标信息
bboxes[:, 0] = (bboxes[:, 0] - left) / w
bboxes[:, 1] = (bboxes[:, 1] - top) / h
bboxes[:, 2] = (bboxes[:, 2] - left) / w
bboxes[:, 3] = (bboxes[:, 3] - top) / h
# 更新crop后的gt box坐标信息以及标签信息
target['boxes'] = bboxes
target['labels'] = labels
return image, target
class Resize(object):
"""对图像进行resize处理,该方法应放在ToTensor前"""
def __init__(self, size=(300, 300)):
self.resize = t.Resize(size)
def __call__(self, image, target):
image = self.resize(image)
return image, target
class ColorJitter(object):
"""对图像颜色信息进行随机调整,该方法应放在ToTensor前"""
def __init__(self, brightness=0.125, contrast=0.5, saturation=0.5, hue=0.05):
self.trans = t.ColorJitter(brightness, contrast, saturation, hue)
def __call__(self, image, target):
image = self.trans(image)
return image, target
class Normalization(object):
"""对图像标准化处理,该方法应放在ToTensor后"""
def __init__(self, mean=None, std=None):
if mean is None:
mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
if std is None:
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
self.normalize = t.Normalize(mean=mean, std=std)
def __call__(self, image, target):
image = self.normalize(image)
return image, target
class AssignGTtoDefaultBox(object):
"""将DefaultBox与GT进行匹配"""
def __init__(self):
self.default_box = dboxes300_coco()
self.encoder = Encoder(self.default_box)
def __call__(self, image, target):
boxes = target['boxes']
labels = target["labels"]
# bboxes_out (Tensor 8732 x 4), labels_out (Tensor 8732)
bboxes_out, labels_out = self.encoder.encode(boxes, labels)
target['boxes'] = bboxes_out
target['labels'] = labels_out
return image, target
重写的dataset类文件代码如下:
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
import os
import torch
import json
from PIL import Image
from lxml import etree
class VOCDataSet(Dataset):
"""读取解析PASCAL VOC2007/2012数据集"""
def __init__(self, voc_root, year="2012", transforms=None, train_set='train.txt'):
assert year in ["2007", "2012"], "year must be in ['2007', '2012']"
# 增加容错能力
if "VOCdevkit" in voc_root:
self.root = os.path.join(voc_root, f"VOC{year}")
else:
self.root = os.path.join(voc_root, "VOCdevkit", f"VOC{year}")
self.img_root = os.path.join(self.root, "JPEGImages")
self.annotations_root = os.path.join(self.root, "Annotations")
txt_list = os.path.join(self.root, "ImageSets", "Main", train_set)
with open(txt_list) as read:
self.xml_list = [os.path.join(self.annotations_root, line.strip() + ".xml")
for line in read.readlines() if len(line.strip()) > 0]
# read class_indict
json_file = "./pascal_voc_classes.json"
assert os.path.exists(json_file), "{} file not exist.".format(json_file)
with open(json_file, 'r') as f:
self.class_dict = json.load(f)
self.transforms = transforms
def __len__(self):
return len(self.xml_list)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
# read xml
xml_path = self.xml_list[idx]
with open(xml_path) as fid:
xml_str = fid.read()
xml = etree.fromstring(xml_str)
data = self.parse_xml_to_dict(xml)["annotation"]
data_height = int(data["size"]["height"])
data_width = int(data["size"]["width"])
height_width = [data_height, data_width]
img_path = os.path.join(self.img_root, data["filename"])
image = Image.open(img_path)
if image.format != "JPEG":
raise ValueError("Image '{}' format not JPEG".format(img_path))
assert "object" in data, "{} lack of object information.".format(xml_path)
boxes = []
labels = []
iscrowd = []
for obj in data["object"]:
# 将所有的gt box信息转换成相对值0-1之间
xmin = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmin"]) / data_width
xmax = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmax"]) / data_width
ymin = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymin"]) / data_height
ymax = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymax"]) / data_height
# 进一步检查数据,有的标注信息中可能有w或h为0的情况,这样的数据会导致计算回归loss为nan
if xmax <= xmin or ymax <= ymin:
print("Warning: in '{}' xml, there are some bbox w/h <=0".format(xml_path))
continue
boxes.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax])
labels.append(self.class_dict[obj["name"]])
if "difficult" in obj:
iscrowd.append(int(obj["difficult"]))
else:
iscrowd.append(0)
# convert everything into a torch.Tensor
boxes = torch.as_tensor(boxes, dtype=torch.float32)
labels = torch.as_tensor(labels, dtype=torch.int64)
iscrowd = torch.as_tensor(iscrowd, dtype=torch.int64)
height_width = torch.as_tensor(height_width, dtype=torch.int64)
image_id = torch.tensor([idx])
area = (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) * (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0])
target = {}
target["boxes"] = boxes
target["labels"] = labels
target["image_id"] = image_id
target["area"] = area
target["iscrowd"] = iscrowd
target["height_width"] = height_width
if self.transforms is not None:
image, target = self.transforms(image, target)
return image, target
def get_height_and_width(self, idx):
# read xml
xml_path = self.xml_list[idx]
with open(xml_path) as fid:
xml_str = fid.read()
xml = etree.fromstring(xml_str)
data = self.parse_xml_to_dict(xml)["annotation"]
data_height = int(data["size"]["height"])
data_width = int(data["size"]["width"])
return data_height, data_width
def parse_xml_to_dict(self, xml):
"""
将xml文件解析成字典形式,参考tensorflow的recursive_parse_xml_to_dict
Args:
xml: xml tree obtained by parsing XML file contents using lxml.etree
Returns:
Python dictionary holding XML contents.
