Horizon - a trustless harmony to ethereum bridge
1. 引言
Horizon Bridge 当前支持Harmony与以太坊,以及Harmony与BSC之间的跨链token转移。
由Harmony和Visa Research团队发布了相关白皮书:
- Horizon: A Gas-Efficient Trustless Bridge for Cross-Chain Transactions
相关开源代码见:
- https://github.com/harmony-one/horizon(Solidity&Java,未审计)
Horizon Bridge的主要特点为:
- A bridge with cross-chain light clients, relayers, and prover full nodes, all trustless, no additional trust assumptions beyond the two blockchains that the bridge is connected to.
- A gas-efficient Harmony light client on Ethereum (could be generalized to other chains) that only requires checkpoint blocks (1 block every x blocks, where 1 ≤ x ≤ 16384, 16384 is the #blocks per epoch) to verify any number of Harmony transaction proofs by the clients.
- A constant-size Harmony light client proof that any user needs to send cross-chain (e.g., Ethereum) to claim their Harmony transaction.
Horizon Bridge当前支持的token转移类型有:
- 1)ETH bridging
- Allows bridging native ETH from Ethereum to receive 1ETH on Harmony
- 2)ERC721 (NFT on Ethereum) bridging
- Allows single or in batch bridging of ERC721 (or NFTs) to Harmony to receive HRC721
- 3)ONE & HRC20 bridging
- Allows bridging Harmony’s native ONE token and any HRC20 issued on Harmony to Ethereum for utilizing Ethereum ecosystem and DApps
- 4)ERC1155 bridging
- Allows single or in batch bridging of ERC1155 to Harmony to receive HRC1155
- 5)HRC721 (NFT on Harmony) bridging
- Allows single or in batch bridging of HRC721 (or NFTs) to Ethereum to receive ERC721
- 6)HRC1155 bridging
- Allows single or in batch bridging of ERC1155 to Ethereum to receive ERC1155
各链各token的映射关系为:
- https://bridge.harmony.one/tokens
Horizon Bridge当前支持Harmony<->以太坊,Harmony<->BSC之间的token转换。
以太坊上的BUSD token 映射到 Harmony上为BUSD,BSC上的BUSD token 映射到 Harmony上为bscBUSD,Harmony token仅支持将bridge来的token映射回源链上,如将Harmony上的BUSD映射回以太坊上,若映射到BSC上将可能造成token永久丢失。
以太坊端Horizon Bridge合约地址为:【不对,当前线上使用的是trusted版本,而不是trustless版本。】
- https://etherscan.io/address/0xf9fb1c508ff49f78b60d3a96dea99fa5d7f3a8a6#code
1.1 relay bridge
在《Horizon: A Gas-Efficient Trustless Bridge for Cross-Chain Transactions》白皮书中之处,跨链交易不仅仅是通过atomic swaps with hash time locked contracts的资产转移。
relay bridge实现在2条链之间双向相互relay区块头。
在relay bridge中,A链的区块头会持续提交到B链的一个智能合约中,在B链的智能合约中会实现a light client logic来验证区块头的有效性。类似地,B链的区块头也会提交到A链的智能合约中,在A链的智能合约中也会实现相应的light client logic来验证B链区块头的有效性。
