小白QT笔记(内含槽函数编程以及qss编程)
PS:前十章的程序大部分是基于正点原子QT文档运用qss文件写ui程序,所以相关方法主要都在第三章。十一章开始是运用connect和槽函数写程序。
笔记目录
- 一、QT的对象树机制
- 二、UI界面控件代码布局
- 三、qss样式表文件(记得在main.cpp加入读写的程序)
-
- 1、ctrl+n (QT->QT Resource File); 名称:style.qss创建qss文件
- 2、在父类(MainWindow里创建)子类对象(QLabel)
- 3、qss文件里根据#目标名字描述属性(重点)
- 4、打开qss文件读取内容(重点)
- 四、样式表
- 五、QCheckBox
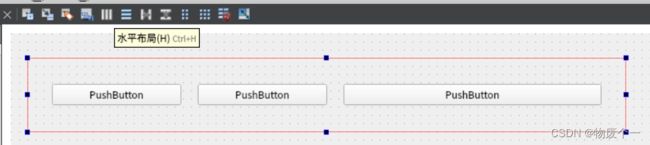
- 六、水平布局
- 七、QSplitter(分裂器)
- 八、 QLineEdit(编写线)
- 九、QTabWidget(面板切换)
- 十、QListWidget(列表项切换)
- 十一、connect函数(重点)
- 十二、自定义信号槽的使用
-
- 1、自定义信号
- 2、自定义槽
- 3、例程:ctrl+n 创建C++的类,**注意要以QObject为基类,否则用不了槽函数机制。**
- 4、Lamda表达式定义函数
- 十三、常用控件
-
- 1、文字控件QLabel
- 2、滑块控件QSlider
- 3、进度条控件QProgressBar
- 4、文本编辑框QTextEdit
- 十四、自定义槽和信号
- 十五、QThread_class
-
- 1.线程类QThread(随便康康就好了,用到自己看手册,看不懂来这看)
-
- 1.1常用共用成员函数
- 1.2 信号槽函数
- 1.3 静态函数
- 1.4 任务处理函数
- 2.使用方式1
-
- 2.1 操作步骤
- 2.2 例程(生成随机数并做冒泡与快速排序)
- ps:主要事项
- 3、使用方式2:添加修改任务类(只需要对使用方式1的例程稍做修改即可)
-
- 3.1 操作步骤
- 3.2 例程(生成随机数并做冒泡排序与快速排序)
- ps:注意事项
- 4、释放线程资源
- 十六、QDate类
- 十七、QTimer类
- 十八、QDateTime
QT快捷键:打出类名后按Alt+Enter自动添加该类头文件。
一、QT的对象树机制
#include "widget.h"
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
{
// 为什么需要设置父对象?因为窗口需要互相联系,比如A需要显示在B上面,A需要指定B为父对象
pushButton = new QPushButton;
// 设置父对象的两种方法
// 1.通过构造函数传参
pushButton->setParent(this);
// 2.通过setParent()方法
pushButton = new QPushButton;
pushButton->setParent(this);
// Qt对象树机制,目的就是方便内存管理
// 动态创建对象还要释放(delete)才能触发析构函数
myWidget = new MyWidget();
}
Widget::~Widget()
{
delete myWidget;
}
二、UI界面控件代码布局
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
//this表示当前的父类,即MainWindow
//先在MainWindow的头文件里声明,然后在cpp文件里调用。查帮助手册。
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
, ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);//初始化父类
//设为窗口无边框
setWindowFlag(Qt::FramelessWindowHint);
//设为背景透明
setAttribute(Qt::WA_TranslucentBackground);
//设置父对象this,即继承父对象的Button
pushButton = new QPushButton(this);
pushButton->setText("Button");
pushButton->setGeometry(50, 150, 100, 50);
this->resize(800,480);
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
三、qss样式表文件(记得在main.cpp加入读写的程序)
1、ctrl+n (QT->QT Resource File); 名称:style.qss创建qss文件
2、在父类(MainWindow里创建)子类对象(QLabel)
//mainwindow.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include 3、qss文件里根据#目标名字描述属性(重点)
style.qss(在父类前面加','(.QMainWindow)表示以下属性只对父类有效)
格式: 父类#子类:状态:状态...{ 属性:参数;属性:参数}
--------------------------------------------Label-------------------------------------------------
QMainWindow {background-color:blue} 背景蓝色
QLabel#label1 {background-color:red} 对象QLabel1红色
QLabel#label2 {background-color:black} 对象Qlabel2黑色
--------------------------------------------pushButton-------------------------------------------------
QPushButton#pushButton_2 { border-image:url(:/icons/sad.gif)} 按钮2用图sad覆盖
QPushButton#pushButton_2:hover { border-image:url(:/icons/dog.png)} 鼠标悬停在按钮2时会出现dog.png
QPushButton#pushButton_2:checked { border-image:url(:/icons/sign.png)} 设置按钮可选中并配图
QPushButton#pushButton_2:checked:hover { border-image:url(:/icons/sign.png)} 设置按钮可选并悬停并配图
