Python自动化运维实战——Telnetlib和Netmiko自动化管理网络设备
❤️博客主页: iknow181
系列专栏: Python、JavaSE、JavaWeb、CCNP
欢迎大家点赞收藏⭐评论✍
![]()
目录
一、前言
二、准备工作
三、Telnetlib
Telnetlib介绍
Telnetlib模块及操作方法介绍
Telnetlib配置设备
Telnetlib批量化部署多台设备
Telnetlib抓取设备配置
四、Netmiko
Netmiko介绍
Netmiko登陆设备并配置
Netmiko配置设备
Netmiko以文件方式配置设备
Netmiko抓取设备配置
Netmiko抓取设备配置并写入文件中
Netmiko批量化部署多台设备
Netmiko批量化抓取设备配置
一、前言
本期小i为大家带来了关于Python自动化运维的技术——利用Python进行网络设备的自动化管理。话不多说,直接上干货!
二、准备工作
在开始之前先做好准备工作,我用的是VMware这款虚拟机和EVE模拟器结合来模拟本次所需要的网络设备,没有VMware和EVE的小伙伴可以参考这两篇文章进行安装。
EVE模拟器的使用-带图超详细(学网络用)_eve虚拟机-CSDN博客
安装虚拟机(VMware)保姆级教程(附安装包)_vmware虚拟机-CSDN博客
先打开VMware,注意两个网络适配器中必须有一个是VMnet1,
确定好之后,点击继续运行此虚拟机。
然后打开EVE,新建一个实验,拖三台路由器,最好用vIOS,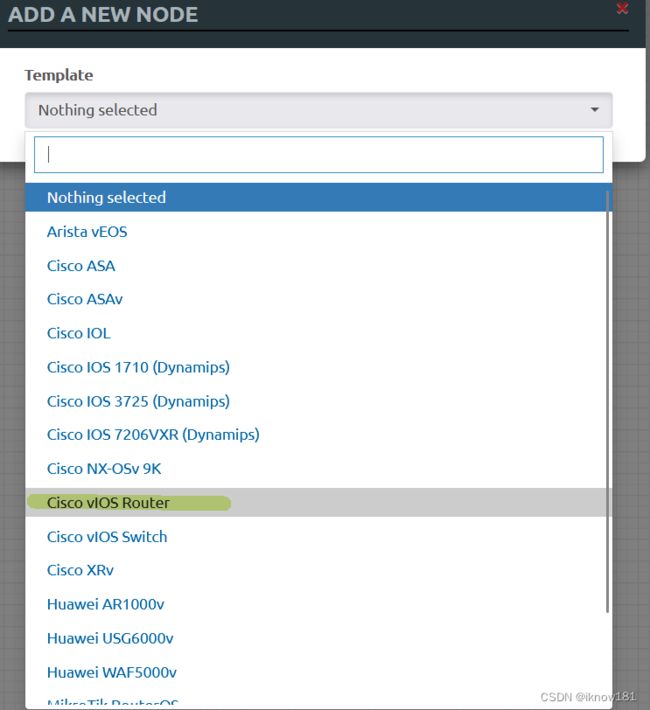
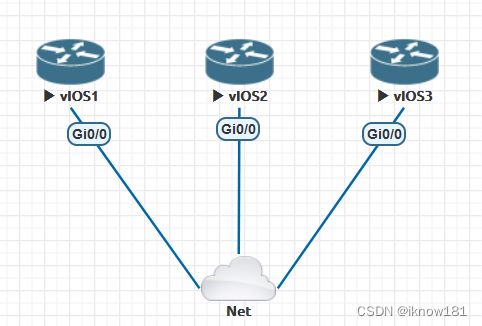
将四台设备连线后开机,如下图。
然后为三台路由器配置ip地址,Net不用配,
注意:这里的ip地址是有讲究的,前24网络位为必须和你的虚拟机的IP网络一致(这就是为什么前面必须用VMnet1),后8位主机位随意,只要不是0,1,2等特殊地址就行,这里我选用188,189,190作为主机位。不清楚你的虚拟机网络地址的可以看EVE的网址。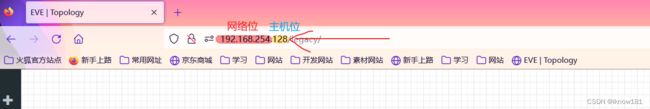
vIOS1:
enable
