Paddle Lite在ARM上的应用,以Yolov5为例
目录
一、Paddle Lite简介
二、环境安装
2.1 本地环境安装(基于python3.6):
2.2 开发板Paddle Lite编译(基于python3.7):
2.2.1 已经编译好的whl包(arm,支持python、耗时分析功能)下载链接
2.2.2 自己编译(本地编译)
三、模型转换(在本地环境中进行)
四、模型部署,推理及应用
4.1 使用 Paddle Lite 执行推理的主要步骤
4.2 以Yolov5为例,使用.nb模型进行推理
4.3 推理结果
一、Paddle Lite简介
Paddle Lite 是一种轻量级、灵活性强、易于扩展的高性能的深度学习预测框架,它可以支持诸如 ARM、OpenCL 、NPU 等等多种终端,同时拥有强大的图优化及预测加速能力。
二、环境安装
2.1 本地环境安装(基于python3.6):
pip3 install paddlelite==2.12 -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/
pip3 install x2paddle -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/2.2 开发板Paddle Lite编译(基于python3.7):
2.2.1 已经编译好的whl包(arm,支持python、耗时分析功能)下载链接
https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_46303486/87364716 https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_46303486/87364716
https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_46303486/87364716
2.2.2 自己编译(本地编译)
(1)基本环境安装(如已安装,请跳过)
sudo apt update
sudo apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
gcc g++ make wget python unzip patchelf python-dev(2) cmake安装,推荐使用3.10及以上版本(如已安装,请跳过)
wget https://www.cmake.org/files/v3.10/cmake-3.10.3.tar.gz
tar -zxvf cmake-3.10.3.tar.gz
cd cmake-3.10.3
./configure
make
sudo make install
(3)下载Paddle Lite源码并编译
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite.git
cd Paddle-Lite
sudo rm -rf third-party
# --with_python=ON和--with_profile=ON为编译参数,编译过程中的可选参数见(4)常用编译参数,
本教程基于python,故使用python编译包
sudo ./lite/tools/build_linux.sh --with_python=ON --with_profile=ON
(4)常用编译参数
| 参数 |
说明 |
可选范围 |
默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| arch |
目标硬件的架构版本 |
armv8 / armv7hf / armv7 |
armv8 |
| toolchain |
C++ 语言的编译器工具链 |
gcc |
gcc |
| with_python |
是否包含 python 编译包,目标应用程序是 python 语言时需配置为 ON |
OFF / ON |
OFF |
| with_cv |
是否将 cv 函数加入编译包中 |
OFF / ON |
OFF |
| with_log |
是否在执行过程打印日志 |
OFF / ON |
ON |
| with_exception |
是否开启 C++ 异常 |
OFF / ON |
OFF |
| with_profile |
是否打开执行耗时分析 |
OFF / ON |
OFF |
| with_precision_profile |
是否打开逐层精度结果分析 |
OFF / ON |
OFF |
| with_opencl |
是否编译支持 OpenCL 的预测库 |
OFF / ON |
OFF |
(5)编译产物
编译成功后,会在/Paddle-Lite/build.lite.linux.armv8.gcc/
inference_lite_lib.armlinux.armv8/python/install/dist 目录下生成对应的.whl包,安装即可。
并且会生成相应的python版本的demo。
三、模型转换(在本地环境中进行)
如果想用 Paddle Lite 运行第三方来源(TensorFlow、Caffe、ONNX、PyTorch)模型,一般需要经过两次转化。即使用 X2paddle 工具将第三方模型转化为 PaddlePaddle 格式,再使用 opt工具 将 PaddlePaddle 模型转化为Padde Lite 可支持格式。
为了简化这一过程,X2Paddle 集成了 opt 工具,提供一键转换 API,以 ONNX 为例(大部分模型都可以转换成ONNX):
TensorFlow、Caffe、PyTorch直接转Padde Lite相关部分的API可参考:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/X2Paddle/blob/develop/docs/inference_model_convertor/convert2lite_api.md![]() https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/X2Paddle/blob/develop/docs/inference_model_convertor/convert2lite_api.md
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/X2Paddle/blob/develop/docs/inference_model_convertor/convert2lite_api.md
from x2paddle.convert import onnx2paddle
model_path = "/pose/light_pose_sim.onnx"
save_dir = "./paddleLite_models/light_pose_sim_paddle"
onnx2paddle(model_path, save_dir,
convert_to_lite=True,
lite_valid_places="arm",
lite_model_type="naive_buffer")
# model_path(str) 为 ONNX 模型路径
# save_dir(str) 为转换后模型保存路径
# convert_to_lite(bool) 表示是否使用 opt 工具,默认为 False
# lite_valid_places(str) 指定转换类型,默认为 arm
# lite_valid_places参数目前可支持 arm、 opencl、 x86、 metal、 xpu、 bm、 mlu、
# intel_fpga、 huawei_ascend_npu、imagination_nna、
# rockchip_npu、 mediatek_apu、 huawei_kirin_npu、 amlogic_npu,可以同时指定多个硬件平台
# (以逗号分隔,优先级高的在前),opt 将会自动选择最佳方式。
# lite_model_type(str) 指定模型转化类型,目前支持两种类型:protobuf 和 naive_buffer,默认为 naive_buffer转换后,会在指定目录下生成.nb文件,该文件就是在部署PaddleLite时需要用到的模型
四、模型部署,推理及应用
经过以上步骤,你已经成功完成了所有准备步骤,接下来就是将相关代码和模型移植到开发板上即可。
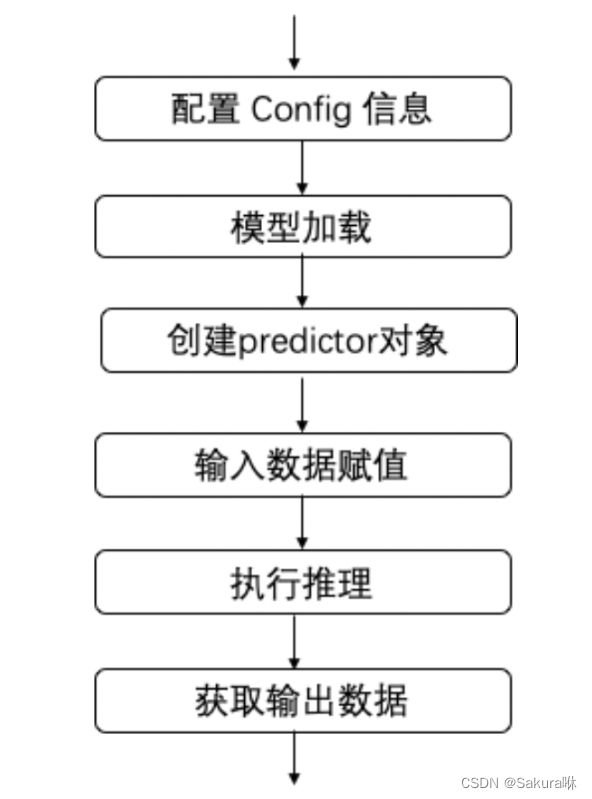
4.1 使用 Paddle Lite 执行推理的主要步骤
# (1) 设置配置信息
config = MobileConfig()
