springboot 中使用groovy脚本的各种方式
springboot 中使用groovy脚本的各种方式
- 准备工作
-
- 1. 环境
- 2. groovy 运行
- 一、动态执行groovy脚本
-
- 1. groovy通过import的方式直接调用java类
- 2. groovy通过GroovyShell预设对象调用JAVA对象的方法
- 3.controller中执行groovy script
- 4. 将所有SpringBean作为groovy变量
- 二、加载并执行groovy脚本文件
-
- 1. new一个groovy对象来隐式加载
-
- 1.1 新建脚本类
- 1.2在java代码中调用:
- 2. 通过evaluate方法调用groovy脚本文件
-
- 2.1 新建一个脚本
- 2.2 evaluate加载并执行脚本
- 3. GroovyClassLoader动态加载Groovy Class
-
- 3.1 新建groovy class
- 3.2 使用反射调用groovy
- 3.3 使用缓存,避免多次编译脚本
- 4. GroovyScriptEngine脚本引擎加载Groovy脚本
-
- 4.1 新建脚本
- 4.2 GroovyScriptEngine加载并执行脚本
- 三、方法使用
-
- 1.groovyShell.parse方法
推荐阅读:groovy的常用操作
准备工作
1. 环境
java1.8,springboot2.1.6
引入依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.6.1version>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>com.examplegroupId>
<artifactId>springboot-demo1artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>springboot-demo1name>
<description>springboot-demo1description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.groovygroupId>
<artifactId>groovy-allartifactId>
<version>2.4.21version>
<scope>compilescope>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
exclude>
excludes>
configuration>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
2. groovy 运行
依赖了groovy后,idea便可以创建groovy class了:
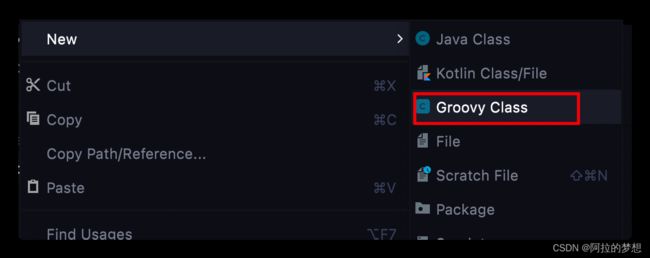
创建了groovy脚本,右键 run 就可以单独运行脚本了,无需配置groovy环境。
一、动态执行groovy脚本
动态执行,就是没有固定的脚本文件,代码是传入的或动态生成的。
1. groovy通过import的方式直接调用java类
package com.demo.groovy;
import groovy.lang.Binding;
import groovy.lang.GroovyShell;
import groovy.lang.Script;
public class GroovyTest1 {
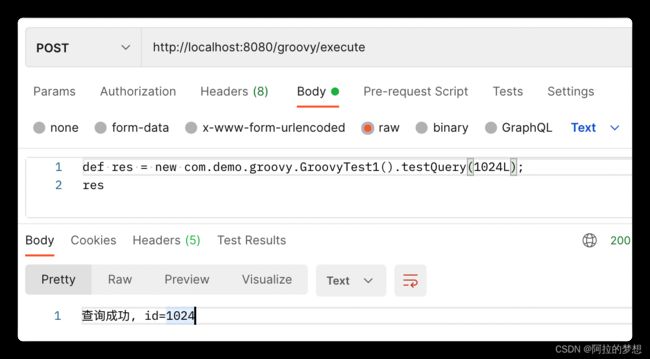
public String testQuery(long id) {
return "查询成功, id=" + id;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
fun1();
}
/**
* groovy可以通过import的方式直接调用java类
*/
private static void fun1() {
//创建脚本对象
GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell();
//脚本内容,内容中倒入了java类
String scriptContent = "import com.demo.groovy.GroovyTest1\n" +
"def res = new GroovyTest1().testQuery(1L);\n" +
"res";
//执行脚本
Script script = groovyShell.parse(scriptContent);
System.out.println(script.run());
}
}
2. groovy通过GroovyShell预设对象调用JAVA对象的方法
groovy支持通过GroovyShell预设对象,在groovy动态脚本中直接调用预设对象的方法
package com.demo.groovy;
import groovy.lang.Binding;
import groovy.lang.GroovyShell;
import groovy.lang.Script;
public class GroovyTest1 {
public String testQuery(long id) {
return "查询成功, id=" + id;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
fun2();
}
/**
*groovy支持通过GroovyShell预设对象,在groovy动态脚本中直接调用预设对象的方法
*/
public static void fun2() {
//1.预设对象,就是将java对象作为变量绑定到groovy中
Binding groovyBinding = new Binding();
groovyBinding.setVariable("groovyTest", new GroovyTest1());
//也可以用setProperty
groovyBinding.setProperty("num", 100L);
//2.创建脚本对象
GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell(groovyBinding);
//3.脚本内容
String scriptContent = "def res = groovyTest.testQuery(num);\n" +
