C#学习笔记(十一)字段、属性、索引器、常量
字段、属性、索引器、常量:这四者放在一起:因为它们都表达数据。一个程序的本质就是:数据+算法。
C#的类型成员:类或者结构体。
1、字段
定义:
字段(field)是一种表示与对象或类型(类与结构体)关联的变量。定义中的两个关键字:对象 或者 类型。那么可以把字段分为两类:
- 与对象关联的字段:实例字段,因为对象是实例化出来的。表述每个对象个体的差异性。
- 与类型关联的字段:静态字段,由static修饰的,静止的。表述整个类的族群特性。
一个可适用于不同个体对象的差异性,实例化不同对象;
一个可适用于描述族群类型的当前状态,统计性,平均值、总数等。
class Student
{
//个体的状态。
public int Age;
public int Score;
public string Name;
// 类型的状态。
public static int AverageAge;
public static int AverageScore;
public static int Amount;
}绑定静态字段和实例字段:
// 绑定静态字段和实例字段。
public Student()
{
Amount++;
}
public static void ReportAmount()
{
Console.WriteLine(Amount);
}Student stu1 = new Student();
Student stu2 = new Student();
Student stu3 = new Student();
Student.ReportAmount();声明:
字段声明不是语句:因为语句只能出现在方法体里面。
对字段显式的初始化赋值和在构造函数中赋值其实是一样的。
class Student
{
public int Age=22;
public Student()
{
}
}class Student
{
public int Age;
public Student()
{
this.Age = 22;
}
}两者是一样的,但是推荐:第一种:因为:将来无论构造器怎么变化,对字段的初始值都不会受到影响。
初始化:
初始化时机:
对于实例字段:在实例创建的时候。 每次创建实例的时候,初始化都会执行。
对于静态字段:运行环境加载数据类型的时候。 只执行一次,就在加载这个数据类型的时候。
当一个数据类型被运行环境加载的时候,它的静态构造器会被调用。因为静态类型只被加载一次,静态构造器只执行一次。
class Student
{
public int Age=20;
public static int Amount=100;
//静态构造器:
static Student()
{
}
}class Student
{
public int Age=20;
public static int Amount;
//静态构造器:
static Student()
{
Student.Amount = 100;
}
}只读字段:一旦初始化,不可再被赋值。
实例只读字段:readonly。只有一次机会赋值,在构造器中,创建对象的时候,给他赋值,一旦赋值,就无法修改。
class Student
{
public readonly int ID;
public static int Amount=100;
//静态构造器:
public Student(int id)
{
this.ID = id;
}
}静态只读字段:readonly。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(Brush.DefaultColor.Red);
Console.WriteLine(Brush.DefaultColor.Green);
Console.WriteLine(Brush.DefaultColor.Blue);
}
}
struct Color
{
public int Red;
public int Green;
public int Blue;
}
class Brush
{
public static readonly Color DefaultColor = new Color() { Red = 0, Green = 0, Blue = 0 };
}它的静态构造函数:
class Brush
{
public static readonly Color DefaultColor;
static Brush()
{
Brush.DefaultColor = new Color() { Red = 0, Green = 0, Blue = 0 };
}
}只读字段:只有一次赋值机会,初始化以后,不可再被赋值。
2、属性:
属性(Property):用于访问对象或类型的特征的成员,特征反映了状态。
举例1:豆腐:属性:温度:可不可吃。
举例2:人类:属性:总量:人类增长还是减少。
属性也是一个语法糖。