configure terminal
hostname R1
interface G0/0
ip address 192.168.254.188 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
vIOS2:
en
conf t
host R3
int G0/0
ip add 192.168.254.189 255.255.255.0
no sh
vIOS3:
en
conf t
host R3
int G0/0
ip add 192.168.254.190 255.255.255.0
no sh
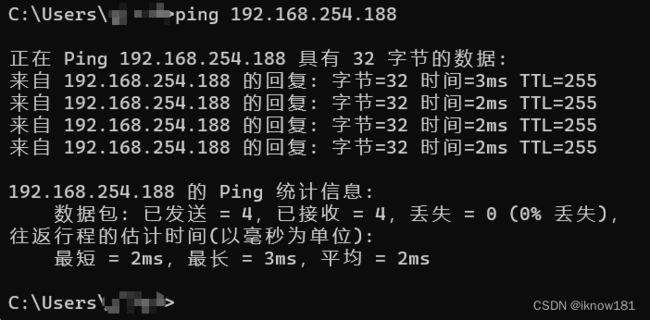
配完后可以用本机ping一下这些设备,看能不能通。
按win + R,输入cmd,进入命令行窗口,输入 ping 192.168.254.188
最后为设备配置telent和ssh,因为Telnetlib和Netmiko分别基于telent和ssh实现连接的。
下面我就以一台设备为例做配置。
telent:
en
conf t
username admin privilege 15 password admin
line vty 0 4
tran in telnet
login local
ssh:
en
conf t
ip domain-name cisco.com
crypto key generate rsa modulus 1024
line vty 0 4
transport input ssh
另外还需在PyCharm中导入Telnetlib和Netmiko库,
Telnetlib直接导入就可以,
import telnetlibNetmiko则需要先下载软件包,打开文件(file)中的设置(setting),找到项目:Project下的Python解释器,点击加号,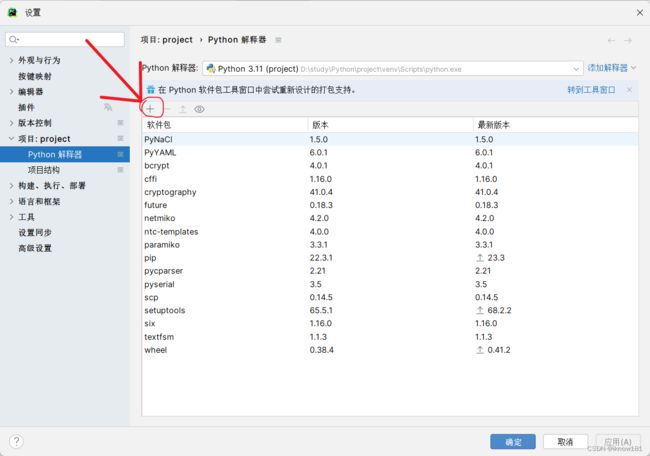
在输入框中输入Netmiko,点击第一个选项netmiko,安装软件包即可。
注意:下载时必须保证一个好的网速,不然会非常慢且容易断开下载从而下载失败。
自此我们的准备工作就全部完成了,下面开始上代码!!!
