数据结构 栈和队列
数据结构 栈和队列
文章目录
- 数据结构 栈和队列
-
- 1. 栈(Stack)
-
- 1.1 概念
- 1.2 栈的模拟实现
- 1.3 栈的使用
- 1.4 栈的应用场景
- 2. 队列(Queue)
-
- 2.1 概念
- 2.2 队列的模拟实现
- 2.3 队列的使用
- 2.4 循环队列
- 2.5 双端队列(Deque)
- 3. 双向操作
-
- 3.1 用队列实现栈
- 3.2 用栈实现队列
1. 栈(Stack)
1.1 概念
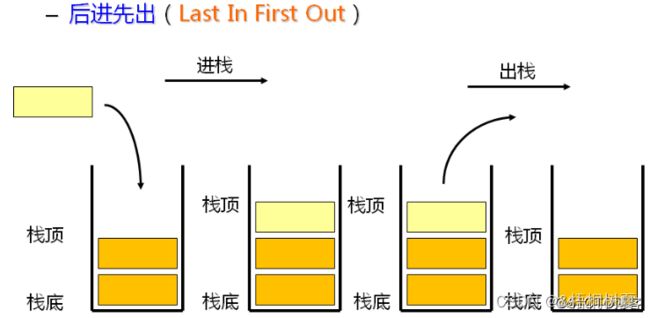
栈是一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作
进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出的原则
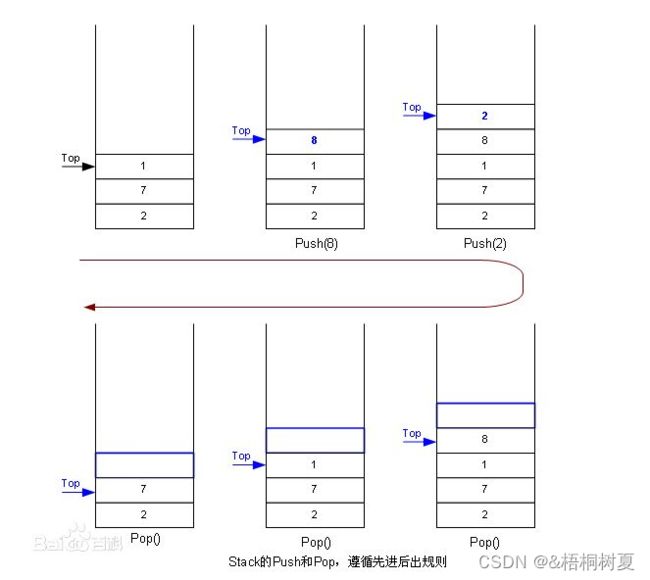
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈,出数据在栈顶
栈在现实生活中的例子:
1.2 栈的模拟实现
-
MyStack构造
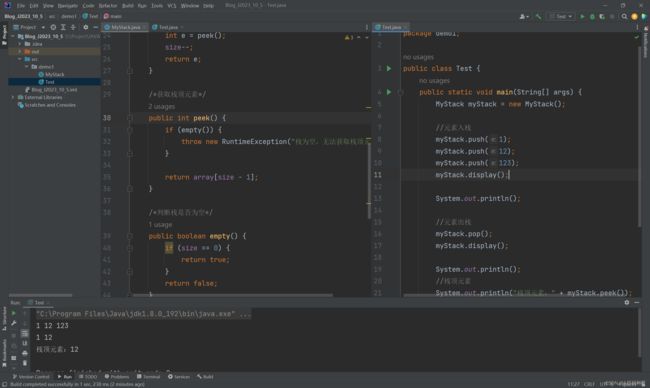
package demo1; import java.util.Arrays; public class MyStack { int[] array; int size; public MyStack() { array = new int[3]; } /*入栈方法*/ public int push(int e) { ensureCapacity(); array[size++] = e; return e; } /*出栈方法*/ public int pop() { int e = peek(); size--; return e; } /*获取栈顶元素*/ public int peek() { if (empty()) { throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,无法获取栈顶元素"); } return array[size - 1]; } /*判断栈是否为空*/ public boolean empty() { if (size == 0) { return true; } return false; } /*扩容*/ public void ensureCapacity() { if (size == array.length) { array = Arrays.copyOf(array,size * 2); } } public void display() { for (int i = 0;i < this.size;i++) { System.out.print(this.array[i] + " "); } } } -
Main函数
package demo1; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { MyStack myStack = new MyStack(); //元素入栈 myStack.push(1); myStack.push(12); myStack.push(123); myStack.display(); System.out.println(); //元素出栈 myStack.pop(); myStack.display(); System.out.println(); //栈顶元素 System.out.println("栈顶元素:" + myStack.peek()); } } //执行结果 1 12 123 1 12 栈顶元素:12
1.3 栈的使用
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| Stack() | 构造一个空的栈 |
| E push(E e) | 将e入栈,并返回e |
| E pop() | 将栈顶元素出栈并返回 |
| E peek() | 获取栈顶元素 |
| int size() | 获取栈中有效元素个数 |
| boolean empty() | 检测栈是否为空 |
package demo2;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Stack1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
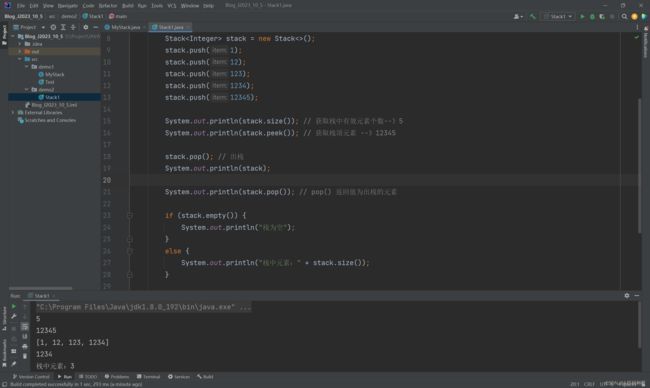
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(12);
stack.push(123);
stack.push(1234);
stack.push(12345);
System.out.println(stack.size()); // 获取栈中有效元素个数--》5
System.out.println(stack.peek()); // 获取栈顶元素 --》12345
stack.pop(); // 出栈