QPushButton{ background-color: #80dd88;font-size: 30px; border-radius:10px} 选中前圆角30px
QPushButton::checked { background-color: green;color: white; 1border-radius:10px} 选中前圆角绿色。选中后白色。
QPushButton{
color:#1E90FF; 字体颜色
border-top:1px; 上边界距离
border-right:1px; 右边界距离
border-style:solid; 固态填充
border-color:#bbbbbb 边界颜色
}
--------------------------------------------radioButton-------------------------------------------------
可用鼠标框选一组按钮单独建立按钮组来做到两组单选
将按钮组下的exclusive(互斥性)取消可多选
QRadioButton::indicator:unchecked{ image:url(:/icons/radioButton_unchecked.png)} 单选按钮未选中
QRadioButton::indicator:checked{ image:url(:/icons/radioButton_checked.png)} 单选按钮选中
QRadioButton { font-size: 30px; color: #99404040;background-color:aadddddd} 设置radioButton里的字号为30px
QRadioButton::indicator { width: 0px; height: 0px} 设置长宽为0像素
ui样式表里添加图片,border是填充到边界
QLabel{
border-image: url(:/icons/dog.png); 图片填充边界
color:red; 字改红色
font-size:30px 字改30px
}
--------------------------------------------CheckedBox------------------------------------------
QCheckBox::indicator:unchecked { image: url(:/icons/unchecked.png)} 未选中状态
QCheckBox::indicator:indeterminate { image: url(:/icons/indeterminate.png)} 半选中状态
QCheckBox::indicator:checked { image: url(:/icons/checked.png)} 选中状态
--------------------------------------------Margin & padding------------------------------------
QPushButton { margin: 50px; 4个方向外边距50像素
background-color: #CDCDB4; 按钮背景颜色
border-width: 50px; 按钮边界宽度
border-color:#458B00; 按钮边界颜色
border-style:solid; 固态填充(没有则前面边界设置不会起作用)
padding:50px 内边距50px
}
--------------------------------------------QHBoxLayout(水平布局)------------------------------
spacing:间隔距离
stretch:拉伸因子(系数),用于控制水平布局的宽度比例。
sizePolicy:大小策略
--------------------------------------------QScrollArea(滚动条)------------------------------
QScrollBar:vertical {width: 10px; background:white;} 垂直滚动条白色宽10px
QScrollBar::handle:vertical { background: rgba(200,200,245,50%); 垂直滚动条滑块,圆角(设置为宽的一半)
border-radius:5px;
}
QScrollBar::handle:vertical:hover { background: rgba(200,200,245,90%); 滑块悬停的颜色
}
QScrollBar::add-line:vertical {
width:0px ; height:0px
}
QScrollBar::sub-line:vertical {
width:0px ; height:0px
}
--------------------------------------------QTabWidget(面板跳转)------------------------------
属性->QTabWidget->tabsCLosable可让窗口出现关闭符号,添加槽函数后可实现关闭
属性->QTabWidget->currentTabText可改变页名称
QTabWidget{border:none } 取消边界
/*QTabBar::tab { width:0px; height:0px} 取消标签
QWidget {background-color: blue} 子类是widget可以改颜色
--------------------------------------------QListWidget(列表跳转)------------------------------
QListView {border:none;
background-color: #dddddd; 列表颜色
}
QListView::item{ height:50px} 列表项单项高度为50px
QListView::item:selected { 列表项被选中时背景颜色为白色,字体颜色为黑色
background-color: white; color:black
}
4、打开qss文件读取内容(重点)
//main.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
// 路径可对qss文件右键点击copy路径
QFile file(":/style.qss");
if(file.exists()){
file.open(QFile::ReadOnly);
QString styleSheet = QLatin1String(file.readAll());
