【计算机实验】四则运算计算器
一、题目要求
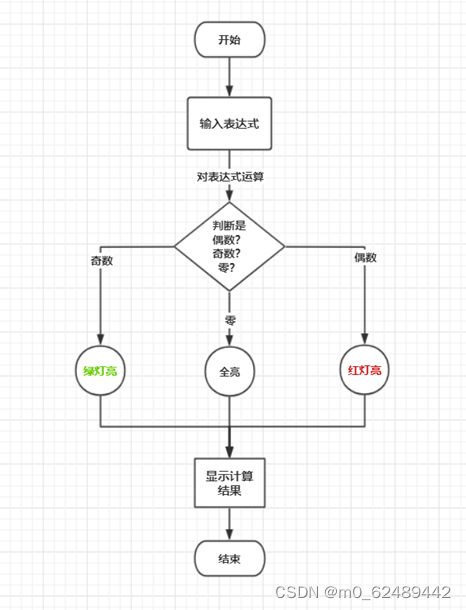
编写一个四则运算计算机,实现简单控制功能,例如:运算 结果为“0”,所有灯亮,运算结果为奇数,红灯亮,结果 为偶数,绿灯亮。
- 正确进行四则运算
- 实现控制功能
- 使用多线程编程
- 界面及交互等
二、设计流程
2.1 设计框图
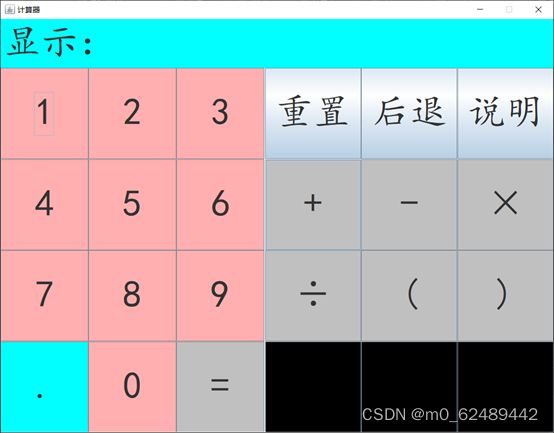
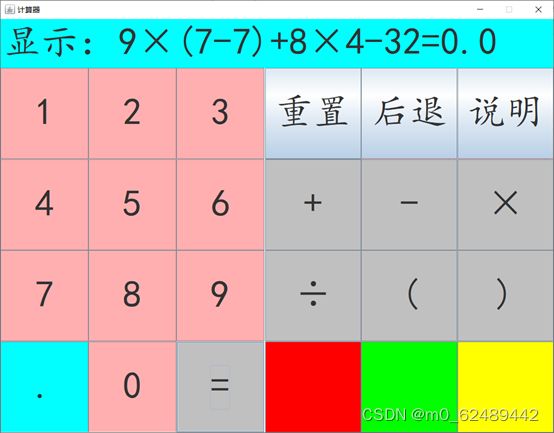
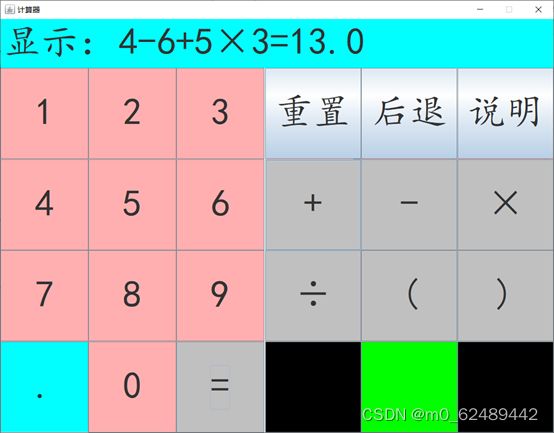
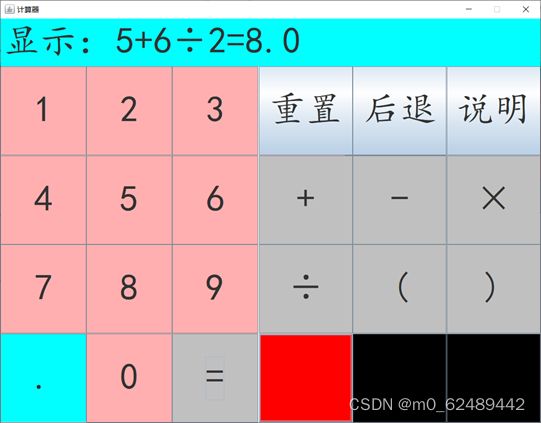
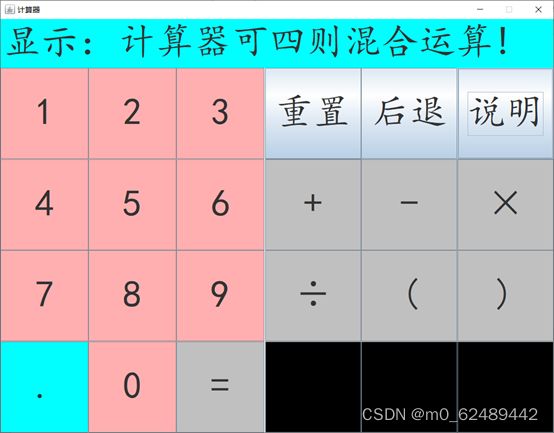
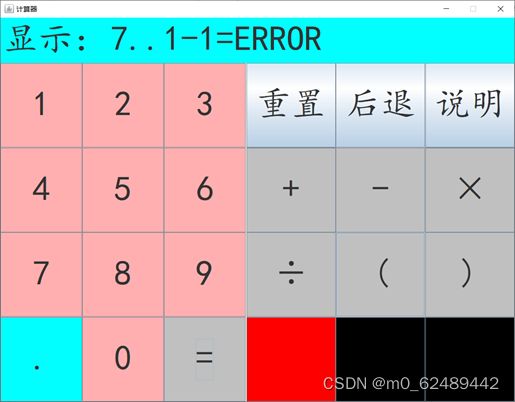
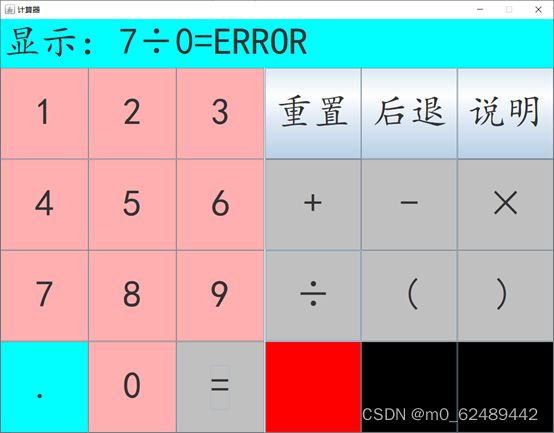
2.2 软件设计效果图
2.2.1 初始界面
2.2.2 结果为零
2.2.3 结果为奇数
2.2.4 结果为偶数
2.2.5 说明界面
2.2.6 报错界面
多个小数点
除数为零
三、关键源码及注释
3.1 主函数
此文件为计算器的入口,运行此函数,可以出现计算器窗口
package caculator;
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Expression();
}}
3.2 计算器主体代码
主要实现计算器的各种功能
package caculator;
public class Expression extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
//继承JF类,实现 ActionListener接口
//添加不同的按钮
JButton[] button_数字 = new JButton[11];
JButton[] button_运算符 = new JButton[7];
JButton[] button_功能 = new JButton[3];
JButton[] button_显示 = new JButton[3];
//成员变量的初始化
{//给每一个按钮设置数字,和小数点
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
button_数字[i] = new JButton("" + i);
button_数字[i].setBackground(Color.pink);
button_数字[i].setSize(1, 1);
button_数字[i].setFont(字体); }
button_数字[10] = new JButton(".");
button_数字[10].setFont(字体);
button_数字[10].setBackground(Color.CYAN);
//定义运算符
button_运算符[0] = new JButton("+");
button_运算符[0].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[0].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[1] = new JButton("-");
button_运算符[1].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[1].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[2] = new JButton("×");
button_运算符[2].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[2].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[3] = new JButton("÷");
button_运算符[3].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[3].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[4] = new JButton("(");
button_运算符[4].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[4].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[5] = new JButton(")");
button_运算符[5].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[5].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[6] = new JButton("=");
button_运算符[6].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[6].setFont(字体);
//设置功能按键
button_功能[0] = new JButton("重置");
button_功能[0].setFont(字体);
button_功能[1] = new JButton("后退");
button_功能[1].setFont(字体);
button_功能[2] = new JButton("说明");
button_功能[2].setFont(字体);
//设置显示按钮
button_显示[0] = new JButton();
button_显示[0].setBackground(Color.black);
button_显示[1] = new JButton();
button_显示[1].setBackground(Color.black);
button_显示[2] = new JButton();
button_显示[2].setBackground(Color.black); }
//构造方法用于布局设计