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // pop() 返回值为出栈的元素
if (stack.empty()) {
System.out.println("栈为空");
}
else {
System.out.println("栈中元素:" + stack.size());
}
}
}
//执行结果
5
12345
[1, 12, 123, 1234]
1234
栈中元素:3
1.4 栈的应用场景
-
改变元素的序列
1. 若进栈序列为 1,2,3,4 ,进栈过程中可以出栈,则下列不可能的一个出栈序列是() A: 1,4,3,2 B: 2,3,4,1 C: 3,1,4,2 D: 3,4,2,1 2.一个栈的初始状态为空。现将元素1、2、3、4、5、A、B、C、D、E依次入栈,然后再依次出栈,则元素出栈的顺序是( ) A: 12345ABCDE B: EDCBA54321 C: ABCDE12345 D: 54321EDCBA 答案:C B -
将递归转化为循环
比如:逆序打印链表
void printList(Test2.ListNode head) { if (head == null) { return; } Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>(); ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null) { stack.push(cur); cur = cur.next; } while(!stack.empty()) { System.out.println(stack.pop().val + " "); } } -
括号匹配
package demo1; import java.util.Stack; public class Test1 { public static boolean isVaild(String s) { Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>(); for (int i = 0;i < s.length();i++) { char a1 = s.charAt(i); if (a1 == '{' || a1 == '[' || a1 == '(') { stack.push(a1); } else { if (stack.empty()) { return false; } char a2 = stack.peek(); if ((a2 == '{' && a1 == '}') || (a2 == '[' && a1 == ']') || (a2 == '(' && a1 == ')')) { stack.pop(); } else { return false; } } } if (!stack.empty()) { return false; } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "(){}[]"; System.out.println(isVaild(s)); } } -
逆波兰表达式求值
package demo1; import java.util.Stack; public class Test2 { public static int evalRPN(String[] tokens) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); for (String x:tokens) { if (isOperation(x)) { stack.push(Integer.parseInt(x)); } else { int num2 = stack.pop(); int num1 = stack.pop(); switch (x) { case "+": stack.push(num1 + num2); break; case "-": stack.push(num1 - num2); break; case "*": stack.push(num1*num2); break; case "/": stack.push(num1/num2); break; } } } return stack.peek(); } public static boolean isOperation(String x) { if (x.equals("+") || x.equals("-") || x.equals("*") || x.equals("/")) { return false; } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { String[] s = {"2","1","+","3","*"}; System.out.println(evalRPN(s)); } } -
出栈入栈次序匹配
