泛型容器-红黑树源码分析附带详细图解
红黑树介绍
1.2-3树
红⿊树是⼀种⾃平衡的⼆叉树,它可以避免⼆分搜索树在极端的情况下蜕化成链表的情况。那么什么是红⿊树呢?要想便于了解红⿊树,我们先了解⼀下跟它息息相关的2-3树。
2-3树是⼀种绝对平衡的多叉树,在这棵树中,任意⼀个节点,它的左右⼦树的⾼度是相同的。如下所示:
正如上⾯介绍过的,2-3树是⼀个多叉树。那为什么叫做2-3树呢? 因为规则定义,2-3树分为两种节点,分别为:2-节点和3-节点。其中,2-节点表示节点中保存⼀个元素,3-节点则表示节点中保存两个元素。
- 演示⼀下如何⽣成⼀个2-3树:
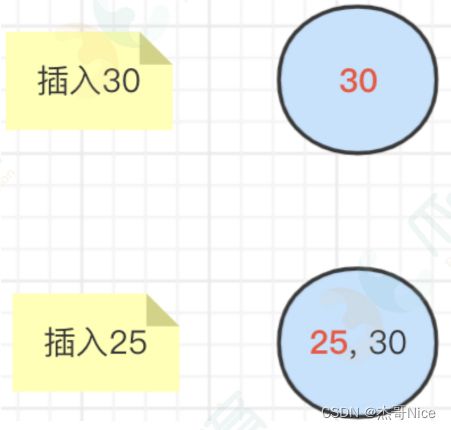
- ⾸先:向2-3树中插⼊30和25
-
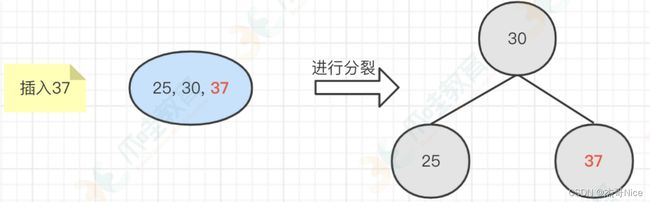
- 当再插⼊37的时候,⼀个节点就容纳了3个元素了,那么就要进⾏分裂操作了,如下所示:
-
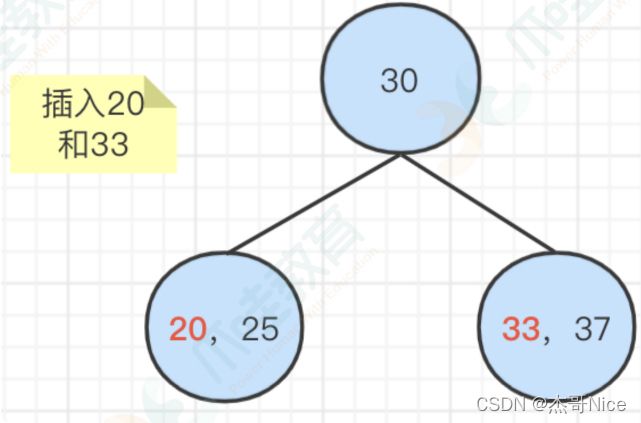
- 然后,我们再插⼊20和33,可以正常的容纳这两个元素
-
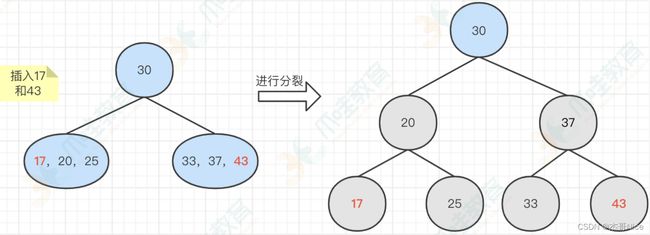
- 我们再继续插⼊17和43,那么出现了两个节点都分别容纳了3个元素,那么这两个节点都需要进⾏分裂操作了
-
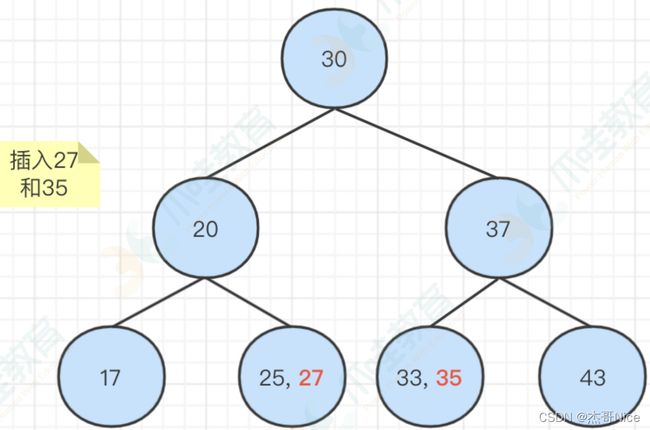
- 插⼊27和35,两个节点都可以容纳这两个新插⼊的元素
-
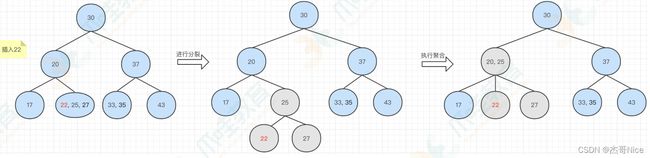
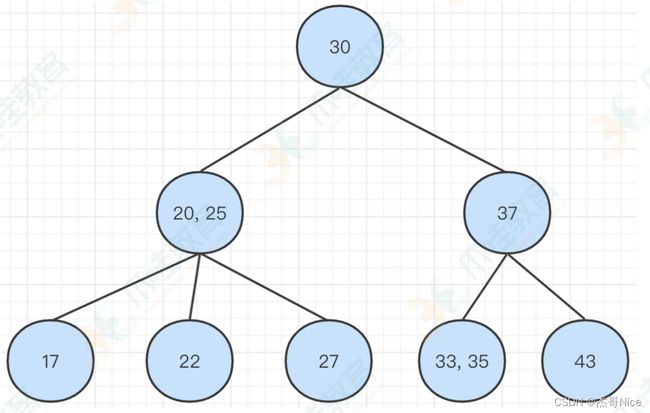
- 那么再最后插⼊22,结果发现,⼀个节点容纳了3个元素,要进⾏分裂,但是分裂后,叶⼦节
点的⾼度不⼀致了,那么就要再进⾏聚合操作,如下所示:
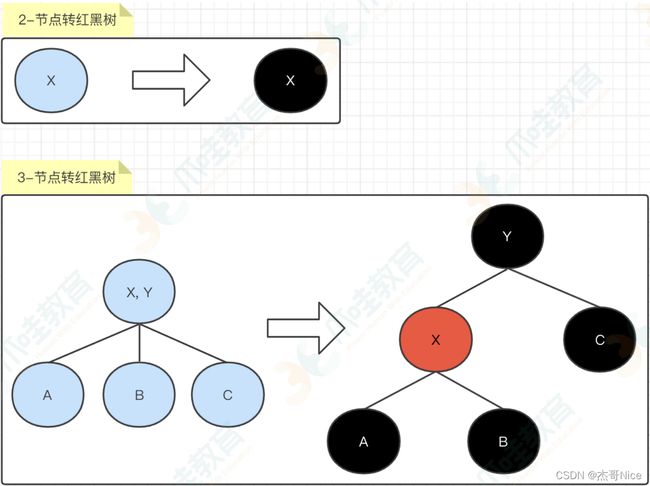
- 那么,我们了解完2-3树之后,我回过头来看⼀下红⿊树,也就是说,2-3树怎么转变成红⿊树呢?⽅式很多,此处我们可以采⽤左倾红⿊树的⽅式,来将2-3树转换为红⿊树,转换规则如下:
-
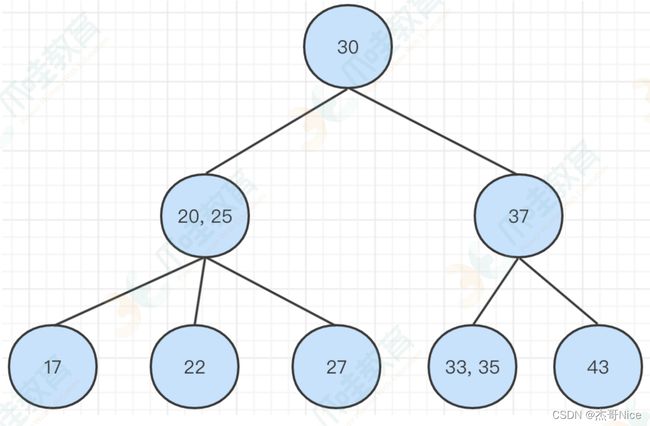
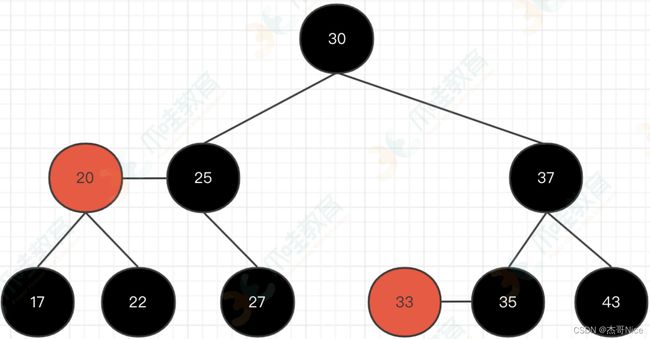
- 我们可以根据上⾯的转换规则,进⾏转换操作。下图是我们上⾯讲2-3树的时候,构造的。
-
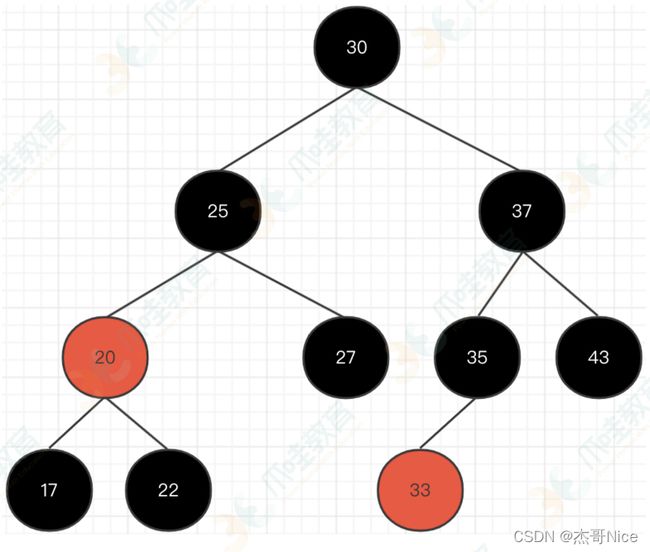
- 那么我们按照规则进⾏转换,如下所示:
-
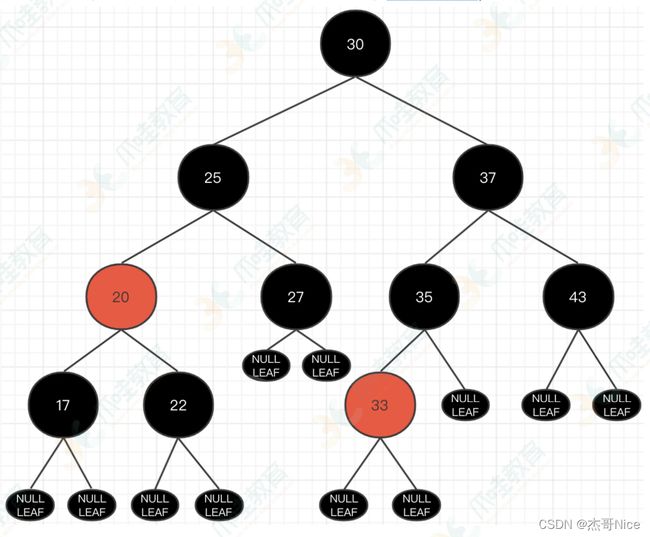
- 我们按照树形结构进⾏修整,那么就是我们今天要介绍的红⿊树。如下所示:
2.红黑树
- ********组成红黑树的五个必要条件********(面试必问)
- 条件⼀:每个节点要么是红⾊,要么是⿊⾊。
- 条件⼆:根节点⼀定是⿊⾊的。
- 条件三:每个叶⼦节点⼀定是⿊⾊。
- 条件四:如果⼀个节点是红⾊,那么它的左右⼦节点⼀定都是⿊⾊的。
- 条件五:从任意⼀个节点到叶⼦节点,所经过的⿊⾊节点的数量⼀样多。
- 完整的红⿊树
一、源码概述