"""
if len(xml) == 0: # 遍历到底层,直接返回tag对应的信息
return {xml.tag: xml.text}
result = {}
for child in xml:
child_result = self.parse_xml_to_dict(child) # 递归遍历标签信息
if child.tag != 'object':
result[child.tag] = child_result[child.tag]
else:
if child.tag not in result: # 因为object可能有多个,所以需要放入列表里
result[child.tag] = []
result[child.tag].append(child_result[child.tag])
return {xml.tag: result}
def coco_index(self, idx):
"""
该方法是专门为pycocotools统计标签信息准备,不对图像和标签作任何处理
由于不用去读取图片,可大幅缩减统计时间
Args:
idx: 输入需要获取图像的索引
"""
# read xml
xml_path = self.xml_list[idx]
with open(xml_path) as fid:
xml_str = fid.read()
xml = etree.fromstring(xml_str)
data = self.parse_xml_to_dict(xml)["annotation"]
data_height = int(data["size"]["height"])
data_width = int(data["size"]["width"])
height_width = [data_height, data_width]
# img_path = os.path.join(self.img_root, data["filename"])
# image = Image.open(img_path)
# if image.format != "JPEG":
# raise ValueError("Image format not JPEG")
boxes = []
labels = []
iscrowd = []
for obj in data["object"]:
# 将所有的gt box信息转换成相对值0-1之间
xmin = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmin"]) / data_width
xmax = float(obj["bndbox"]["xmax"]) / data_width
ymin = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymin"]) / data_height
ymax = float(obj["bndbox"]["ymax"]) / data_height
boxes.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax])
labels.append(self.class_dict[obj["name"]])
iscrowd.append(int(obj["difficult"]))
# convert everything into a torch.Tensor
boxes = torch.as_tensor(boxes, dtype=torch.float32)
labels = torch.as_tensor(labels, dtype=torch.int64)
iscrowd = torch.as_tensor(iscrowd, dtype=torch.int64)
height_width = torch.as_tensor(height_width, dtype=torch.int64)
image_id = torch.tensor([idx])
area = (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) * (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0])
target = {}
target["boxes"] = boxes
target["labels"] = labels
target["image_id"] = image_id
target["area"] = area
target["iscrowd"] = iscrowd
target["height_width"] = height_width
return target
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
images, targets = tuple(zip(*batch))
# images = torch.stack(images, dim=0)
#
# boxes = []
# labels = []
# img_id = []
# for t in targets:
# boxes.append(t['boxes'])
# labels.append(t['labels'])
# img_id.append(t["image_id"])
# targets = {"boxes": torch.stack(boxes, dim=0),
# "labels": torch.stack(labels, dim=0),
# "image_id": torch.as_tensor(img_id)}
return images, targets
3、分割任务
import os
import torch.utils.data as data
from PIL import Image
class VOCSegmentation(data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, voc_root, year="2012", transforms=None, txt_name: str = "train.txt"):
super(VOCSegmentation, self).__init__()
assert year in ["2007", "2012"], "year must be in ['2007', '2012']"
root = os.path.join(voc_root, "VOCdevkit", f"VOC{year}")
assert os.path.exists(root), "path '{}' does not exist.".format(root)
image_dir = os.path.join(root, 'JPEGImages')
mask_dir = os.path.join(root, 'SegmentationClass')
txt_path = os.path.join(root, "ImageSets", "Segmentation", txt_name)
assert os.path.exists(txt_path), "file '{}' does not exist.".format(txt_path)
with open(os.path.join(txt_path), "r") as f:
file_names = [x.strip() for x in f.readlines() if len(x.strip()) > 0]
self.images = [os.path.join(image_dir, x + ".jpg") for x in file_names]
self.masks = [os.path.join(mask_dir, x + ".png") for x in file_names]
assert (len(self.images) == len(self.masks))
self.transforms = transforms
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""
Args:
index (int): Index
Returns:
tuple: (image, target) where target is the image segmentation.
