聪明的人脸识别4——Pytorch 利用Retinaface+Facenet搭建人脸识别平台
睿智的目标检测51——Pytorch 利用Retinaface+Facenet搭建人脸识别平台
- 学习前言
- 什么是Retinface和Facenet
-
- 1、Retinface
- 2、Facenet
- 整体实现代码
- 实现流程
-
- 一、数据库的初始化
- 二、检测图片的处理
-
- 1、人脸的截取与对齐
- 2、利用Facenet对矫正后的人脸进行编码
- 3、将实时图片中的人脸特征与数据库中的进行比对
- 4、图片绘制
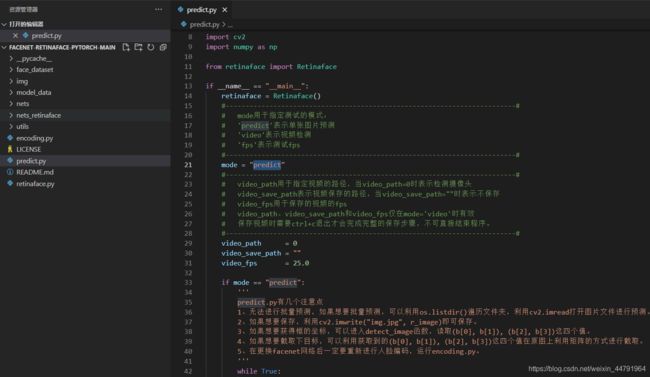
- 使用Retinaface+Facenet进行人脸识别:
学习前言
我又死了我又死了我又死了!
![]()
什么是Retinface和Facenet
1、Retinface
Retinaface是来自insightFace的又一力作,基于one-stage的人脸检测网络。
同时开源了代码与数据集,在widerface上有非常好的表现。
![]()
2、Facenet
谷歌人脸识别算法,发表于 CVPR 2015,利用相同人脸在不同角度等姿态的照片下有高内聚性,不同人脸有低耦合性,提出使用 cnn + triplet mining 方法,在 LFW 数据集上准确度达到 99.63%。
通过 CNN 将人脸映射到欧式空间的特征向量上,实质上:不同图片人脸特征的距离较大;通过相同个体的人脸的距离,总是小于不同个体的人脸这一先验知识训练网络。
测试时只需要计算人脸特征EMBEDDING,然后计算距离使用阈值即可判定两张人脸照片是否属于相同的个体。
![]()
简单来讲,在使用阶段,facenet即是:
1、输入一张人脸图片
2、通过深度卷积网络提取特征
3、L2标准化
4、得到一个长度为128特征向量。
整体实现代码
https://github.com/bubbliiiing/facenet-retinaface-pytorch
Retinaface原理和Facenet原理可以参考我的另外两篇博客。
睿智的目标检测42——Pytorch搭建Retinaface人脸检测与关键点定位平台
聪明的人脸识别3——Pytorch 搭建自己的Facenet人脸识别平台
实现流程
一、数据库的初始化
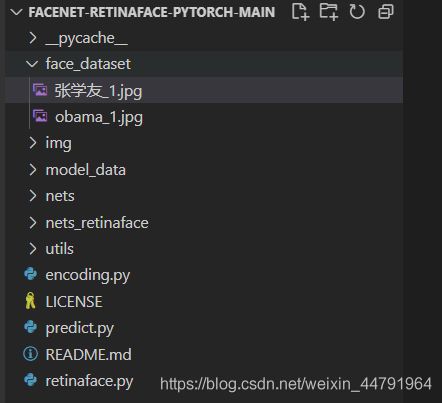
face_dataset里面装的是想要识别的人脸,在图片中看到的obama_1.jpg指的就是obama的第一张人脸图片,可以配置多张图片都指向obama,如obama_2.jpg、obama_3.jpg,需要注意的是,face_dataset里面每张图片都只能包含一张人脸,即目标人脸。
数据库中每一张图片对应一个人的人脸,图片名字中“_”靠左的部分就是这个人的名字。
数据库初始化指的是人脸数据库的初始化。
想要实现人脸识别,首先要知道自己需要识别哪些人脸,在这一步中,我们会讲识到的人脸进行编码并放入数据库中。
数据库的初始化具体执行的过程就是:
1、遍历数据库中所有的图片。
2、利用Retinaface检测每个图片中的人脸位置。
3、将人脸截取下来。
4、将获取到的人脸进行对齐。
5、利用Facenet将人脸进行编码。
6、将所有人脸编码的结果放在一个列表中。
7、保存成npy的形式。
第6步得到的列表就是已知的所有人脸的特征列表,在之后获得的实时图片中的人脸都需要与已知人脸进行比对,这样我们才能知道谁是谁。
实现代码如下:
import os
from retinaface import Retinaface
'''
在更换facenet网络后一定要重新进行人脸编码,运行encoding.py。
'''
retinaface = Retinaface(1)
list_dir = os.listdir("face_dataset")
image_paths = []
names = []
for name in list_dir:
image_paths.append("face_dataset/"+name)
names.append(name.split("_")[0])
retinaface.encode_face_dataset(image_paths,names)
二、检测图片的处理
1、人脸的截取与对齐
![]()
利用Retinaface我们可以获得一张图片中人脸的位置,但是我们截取下来的人脸是这样的:
![]()
我们可以很明显的看出来人脸是歪着的,我们如果人脸可以正过来,那么将对人脸的特征提取非常有好处。
![]()
下面这张图看着就正多了。
常见的对齐方法有很多,在本篇博客里我们使用双眼坐标进行旋正。
利用双眼坐标进行旋正需要用到两个参数,如图所示分别是:
1、眼睛连线相对于水平线的倾斜角。
2、图片的中心。
![]()
利用这两个参数我们可以知道需要图片需要旋转的角度是多少,图片旋转的中心是什么。
代码实现如下,其中landmark是五个人脸特征点的位置:
#-------------------------------------#
# 人脸对齐
#-------------------------------------#
def Alignment_1(img,landmark):
if landmark.shape[0]==68:
x = landmark[36,0] - landmark[45,0]
y = landmark[36,1] - landmark[45,1]
elif landmark.shape[0]==5:
x = landmark[0,0] - landmark[1,0]
y = landmark[0,1] - landmark[1,1]
# 眼睛连线相对于水平线的倾斜角
if x==0:
angle = 0
else:
# 计算它的弧度制
angle = math.atan(y/x)*180/math.pi
center = (img.shape[1]//2, img.shape[0]//2)
RotationMatrix = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1)
# 仿射函数
new_img = cv2.warpAffine(img,RotationMatrix,(img.shape[1],img.shape[0]))
RotationMatrix = np.array(RotationMatrix)
new_landmark = []
for i in range(landmark.shape[0]):
