02、Flink Client 实现原理与源码解析
文章目录
- Flink Client 实现原理
-
- Flink Client 主要功能
- Application Code 运行
- ExecutionEnvironment 分类
- CliFrontend
-
- 构建CliFrontend 对象
- 调用 parseAndRun方法来执行任务
-
- run 方法
-
- ProgramOptions 属性
- PackagedProgram
-
- URLClassLoader
- Flink 的类加载机制
- executeProgram执行用户代码
个人公众号:

Flink Client 实现原理
在我们解读Flink Client 源码之前,我们先要了解清楚它的实现原理。
Flink Client 主要功能
我们可以看到,FLink Client 主要三个任务,第一个是运行Application,第二个是是对任务的操作管理,第三个是在Client端对集群的管理。
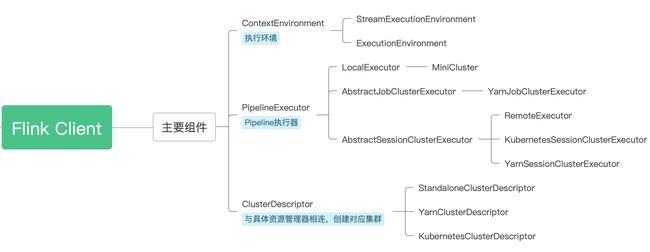
##Flink Client 主要组件
ContexEnvironment: 构建出不同的执行环境
PipelineExecutor: 对 Stream Graph的执行生成JobGraph
CluterDescriptor: 对不同集群的连接
Application Code 运行
当我们提交运行我们代码的代码时,客户端同时主要做三件事:
1、通过ClusterClientServiceLoader去加载ClusterClientFactory, 从而创建集群。
2、通过ContexEnvironmentFactory去创建ContexEnvironment,从而构建StreamExecutionEnvironment
3、构建PackagedProgram,获得Flink任务运行时所需要的环境,从而通过反射调用我们的代码的main()方法,进儿通过StreamExecutionEnvironment去执行execute()方法获得StreamGraph,将StreamGraph提交给PipelineExecutor去执行生成JobGraph对象,最终将JobGraph提交给Cluster。
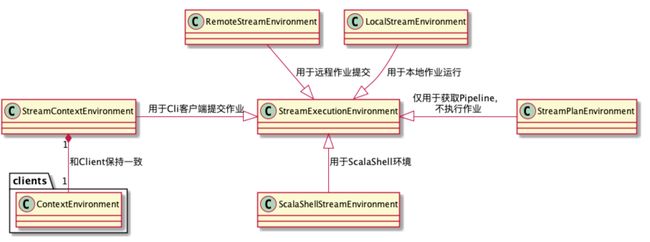
ExecutionEnvironment 分类
#Flink Client 源码解析
通过上问的解答,我们大概了解了Flink Client 提交作业的流程,那么接下来让我们走进源码中,看看时如何实现的。
CliFrontend
当我们用户在客户端运行任务时,flink run.sh 会调用 CliFrontend 类中的main()方法,那么就让我们具体看下main()方法。
/** Submits the job based on the arguments. */
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// 从系统环境中( 环境变量或者当前目录的 conf 或者 ../conf 目录)获取配置文件( flink-conf.yaml )位置
EnvironmentInformation.logEnvironmentInfo(LOG, "Command Line Client", args);
// 1. find the configuration directory 解析 flink-conf.yaml 文件,把属性放到 Configuration 里面
final String configurationDirectory = getConfigurationDirectoryFromEnv();
// 2. load the global configuration 加载全局配置并添加给定的动态属性配置。
final Configuration configuration =
GlobalConfiguration.loadConfiguration(configurationDirectory);
// 3. load the custom command lines 初始化自定义的命令行参数
final List<CustomCommandLine> customCommandLines =
loadCustomCommandLines(configuration, configurationDirectory);
int retCode = 31;
try {
//4. 初始化 CliFronted ,使用构造函数,把 CliFrontend 类的一些属性赋值,给后续执行时提供属性
final CliFrontend cli = new CliFrontend(configuration, customCommandLines);
SecurityUtils.install(new SecurityConfiguration(cli.configuration));
//5. 调用 parseAndRun 方法来执行任务
retCode = SecurityUtils.getInstalledContext().runSecured(() -> cli.parseAndRun(args));