三、Telnetlib
Telnetlib介绍
Telnetlib模块是Python提供的可用于Telnet连接使用的模块,值得注意的是,在现有的生产环境中,Telnet协议连接已经使用的较为少见了(原因也非常简单,Telnet协议是明文传输的协议,所以在数据传输,尤其是在公网上传输的时候极其不安全)。 且telnetlib已逐渐弃用,并计划在Python 3.13 版本中删除
Telnetlib模块及操作方法介绍
1. Telnet(host=None, port=0, timeout=None):
Telnet类的构造函数,用于创建一个Telnet对象。参数host是远程主机的地址,port是远程主机的端口号,timeout是连接超时时间。
2. open(host, port=23, timeout=None):打开一个Telnet连接。参数host和port与Telnet构造函数中的相同。
3. read_until(expected, timeout=None):读取输入直到遇到预期的字符串。参数expected是预期的字符串,timeout是读取超时时间。
4. read_very_eager():读取输入缓冲区中的所有数据,不会阻塞。
5. write(data):向远程主机发送数据。参数data是要发送的数据。
6. close():关闭Telnet连接。
7. set_debuglevel(level):设置调试级别,用于输出调试信息。
8. set_option_negotiation_callback(callback):设置选项协商回调函数。
9. expect(list, timeout=None):等待预期的字符串出现,返回匹配的字符串。参数list是一个字符串列表,每个字符串表示一个预期的字符串,timeout是等待超时时间。
10. expect_regexp(list, timeout=None):等待预期的正则表达式出现,返回匹配的字符串。参数list是一个正则表达式列表,每个正则表达式表示一个预期的字符串,timeout是等待超时时间。
11. set_echo(option):设置是否回显输入。
12. set_timeout(timeout):设置读取超时时间。
13. set_option_negotiation_callback(callback):设置选项协商回调函数。
14. set_option_negotiation_callback(callback):设置选项协商回调函数。Telnetlib配置设备
import telnetlib
host = '192.168.2541.188' # 要远程管理的主机,确保IP可达,telnet服务打开
username = 'admin' # telnet的用户名
password = 'admin' # telnet的密码
tn = telnetlib.Telnet(host) # 调用telnetlib的Telnet(),赋值给tn
tn.read_until(b"Username:") # b表示等待期望的字符出现
tn.write(username.encode("ascii") + b"\n") # 通过tn.write()的方式输入用户名,b/n表示回车
tn.read_until(b"Password:") # b表示等待期望的字符出现
tn.write(password.encode("ascii") + b"\n") # 通过tn.write()的方式输入密码,b/n表示回车
# 通过write函数输入配置命令
tn.write(b"enable\n")
tn.write(b"configure terminal\n")
tn.write(b"username CCIE password CCIE\n")
tn.write(b"end\n")
tn.write(b"wr\n")
tn.write(b"exit\n")
print(tn.read_all().decode("ascii")) # 通过read_all()方法记录配置命令的过程并且可以在EVE中看到相应的日志信息,代表192.168.254.1这个用户连接了此设备。 # 优化部分:通过函数调用的形式
import telnetlib
def run_telnet(host, username, password):
# 通过Telnet登录网络设备
tn = telnetlib.Telnet(host, port=23, timeout=10)
# 输入用户名
tn.read_until(b"Username:")
tn.write(username.encode("ascii") + b"\n")
# 输入密码
tn.read_until(b"Password:")
tn.write(password.encode("ascii") + b"\n")
# 登录完成后执行命令
tn.write(b"enable\n")
tn.write(b"configure terminal\n")
tn.write(b"username CCIECLUB privilege 15 password CCIECLUB\n")
tn.write(b"end\n")
tn.write(b"exit\n")
tn.write(b"wr\n")
print(tn.read_all().decode("ascii"))
run_telnet('192.168.254.188', "admin", "admin")
run_telnet('192.168.254.189', "admin", "admin")
run_telnet('192.168.254.190', "admin", "admin")Telnetlib批量化部署多台设备
import telnetlib
def run_telnet(host, username, password, commands):
# 通过Telnet登录网络设备
tn = telnetlib.Telnet(host, port=23, timeout=10)
tn.set_debuglevel(1)
# 输入用户名
tn.read_until(b"Username:")
tn.write(username.encode("ascii") + b"\n")
# 输入密码
tn.read_until(b"Password:")