一个简单的例子是:BTC relay,单向地将Bitcoin区块头提交到以太坊。以太坊智能合约会计算所提交的Bitcoin区块头difficulty。A proof of the validity of each header amounts to checking it resides on the longest chain of submitted headers。【Interlay实现了BTC SPV以太坊合约代码:https://github.com/interlay/btc-relay-solidity。】
light client可用于高效实现跨链交易。跨链交易包括:
- exchanging cryptocurrencies
- 将资产转移到侧链
- sharding 区块链。
light client使得用户可生成short cryptographic inclusion proofs about past events recorded on a blockchain。
在类似比特币和以太坊的PoW链中,light client可提供the sequence of all block headers to prove to any verifier that the event is recorded on the honest chain that is the longest, 或更准确地说,是the most computationally-difficult chain。
light client proof的最大特点是便携性,即将light client proof提交到目标链,可使目标链相信在源链上确实记录了某特定event。
针对PoW链的light client研究有:
- Bitcoin SPV client:相关论文有:2008年 《Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system》
- proofs of proof-of-work:相关论文有:2016年《Proofs of proofs of Work with Sublinear Complexity》和 2017年论文《Non-interactive proofs of proof-of-work》
- FlyClient:相关论文有:2020年《FlyClient: super-light clients for cryptocurrencies》
但是,目前没有针对采用BFT共识的Proof-of-stake链的light client研究。当聚合来自足够数量的attestation签名时,并不知道这些attestation实际是否来自于有stake的validators。唯一可确认的办法是,可如全节点一样知道每个validator的balance(即state)。
1.2 Horizon的主要贡献
Horizon提供了gas-efficient, cross-chain bridge协议来将BFT链上的资产转移到支持智能合约的其他链(如以太坊)。为此,主要贡献为:
- 构建了a super-light client for BFT chains:allows a client to prove to any external entity that a transaction has been recorded on the BFT chain by providing a cryptographic proof that is constant size in the length of the chain。
- 在目标链上构建了bridge合约:用于atomic verification of super-light client proofs,以确认BFT链上确实锁定了特定数量的token。一旦验证通过,该合约还可在目标链上unlock/mint等额的token。
- 构建了relay node:可定期向目标链合约传输固定大小的checkpoint信息(为BFT链的commitments)。这些checkpoint信息后续可用于验证所提交的super-light client proofs。由relayer提交的checkpoint的总量与链长呈线性关系,因此可根据实际情况来调整checkpoint的提交频率。
- 高效的chain commitment机制:实现prove inclusion of a block in a blockchain with a constant-size commitment and logarithmic block inclusion proofs。
- 未来将提出stateless bridge合约设计:使得仅需向合约发送a small self-sufficient cross-chain交易,而不再需要任何pre-relayed checkpoint information。仅需要在交易中包含a logarithmic-size (in the chain length) inclusion proof ,使其成为第一个仅需logarithmic-size, cross-chain proofs的BFT bridge protocol。
Horizon Bridge中未来将支持使用FlyClient的logarithmic-size proofs来将PoW(如比特币或以太坊)链上资产转移到BFT链上。这要求在每个区块头中包含特定的chain commitments(以Merkle roots形式),但是,对于比特币和以太坊来说,未来不太可能通过软分叉的方式在其区块头中包含相应的chain commitments。