当我们掌握了红⿊树的理论知识之后,下⾯我们就来开始分析HashMap的源码了。那我们从哪⾥开始⼊⼿呢?要回答这个问题,那么就要从我们最常使⽤HashMap的场景出发了。当我们想要是⽤HashMap的时候,我们⾸先会通过HashMap的构造⽅法创建HashMap,然后通过put⽅法向HashMap对象赋值。那么我们就可以通过构造函数+put这两点进⾏源码的切⼊点。
1.1 HashMap的构造函数
- 我们先来看HashMap的构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty HashMap with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}通过源码我们可以看到只有⼀⾏代码,即:给loadFactor赋值。
那么loadFactor是什么呢?它是HashMap的加载因⼦,也就是说,元素所占的空间达到加载因⼦的规定值的时候,那么就会
执⾏扩容。
那么初始化加载因⼦的时候,赋值给它DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR属性了。
DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR这个值是多少呢?我们去源码中寻找答案。
/** * The load factor used when none specified in constructor. */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;通过上⾯截图,我们知道了,加载因⼦默认被赋值为0.75f,那么其实⼤部分同学都是知道HashMap的结构在JDK8之前是【数组+链表】,⽽从JDK8之后,存储结构就变为了【数组+链表+红⿊树】了。那么这个0.75的含义就是:如果数组中存储的元素⻓度达到了原⻓度的75%或者3/4的话,那么就需要执⾏扩容操作了。
构造函数就这么⼀⾏代码,即:给loadFactor赋值为0.75f。是不是很简单。那我们看完了构造函数的代码,我们就来把视⻆转到put⽅法吧。
1.2 put方法
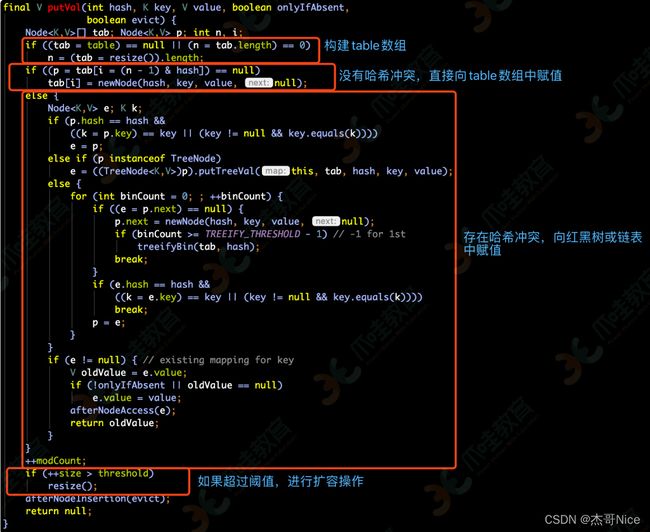
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}- put⽅法⾥⾯,只是调⽤了putVal⽅法,如下是putVal⽅法:
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods.
*
* @param hash key的哈希值
* @param key key值
* @param value value值
* @param onlyIfAbsent 如果是true,则不改变已存在的value值
* @param evict 驱逐,赶出,逐出 if false, the table is in creation mode.
*
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
// eg1: hash=0 key=0 value="a0" onlyIfAbsent=false evict=true
// eg2: hash=1 key=1 value="a1" onlyIfAbsent=false evict=true