tn.write(password.encode("ascii") + b"\n")
# 登录完成后执行命令
for command in commands:
tn.write(command.encode("ascii") + b"\n")
print(tn.read_all().decode("ascii"))
tn.close()
commands = ['enable', 'configure terminal', 'username CCIE password CCIE', 'end', 'exit']
run_telnet('192.168.254.220', "admin", "admin", commands)
run_telnet('192.168.254.221', "admin", "admin", commands)
run_telnet('192.168.254.222', "admin", "admin", commands)Telnetlib抓取设备配置
堪称写实验报告神器,一键导出配置到一个txt文档,告别手动一个一个的show,display。
import telnetlib
import time
def run_telnet(host, username, password):
# 通过Telnet登录网络设备
tn = telnetlib.Telnet(host, port=23, timeout=10)
# 输入用户名
tn.read_until(b"Username:")
tn.write(username.encode("ascii") + b"\n")
# 输入密码
tn.read_until(b"Password:")
tn.write(password.encode("ascii") + b"\n")
# 登录完成后执行命令
tn.write(b"enable\n")
tn.write(b"terminal length 0\n") # 取消分段显示
time.sleep(1)
tn.write(b"show running-config\n")
time.sleep(5)
out = tn.read_very_eager().decode("ascii")
print(out)
file = open(file="E:\\1.txt", mode='a')
file.write(out)
file.close()
tn.close()
run_telnet('192.168.254.188', "admin", "admin")
run_telnet('192.168.254.189', "admin", "admin")
run_telnet('192.168.254.190', "admin", "admin")这边结果太长了我就不贴出来了。
四、Netmiko
Netmiko介绍
Netmiko是一款Python库,被广泛用于自动化网络设备管理任务。作为一个重要的开源库,它通过简化与网络设备的TCP连接,实现了快速执行相关任务的能力。Netmiko基于Paramiko库的基础架构,支持绝大多数的网络设备,包括Cisco, Juniper, Arista等。它提供了连接网络设备并执行特定任务的接口,例如SSH, Telnet以及串口这些网络协议的相关处理。 Netmiko在 Github 上是开源的,它的源代码可以在 GitHub 网站上进行获取和修改。Netmiko 项目的 GitHub 地址为:https://github.com/ktbyers/netmiko
Netmiko登陆设备并配置
from netmiko import ConnectHandler # 导入函数,通过该函数实现SSH登录网络设备
# 创建字典,Netmiko支持多厂商,Arista、Cisco、HP、Juniper、Huawei、Extreme等主流厂商
# 同时,Netmiko支持不同平台的网络设备,如Cisco的IOS、Cisco IOS-XE、Cisco ASA、Cisco NX-OS
R1 = {
"device_type": "cisco_ios", # 由于不同厂商的设备在登陆后命令行特性不一致,需要通过"device_type"来指定登陆设备的类型
"ip": "192.168.254.188", # 远端主机IP
"username": "admin", # SSH登录到远端主机使用的用户名
"password": "admin" # SSH登录到远端主机使用的密码
}
with ConnectHandler(**R1) as connect:
print("Successfully connected to" + " " + R1["ip"]) # 打印连接成功
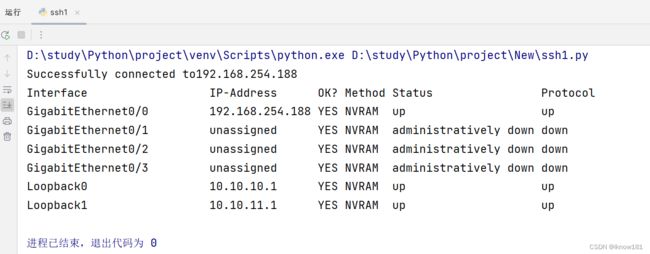
result = connect.send_command("show ip int b") # send command()只支持向设备发送一条命令,一般来说是show/display类的查询命令,用于查看设备的某些信息。当此命令发出后,该函数会一直等待,直到收到设备完整的回显内容为止。如果在一定时间内依然没有读到完整的回显内容,Netmiko则会返回一个OSError
print(result)Netmiko配置设备
from netmiko import ConnectHandler
R1 = {
"device_type": "cisco_ios",
"ip": "192.168.2541.188",
"username": "admin",
"password": "admin"
}
with ConnectHandler(**R1) as connect:
print("Successfully connected to" + R1["ip"])
commands = ['interface g0/0', "description This is a physical interface"]
result = connect.send_config_set(commands)
print(commands)
# send_config_set():用于向设备发送一条或多条配置命令,此处一定是配置命令,因为send_config_set()本身会自动加上configure terminal命令进入配置模式(在结束的时候也会自动加上end),因此,如果要在此时使用show等查看命令,需要在前面加上do(如: do show ip interface brief),否则会无效。
# send_config_set()一般搭配列表来使用
from netmiko import ConnectHandler