qApp->setStyleSheet(styleSheet);
file.close();
}
MainWindow w;
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
四、样式表
//可上网搜索RGB配表来配置颜色,以下是改变Widget颜色
QWidget{background-color: rgb(220,220,220) }//QWidget{background-color:#DCDCDC}
五、QCheckBox
//widget.cpp的三态信号,一般不用。一般用复选按钮在ui设置中添加按钮组和取消exculsive就行了。
void Widget::on_checkBox_stateChanged(int arg1)
{
switch (arg1) {
case Qt::Checked:
qDebug() << "checked"<< endl;
break;
case Qt::PartiallyChecked:
qDebug() << "PartiallyChecked" << endl;
break;
case Qt::Unchecked:
qDebug() << "UnChecked"<< endl;
break;
}
}
六、水平布局
//widget.cpp
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include 七、QSplitter(分裂器)
orientation:设置方向,可设置水平或垂直方向
opaqueResize:为false时,在拖动的时候会显示一条灰色的线条,在拖动到位并释放鼠标后再显示分隔线条,默认为true,实时更新子控件大小。
childrenCollapsible:为true时,用户可以将子部件的大小调整为0。
handleWidth:改变分界线的宽度
修改样式表可以改分界线的颜色
八、 QLineEdit(编写线)
属性栏:echoMode可以调密码输入格式
九、QTabWidget(面板切换)
//widget.cpp
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
}
Widget::~Widget()
{
delete ui;
this->setLayout(ui->horizontalLayout);
}
void Widget::on_tabWidget_tabCloseRequested(int index)
{
ui->tabWidget->removeTab(index);//点一下就关掉
}
void Widget::on_listWidget_currentRowChanged(int currentRow)
{//currentRowChanged:当前行改变信号
ui->tabWidget->setCurrentIndex(currentRow);//横排页面切换,根据ListWidget当前行下标索引
}
十、QListWidget(列表项切换)
//widget.cpp
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include //qq_items.h
#ifndef QQ_ITEMS_H
#define QQ_ITEMS_H
#include 十一、connect函数(重点)
//样式: connect(信号发出者的名字,信号函数指针,信号接受者的指针,接受者执行的函数指针)
//按钮:信号发出者->QPushButton;窗口:信号的接收者和处理者->QWidget
[signal] void QAbstractButton::clicked(bool checked = false)
[slot] bool QWidget::close();
//单击按钮关闭窗口
*用法1:connect(发送方, 信号指针,接收方,槽函数指针);
*用法2:connect(发送方, 信号指针, Lamda表达式匿名函数(见十二节));
*用法3:connect(发送方,SIGNAL(信号函数),接收方,SLOT(槽函数));
*用法1和用法2是QT5才兼容的,用法3是QT4、5都兼容的。用法3在填写函数时不会自动补全,而且如果函数名字打错
*也不会报错。如果见到的话注意一下。下面是对应3种用法:
connect(ui->closeBtn,&QPushButton::clicked,this,&QMainWindow::close);
connect(slider,&QSlider::valueChanged,[proBar](int value){
proBar->setValue(value);
});
connect(btn10,SIGNAL(clicked()), this,SLOT(showMaximized()));
*****************************************************************************
ps:signal函数里如果有3个参数,则槽函数slot必会接收到3个相同参数。但是接收归接收,用不用是自己决定的。即槽函数中你只定2个参数也是可以的。(自己理解一下)
十二、自定义信号槽的使用
1、自定义信号
要求:
1、信号是类的成员函数
2、返回值是void类型
3、信号的名字随便取
4、参数可以指定也能重载
5、信号需要使用signals关键字进行声明,使用方法类似与public等关键字
6、信号函数需要声明但不用定义
7、在程序中发送自定义信号:本质就是调用信号函数
- 习惯性在信号函数前加关键字:emit
- emit只是显示的声明一下信号要被送达,没有特殊含义
//例子:
class Test : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
signals:
void testsignal();
void testsignal(int a);
};
2、自定义槽
要求:
1、返回值是void函数
2、槽也是函数,因此也支持重载
-槽函数需要指定多少个参数,视连接的信号的参数个数而定
-举例:
-信号函数:void testsig(int a, double b);
-槽函数: void testslot(int a, double b);
3、槽函数可以使用关键字进行声明:slots
-public slots:
-private slots:
-protected slots:
3、例程:ctrl+n 创建C++的类,注意要以QObject为基类,否则用不了槽函数机制。
//grilfriend.h
#ifndef GRILFRIEND_H
#define GRILFRIEND_H
#include //me.h
#ifndef ME_H