// eg3: hash=16 key=16 value="a16" onlyIfAbsent=false evict=true
// eg4: hash=32 key=32 value="a32" onlyIfAbsent=false evict=true
// eg5: 由于执行步骤与eg4相似,故略过。
// eg6: hash=128 key=128 value="a128" onlyIfAbsent=false evict=true
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
Node[] tab;
Node p;
int n, i;
// eg1: table=null
// eg2: table是长度为16的Node数组,且table[1]=Node(1, 1, "a1", null)
// eg3: table是长度为16的Node数组,且table[1]=Node(1, 1, "a1", null) ... table[6]=Node(6, 6, "a6", null)
// eg4: table是长度为16的Node数组,且table[1]=Node(1, 1, "a1", null) ... table[6]=Node(6, 6, "a6", null)
// eg6: table是长度为16的Node数组,且table[1]=Node(1, 1, "a1", null) ... table[6]=Node(6, 6, "a6", null)
/** 如果是空的table,那么默认初始化一个长度为16的Node数组*/
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) {
// eg1: resize返回(Node[]) new Node[16],所以:tab=(Node[]) new Node[16], n=16
n = (tab = resize()).length;
}
// eg1: i = (n-1)&hash = (16-1)&0 = 1111&0000 = 0000 = 0; 即:p=tab[0]=null
// eg2: i = (n-1)&hash = (16-1)&1 = 1111&0001 = 0001 = 1; 即:p=tab[1]=null
// eg3: i = (n-1)&hash = (16-1)&16 = 1111&10000 = 0000 = 0; 即:p=tab[0]=Node(0, 0, "a0", null)
// eg4: i = (n-1)&hash = (16-1)&32 = 1111&100000 = 0000 = 0; 即:p=tab[0]=Node(0, 0, "a0", null)
// eg6: i = (n-1)&hash = (16-1)&128 = 1111&10000000 = 0000 = 0; 即:p=tab[0]=Node(0, 0, "a0", null)
/** 如果计算后的下标i,在tab数组中没有数据,那么则新增Node节点*/
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) {
// eg1: tab[0] = newNode(0, 0, "a0", null)