R1 = {
"device_type": "cisco_ios",
"ip": "192.168.254.188",
"username": "admin",
"password": "admin"
}
with ConnectHandler(**R1) as connect:
print("Successfully connected to " + R1["ip"])
commands = ['do sh ip int b']
result = connect.send_config_set(commands)
print(result)Netmiko以文件方式配置设备
首先在当前目录下(使用的相对路径)创建一个txt文本——Lab,在里面写入需要执行的命令。
do show ip int b
from netmiko import ConnectHandler
R1 = {
"device_type": "cisco_ios",
"ip": "192.168.254.188",
"username": "admin",
"password": "admin"
}
with ConnectHandler(**R1) as connect:
print("Successfully connected to " + R1["ip"])
File_configure = connect.send_config_from_file("Lab.txt") # 相对路径
print(File_configure)
# connect.send_config_from_file():在配置命令数量较多的时候,将所有配置命令都填入列表中会显得列表很臃肿,因为代码过长,所以导致可读性变差、还会有可能出现设备超时的情况。所以我们可以先把所有的配置命令写入一个配置文件中,然后使用send_config_from_file()去读取该文件的内容帮助我们完成配置。
# 和send_config_set()一样,send_config_from_file()也会自动的去添加"configure terminal"和 "end"命令,所以直接写要配置的命令就可以Netmiko抓取设备配置
from netmiko import ConnectHandler
R1 = {
"device_type": "cisco_ios",
"ip": "192.168.254.188",
"username": "admin",
"password": "admin"
}
with ConnectHandler(**R1) as connect:
print("Successfully connected to " + R1["ip"])
running_config = connect.send_command("show running-config")
print(running_config)Netmiko抓取设备配置并写入文件中
from netmiko import ConnectHandler
R1 = {
"device_type": "cisco_ios",
"ip": "192.168.254.188",
"username": "admin",
"password": "admin"
}
with ConnectHandler(**R1) as connect:
print("Successfully connected to " + R1["ip"])
running_config = connect.send_command("show running-config")
print(running_config)
file = open(file="R1_config.txt", mode="a") # 以写的方式打开文件
file.write(running_config)
file.close()Netmiko批量化部署多台设备
from netmiko import ConnectHandler
host = {
"192.168.254.188",
"192.168.254.189",
"192.168.254.190",
}
for ip in host:
Router = {
"device_type": "cisco_ios",
"ip": ip,
"username": "admin",
"password": "admin"
}
with ConnectHandler(**Router) as connect:
print("Successfully connected to " + Router["ip"])
command = ["username abc password abc"]
run_command = connect.send_config_set(command)
print(run_command)Netmiko批量化抓取设备配置
在lab.txt文本中写入需要抓取的目标设备IP 192.168.254.188 192.168.254.189 192.168.254.19
from netmiko import ConnectHandler
f = open("Lab.txt", mode='r')
for ips in f.readlines():
ip = ips.strip()
Router = {
"device_type": "cisco_ios",
"ip": ip,
"username": "admin",
"password": "admin"
}
with ConnectHandler(**Router) as connect:
print("Successfully connected to " + Router["ip"])
running_config = connect.send_command("show running-config")
print(running_config)
# 写入文件中
backup_file_name = open(file="backup.txt", mode='a')
backup_file_name.write(running_config)
![]()