package demo1; import java.util.Stack; public class Test3 { /*出栈入栈次序匹配*/ public static boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushV, int[] popV) { // write code here Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); int j = 0; for (int i = 0;i < pushV.length;i++) { stack.push(pushV[i]); while (!stack.empty() && j < popV.length && stack.peek() == popV[j]) { stack.pop(); j++; } } return stack.empty(); } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a1 = {1,2,3,4,5}; int[] a2 = {4,5,3,2,1}; System.out.println(IsPopOrder(a1,a2)); } } -
最小栈
class MinStack { /*最小栈*/ int[] array; int size; public MinStack() { array = new int[3]; } public int push(int val) { ensureCapicity(); array[size++] = val; return val; } public int pop() { if (empty()) { System.out.println("栈为空"); } else { int e = top(); size--; return e; } return 0; } public int top() { return array[size-1]; } public int getMin() { int min = array[size-1]; int x = size; while(x > 0) { if (array[x-1] < min) { min = array[x-1]; } x--; } return min; } public boolean empty() { return size == 0; } public void ensureCapicity() { if (size == array.length) { array = Arrays.copyOf(array,size * 2); } } }
2. 队列(Queue)
2.1 概念
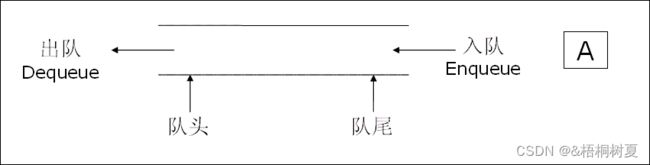
队列是一种只允许在一段进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性
队列遵循先进先出的原则,同时有以下两种操作:
入队列:进行插入操作,其一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear)
出队列:进行删除操作,其一端称为队头(Head/Front)
2.2 队列的模拟实现
在这里我们使用链式结构来实现队列
-
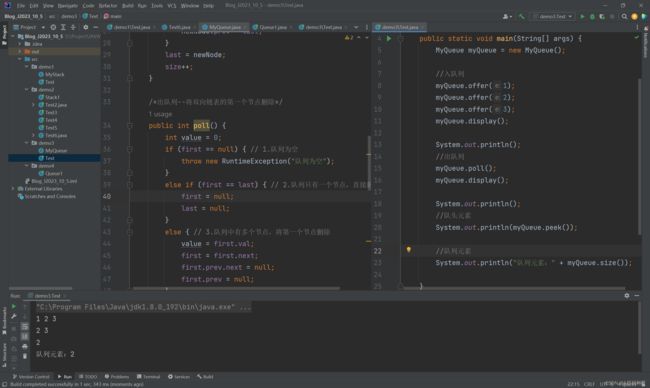
MyQueue构造
package demo3; public class MyQueue { public static class ListNode { ListNode next; ListNode prev; int val; public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } } ListNode first; // 队头 ListNode last; // 队尾 int size = 0; /*入队列--向双向链表位置插入新的节点*/ public void offer(int e) { ListNode newNode = new ListNode(e); if (first == null) { first = newNode; } else { last.next = newNode; newNode.prev = last; } last = newNode; size++; } /*出队列--将双向链表的第一个节点删除*/ public int poll() { int value = 0; if (first == null) { // 1.队列为空 throw new RuntimeException("队列为空"); } else if (first == last) { // 2.队列只有一个节点,直接删除 first = null; last = null; } else { // 3.队列中有多个节点,将第一个节点删除 value = first.val; first = first.next; first.prev.next = null; first.prev = null; } size--; return value; } /*获取队头元素--获取链表中第一个节点的值域*/ public Object peek() { if (first == null) { return null; } return first.val; } public int size() { return size; } public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } public void display() { ListNode cur = first; for (int i = 0;i < size;i++) { System.out.print(cur.val + " "); cur = cur.next; } } } -