目前,Horizon Bridge中采用的是Rainbow bridge的SPV方案,需要relay node定期将最新的比特币/以太坊区块头发送到BFT链上的合约。 这将导致在BFT链上的合约需要较大的存储和计算开销,因此要求BFT链具有足够低的gas cost(如Harmony 和 NEAR)来平衡相应的存储和计算开销,直到比特币和以太坊支持chain commitments。
1.3 light client
Bitcoin论文中提到了一种快速同步机制,名为simplified payment verification,支持快速验证链上交易。
对于比特币和以太坊,其区块头中包含了足够的信息,以确认:
- 1)PoW是有效的。
- 2)区块中包含了特定的交易。
- 3)区块在正确链的特定位置。
交易验证过程中利用了a Merkle tree commitment to all transactions in a block which is stored in each block header。
light client并不会验证整个链上的所有交易。
2016年《Proofs of proofs of Work with Sublinear Complexity》和 2017年论文《Non-interactive proofs of proof-of-work》中提出了proofs of proof-of-work(PoPoW),使Prover to convince a verifier with high probability in logarithmic time and communication that a chain contains a sufficient amount of work。PoPoW有一些缺陷,B¨unz等人2020年《FlyClient: super-light clients for cryptocurrencies》进行了改进,可克服PoPoW的缺陷。
FlyClient采用probabilistic sampling技术来randomly sample a logarithmic number of block headers (in the chain length) from a PoW-based blockchain with variable block difficulty。FlyClient使用一种名为Merkle mountain range(MMR)的efficiently-updatable commitment mechanism,支持Prover commit to an entire blockchain with a small (constant-size) commitment while offering logarithmic block inclusion proofs with postion binding guarantees。
1.4 现有跨链方案
-
1)Rainbow Bridge:
使用light client来将ERC-20 token在以太坊和NEAR PoS链上进行相互传输。Rainbow协议在2个链上都部署了light client智能合约,relayer会定期将区块头发送到light client。
即,以太坊relayer将每个以太坊区块头发送到NEAR合约,NEAR relayer每4小时发送一个NEAR区块头发送到以太坊合约。因此,两个合约可独立验证对方链的inclusion of 某 evnet。
尽管Rainbow Bridge支持trustless cross-chain transfers,其仍然有性能和安全问题:- (1)relayers需要持续将以太坊和NEAR区块头发送到智能合约,需要大量的gas cost。
- (2)为了避免NEAR合约中持续增加的状态,bridge中限制了仅保存最近7天同步的区块头。若合约也将验证限制为仅7天log,则将大幅降低light client的安全性。malicious以太坊relayer可开始创建a fake chain of only seven days worth of headers appended to a valid prefix and present it to the NEAR合约。若该NEAR合约也包含了previous seven-day logs from old blocks on the NEAR blockchain,则将需要大量的gas cost。
- (3)Rainbow的以太坊端合约并没有验证每个NEAR区块头中的所有validator签名。
-
2)XCLAIM:为trustless, cross-chain exchanges,其中每个链上的合约会govern the exchanges between the two chains (如Bitcoin和以太坊),并会惩罚将malicious方的质押物给honest方。
XCLAIM协议中要求在vault在以太坊合约中锁定足够的质押物;用户将其比特币发送到vault中,并向合约提交证明来说明该交易已记录在比特币链上;relay合约验证该proof并确认该lock已正确执行;合约给收款方release Ethereum tokens。
XCLAIM协议中主要包含3方:- (1)用户:将资产由比特币转移至以太坊;
- (2)valut:接收并锁定用户发来的比特币资金;
- (3)名为BTCRelay的以太坊relay合约:存储了比特币区块头,以验证SPV proofs。
-