#define ME_H
#include //me.cpp
#include "me.h"
#include //myWindow.h
#ifndef MYWINDOW_H
#define MYWINDOW_H
#include //myWindow.cpp
#include 4、Lamda表达式定义函数
格式:[可访问外部变量](参数表)->返回值( 函数体 )
[变量1,变量2...](){} 指定部分变量访问
[=](){} 值传递捕获所有外部变量 (内部无法改变实际变量)
[&](){} 址传递形式捕获所有外部变量 (内部可以改变实际变量)
例1:
int num = 250 ,num2 = 360;
[&]()->void
{
qDebug() << "be heated" ;
num = 900;
qDebug() << num;
qDebug() << num2;
}();
例2:
auto btn = new QPushButton("mouse",this);
btn->move(300,0);
connect(btn,&QPushButton::pressed,[](){
qDebug() << "be heated";
});
connect(btn,&QPushButton::released,[](){
qDebug() << "wo shi feiwu";
});
例3:函数指针指向Lamda函数
int num = 1,num2 = 2;
void (*pFun)(int&) = [](int& n)->void{
n = 250;
qDebug() << n;
};
pFun(num);
qDebug() << num;
十三、常用控件
1、文字控件QLabel
QLabel* laber = new QLabel;
laber->setParent(this);
laber->move(0,100);
laber->setText("wo shi fei wu");
//QFont(const QString &family, int pointSize = -1, int weight = -1, bool italic = false);
//参数:(字体样式,字号大小,加粗大小,是否斜体)
laber->setFont(QFont("KaiTi",20,10,1));
****************************************************************************************
常用字体:(替换"KaiTi")
宋体 SimSun
黑体 SimHei
微软雅黑 Microsoft YaHei
微软正黑体 Microsoft JhengHei
新宋体 NSimSun
新细明体 PMingLiU
细明体 MingLiU
标楷体 DFKai-SB
仿宋 FangSong
楷体 KaiTi
仿宋_GB2312 FangSong_GB2312
楷体_GB2312 KaiTi_GB2312
宋体:SimSuncss
Mac OS的一些:
华文细黑:STHeiti Light [STXihei]
华文黑体:STHeiti
华文楷体:STKaiti
华文宋体:STSong
华文仿宋:STFangsong
儷黑 Pro:LiHei Pro Medium
儷宋 Pro:LiSong Pro Light
標楷體:BiauKai
蘋果儷中黑:Apple LiGothic Medium
蘋果儷細宋:Apple LiSung Light
Windows的一些:
新細明體:PMingLiU
細明體:MingLiU
標楷體:DFKai-SB
黑体:SimHei
新宋体:NSimSun
仿宋:FangSong
楷体:KaiTi
仿宋_GB2312:FangSong_GB2312
楷体_GB2312:KaiTi_GB2312
微軟正黑體:Microsoft JhengHei
微软雅黑体:Microsoft YaHei
装Office会生出来的一些:
隶书:LiSu
幼圆:YouYuan
华文细黑:STXihei
华文楷体:STKaiti
华文宋体:STSong
华文中宋:STZhongsong
华文仿宋:STFangsong
方正舒体:FZShuTi
方正姚体:FZYaoti
华文彩云:STCaiyun
华文琥珀:STHupo
华文隶书:STLiti
华文行楷:STXingkai
华文新魏:STXinwei
2、滑块控件QSlider
QSlider* slider = new QSlider;
slider->setParent(this);
slider->move(300,100);
slider->setValue(0);
//信号valueChanged里自带参数value传到槽函数
connect(slider,&QSlider::valueChanged,[label](int value){
// label->setFont(QFont("KaiTi",value,10,1));//根据value改变字号大小
// label->resize(value+500,value+500);
label->setNum(value);//实时显示value值
3、进度条控件QProgressBar
QProgressBar* proBar = new QProgressBar;
proBar->setParent(this);
proBar->move(0,200);
proBar->resize(this->size().width(),20);
proBar->setValue(50);
// proBar->setMaximum(99);
connect(slider,&QSlider::valueChanged,[proBar](int value){
proBar->setValue(value);//根据滑块的值进度条改变
});
4、文本编辑框QTextEdit
QTextEdit* edit = new QTextEdit;
edit->move(0,300);
edit->resize(500,500);
edit->setParent(this);
edit->setFontUnderline(1);
edit->setFontPointSize(qreal(50.5));
edit->setText("wo zhen shi ge tie fei wu");
connect(edit,&QTextEdit::textChanged,[label,edit](){
QString text = edit->toPlainText();//获取文本内容
label->setText(text);
});
十四、自定义槽和信号
//explicit关键字 修斯函数 参数 无法自动转换类型