config.set_model_from_file("Your dictionary/opt.nb")
# (2) 创建预测器
predictor = create_paddle_predictor(config)
# (3) 获取输入Tensor的引用,用来设置输入数据,参数表示第几个输入,单输入时为0
input_tensor = predictor.get_input(0)
input_tensor.from_numpy(input_data)
# (4) 执行推理,需要在设置输入数据后使用
predictor.run()
# (5) 获取输出Tensor的引用,用来设置输出数据,参数表示第几个输出,单输出时为0
output_tensor = predictor.get_output(0)
# 将tensor数据类型转为ndarray类型
ort_outs = output_tensor.numpy()4.2 以Yolov5为例,使用.nb模型进行推理
代码是从Yolov5官方源码中扣出来的,修改main函数中的路径即可!
import cv2
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime as rt
from paddlelite.lite import *
CLASSES = {
0: 'person',
1: 'bicycle',
2: 'car',
3: 'motorbike',
4: 'aeroplane',
5: 'bus',
6: 'train',
7: 'truck',
8: 'boat',
9: 'traffic light',
10: 'fire hydrant',
11: 'stop sign',
12: 'parking meter',
13: 'bench',
14: 'bird',
15: 'cat',
16: 'dog',
17: 'horse',
18: 'sheep',
19: 'cow',
20: 'elephant',
21: 'bear',
22: 'zebra',
23: 'giraffe',
24: 'backpack',
25: 'umbrella',
26: 'handbag',
27: 'tie',
28: 'suitcase',
29: 'frisbee',
30: 'skis',
31: 'snowboard',
32: 'sports ball',
33: 'kite',
34: 'baseball bat',
35: 'baseball glove',
36: 'skateboard',
37: 'surfboard',
38: 'tennis racket',
39: 'bottle',
40: 'wine glass',
41: 'cup',
42: 'fork',
43: 'knife',
44: 'spoon',
45: 'bowl',
46: 'banana',
47: 'apple',
48: 'sandwich',
49: 'orange',
50: 'broccoli',
51: 'carrot',
52: 'hot dog',
53: 'pizza',
54: 'donut',
55: 'cake',
56: 'chair',
57: 'sofa',
58: 'potted plant',
59: 'bed',
60: 'dining table',
61: 'toilet',
62: 'tvmonitor',
63: 'laptop',
64: 'mouse',
65: 'remote',
66: 'keyboard',
67: 'cell phone',
68: 'microwave',
69: 'oven',
70: 'toaster',
71: 'sink',
72: 'refrigerator',
73: 'book',
74: 'clock',
75: 'vase',
76: 'scissors',
77: 'teddy bear',
78: 'hair drier',
79: 'toothbrush'
}
def box_iou(box1, box2, eps=1e-7):
(a1, a2), (b1, b2) = box1.unsqueeze(1).chunk(2, 2), box2.unsqueeze(0).chunk(2, 2)
inter = (np.min(a2, b2) - np.max(a1, b1)).clamp(0).prod(2)
return inter / ((a2 - a1).prod(2) + (b2 - b1).prod(2) - inter + eps)
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better val mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
def onnx_inf(onnxModulePath, data):
sess = rt.InferenceSession(onnxModulePath)
input_name = sess.get_inputs()[0].name
output_name = sess.get_outputs()[0].name
pred_onnx = sess.run([output_name], {input_name: data.reshape(1, 3, 640, 640).astype(np.float32)})
return pred_onnx
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
# isinstance 用来判断某个变量是否属于某种类型
y = np.copy(x)
y[..., 0] = x[..., 0] - x[..., 2] / 2 # top left x
y[..., 1] = x[..., 1] - x[..., 3] / 2 # top left y
y[..., 2] = x[..., 0] + x[..., 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[..., 3] = x[..., 1] + x[..., 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= 0.45)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def non_max_suppression(
prediction,
conf_thres=0.25,
iou_thres=0.45,
classes=None,
agnostic=False,
multi_label=False,
labels=(),
max_det=300,
nm=0, # number of masks
):
"""Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results to reject overlapping detections
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
if isinstance(prediction, (list, tuple)): # YOLOv5 model in validation model, output = (inference_out, loss_out)
prediction = prediction[0] # select only inference output
bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch size
nc = prediction.shape[2] - nm - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Settings
max_wh = 7680 # (pixels) maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
mi = 5 + nc # mask start index
output = [np.zeros((0, 6 + nm))] * bs
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
lb = labels[xi]
v = np.zeros(len(lb), nc + nm + 5)