Main函数
package demo3; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(); //入队列 myQueue.offer(1); myQueue.offer(2); myQueue.offer(3); myQueue.display(); System.out.println(); //出队列 myQueue.poll(); myQueue.display(); System.out.println(); //队头元素 System.out.println(myQueue.peek()); //队列元素 System.out.println("队列元素:" + myQueue.size()); } } //执行结果 1 2 3 2 3 2 队列元素:2
2.3 队列的使用
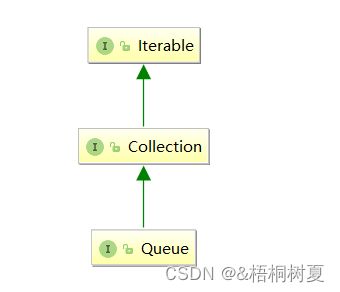
在Java中,Queue是个接口,底层是通过链表实现的:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| boolean offer(E e) | 入队列 |
| E poll() | 出队列 |
| peek() | 获取队头元素 |
| int size() | 获取队列中有效元素个数 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 检测队列是否为空 |
注:Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkListed的对象, 因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口
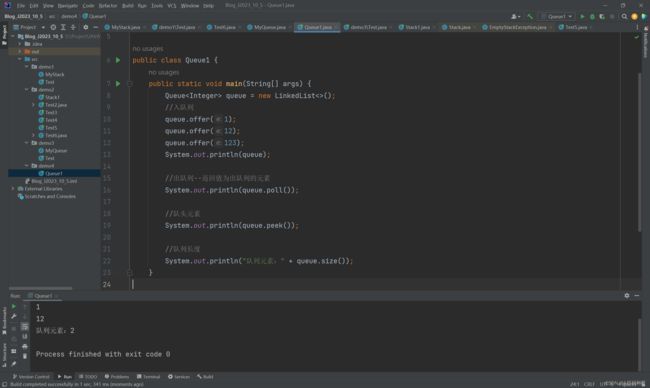
package demo4;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Queue1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//入队列
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(12);
queue.offer(123);
System.out.println(queue);
//出队列--返回值为出队列的元素
System.out.println(queue.poll());
//队头元素
System.out.println(queue.peek());
//队列长度
System.out.println("队列元素:" + queue.size());
}
}
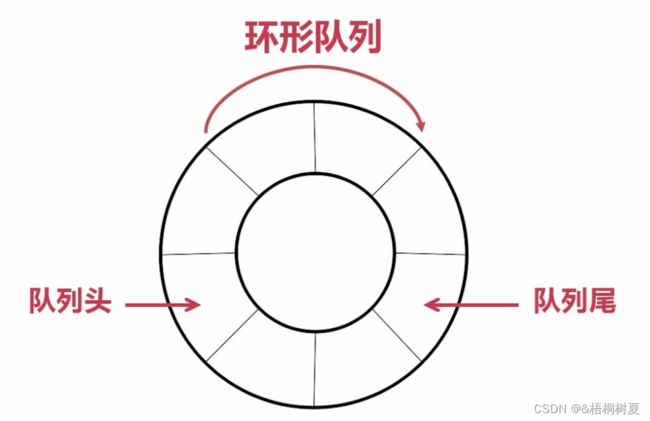
2.4 循环队列
实际上我们有时还会使用一种队列叫循环队列(环形队列),通常使用数组实现
数组下标循环的小技巧
-
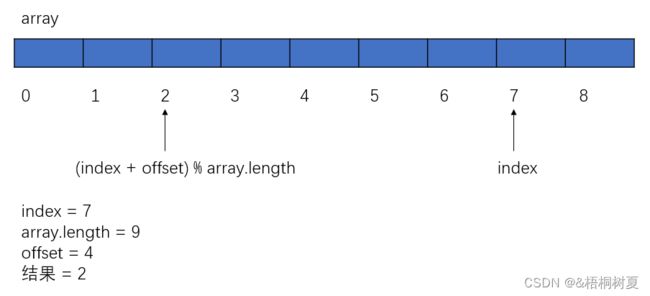
下标最后再往后(offset小于array.length): index = (index+offset)%array.length
-
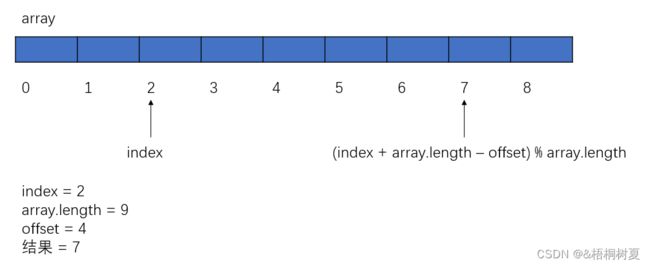
下标最前再往前(offset小于array.length): index = (index + array.length - offset) % array.length
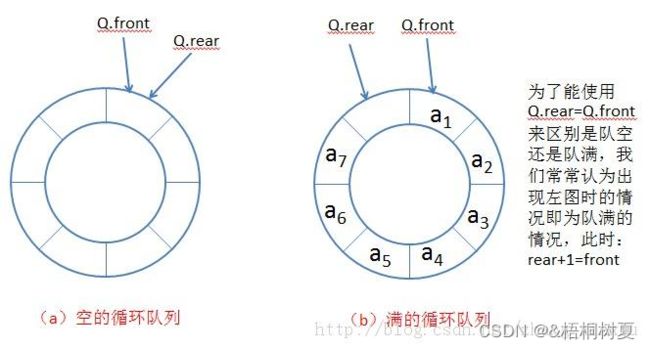
如何区分空与满
在这里我们通过保留一个位置来进行代码实现:
package demo2;
class MyCircularQueue {
public int[] elm;
public int front; //队头
public int rear; //队尾
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
elm = new int[k+1];
}
/*入队*/
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
elm[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%elm.length;
return true;
}
/*出队*/
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
front = (front + 1)% elm.length;
return true;
}
/*获得对头元素*/
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elm[front];
}