"""
img = Image.open(self.images[index]).convert('RGB')
target = Image.open(self.masks[index]) # gqr:读取的mask文件是一个单通道的掩膜数据
if self.transforms is not None:
img, target = self.transforms(img, target)
return img, target
def __len__(self):
return len(self.images)
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
images, targets = list(zip(*batch))
batched_imgs = cat_list(images, fill_value=0) # gqr:将不同尺寸的数据打包桶相同尺寸大小的tensor,有利于加速训练
batched_targets = cat_list(targets, fill_value=255) # gqr:将不同尺寸的数据打包桶相同尺寸大小的tensor,有利于加速训练
return batched_imgs, batched_targets
def cat_list(images, fill_value=0):
# 计算该batch数据中,channel, h, w的最大值
max_size = tuple(max(s) for s in zip(*[img.shape for img in images]))
batch_shape = (len(images),) + max_size
batched_imgs = images[0].new(*batch_shape).fill_(fill_value)
for img, pad_img in zip(images, batched_imgs):
pad_img[..., :img.shape[-2], :img.shape[-1]].copy_(img)
return batched_imgs
# dataset = VOCSegmentation(voc_root="/data/", transforms=get_transform(train=True))
# d1 = dataset[0]
# print(d1)
重写的transforms代码:
import numpy as np
import random
import torch
from torchvision import transforms as T
from torchvision.transforms import functional as F
def pad_if_smaller(img, size, fill=0):
# 如果图像最小边长小于给定size,则用数值fill进行padding
min_size = min(img.size)
if min_size < size:
ow, oh = img.size
padh = size - oh if oh < size else 0
padw = size - ow if ow < size else 0
img = F.pad(img, (0, 0, padw, padh), fill=fill)
return img
class Compose(object):
def __init__(self, transforms):
self.transforms = transforms
def __call__(self, image, target):
for t in self.transforms:
image, target = t(image, target)
return image, target
class RandomResize(object):
def __init__(self, min_size, max_size=None):
self.min_size = min_size
if max_size is None:
max_size = min_size
self.max_size = max_size
def __call__(self, image, target):
size = random.randint(self.min_size, self.max_size)
# 这里size传入的是int类型,所以是将图像的最小边长缩放到size大小
image = F.resize(image, size)
# 这里的interpolation注意下,在torchvision(0.9.0)以后才有InterpolationMode.NEAREST
# 如果是之前的版本需要使用PIL.Image.NEAREST
target = F.resize(target, size, interpolation=T.InterpolationMode.NEAREST)
return image, target
class RandomHorizontalFlip(object):
def __init__(self, flip_prob):
self.flip_prob = flip_prob
def __call__(self, image, target):
if random.random() < self.flip_prob:
image = F.hflip(image)
target = F.hflip(target)
return image, target
class RandomCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image, target):
image = pad_if_smaller(image, self.size)
target = pad_if_smaller(target, self.size, fill=255)
crop_params = T.RandomCrop.get_params(image, (self.size, self.size))
image = F.crop(image, *crop_params)
target = F.crop(target, *crop_params)
return image, target
class CenterCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image, target):
image = F.center_crop(image, self.size)
target = F.center_crop(target, self.size)
return image, target
class ToTensor(object):
def __call__(self, image, target):
image = F.to_tensor(image)
target = torch.as_tensor(np.array(target), dtype=torch.int64)
return image, target
class Normalize(object):
def __init__(self, mean, std):
self.mean = mean
self.std = std
def __call__(self, image, target):
image = F.normalize(image, mean=self.mean, std=self.std)
return image, target