创建类时要注意只以需要的属性为原则去选择基类,不一定要Add_Object
自定义槽:
1、有函数声明且有实现
2、返回值类型为void
3、槽函数 可以带参 可以重载(槽函数实参从信号来)
自定义信号:
1、卸载Signal:下
2、只需声明 无需实现
3、返回值为 void
4、支持带参 且可重载
十五、QThread_class
1.线程类QThread(随便康康就好了,用到自己看手册,看不懂来这看)
1.1常用共用成员函数
// QThread 类常用 API
// 构造函数
QThread::QThread(QObject *parent = Q_NULLPTR);
// 判断线程中的任务是不是处理完毕了
bool QThread::isFinished() const;
// 判断子线程是不是在执行任务
bool QThread::isRunning() const;
// Qt中的线程可以设置优先级
// 得到当前线程的优先级
Priority QThread::priority() const;
void QThread::setPriority(Priority priority);
优先级:
QThread::IdlePriority --> 最低的优先级
QThread::LowestPriority
QThread::LowPriority
QThread::NormalPriority
QThread::HighPriority
QThread::HighestPriority
QThread::TimeCriticalPriority --> 最高的优先级
QThread::InheritPriority --> 子线程和其父线程的优先级相同, 默认是这个
// 退出线程, 停止底层的事件循环
// 退出线程的工作函数
void QThread::exit(int returnCode = 0);
// 调用线程退出函数之后, 线程不会马上退出因为当前任务有可能还没有完成, 调回用这个函数是
// 等待任务完成, 然后退出线程, 一般情况下会在 exit() 后边调用这个函数
bool QThread::wait(unsigned long time = ULONG_MAX);
1.2 信号槽函数
// 和调用 exit() 效果是一样的
// 代用这个函数之后, 再调用 wait() 函数
[slot] void QThread::quit();
// 启动子线程
[slot] void QThread::start(Priority priority = InheritPriority);
// 线程退出, 可能是会马上终止线程, 一般情况下不使用这个函数
[slot] void QThread::terminate();
// 线程中执行的任务完成了, 发出该信号
// 任务函数中的处理逻辑执行完毕了
[signal] void QThread::finished();
// 开始工作之前发出这个信号, 一般不使用
[signal] void QThread::started();
1.3 静态函数
// 返回一个指向管理当前执行线程的QThread的指针
[static] QThread *QThread::currentThread();
// 返回可以在系统上运行的理想线程数 == 和当前电脑的 CPU 核心数相同
[static] int QThread::idealThreadCount();
// 线程休眠函数
[static] void QThread::msleep(unsigned long msecs); // 单位: 毫秒
[static] void QThread::sleep(unsigned long secs); // 单位: 秒
[static] void QThread::usleep(unsigned long usecs); // 单位: 微秒
1.4 任务处理函数
// 子线程要处理什么任务, 需要写到 run() 中
[virtual protected] void QThread::run();
2.使用方式1
2.1 操作步骤
-
需要创建一个线程类的子类,让其继承QT中的线程类QThread,比如:
//mythread.h里基类改成QThread class MyThread:public QThread { ...... } -
重写父类的 run () 方法,在该函数内部编写子线程要处理的具体的业务流程
class MyThread:public QThread { ...... protected: void run() override; //override 关键字用于重载一个虚函数 { ........ } } -
在主线程中创建子线程对象,new 一个就可以了
MyThread * subThread = new MyThread; -
启动子线程,调用 start () 方法
subThread->start();
ps:主线程和子线程之间信号传递应使用信号槽传参,不能在类的外部调用 run () 方法启动子线程,
在外部调用 start () 相当于让 run () 开始运行。
当子线程别创建出来之后,父子线程之间的通信可以通过信号槽的方式,注意事项:
- 在 Qt 中在子线程中不要操作程序中的窗口类型对象,不允许,如果操作了程序就挂了
- 只有主线程才能操作程序中的窗口对象,默认的线程就是主线程,自己创建的就是子线程
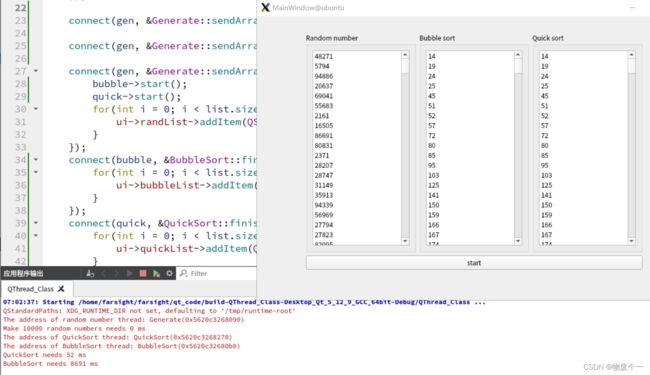
2.2 例程(生成随机数并做冒泡与快速排序)
//mainwindow.h
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H
#include //mythread.h(mythread这个类是我自己创建的)
#ifndef MYTHREAD_H
#define MYTHREAD_H
#include //mythread.cpp
#include "mythread.h"
#include //mainwindow.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include "mythread.h"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
, ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
// 1、创建子线程对象
Generate* gen = new Generate;
//注册连接主进程的发送函数和子进程的接收函数
connect(this,&MainWindow::starting,gen,&Generate::recvNum);
// 2、注册启动随机数生成子线程