"res";
//4.执行脚本,得到返回值
Object evaluate = groovyShell.evaluate(scriptContent);
System.out.println(evaluate);
}
}
groovyShell.evaluate()方法中会先parse脚本为Script对象。parse相对耗时,如果脚本内容是固定的,可以parse后作为全局变量使用。
3.controller中执行groovy script
package com.demo.groovy;
import groovy.lang.GroovyShell;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/groovy")
public class GroovyController {
@PostMapping("/execute")
public Object execute(@RequestBody String scriptContent) {
log.info("开始执行脚本,scriptContent={}", scriptContent);
GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell();
Object res = groovyShell.evaluate(scriptContent);
log.info("结束脚本执行,res={}", res);
return res;
}
}
4. 将所有SpringBean作为groovy变量
上文说到,可以通过setVariable和setProperty将对象作为变量传入groovy脚本。那么,我们就可以通过ApplicationContext获取所有bean,然后作为变量传入groovy。
如此以来,就可以在groovy脚本中使用所有Spring Bean对象了!
使用配置类,将所有bean绑定到groovy。因为这些bean都是通用的,存入一次,重复使用即可。
package com.demo.groovy;
import groovy.lang.Binding;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class GroovyBindingConfig {
@Bean("groovyBinding")
public Binding groovyBinding(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Binding groovyBinding = new Binding();
Map<String, Object> beanMap = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Object.class);
//遍历设置所有bean,可以根据需求在循环中对bean做过滤
for (String beanName : beanMap.keySet()) {
groovyBinding.setVariable(beanName, beanMap.get(beanName));
}
return groovyBinding;
}
/*@Bean("groovyBinding1")
public Binding groovyBinding1() {
Map beanMap = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Object.class);
return new Binding(beanMap); //如果不需要对bean做过滤,直接用beanMap构造Binding对象即可
}*/
}
新建个service类用来注入,并测试
package com.demo.groovy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
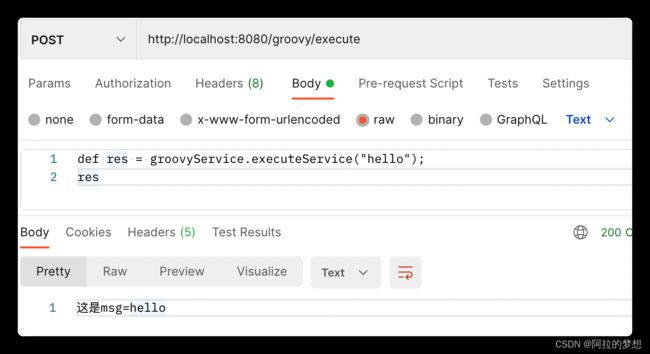
public class GroovyService {
public String executeService(String msg){
return "这是msg="+msg;
}
}
控制器:
package com.demo.groovy;
import groovy.lang.Binding;
import groovy.lang.GroovyShell;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/groovy")
public class GroovyController {
@Resource
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
//注入绑定对象
@Resource
private Binding groovyBinding;
@PostMapping("/execute")
public Object execute(@RequestBody String scriptContent) {
log.info("开始执行脚本,scriptContent={}", scriptContent);
//shell中加入绑定对象
GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell(groovyBinding);
Object res = groovyShell.evaluate(scriptContent);
log.info("结束脚本执行,res={}", res);
return res;
}
}
二、加载并执行groovy脚本文件
下面介绍一种隐式加载方式和三种显示加载方式
1. new一个groovy对象来隐式加载
1.1 新建脚本类
这个脚本必须在项目src下,也就是与java代码在一起,就可以直接new这个groovy类的对象,然后调用它的方法了。
demo.groovy
package com.demo.groovy
interface Simple {
String str1();
}
class Example implements Simple {
@Override
String str1() {
println System.currentTimeMillis()+"==11111"
}
}
1.2在java代码中调用:
package com.demo.groovy;