3)tBTC:为multi-wallet, multi-signer协议,提供了a BTC-backed bearer asset on Ethereum。tBTC致力于解决因地理分隔的signers的单点故障问题,为a multi-wallet scheme。signers使用multi-party threshold ECDSA协议来共同创建a signing group wallet which is created by randomly selecting a set of signers from the eligible pool of signers。
tBTC依赖于质押来防止signers作弊:(需要有复杂的机制来监测和处理undercollateralization signers。)- (1)To liquidate deposits in case they are in danger of undercollateralization;
- (2)To punish a signing group if it signs an unauthorized piece of data is once distributed key generation is complete;
- (3)To punish a signing group that fails to produce a signature for the system when requested;
- (4)To ensure a depositor is refunded if the signing group fails to form。
-
4)Waterloo:为以太坊和EOS的跨链桥,以太坊上的light client合约会验证EOS区块头。EOS采用delegated PoS共识,EOS token holders可持续投票(即delegate)给其喜欢的产块者。Waterloo并不会relay所有的EOS区块头,而进行relay the changes in the set of EOS block producers。
1.5 Harmony链
Harmony为受RapidChain和OmniLedger启发的sharded PoS链,采用FBFT共识。
Harmony以固定的时间间隔(如24小时)做为epoch。在每个epoch中,网络会分为一组shards,每个shard维护a seperate blockchain in parallel to other shards。
在每个epoch的末尾,由名为beacon shard的特殊shard,采用distributed random generation (DRG)来随机生成每个shard的validators。beacon shard在每个epoch也会进行re-elect。beacon shard中会存储网路配置信息(即validator identities和shard assignments)。此外,token holders可在beacon shard中存入stake来成为共识协议中的validators。
每个epoch会在每个shard执行多次BFT共识协议,每次执行会生成一个区块并添加到shard chain中。在每个epoch中,validator set和shards都是固定的,但是跨epoch,在每个epoch末端,beacon shard会执行shard reconfiguration协议而可能变化。
每个epoch中,beacon chain的最后一个区块称为epoch block,存储了下一epoch所有shard members的identities(即公钥)。每个identity包含了节点的ECDSA地址、BLS公钥,以及在共识中的质押,以decimal number between 0 and 1来表示。
每次执行BFT共识,leader会由前一epoch末端DRG生成的随机数来选择。每次运行BFT共识,该leader会运行aggregate BLS signature协议来收集validators的投票,该签名为constant-sized, threshold aggregate signature,然后将该签名广播到shard。在通过区块认证后,该aggregate signatures会包含在区块头中。当有新的区块提交到shard chain(由shard维护的链),该shard的validators会将区块头发送到beacon shard,beacon shard将验证区块头内容(即previous hash和aggregate signature),然后将其广播到所有shard,以便可进行后续的跨shard验证。
2. Horizon Bridge
Horizon Bridge在Harmony链端主要有:
- 1)Bridge合约
- 2)Ethereum Light Client (ELC)合约
- 3)Ethereum Verifier(EVerifier)合约
- 4)Ethereum Prover(EProver):为一个以太坊全节点,或者为可访问一个全节点的client
- 5)Ethereum Relayer:负责将每个以太坊区块头信息relay到ELC合约。
Horizon Bridge在以太坊链端主要有:
- 1)Bridge合约
- 2)Harmony Light Client (HLC)合约
- 3)Harmony Verifier(HVerifier)合约
- 4)Harmony Prover(HProver):为一个Harmony全节点,或者为可访问一个全节点的client