connect(ui->start,&QPushButton::clicked,this,[=](){
emit starting(10000);//发射告诉线程要产生10000个随机数
gen->start();//随机数生成子线程开启
});
//注册接收随机数组的连接
connect(gen, &Generate::sendArray, bubble,&BubbleSort::recvArray);
connect(gen, &Generate::sendArray, quick, &QuickSort::recvArray);
//注册接受子进程发送的数据
connect(gen, &Generate::sendArray, this, [=](QVector<int> list){
bubble->start();
quick->start();
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
//将list中的当前数据强转成QString
ui->randList->addItem(QString::number(list.at(i)));
}
});
//显示冒泡排序后的数组
connect(bubble, &BubbleSort::finish, this, [=](QVector<int> list){
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
ui->bubbleList->addItem(QString::number(list.at(i)));
}
});
//显示快速排序后的数组
connect(quick, &QuickSort::finish, this, [=](QVector<int> list){
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
ui->quickList->addItem(QString::number(list.at(i)));
}
});
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
//main.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include " );
MainWindow w;
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
//以下是结果和三个线程地址,通过比较明显发现10000个随机数快速排序的效率是远高于冒泡排序的,约167倍。
ps:主要事项
如果要在Qt信号槽中使用自定义类型,需要注意使用qRegisterMetaType对自定义类型进行注册,当然在不跨线程时使用自定义类型signal/slot来传递,可能不会出现什么问题;一旦涉及跨线程就很容易出错,回想下信号槽的作用就是用来对象与对象之间通信的,难免会跨线程,建议在使用自定义类型利用信号槽通信时,最好先通过qRegisterMetaType()将自定义类型进行注册,以免出错。
总结qRegisterMetaType使用方法如下:(网上查到的,例子中我直接在ui界面实例化之前就注册了)
1、注册位置:在第一次使用此类链接跨线程的signal/slot之前,一般在当前类的构造函数中进行注册;
2、注册方法:在当前类的顶部包含:#include ,构造函数中加入代码:qRegisterMetaType(“Myclass”);
3、Myclass的引用类型需单独注册:qRegisterMetaType(“Myclass&”);
3、使用方式2:添加修改任务类(只需要对使用方式1的例程稍做修改即可)
3.1 操作步骤
-
创建一个新的类,让这个类从QObject派生
class MyWork:public QObject { ....... } -
在这个类中添加一个公共的成员函数,函数体就是我们要子线程执行的业务逻辑。
class MyWork:public QObject { public: ....... // 函数名自己指定, 叫什么都可以, 参数可以根据实际需求添加 void working(); } -
在主线程中创建一个QThread对象,这就是子线程的对象。
QThread* sub = new QThread; -
在主线程中创建工作的类对象(千万不要指定给创建的对象指定父对象)
MyWork* work = new MyWork(this); // error MyWork* work = new MyWork; // ok -
将MyWork对象移动到创建的子线程对象中,需要调用QObject类提供的moveToThread()方法
void QObject::moveToThread(QThread *targetThread); 如果给work指定了父对象, 这个函数调用就失败了 提示: QObject::moveToThread: Cannot move objects with a parent work->moveToThread(sub); // 移动到子线程中工作 -
启动子线程,调用 start(), 这时候线程启动了,但是移动到线程中的对象并没有工作
-
调用 MyWork 类对象的工作函数,让这个函数开始执行,这时候是在移动到的那个子线程中运行的
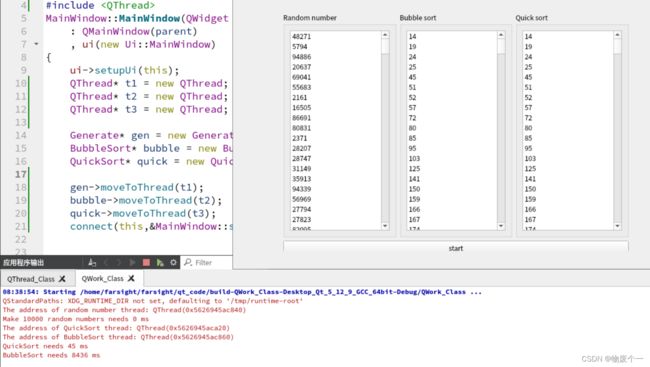
3.2 例程(生成随机数并做冒泡排序与快速排序)
//mainwindow.h
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H
#include //mythread.h
#ifndef MYTHREAD_H
#define MYTHREAD_H
#include //main.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include " );
MainWindow w;
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
//mainwindow.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include "mythread.h"
#include #include "mythread.h"
#include ps:注意事项
1、方式2的自定义类一定要基于QObject,因为里面有个方法叫moveToThread。
2、new任务对象的时候不能指定父对象,如果指定了就放不进线程里了。(一人一个爹)
3、多个任务对象可以放到同一个线程里执行,但是不是同步执行,是顺序执行。
4、释放线程资源
方法一:直接给线程指定父对象(见第一章)
QThread* t1 = new QThread(this);