Expression() {
//对每一个组件注册监听内部类
for (i = 0; i < 11; i++)
button_数字[i].addActionListener(this);
for (i = 0; i < 7; i++)
button_运算符[i].addActionListener(this);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
button_功能[i].addActionListener(this);
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
JPanel p2 = new JPanel();
JPanel p3 = new JPanel();
//流水式布局
FlowLayout flow = new FlowLayout();
//对齐值
flow.setAlignment(FlowLayout.LEADING);
p1.setLayout(flow);
p1.setBackground(Color.cyan);
JLabel 显示 = new JLabel("显示:");
显示.setSize(300, 100);
显示.setFont(字体);
p1.add(显示);
标签显示.setFont(字体);
p1.add(标签显示);
p2.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 3));
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
p2.add(button_数字[i]);
p2.add(button_数字[10]);
p2.add(button_数字[0]);
p2.add(button_运算符[6]);
p3.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 3));
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
p3.add(button_功能[i]);
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
p3.add(button_运算符[i]);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
p3.add(button_显示[i]);
//位置显示
add(p1, BorderLayout.NORTH);
add(p2, BorderLayout.CENTER);
add(p3, BorderLayout.EAST);
//设置名称
setTitle("计算器");
//设置大小
setBounds(300, 100, 900, 700);
//设置是否可见
setVisible(true);
//设置是否可以更改大小
setResizable(false);
//设置关闭方式
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
//实现ActionListener接口的actionPerformed方法,用于事件处理响应
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JButton curr = (JButton) e.getSource();
//这些按钮可以用于(P)且以输入字符长度小于40
if (p && 标签显示.getText().length() < 40) {
//在显示框里显示数字
for (i = 0; i < 11; i++)
if (curr == button_数字[i]) {
标签显示.setText(标签显示.getText() + button_数字[i].getText());
break;
}
//在显示框里显示运算符
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
if (curr == button_运算符[i]) {
标签显示.setText(标签显示.getText() + button_运算符[i].getText());
break;
}
//当按下等于号的时候
if (curr == button_运算符[6]) {
changeColor 改颜色 = new changeColor();
改颜色.start();
标签显示.setText(标签显示.getText() + button_运算符[6].getText());
标签显示.setText(标签显示.getText() + EvaluateEcpression());
p = false;
}
if (curr == button_功能[1] && 标签显示.getText().compareTo("") != 0)
//事件源为“后退”按钮,且label中有字符存在
标签显示.setText((标签显示.getText().substring(0, 标签显示.getText().length() - 1)));
}
//事件源设为“重置按钮”
if (curr == button_功能[0]) {
changeColor2 恢复=new changeColor2();
恢复.start();
标签显示.setText("");
p = true;
}
//事件源为“说明”按钮
if (curr == button_功能[2]) {
标签显示.setText("计算器可四则混合运算!");
p = false;
} }
//多线程1,结果显示和亮灯构成多线程操作
public class changeColor extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
//休眠0.3秒
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int a = (int) 结果;
if (a==0){button_显示[0].setBackground(Color.red);button_显示[1].setBackground(Color.green);button_显示[2].setBackground(Color.YELLOW);}