v[:, :4] = lb[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(lb)), lb[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = np.concatenate((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box/Mask
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4]) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
mask = x[:, mi:] # zero columns if no masks
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:mi] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = np.concatenate((box[i], x[i, 5 + j, None], j[:, None].float(), mask[i]), 1)
else: # best class only
conf = np.max(x[:, 5:mi], 1).reshape(box.shape[:1][0], 1)
j = np.argmax(x[:, 5:mi], 1).reshape(box.shape[:1][0], 1)
x = np.concatenate((box, conf, j, mask), 1)[conf.reshape(box.shape[:1][0]) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == np.array(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
index = x[:, 4].argsort(axis=0)[:max_nms][::-1]
x = x[index]
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = nms_boxes(boxes, scores)
i = i[:max_det] # limit detections
# 用来合并框的
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = np.multiply(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
return output
def clip_boxes(boxes, shape):
# Clip boxes (xyxy) to image shape (height, width)
boxes[..., [0, 2]] = boxes[..., [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[..., [1, 3]] = boxes[..., [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
def scale_boxes(img1_shape, boxes, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
boxes[..., [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
boxes[..., [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
boxes[..., :4] /= gain
clip_boxes(boxes, img0_shape)
return boxes
if __name__ == "__main__":
PaddleLite_ModulePath = "/PATH_to_nb_Model"
IMG_Path = "/PATH_to_test.jpg"
imgsz = (640, 640)
img = cv2.imread(IMG_Path)
img = cv2.resize(img, (640, 640))
# preprocess
im = letterbox(img, imgsz, auto=True)[0] # padded resize
im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im) # contiguous
im = im.astype(np.float32)
im /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if len(im.shape) == 3:
im = im[None] # expand for batch dim
# 1. 设置配置信息
config = MobileConfig()
config.set_model_from_file(PaddleLite_ModulePath)
# 2. 创建预测器
predictor = create_paddle_predictor(config)
# 3. 获取输入Tensor的引用,用来设置输入数据,参数表示第几个输入,单输入时为0
input_tensor = predictor.get_input(0)
input_tensor.from_numpy(im)
# 4. 执行推理,需要在设置输入数据后使用
predictor.run()
print("predictor:", predictor)
# 5. 获取输出Tensor的引用,用来设置输出数据,参数表示第几个输出,单输出时为0
output_tensor = predictor.get_output(0)
pred = output_tensor.numpy()
# NMS
conf_thres = 0.25 # confidence threshold
iou_thres = 0.45 # NMS IOU threshold
max_det = 1000 # maximum detections per image
classes = None # filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3
agnostic_nms = False # class-agnostic NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, classes, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det)
# Process predictions
seen = 0
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # per image
seen += 1
if len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
det[:, :4] = scale_boxes(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], img.shape).round()
# print(pred)
outputs = pred[0][:, :6]
if len(outputs[:, 4:] > 0):
for i in outputs:
prob = i[4]
cls = int(i[5])
prob = np.around(prob, decimals=2)
if prob >= 0.4:
all_pred_boxes = i[:4]
for b in range(len(all_pred_boxes)):
x1 = int(all_pred_boxes[0])
y1 = int(all_pred_boxes[1])
x2 = int(all_pred_boxes[2])
y2 = int(all_pred_boxes[3])
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 1)
cv2.putText(img, CLASSES[cls]+' '+str(prob), (x1, y1), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, 0.8, (0, 255, 0), 1, 4)
cv2.imwrite('./data/images/test_paddle_03.png', img)4.3推理结果