VS中通过代码提示:propfull,快速生成属性完整声明结构。
简易声明代码提示:prop,一般传递数据用的。
VS中是属性的另一种写法:
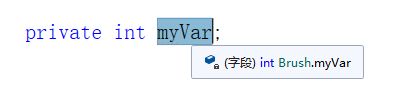
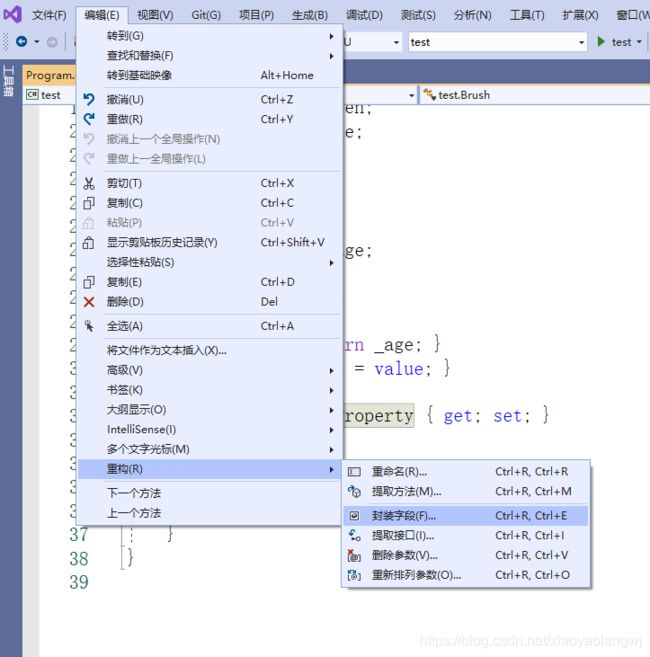
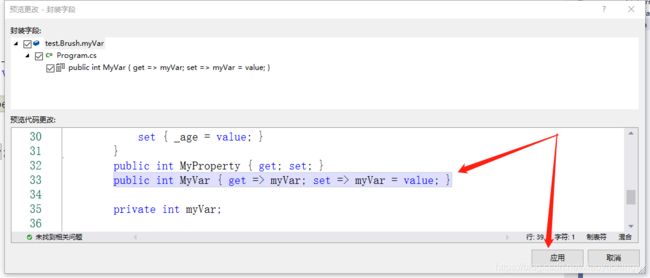
首先写一个私有字段:
选中字段:点击【编辑】【重构】【封装字段】或者直接按【Ctrl+R+E】
即可实现属性的重构。
只读属性:只有get方法,没有set方法。
private bool canWork;
public bool CanWork
{
get { return canWork; }
}只读属性,通过方法来完成动态计算赋值。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.Age = 12;
Console.WriteLine(stu.CanWork);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get { return age; }
set { age = value; }
}
public bool CanWork
{
get {
if (this.age>=16)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
}
或者:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.Age = 12;
Console.WriteLine(stu.CanWork);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get { return age; }
set
{
age = value;
this.CalculateCanWork();
}
}
private bool canWork;
public bool CanWork
{
get { return canWork; }
}
private void CalculateCanWork()
{
if (this.age>=16)
{
this.canWork = true;
}
else
{
this.canWork = false;
}
}
}3、索引器
索引器用来检索集合的。拥有索引器的类一般都是集合类型的类(非集合类型的类也可以)。它使对象能够用与数组相同的方式(即使用下标)进行索引。
索引器的声明:
VS中代码提示:indexer。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu["Math"] = 90;
var mathScore = stu["Math"];
Console.WriteLine(mathScore);
}
}
class Student
{
private Dictionary scoreDictionary = new Dictionary();
// 返回可控的int类型
public int? this[string subject]
{
get {
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
return this.scoreDictionary[subject];
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
set {
if (value.HasValue==false)
{
throw new Exception("Score cannot be null.");
}
if (this.scoreDictionary.ContainsKey(subject))
{
this.scoreDictionary[subject] = value.Value; // 此处可控类型还有一个Value可以用。
}
else
{
this.scoreDictionary.Add(subject, value.Value);
}
}
}
} 4、常量constant
const关键字修饰。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(WASPEC.WebsiteURL);
}
}
class WASPEC
{
public const string WebsiteURL = "http://www.waspec.org";
}只读类型readonly
- 为了防止对象的值被改变——只读字段
- 为了提高程序可读性和执行效率——常量
- 向外暴漏不允许修改的数据——只读属性(静态或非静态),功能与常量有一些重叠。
- 当希望成为常量的值其类型不能被常量声明接受时(类/自定义结构体)——静态只读字段。