else if (a % 2 == 0) button_显示[0].setBackground(Color.red);
else if (a % 2 != 0) button_显示[1].setBackground(Color.green);
}
}
//多线程2,清空显示屏和熄灭等为多线成操作
public class changeColor2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
//休眠0.3秒
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
button_显示[0].setBackground(Color.black);
button_显示[1].setBackground(Color.black);
button_显示[2].setBackground(Color.black);
}
}
//数值计算————主体
String EvaluateEcpression() {
//大循环,对表达式字符串进行分析
while (true) {
//i等于字符串数组的长度,说明循环结束
if (i == 标签显示.getText().length())
break;
//为数字字符
if (In(a[i]) == -1) {
number = number * 10 + (a[i] - 48);
integer = true;
if (decimal)
decimalnum = decimalnum * 10;
i++;
} //为小数点
else if (a[i] == '.') {
//一个数字中有多个小数点的情况
if (decimal)
return "ERROR";
decimal = integer = true;
i++;
} //当输入的字符为为运算符时
else if (In(a[i]) > -1 && In(a[i]) < 7) {
//如果是负号,且之前是左括号或者没有符号,数字栈压入0
if (In(a[i]) == 1 && (i == 0 || In(a[i - 1]) == 4))
OPND.push(new Float(0));
//首先将此运算符前面的数字压入数字栈里
if (integer) {
OPND.push(new Float(number / decimalnum));
number = 0;
decimalnum = 1;
integer = decimal = false;
}
//运算符优先级的判断和处理
switch (Precede(In(OPTR.peek()), In(a[i]))) {
case 2://栈顶运算符优先级大于当前运算符
if (OPND.empty()) return "ERROR";
float x = OPND.pop();
if (OPND.empty()) return "ERROR";
float y = OPND.pop();
//获取运算数栈顶的两个元素,如果栈空则返回“ERROR”
char theta = OPTR.pop();
if (In(theta) == 3 && x == 0) return "ERROR";
//判断除数是否为零,如果是,返回“ERROR”;
OPND.push(new Float(Operate(y, theta, x)));
break;
case 1://栈顶运算符优先级等于当前运算符
OPTR.pop();
i++; break;
case 0://栈顶运算符优先级小于当前运算符
OPTR.push(new Character(a[i]));
i++; break;
case -1://运算符顺序错误
return "ERROR";
}
}
}
if (OPND.empty()) return "ERROR";
else {
结果 = OPND.peek();
return ("" + OPND.peek());
}//返回栈顶元素为计算结果
}
//数值计算————将得到的字符量处理,得到不同的返回值,供以运算判断
int In(char t) {
if (t > 47 && t < 58) return -1; //当字符是数字的时候
switch (t) {
case '+':
i = 0;
break;
case '-':
i = 1;
break;
case '×':
i = 2;
break;
case '÷':
i = 3;
break;
case '(':
i = 4;
break;
case ')':
i = 5;
break;
case '=':
i = 6;
break;
}
return i;
}
//数值计算————根据优先级表,判断两符号的有限关系
int Precede(int t1, int t2) {
int relationship[][] = {
{2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2},
{2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2},
{2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 2, 2},
{2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 2, 2},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, -1},
{2, 2, 2, 2, -1, 2, 2},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 1},
};//优先级表使用int类型的二维数组relationship保存,其中2为‘>’,1为‘=’,0为‘<’,-1为错误
return relationship[t1][t2];
}
//数值计算————进行运算函数,a和b做theta二元运算
float Operate(float a, char theta, float b) {
float i = 0;
switch (theta) {
case '+':
i = a + b;
break;
case '-':
i = a - b;
break;
case '×':
i = a * b;