import java.io.IOException;
public class GroovyTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
new Example().str1()
}
}
这是隐式加载方式,脚本就像普通的java类,只会加载一次,如果脚本变化了,运行中的程序不会变。要想动态感知变化,那么得每次使用重新加载或定时加载。
下面是显示加载的方式。
2. 通过evaluate方法调用groovy脚本文件
2.1 新建一个脚本
2.2 evaluate加载并执行脚本
package com.demo.groovy
def sayHello(String name) {
println 'Hello ,'+name;
}
sayHello(name)
调用脚本并执行:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Binding binding = new Binding();
binding.setProperty("name","张三");
GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell(binding);
groovyShell.evaluate(new File("src/main/java/com/demo/groovy/demo.groovy"));
}
执行结果:
Hello ,张三
3. GroovyClassLoader动态加载Groovy Class
你也许熟悉Java的ClassLoader类加载器,当运行Java程序时,首先运行JVM(Java虚拟机),然后再把Java class加载到JVM运行,负责加载Java class的这部分就叫做Class Loader。而GroovyClassLoader,顾名思义,就是用来加载Groovy类的加载器。
3.1 新建groovy class
src/main/java/com/demo/groovy/demo.groovy
package com.demo.groovy
class demo02 {
String sayHello(String name, String sex, int age) {
return "name: " + name + ", sex: " + sex + ", age: " + age;
}
}
3.2 使用反射调用groovy
package com.demo.groovy;
import groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader;
import groovy.lang.GroovyObject;
import org.codehaus.groovy.control.CompilerConfiguration;
import java.io.File;
/**
* 使用反射调用groovy
**/
public class Test02 {
private static GroovyClassLoader groovyClassLoader = null;
public static void initGroovyClassLoader() {
CompilerConfiguration config = new CompilerConfiguration();
config.setSourceEncoding("UTF-8");
// 设置该GroovyClassLoader的父ClassLoader为当前线程的加载器(默认)
groovyClassLoader = new GroovyClassLoader(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), config);
}
/**
* 通过GroovyClassLoader加载GroovyShell_2,并反射调用其sayHello(String name, String sex, int age)方法
*/
public static String invokeSayHello(String name, String sex, int age) {
String result = "";
File groovyFile = new File("src/main/java/com/demo/groovy/demo.groovy");
if (!groovyFile.exists()) {
return result;
}
try {
// 获得GroovyShell_2加载后的class
Class<?> groovyClass = groovyClassLoader.parseClass(groovyFile);
// 获得GroovyShell_2的实例
GroovyObject groovyObject = (GroovyObject) groovyClass.newInstance();
// 反射调用sayHello方法得到返回值
Object methodResult = groovyObject.invokeMethod("sayHello", new Object[]{name, sex, age});
if (methodResult != null) {
result = methodResult.toString();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
initGroovyClassLoader();
System.out.println(invokeSayHello("张三", "男", 25));
}
}
执行结果

其方式和Java中类的加载反射类似,这里不再熬述。需要注意的是GroovyClassLoader与Java中的加载器一样,同一个类名的类只能加载一次,如果想再次加载,必须调用GroovyClassLoader的clearCache()方法移除所有已经加载的Groovy Class。
3.3 使用缓存,避免多次编译脚本
编译一次脚本后,放入缓存,下次从库里查询出脚本的更新时间,若时间没变,则使用缓存中的,若变了,则重新编译脚本。
//编译并缓存
public Class getGroovyScriptClass(String scriptCode) {
Example example = new Example(ScriptDef.class);
example.createCriteria().andEqualTo("code", scriptCode).andEqualTo("deleted", 0);