- 5)Harmony Relayer:负责将Harmony的每个checkpoint block header信息relay到HLC合约。
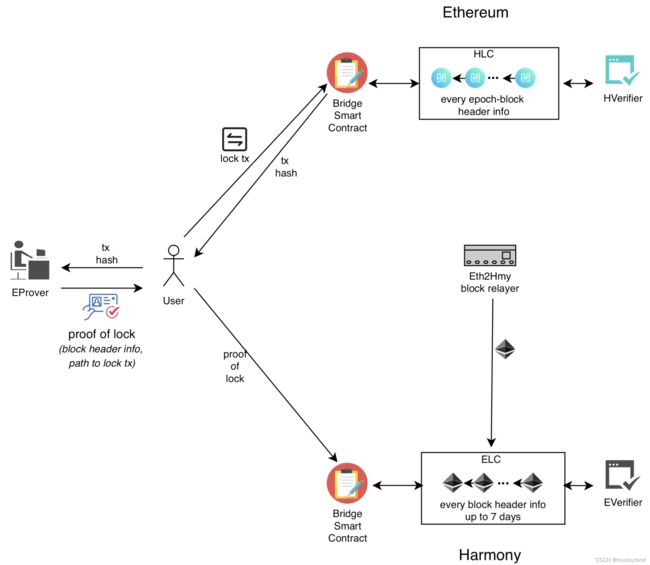
2.1 由以太坊转移到Harmony
资产由以太坊转移到Harmony的流程为:
- 1)用户将其ERC20资产发送到以太坊Bridge合约来锁定资产,并获取相应的交易hash。
- 2)用户将该交易hash发送给EProver来获取proof-of-lock。(包含block header info, path to lock tx)
- 3)用户将获得的proof-of-lock发送给Harmony的Bridge合约。
- 4)Harmony上的Bridge合约会触发ELC合约和EVerifier合约,验证该proof-of-lock有效后会mint等额的HRC20。
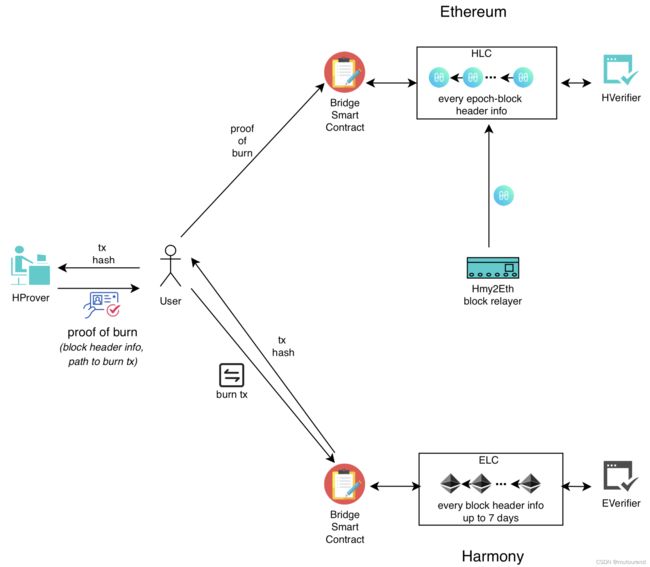
2.2 由Harmony到以太坊
主要分为2部分:
- 1)Relay/Contract Sync:Relayer将Harmony链的epoch blocks headers定期发送给以太坊链上的HLC合约。
- 2)Cross-Chain Transaction:用户发起的跨链交易。
资产由Harmony赎回到以太坊的流程为:
- 1)用户调用Harmony Bridge合约来burn HRC20,然后获取相应的交易hash。
- 2)用户将该交易hash发送给HProver,以获取proof-of-burn。
- 3)用户将该proof-of-burn发送到以太坊上的Bridge合约。
- 4)以太坊上的Bridge合约会触发HLC和HVerifier合约,验证proof-of-burn有效后会unlock等额的ERC20。
2.2.1 Relay/Contract Sync
在每个epoch(即24小时)的末端,relayer会给以太坊HLC合约发送最新的epoch block header B i B_i Bi(由beacon shard 维护),该block中包含了足够的信息,使得HLC后续可验证任何在harmony链上的inclusion交易。
HLC合约中会验证the inclusion of a burn transaction T b u r n T_{burn} Tburn。交易 T b u r n T_{burn} Tburn是用户向Harmony bridge合约提交产生的,会将Harmony链上的 x x x coins发送到null 地址(即永久删除)。
将inclusion proof for a burn transaction称为proof of burn (PoB)。
为了便于表达,仅考虑一个shard(即beacon shard), T b u r n T_{burn} Tburn被记录在beacon chain上。
-
Proofs of Burn (PoB):可让以太坊上的HLC合约确认:
- (1) T b u r n T_{burn} Tburn交易被包含在a block with header B k B_k Bk;【用 B k B_k Bk中存储的Merkle root,借助transaction Merkle proof来证明】
- (2)对应 B k B_k Bk的区块被包含在Harmony链上。【需要在epoch block B i B_i Bi中添加新的chain commitment。受FlyClient启发,Horizon中使用了一种名为MMR (Merkle Mountain Range)的merkle tree变种,来表达在2个epoch block之间所加的所有block headers。以太坊HLC合约可验证the inclusion of B k B_k Bk within the epoch using the roof of the MMR stored at B i B_i Bi。】
-
Checkpoint Blocks:跨链交易的确认延迟时间取决于 relayer向以太坊HLC提交epoch block headers的频率。由于Harmony中每个epoch block的生成间隔是24小时,因此,跨链交易一半需要12个小时来确认。为了减少确认延迟,可在Harmony链的epoch中间定期生成checkpoint blocks。只要其区块头中包含了MMR root,即可撑起为checkpoint block,该MMR root中计算的是至前一checkpoint block之后增加的所有区块头。因此,可将epoch block也看成是checkpoint blocks。
在每个check point block header B i B_i Bi中包含了以下要素:【其中前4个在每个区块中都包含】- (1)区块高度 i i i
- (2)Quorum signature B i . s i g B_i.sig Bi.sig,由consensus validators生成的aggregate BLS signature。
- (3)Quorum public keys B i . p k s B_i.pks Bi.pks,列出了每个consensus validator的公钥地址。
- (4)Transaction Merkle root B i . t m r B_i.tmr Bi.tmr created on all transactions included in B i B_i Bi。