} catch (Throwable t) {
final Throwable strippedThrowable =
ExceptionUtils.stripException(t, UndeclaredThrowableException.class);
LOG.error("Fatal error while running command line interface.", strippedThrowable);
strippedThrowable.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.exit(retCode);
}
}
构建CliFrontend 对象
我们看到前面三步都是加载配置文件,第四步是通过前面的配置构造出 CliFrontend 对象,让我们进一步看下 CliFrontend 的属性
public CliFrontend(Configuration configuration, List<CustomCommandLine> customCommandLines) {
this(configuration, new DefaultClusterClientServiceLoader(), customCommandLines);
}
public CliFrontend(
Configuration configuration,
ClusterClientServiceLoader clusterClientServiceLoader,
List<CustomCommandLine> customCommandLines) {
// 初始化了配置,就是 flink-conf.yaml 的属性
this.configuration = checkNotNull(configuration);
// 初始化了自定义的命令行参数
this.customCommandLines = checkNotNull(customCommandLines);
//初始化了 clusterClientServiceLoader,使用 SPI 加载了 org.apache.flink.client.deployment.StandaloneClientFactory 类
this.clusterClientServiceLoader = checkNotNull(clusterClientServiceLoader);
FileSystem.initialize(
configuration, PluginUtils.createPluginManagerFromRootFolder(configuration));
this.customCommandLineOptions = new Options();
for (CustomCommandLine customCommandLine : customCommandLines) {
customCommandLine.addGeneralOptions(customCommandLineOptions);
customCommandLine.addRunOptions(customCommandLineOptions);
}
//初始化了客户端超时时间
this.clientTimeout = configuration.get(ClientOptions.CLIENT_TIMEOUT);
// 初始化了默认的并行度
this.defaultParallelism = configuration.getInteger(CoreOptions.DEFAULT_PARALLELISM);
}
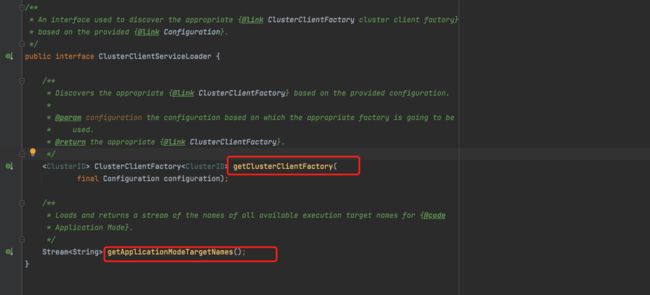
我们看到在掉用CliFrontend构造时,初始化了DefaultClusterClientServiceLoader(),而该类实现了ClusterClientServiceLoader接口,在ClusterClientServiceLoader接口中定义了两个方法,getClusterClientFactory,一个是getApplicationModeTargetNames。
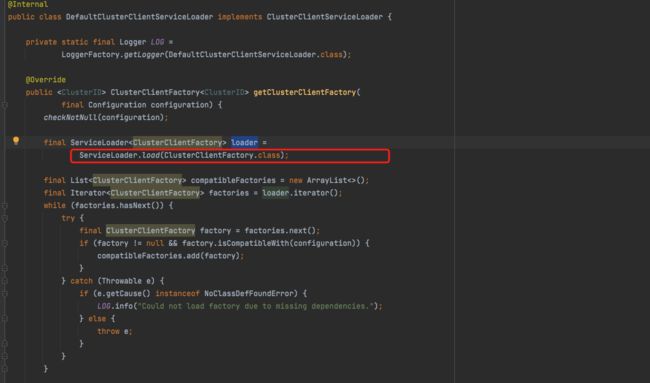
我们进一步看下 DefaultClusterClientServiceLoader类中对 getClusterClientFactory 方法的实现
我们可以看到getClusterClientFactory()通过SPI技术加载了ClusterClientFactory,而ClusterClientFactory接口中创建了Flink集群客户端所需的所有信息,为创建集群做准备。
调用 parseAndRun方法来执行任务
parseAndRun 方法里有一个 switch case,根据命令行不同的动作类型,执行不同的动作,这里我们重点看执行的 run 方法
run 方法
run 方法中,用两个对象,ProgramOptions(执行程序选项)和 Configuration (配置),来构建一个 PackagedProgram,去执行程序。
/**
* Executions the run action.