example.orderBy("id").desc();
List<ScriptDef> scriptDefs = scriptDefMapper.selectByExample(example);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(scriptDefs)) {
log.error("脚本不存在,scripCode={}", scriptCode);
return null;
}
//1.从数据库查询脚本
ScriptDef scriptEntity = scriptDefs.get(0);
String updateTime = scriptEntity.getUpdatedAt().toString();
String updateKey = scriptCode + "-" + updateTime;
String lastUpdateTime = (String) redisService.getLocal(updateKey);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(lastUpdateTime)) {
//2.从缓存中获取脚本class对象
Class cachedClass = (Class) redisService.getLocal(scriptCode);
if (cachedClass != null) {
return cachedClass;
}
}
//3.无缓存,解析为class对象
//File groovyFile = new File("D:\\ideaProject\\document\\service\\src\\main\\java\\com\\demo\\devops\\service\\impl\\DocVerifyScript.groovy");
CompilerConfiguration config = new CompilerConfiguration();
config.setSourceEncoding("UTF-8");
GroovyClassLoader groovyClassLoader = new GroovyClassLoader(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), config);
Class<?> groovyClass = groovyClassLoader.parseClass(scriptEntity.getContent());
redisService.setLocal(updateKey, updateKey);
redisService.setLocal(scriptCode, groovyClass);
return groovyClass;
}
// 调用
public void collectHostInterfaceAddresses() {
String logPrefix = "定时任务【采集ip地址】,";
log.info(logPrefix + "开始");
try {
Class<?> groovyClass = this.groovyScriptService.getGroovyScriptClass("ip_script");
// 获得Groovy的实例
GroovyObject groovyObject = (GroovyObject) groovyClass.newInstance();
// 反射调用方法得到返回值
groovyObject.invokeMethod("execute", new Object[]{});
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(logPrefix, e);
}
log.info(logPrefix + "结束");
}
4. GroovyScriptEngine脚本引擎加载Groovy脚本
4.1 新建脚本
src/main/java/com/demo/groovy/demo.groovy

4.2 GroovyScriptEngine加载并执行脚本
package com.demo.groovy;
import groovy.lang.Binding;
import groovy.util.GroovyScriptEngine;
/**
* GroovyScriptEngine加载并执行脚本
**/
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// GroovyScriptEngine的根路径,如果参数是字符串数组,说明有多个根路径
GroovyScriptEngine engine = new GroovyScriptEngine("src/main/java/com/demo/groovy");
Binding binding = new Binding();
binding.setVariable("name", "张三");
Object result1 = engine.run("demo.groovy", binding);
binding.setVariable("name", "李四");
Object result2 = engine.run("demo.groovy", binding);
}
}
三、方法使用
1.groovyShell.parse方法
parse 方法可以将脚本加载到内存,以备使用。
使用场景:一次解析脚本,多次执行脚本的情况;
如下:
parse解析脚本后,可以循环多次执行脚本,用script.setBinding方法传入不同的参数。
script.run来执行脚本;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String scriptContent = "println \"收到$name\"";
GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell();
Script script = groovyShell.parse(scriptContent);
int i = 0;
while (i < 5) {
i++;
Binding binding = new Binding();
binding.setProperty("name", i);
script.setBinding(binding);
script.run();
}
}