break;
case '÷':
i = a / b;
break;
}
return i;
}
}
四、问题及解决方法
4.1 对于输入的字符串如何识别,并正确进行结果运算
对于输入今来的字符串首先进行分割处理,判断时数字还是字符,完后按照字符的优先级进行压栈出栈操作,转换为两元运算,最后整体运算得出最后的结果。
4.2 多线程操作
多线程可以用于两种及两种以上并行的、没有相互依赖管线的、没有先后之分的运算。则可用于对于结果的显示,和结果的亮灯控制操作。
完整源码
main.java
package caculator;
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Expression();
}
}
Expression.java
package caculator;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Expression extends JFrame implements ActionListener { //继承JF类,实现 ActionListener接口
boolean p = true;
float 结果;
Font 字体 = new Font("楷体", 5, 60);
JLabel 标签显示 = new JLabel();
JButton[] button_数字 = new JButton[11];
JButton[] button_运算符 = new JButton[7];
JButton[] button_功能 = new JButton[3];
JButton[] button_显示 = new JButton[3];
//成员变量的初始化
{
//给每一个按钮设置数字,和小数点
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
button_数字[i] = new JButton("" + i);
button_数字[i].setBackground(Color.pink);
button_数字[i].setSize(1, 1);
button_数字[i].setFont(字体);
}
button_数字[10] = new JButton(".");
button_数字[10].setFont(字体);
button_数字[10].setBackground(Color.CYAN);
//定义运算符
button_运算符[0] = new JButton("+");
button_运算符[0].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[0].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[1] = new JButton("-");
button_运算符[1].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[1].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[2] = new JButton("×");
button_运算符[2].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[2].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[3] = new JButton("÷");
button_运算符[3].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[3].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[4] = new JButton("(");
button_运算符[4].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[4].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[5] = new JButton(")");
button_运算符[5].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[5].setFont(字体);
button_运算符[6] = new JButton("=");
button_运算符[6].setBackground(Color.lightGray);
button_运算符[6].setFont(字体);
//设置功能按键
button_功能[0] = new JButton("重置");
button_功能[0].setFont(字体);
button_功能[1] = new JButton("后退");
button_功能[1].setFont(字体);
button_功能[2] = new JButton("说明");
button_功能[2].setFont(字体);
//设置显示按钮
button_显示[0] = new JButton();
button_显示[0].setBackground(Color.black);
button_显示[1] = new JButton();
button_显示[1].setBackground(Color.black);
button_显示[2] = new JButton();
button_显示[2].setBackground(Color.black);
}
//构造方法用于布局设计
Expression() {
int i = 0;
//对每一个组件注册监听内部类
for (i = 0; i < 11; i++)
button_数字[i].addActionListener(this);
for (i = 0; i < 7; i++)
button_运算符[i].addActionListener(this);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
button_功能[i].addActionListener(this);
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