- (5)Checkpoint Merkle root B i . c m r B_i.cmr Bi.cmr created on all block headers between B i − Δ B_{i-\Delta} Bi−Δ and B i B_i Bi,其中 Δ \Delta Δ为两个checkpoint block之间的区块数差距。
-
Checkpoint Verification:relayer 会向 以太坊HLC合约发起sync transaction T s y n c T_{sync} Tsync来发送每个checkpoint block header B i B_i Bi。收到 T s y n c T_{sync} Tsync之后,HLC合约会验证checkpoint信息是否有效,应同时满足如下2个条件:【若满足,会将 B i B_i Bi存储在HLC合约中,以便于进行后续跨链验证。】
- (1) i > j i> j i>j,其中 j j j为HLC合约中已存储的最新checkpoint block height。
- (2) Q u o r u m V e r i f y ( B i . s i g , B i . p k s ) = 1 QuorumVerify(B_i.sig, B_i.pks)=1 QuorumVerify(Bi.sig,Bi.pks)=1
2.2.2 Cross-Chain Transaction
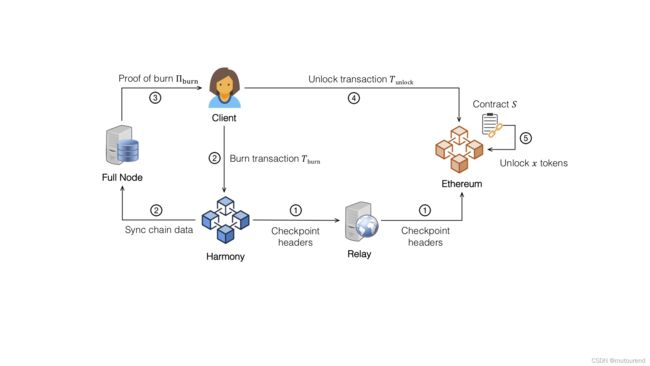
用户向Harmony bridge合约发起 T b u r n T_{burn} Tburn交易,一旦该交易在Harmony链上确认,用户可想全节点 F F F发起请求,收到用户发来的请求, F F F发现在block B k B_k Bk中包含了 T b u r n T_{burn} Tburn交易, F F F会生成相应的Proof of Burn Π b u r n \Pi_{burn} Πburn。
其中 Π b u r n \Pi_{burn} Πburn中包含了2个Merkle proof Π B \Pi_B ΠB和 Π T \Pi_T ΠT:
- Π B \Pi_B ΠB:采用存储在 B k B_k Bk之后的第一个checkpoint block B i B_i Bi中的checkpoint Merkle root c m r i cmr_i cmri来生成的Merkle proof。
- Π T \Pi_T ΠT:采用transaction Merkle root B k . t m r B_k.tmr Bk.tmr生成的Merkle proof。
然后 F F F会将 Π b u r n 、 i 和 B k \Pi_{burn}、i和B_k Πburn、i和Bk发送给用户,基于此用户构建unlock transaction T u n l o c k T_{unlock} Tunlock 并提交到以太坊上的bridge合约。若全节点不可信,该交易可能失败,此时用户可换一个全节点来请求证明并提交交易。
以太坊的brige合约会进行PoB verification and Asset Unlocking:收到 T u n l o c k T_{unlock} Tunlock,以太坊bridge合约会从其state中获取 B i B_i Bi( i i i已在 T u n l o c k T_{unlock} Tunlock中由用户指定),bridge会进行一些利的验证,通过后会为接收方unlock相应数量的token。
3 多relayer模式
若只有一个relayer,则容易受DOS攻击,使得无法工作。解决方案有:
- 有一组relayer冗余地向合约提交相同的checkpoint信息,但是,这将增加relay环节的gas费用。
- 一次仅有一个relayer向合约relay消息,其他 n − 1 n-1 n−1个relayer仅读取并验证合约状态,若第一个relayer relay失败,第二个relayer再去relay。
4. stateless bridge contract
在某些场景,可设计无需relayer的bridge协议:
- 增加another layer of chain commitments to every checkpoint block in the form of an MMR constructed over all checkpoint blocks。
相应的proof中包含了如下信息:
- 1)The header of the block B t x B_{tx} Btx containing T b u r n T_{burn} Tburn。
- 2)The header of the first checkpoint block B c p B_{cp} Bcp after B t x B_{tx} Btx。
- 3)A Merkle proof showing that T b u r n T_{burn} Tburn was included in B t x B_{tx} Btx。
- 4)A Merkle proof showing that B c p B_{cp} Bcp was included in the chain of checkpoint blocks。
参考资料
[1] Harmony Fast Byzantine Fault Tolerance (FBFT)共识
[2] All harmony one bridges
[3] Horizon Bridge
[4] Harmony<>Cosmos Bridge #73