/*获取队尾元素*/
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int index = rear == 0 ? elm.length -1 : rear - 1;
return elm[index];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear+1)% elm.length == front;
}
}
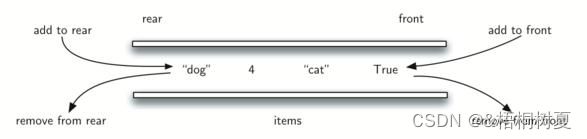
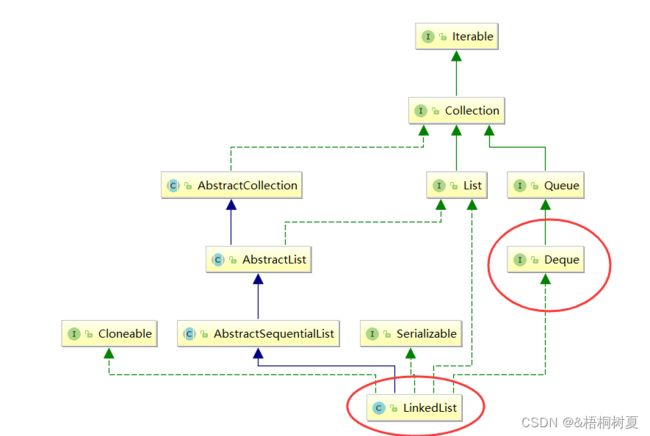
2.5 双端队列(Deque)
双端队列是指允许两端都可以进行入队和出队操作的队列,deque是"double ended queue" 的简称。那就说明元素可以从队头出队和入队,也可以coon队尾出队和入队
Deque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList的对象
栈和队列均可以使用Deque接口(本文仅做简单介绍)
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeeque<>(); //双端队列的线性实现
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //双端队列的链式实现
3. 双向操作
我们可以利用栈来实现队列,也可以利用队列来实现栈
3.1 用队列实现栈
package demo5;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> q1;
Queue<Integer> q2;
public MyStack() {
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/*入栈*/
public void push(int x) {
if(!q1.isEmpty()) {
q1.offer(x);
}
else if(!q2.isEmpty()) {
q2.offer(x);
}
else {
q1.offer(x);
}
}
/*出栈*/
public int pop() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (!q1.isEmpty()) {
int size = q1.size();
for (int i = 0;i < size - 1;i++) {
q2.offer(q1.poll());
}
return q1.poll();
}
else {
int size = q2.size();
for (int i = 0;i < size -1;i++) {
q1.offer(q2.poll());
}
return q2.poll();
}
}
/*获取栈顶元素*/
public int top() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (!q1.isEmpty()) {
int size = q1.size();
int x = -1;
for (int i = 0;i < size;i++) {
x = q1.poll();
q2.offer(x);
}
return x;
}
else {
int size = q2.size();
int x = -1;
for (int i = 0;i < size;i++) {
x = q2.poll();
q1.offer(x);
}
return x;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty() && q2.isEmpty();
}
}
3.2 用栈实现队列
package demo5;
import java.util.Stack;
public class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> s1;
Stack<Integer> s2;
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new Stack<>();
s2 = new Stack<>();
}
/*入队列*/
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
/*出队列*/
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (s2.isEmpty()) {
while(!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.pop();
}
/*获取队头元素*/
public int peek() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (s2.isEmpty()) {
while(!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.empty() && s2.empty();
}
}