QThread* t2 = new QThread(this);
QThread* t3 = new QThread(this);
方法二:添加释放函数
connect(this,&MainWindow::destroyed,this,[=](){
t1->quit();//退出线程的工作函数
/*
*调用线程退出函数之后, 线程不会马上退出因为当前任务有可能还没有完成, 调用wait()是
*等待任务完成, 然后退出线程, 一般情况下会在 exit() 后边调用这个函数
*/
t1->wait();
t1->deleteLater();//delete t1
t2->quit();
t2->wait();
t2->deleteLater();//delete t1
t3->quit();
t3->wait();
t3->deleteLater();//delete t1
gen->deleteLater();
bubble->deleteLater();
quick->deleteLater();
});
十六、QDate类
QDate 类可以封装日期信息也可以通过这个类得到日期相关的信息,包括: 年 , 月 , 日。
// 构造函数
QDate::QDate();
QDate::QDate(int y, int m, int d);
// 公共成员函数
// 重新设置日期对象中的日期
bool QDate::setDate(int year, int month, int day);
// 给日期对象添加 ndays 天
QDate QDate::addDays(qint64 ndays) const;
// 给日期对象添加 nmonths 月
QDate QDate::addMonths(int nmonths) const;
// 给日期对象添加 nyears 月
QDate QDate::addYears(int nyears) const;
// 得到日期对象中的年/月/日
int QDate::year() const;
int QDate::month() const;
int QDate::day() const;
void QDate::getDate(int *year, int *month, int *day) const;
// 日期对象格式化
/*
d - The day as a number without a leading zero (1 to 31)
dd - The day as a number with a leading zero (01 to 31)
ddd - The abbreviated localized day name (e.g. 'Mon' to 'Sun'). Uses the system locale to localize the name, i.e. QLocale::system().
dddd - The long localized day name (e.g. 'Monday' to 'Sunday'). Uses the system locale to localize the name, i.e. QLocale::system().
M - The month as a number without a leading zero (1 to 12)
MM - The month as a number with a leading zero (01 to 12)
MMM - The abbreviated localized month name (e.g. 'Jan' to 'Dec'). Uses the system locale to localize the name, i.e. QLocale::system().
MMMM - The long localized month name (e.g. 'January' to 'December'). Uses the system locale to localize the name, i.e. QLocale::system().
yy - The year as a two digit number (00 to 99)
yyyy - The year as a four digit number. If the year is negative, a minus sign is prepended, making five characters.
*/
//格式成自己想要的日期
QString QDate::toString(const QString &format) const;
// 操作符重载 ==> 日期比较
bool QDate::operator!=(const QDate &d) const;
bool QDate::operator<(const QDate &d) const;
bool QDate::operator<=(const QDate &d) const;
bool QDate::operator==(const QDate &d) const;
bool QDate::operator>(const QDate &d) const;
bool QDate::operator>=(const QDate &d) const;
// 静态函数 -> 得到本地的当前日期
[static] QDate QDate::currentDate();
例子:
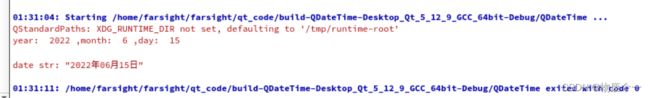
QDate d = QDate::currentDate();
qDebug() << "year: " << d.year() << ",month: " << d.month() << ",day: " << d.day() << endl;
//QString str = d.toString("yyyy-MM-dd");分隔符'-'可以换其它形式
QString str = d.toString("yyyy年MM月dd日");
qDebug() << "date str:" << str << endl;
十七、QTimer类
QTime 类可以封装时间信息也可以通过这个类得到时间相关的信息,包括: 时 , 分 , 秒 , 毫秒。
// 构造函数
QTime::QTime();
/*
h ==> 取值范围: 0 ~ 23
m and s ==> 取值范围: 0 ~ 59
ms ==> 取值范围: 0 ~ 999
*/
QTime::QTime(int h, int m, int s = 0, int ms = 0);
// 公共成员函数
// Returns true if the set time is valid; otherwise returns false.