// eg2: tab[1] = newNode(1, 1, "a1", null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
} else { /** 如果计算后的下标i,在tab数组中已存在数据,则执行以下逻辑 */
Node e;
K k;
// eg3: p.hash==0, hash==16,所以返回false
// eg4: p.hash==0, hash==32,所以返回false
// eg6: p.hash==0, hash==128,所以返回false
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { /** 如果与已存在的Node是相同的key值*/
e = p;
}
// eg3: p instanceof Node,所以为false
// eg4: p instanceof Node,所以为false
// eg6: p instanceof Node,所以为false
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) { /** 如果与已存在的Node是相同的key值,并且是树节点*/
e = ((TreeNode) p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
} else { /** 如果与已存在的Node是相同的key值,并且是普通节点,则循环遍历链式Node,并对比hash和key,如果都不相同,则将新的Node拼装到链表的末尾。如果相同,则进行更新。*/
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
// eg3: p.next == null
// eg4-loop1: p.next == Node(16, 16, "a16", null) 不为空
// eg4-loop2: p.next == null
/** 获得p节点的后置节点,赋值给e。直到遍历到横向链表的最后一个节点,即:该节点的next后置指针为null */
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// eg3: p.next = newNode(16, 16, "a16", null);
// eg4-loop2: p.next == newNode(32, 32, "a32", null);
// eg6: p.next == newNode(128, 128, "a128", null);
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// eg3: binCount == 0
// eg4-loop2: binCount == 1
/** binCount从0开始,如果Node链表大于8个Node,那么试图变为红黑树 */
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) {
// eg6: tab={newNode(0, 0, "a0", [指向后面1个链表中的7个node]), newNode(1, 1, "a1", null)}, hash=128