*
* @param args Command line arguments for the run action.
*/
protected void run(String[] args) throws Exception {
LOG.info("Running 'run' command.");
final Options commandOptions = CliFrontendParser.getRunCommandOptions();
final CommandLine commandLine = getCommandLine(commandOptions, args, true);
// evaluate help flag
if (commandLine.hasOption(HELP_OPTION.getOpt())) {
CliFrontendParser.printHelpForRun(customCommandLines);
return;
}
final CustomCommandLine activeCommandLine =
validateAndGetActiveCommandLine(checkNotNull(commandLine));
//1. ProgramOptions(执行程序选项)
final ProgramOptions programOptions = ProgramOptions.create(commandLine);
final List<URL> jobJars = getJobJarAndDependencies(programOptions);
//2. Configuration (获得配置)
final Configuration effectiveConfiguration =
getEffectiveConfiguration(activeCommandLine, commandLine, programOptions, jobJars);
LOG.debug("Effective executor configuration: {}", effectiveConfiguration);
//3.来构建一个 PackagedProgram(打包的程序,就是把所有必要的信息,包括运行时参数和程序配置打包到一个对象里面)
try (PackagedProgram program = getPackagedProgram(programOptions, effectiveConfiguration)) {
// 4.执行用户代码
executeProgram(effectiveConfiguration, program);
}
}
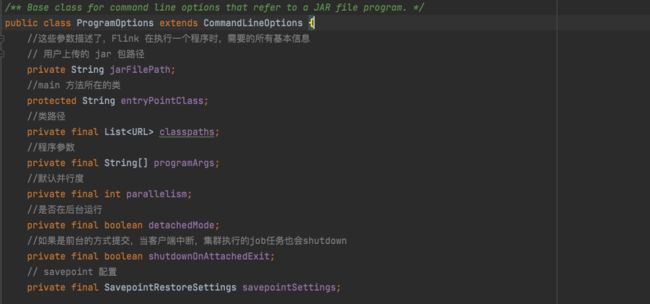
ProgramOptions 属性
在ProgramOptions中的属性描述了,Flink 在执行一个程序时,需要的所有基本信息
PackagedProgram
我们可以看到PackagedProgram 描述了Flink 任务运行时所需要的环境,有了这些属性,我们的任务就可以运行了。
URLClassLoader
这里我们想要表达的是,Flink 的类加载机制和 Java 虚拟机默认提供的类加载机制是不同的。
Java 虚拟机提供的默认类加载机制,我们可以再复习一下,(双亲委派),如果一个类加载器收到了类加载请求,自己默认不加载,而是把这个请求委派给父类加载器去加载,一直传递到顶层的 BootStrap ClassLoader 中。父加载器加载不到才让下面的类加载器加载。
如果 Flink 使用这种类加载机制,可能会带来的问题是:Flink 集群运行着 Flink 框架的代码,这些代码包括了 Flink 的各种依赖。而用户编写的复杂的应用程序,可能也会包含很多复杂的依赖。其中必然有类全限定名同名的类。那么在加载用户的类时,一看已经被父类加载器加载了,就不会再加载了,那用户的程序必然就会报错了。
Flink 的类加载机制
Flink 可以在 flink-conf.yml 中配置不同的类加载机制(默认就是 child-first):
classloader.resolve-order: parent-first
classloader.resolve-order: child-first
我们直接看一下这个 ChildFirstClassLoader 类的 loadClassWithoutExceptionHandling 方法:
@Override
protected Class<?> loadClassWithoutExceptionHandling(String name, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 首先,检查这个类是否已经被加载过
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
// alwaysParentFirstPatterns 中配置的类,要在父类中优先加载
for (String alwaysParentFirstPattern : alwaysParentFirstPatterns) {
if (name.startsWith(alwaysParentFirstPattern)) {
return super.loadClassWithoutExceptionHandling(name, resolve);
}
}
try {
// 用户的类,不让父类加载器加载,而是自己直接加载
c = findClass(name);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// let URLClassLoader do it, which will eventually call the parent
c = super.loadClassWithoutExceptionHandling(name, resolve);
}