bool QTime::setHMS(int h, int m, int s, int ms = 0);
QTime QTime::addSecs(int s) const;
QTime QTime::addMSecs(int ms) const;
// 示例代码
QTime n(14, 0, 0); // n == 14:00:00
QTime t;
t = n.addSecs(70); // t == 14:01:10
t = n.addSecs(-70); // t == 13:58:50
t = n.addSecs(10 * 60 * 60 + 5); // t == 00:00:05
t = n.addSecs(-15 * 60 * 60); // t == 23:00:00
// 从时间对象中取出 时/分/秒/毫秒
// Returns the hour part (0 to 23) of the time. Returns -1 if the time is invalid.
int QTime::hour() const;
// Returns the minute part (0 to 59) of the time. Returns -1 if the time is invalid.
int QTime::minute() const;
// Returns the second part (0 to 59) of the time. Returns -1 if the time is invalid.
int QTime::second() const;
// Returns the millisecond part (0 to 999) of the time. Returns -1 if the time is invalid.
int QTime::msec() const;
// 时间格式化
/*
-- 时 --
h ==> The hour without a leading zero (0 to 23 or 1 to 12 if AM/PM display)
hh ==> The hour with a leading zero (00 to 23 or 01 to 12 if AM/PM display)
H ==> The hour without a leading zero (0 to 23, even with AM/PM display)
HH ==> The hour with a leading zero (00 to 23, even with AM/PM display)
-- 分 --
m ==> The minute without a leading zero (0 to 59)
mm ==> The minute with a leading zero (00 to 59)
-- 秒 --
s ==> The whole second, without any leading zero (0 to 59)
ss ==> The whole second, with a leading zero where applicable (00 to 59)
-- 毫秒 --
zzz ==> The fractional part of the second, to millisecond precision,
including trailing zeroes where applicable (000 to 999).
-- 上午或者下午
AP or A ==> 使用AM/PM(大写) 描述上下午, 中文系统显示汉字
ap or a ==> 使用am/pm(小写) 描述上下午, 中文系统显示汉字
*/
//格式化成自己想要的时间格式
QString QTime::toString(const QString &format) const;
// 阶段性计时
// 过时的API函数
// 开始计时
void QTime::start();
// 计时结束
int QTime::elapsed() const;
// 重新计时
int QTime::restart();
// 推荐使用的API函数
// QElapsedTimer 类
void QElapsedTimer::start();
qint64 QElapsedTimer::restart();
qint64 QElapsedTimer::elapsed() const;
// 操作符重载 ==> 时间比较
bool QTime::operator!=(const QTime &t) const;
bool QTime::operator<(const QTime &t) const;
bool QTime::operator<=(const QTime &t) const;
bool QTime::operator==(const QTime &t) const;
bool QTime::operator>(const QTime &t) const;
bool QTime::operator>=(const QTime &t) const;
// 静态函数 -> 得到当前时间
[static] QTime QTime::currentTime();
例子:
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include 十八、QDateTime
QDateTime 类可以封装日期和时间信息也可以通过这个类得到日期和时间相关的信息,包括: 年 , 月 , 日 , 时 , 分 , 秒 , 毫秒。其实这个类就是 QDate 和 QTime 这两个类的结合体。
// 构造函数
QDateTime::QDateTime();
QDateTime::QDateTime(const QDate &date, const QTime &time, Qt::TimeSpec spec = Qt::LocalTime);
// 公共成员函数
// 设置日期
void QDateTime::setDate(const QDate &date);
// 设置时间
void QDateTime::setTime(const QTime &time);
// 给当前日期对象追加 年/月/日/秒/毫秒, 参数可以是负数
QDateTime QDateTime::addYears(int nyears) const;
QDateTime QDateTime::addMonths(int nmonths) const;
QDateTime QDateTime::addDays(qint64 ndays) const;
QDateTime QDateTime::addSecs(qint64 s) const;
QDateTime QDateTime::addMSecs(qint64 msecs) const;
// 得到对象中的日期
QDate QDateTime::date() const;
// 得到对象中的时间
QTime QDateTime::time() const;
// 日期和时间格式, 格式字符参考QDate 和 QTime 类的 toString() 函数
QString QDateTime::toString(const QString &format) const;
// 操作符重载 ==> 日期时间对象的比较
bool QDateTime::operator!=(const QDateTime &other) const;
bool QDateTime::operator<(const QDateTime &other) const;
bool QDateTime::operator<=(const QDateTime &other) const;
bool QDateTime::operator==(const QDateTime &other) const;
bool QDateTime::operator>(const QDateTime &other) const;
bool QDateTime::operator>=(const QDateTime &other) const;
// 静态函数
// 得到当前时区的日期和时间(本地设置的时区对应的日期和时间)
[static] QDateTime QDateTime::currentDateTime();