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
}
// eg3: break
// eg4-loop2: break
break;
}
// eg4-loop1: e.hash==16 hash==32 所以返回false
/** 针对链表中的每个节点,都来判断一下,是否待插入的key与已存在的链表节点相同,如果相同,则跳出循环,并在后续的操作中,将该节点内容更新为最新的插入值 */
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
break;
}
// eg4-loop1: p=e=Node(16, 16, "a16", null)
p = e;
}
}
// eg3: e = null
// eg4: e = null
/** 如果存在相同的key值*/
if (e != null) {
// egx: String oldValue = "v1"
V oldValue = e.value;
// egx: onlyIfAbsent=false
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) {
// egx: e = Node(3366, "k1", "v2", null)
/** 则将新的value值进行更新*/
e.value = value;
}
afterNodeAccess(e);
// egx: 返回oldValue="v1"
return oldValue;
}
}
// eg1: modCount==0 ++modCount==1
// eg2: modCount==1 ++modCount==2
// eg3: modCount==7 ++modCount==8
// eg4: modCount==8 ++modCount==9
++modCount;
// eg1: size=0, threshold=12
// eg2: size=1, threshold=12
// eg3: size=7, threshold=12
// eg4: size=8, threshold=12
if (++size > threshold) {
resize();
}
afterNodeInsertion(evict); /** doing nothing */
return null;
} - 代码分解为如下几步:
- 正如上⾯源码截图中所描述的,整个putVal⼀共执⾏了三部分内容,分别是:
① 创建table数组
②向table数组中赋值,这⾥⾯分为哈希不冲突和哈希冲突两种情况。
③如果超过阈值,则进⾏扩容操作。
参考文档:JDK1.8 HashMap源码解析+最全面试题_Saintmm的博客-CSDN博客 JDK1.8 HashMap源码解析+最全面试题
图解TreeMap的红黑树平衡操作fixAfterInsertion(),接着手撕红黑树添加节点_Saintmm的博客-CSDN博客 图解TreeMap的红黑树平衡操作fixAfterInsertion(),接着手撕红黑树添加节点
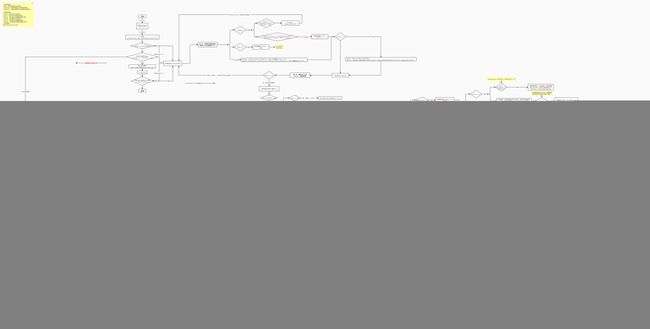
源码干货-put方法源码流程图