} else if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
简单描述一下如下:
- 调用 findLoadedClass() 方法检查全限定名对应的类是否已经加载过,若没有加载过,再继续往下执行;
- 检查要加载的类是否以 alwaysParentFirstPatterns 集合中的前缀开头。如果是,则调用父类的对应方法,以 parent-first 的方式来加载它;
- 如果类不符合 alwaysParentFirstPatterns 集合的条件,就调用 findClass() 方法在用户代码中查找并获取该类的定义(该方法在URLClassLoader中有默认实现)。如果找不到,再fallback到父加载器来加载。
那这样就说完了 Flink 的类加载机制了。
executeProgram执行用户代码
PackagedProgram 构建完后,开始执行用户代码。
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Interaction with programs and JobManager
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
protected void executeProgram(final Configuration configuration, final PackagedProgram program) throws ProgramInvocationException {
ClientUtils.executeProgram(new DefaultExecutorServiceLoader(), configuration, program, false, false);
}
我们看 ClientUtils.executeProgram() 方法,在executeProgram方法执行的时候初始化了DefaultExecutorServiceLoader对象,而DefaultExecutorServiceLoader实现了PipelineExecutorServiceLoader接口,从而通过SPI技术获得PipelineExecutorFactory,最后创建了PipelineExecutor。
同时在ClientUtils.executeProgram方法中通过Cline 端获取了 ContextEnvironment和StreamContextEnvironment 的环境,

而StreamContextEnvironment集成了StreamExecutionEnvironment类,重写了execute 方法,在execute 方法中通过StreamGraph 得到了JobExecutionResult。
public JobExecutionResult execute(StreamGraph streamGraph) throws Exception {
final JobClient jobClient = executeAsync(streamGraph);
final List jobListeners = getJobListeners();
try {
final JobExecutionResult jobExecutionResult = getJobExecutionResult(jobClient);
jobListeners.forEach(
jobListener -> jobListener.onJobExecuted(jobExecutionResult, null));
return jobExecutionResult;
} catch (Throwable t) {
jobListeners.forEach(
jobListener ->
jobListener.onJobExecuted(
null, ExceptionUtils.stripExecutionException(t)));
ExceptionUtils.rethrowException(t);
// never reached, only make javac happy
return null;
}
}
在executeProgram() 方法中有一个相当经典的 ContextClassLoader 的使用方式
先把 ContextClassLoader 切换为 UserCodeClassLoader,使用这个类加载器来加载 main 方法的代码;
执行完了之后,再把上下文类加载器切换回去。程序在执行代码的时候,当需要执行每个类时,ClassLoader 就会去加载这个类,可以通过 Debug ClassLoader 类的 loadClass() 方法看出来。
//通过反射的方式, 调用用户程序的mian方法..
program.invokeInteractiveModeForExecution();
我们看到通过反射调用我们程序的主方法。
public void invokeInteractiveModeForExecution() throws ProgramInvocationException {
FlinkSecurityManager.monitorUserSystemExitForCurrentThread();
try {
//过调用底层的callMainMethod方法,通过反射的方式去调用main方法
callMainMethod(mainClass, args);
} finally {
FlinkSecurityManager.unmonitorUserSystemExitForCurrentThread();
}
}
当mainMethod.invoke开始执行的时候,各个operator会生成对应的Transformation等封装的逻辑实例,直到运行到StreamExecutionEnvironment.execute()后,才开始懒执行。类似于Spark中的action算子,才开始真正的执行代码。