JPanel p2 = new JPanel();
JPanel p3 = new JPanel();
//流水式布局
FlowLayout flow = new FlowLayout();
//对齐值
flow.setAlignment(FlowLayout.LEADING);
p1.setLayout(flow);
p1.setBackground(Color.cyan);
JLabel 显示 = new JLabel("显示:");
显示.setSize(300, 100);
显示.setFont(字体);
p1.add(显示);
标签显示.setFont(字体);
p1.add(标签显示);
p2.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 3));
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
p2.add(button_数字[i]);
p2.add(button_数字[10]);
p2.add(button_数字[0]);
p2.add(button_运算符[6]);
p3.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 3));
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
p3.add(button_功能[i]);
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
p3.add(button_运算符[i]);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
p3.add(button_显示[i]);
//位置显示
add(p1, BorderLayout.NORTH);
add(p2, BorderLayout.CENTER);
add(p3, BorderLayout.EAST);
//设置名称
setTitle("计算器");
//设置大小
setBounds(300, 100, 900, 700);
//设置是否可见
setVisible(true);
//设置是否可以更改大小
setResizable(false);
//设置关闭方式
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
//实现ActionListener接口的actionPerformed方法,用于事件处理响应
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JButton curr = (JButton) e.getSource();
int i;
//这些按钮可以用于(P)且以输入字符长度小于40
if (p && 标签显示.getText().length() < 40) {
for (i = 0; i < 11; i++)
if (curr == button_数字[i]) {
标签显示.setText(标签显示.getText() + button_数字[i].getText());
break;
}
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
if (curr == button_运算符[i]) {
标签显示.setText(标签显示.getText() + button_运算符[i].getText());
break;
}
if (curr == button_运算符[6]) {
changeColor 改颜色 = new changeColor();
改颜色.start();
标签显示.setText(标签显示.getText() + button_运算符[6].getText());
标签显示.setText(标签显示.getText() + EvaluateEcpression());
p = false;
}
if (curr == button_功能[1] && 标签显示.getText().compareTo("") != 0)//事件源为“后退”按钮,且label中有字符存在
标签显示.setText((标签显示.getText().substring(0, 标签显示.getText().length() - 1)));
}
if (curr == button_功能[0]) {//事件源设为“重置按钮”
changeColor2 恢复=new changeColor2();
恢复.start();
标签显示.setText("");
p = true;
}
if (curr == button_功能[2]) {//事件源为“说明”按钮
标签显示.setText("计算器可四则混合运算!");
p = false;
}
}
//多线程1
public class changeColor extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
//休眠0.3秒
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int a = (int) 结果;
if (a==0){button_显示[0].setBackground(Color.red);button_显示[1].setBackground(Color.green);button_显示[2].setBackground(Color.YELLOW);}
else if (a % 2 == 0) button_显示[0].setBackground(Color.red);
else if (a % 2 != 0) button_显示[1].setBackground(Color.green);
}
}
//多线程2
public class changeColor2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
//休眠0.3秒
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
button_显示[0].setBackground(Color.black);