pts = []
pts.append(RotationMatrix[0,0]*landmark[i,0]+RotationMatrix[0,1]*landmark[i,1]+RotationMatrix[0,2])
pts.append(RotationMatrix[1,0]*landmark[i,0]+RotationMatrix[1,1]*landmark[i,1]+RotationMatrix[1,2])
new_landmark.append(pts)
new_landmark = np.array(new_landmark)
return new_img, new_landmark
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
#---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image):
# 绘制人脸框
image = np.array(image, np.float32)
old_image = np.array(image.copy(), np.uint8)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# Retinaface检测部分-开始
#---------------------------------------------------#
im_height, im_width, _ = np.shape(image)
# 它的作用是将归一化后的框坐标转换成原图的大小
scale = torch.Tensor([np.shape(image)[1], np.shape(image)[0], np.shape(image)[1], np.shape(image)[0]])
scale_for_landmarks = torch.Tensor([np.shape(image)[1], np.shape(image)[0], np.shape(image)[1], np.shape(image)[0],
np.shape(image)[1], np.shape(image)[0], np.shape(image)[1], np.shape(image)[0],
np.shape(image)[1], np.shape(image)[0]])
if self.letterbox_image:
image = letterbox_image(image,[self.cfg["image_size"], self.cfg["image_size"]])
anchors = Anchors(self.cfg, image_size=(self.cfg["image_size"], self.cfg["image_size"])).get_anchors()
else:
anchors = Anchors(self.cfg, image_size=(im_height, im_width)).get_anchors()
# pytorch
image = preprocess_input(image).transpose(2, 0, 1)
# 增加batch_size维度
image = torch.from_numpy(image).unsqueeze(0).type(torch.FloatTensor)
if self.cuda:
scale = scale.cuda()
scale_for_landmarks = scale_for_landmarks.cuda()
image = image.cuda()
anchors = anchors.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
loc, conf, landms = self.net(image) # forward pass
boxes = decode(loc.data.squeeze(0), anchors, self.cfg['variance'])
boxes = boxes * scale
boxes = boxes.cpu().numpy()
conf = conf.data.squeeze(0)[:,1:2].cpu().numpy()
landms = decode_landm(landms.data.squeeze(0), anchors, self.cfg['variance'])
landms = landms * scale_for_landmarks
landms = landms.cpu().numpy()
boxes_conf_landms = np.concatenate([boxes,conf,landms],-1)
boxes_conf_landms = non_max_suppression(boxes_conf_landms, self.confidence)
if len(boxes_conf_landms)<=0:
return old_image
boxes_conf_landms = np.array(boxes_conf_landms)
if self.letterbox_image:
boxes_conf_landms = retinaface_correct_boxes(boxes_conf_landms, np.array([self.cfg["image_size"], self.cfg["image_size"]]), np.array([im_height, im_width]))
#---------------------------------------------------#
# Retinaface检测部分-结束
#---------------------------------------------------#
2、利用Facenet对矫正后的人脸进行编码
![]()
Facenet是一个人脸特征获取的模型,将第1步获得的对齐人脸传入Facenet模型就可以得到每个人脸的特征向量。
将所有特征向量保存在一个列表中,在第3步进行比对。
#-----------------------------------------------#
# Facenet编码部分-开始
#-----------------------------------------------#
face_encodings = []
for boxes_conf_landm in boxes_conf_landms:
#----------------------#
# 图像截取,人脸矫正
#----------------------#
crop_img = np.array(old_image)[int(boxes_conf_landm[1]):int(boxes_conf_landm[3]), int(boxes_conf_landm[0]):int(boxes_conf_landm[2])]
landmark = np.reshape(boxes_conf_landm[5:],(5,2)) - np.array([int(boxes_conf_landm[0]),int(boxes_conf_landm[1])])
crop_img,_ = Alignment_1(crop_img,landmark)
#----------------------#
# 人脸编码
#----------------------#
crop_img = np.array(letterbox_image(np.uint8(crop_img),(self.input_shape[1],self.input_shape[0])))/255
crop_img = np.expand_dims(crop_img.transpose(2, 0, 1),0)
with torch.no_grad():
crop_img = torch.from_numpy(crop_img).type(torch.FloatTensor)
if self.cuda:
crop_img = crop_img.cuda()
# 利用facenet_model计算长度为128特征向量
face_encoding = self.facenet(crop_img)[0].cpu().numpy()
face_encodings.append(face_encoding)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# Facenet编码部分-结束
#-----------------------------------------------#
3、将实时图片中的人脸特征与数据库中的进行比对
![]()
这个比对过程需要循环实现,具体对实时图片中的每一个人脸进行循环:
1、获取实时图片中的每一个人脸特征。
2、将每一个人脸特征和数据库中所有的人脸进行比较,计算距离。如果距离小于门限值,则认为其具有一定的相似度。
3、获得每一张人脸在数据库中最相似的人脸的序号。
4、判断这个序号对应的人脸距离是否小于门限,是则认为人脸识别成功,他就是这个人。
实现代码如下:
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 人脸特征比对-开始
#-----------------------------------------------#
face_names = []
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
# 取出一张脸并与数据库中所有的人脸进行对比,计算得分
matches, face_distances = compare_faces(self.known_face_encodings, face_encoding, tolerance = self.facenet_threhold)
name = "Unknown"
# 取出这个最近人脸的评分
best_match_index = np.argmin(face_distances)
if matches[best_match_index]:
name = self.known_face_names[best_match_index]
face_names.append(name)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 人脸特征比对-结束
#-----------------------------------------------#
4、图片绘制
这一部分只是检测结果绘制在图片上,由绘制代码组成。
for i, b in enumerate(results):
text = "{:.4f}".format(b[4])
b = list(map(int, b))
cv2.rectangle(old_image, (b[0], b[1]), (b[2], b[3]), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cx = b[0]
cy = b[1] + 12
cv2.putText(old_image, text, (cx, cy),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 255))
# landms
cv2.circle(old_image, (b[5], b[6]), 1, (0, 0, 255), 4)
cv2.circle(old_image, (b[7], b[8]), 1, (0, 255, 255), 4)
cv2.circle(old_image, (b[9], b[10]), 1, (255, 0, 255), 4)
cv2.circle(old_image, (b[11], b[12]), 1, (0, 255, 0), 4)
cv2.circle(old_image, (b[13], b[14]), 1, (255, 0, 0), 4)
name = face_names[i]
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
cv2.putText(old_image, name, (b[0] , b[3] - 15), font, 0.75, (255, 255, 255), 2)
使用Retinaface+Facenet进行人脸识别:
在GITHUB上下载好库后将库解压。

下载对应的权重,README中会有下载连接,百度网盘下载或者GITHUB下载均可。
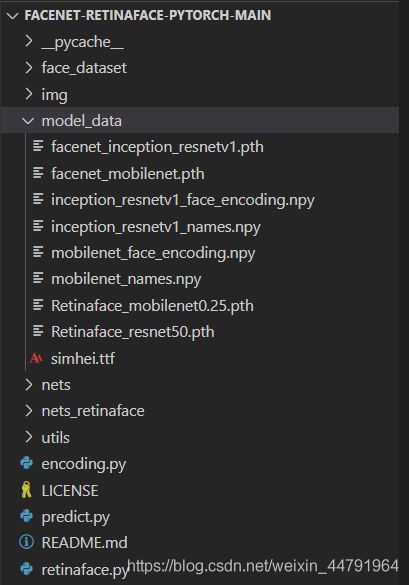
在retinaface.py里面,根据自身需求修改retinaface_model_path、retinaface_backbone、facenet_model_path、facenet_backbone四个参数。
运行encoding.py进行人脸数据集编码。
![]()
运行predict.py进行人脸图片的预测。