button_显示[1].setBackground(Color.black);
button_显示[2].setBackground(Color.black);
}
}
//数值计算————主体
String EvaluateEcpression() {
char[] a;
//存放表达式的字符数组
int i = 0;
//字符串下标的变量
a = 标签显示.getText().toCharArray();
//获得表达式字符数组
Stack OPND = new Stack();
//运算数栈,为浮点型
Stack OPTR = new Stack();
//运算符栈,为浮点型
OPTR.push('=');
//符号栈压入“=”
float number = 0;
//拼合数字使用的变量,并对其初始化
int decimalnum = 1;
//
boolean integer = false;
boolean decimal = false;
while (true) { //大循环,对表达式字符串进行分析
//i等于字符串数组的长度,说明循环结束
if (i == 标签显示.getText().length())
break;
//为数字字符
if (In(a[i]) == -1) {
number = number * 10 + (a[i] - 48);
integer = true;
if (decimal)
decimalnum = decimalnum * 10;
i++;
} else if (a[i] == '.') {//为小数点
if (decimal) //一个数字中有多个小数点的情况
return "ERROR";
decimal = integer = true;
i++;
} else if (In(a[i]) > -1 && In(a[i]) < 7) { //为运算符
//如果是负号,且之前是左括号或者没有符号,数字栈压入0
if (In(a[i]) == 1 && (i == 0 || In(a[i - 1]) == 4))
OPND.push(new Float(0));
if (integer) { //首先将此运算符前面的数字压入数字栈里
OPND.push(new Float(number / decimalnum));
number = 0;
decimalnum = 1;
integer = decimal = false;
}
//运算符优先级的判断和处理
switch (Precede(In(OPTR.peek()), In(a[i]))) {
case 2://栈顶运算符优先级大于当前运算符
if (OPND.empty()) return "ERROR";
float x = OPND.pop();
if (OPND.empty()) return "ERROR";
float y = OPND.pop();//获取运算数栈顶的两个元素,如果栈空则返回“ERROR”
char theta = OPTR.pop();
if (In(theta) == 3 && x == 0) return "ERROR";//判断除数是否为零,如果是,返回“ERROR”;
OPND.push(new Float(Operate(y, theta, x)));
break;
case 1://栈顶运算符优先级等于当前运算符
OPTR.pop();
i++;
break;
case 0://栈顶运算符优先级小于当前运算符
OPTR.push(new Character(a[i]));
i++;
break;
case -1://运算符顺序错误
return "ERROR";
}
}
}
if (OPND.empty()) return "ERROR";
else {
结果 = OPND.peek();
return ("" + OPND.peek());
}//返回栈顶元素为计算结果
}
//数值计算————将得到的字符量处理,得到不同的返回值
int In(char t) {
int i = 0;
if (t > 47 && t < 58) return -1; //当字符是数字的时候
switch (t) {
case '+':
i = 0;
break;
case '-':
i = 1;
break;
case '×':
i = 2;
break;
case '÷':
i = 3;
break;
case '(':
i = 4;
break;
case ')':
i = 5;
break;
case '=':
i = 6;
break;
}
return i;
}
//数值计算————根据优先级表,判断两符号的有限关系
int Precede(int t1, int t2) {
int relationship[][] = {
{2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2},
{2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2},
{2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 2, 2},
{2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 2, 2},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, -1},
{2, 2, 2, 2, -1, 2, 2},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 1},
};//优先级表使用int类型的二维数组relationship保存,其中2为‘>’,1为‘=’,0为‘<’,-1为错误
return relationship[t1][t2];
}
//数值计算————进行运算函数,a和b做theta二元运算
float Operate(float a, char theta, float b) {
float i = 0;
switch (theta) {
case '+':
i = a + b;
break;
case '-':
i = a - b;
break;
case '×':
i = a * b;
break;
case '÷':
i = a / b;
break;
}
return i;
}
}