vue3学习源码笔记(小白入门系列)------KeepAlive 原理
目录
- 说明
-
- 组件是如何被缓存的,什么时候被激活
- 对于KeepAlive 中组件 如何完成激活的
- 对于KeepAlive 中组件 如何完成休眠的
- 总结
说明
Vue 内置了 KeepAlive 组件,实现缓存多个组件实例切换时,完成对卸载组件实例的缓存,从而使得组件实例在来会切换时不会被重复创建。
<template>
<KeepAlive>
<component :is="xxx" />
</KeepAlive>
</template>
当动态组件在随着 xxx 变化时,如果没有 KeepAlive 做缓存,那么组件在来回切换时就会进行重复的实例化,这里就是通过 KeepAlive 实现了对不活跃组件的缓存,只有第一次加载会初始化 instance,后续会使用 缓存的 vnode 再强制patch 下 防止遗漏 有 组件 props 导致的更新,省略了(初始化 instance 和 全量生成组件dom 结构的过程)。
组件是如何被缓存的,什么时候被激活
先得看下 KeepAlive 的实现 ,它本身是一个抽象组件,会将子组件渲染出来
const KeepAliveImpl = {
// 组件名称
name: `KeepAlive`,
// 区别于其他组件的标记
__isKeepAlive: true,
// 组件的 props 定义
props: {
include: [String, RegExp, Array],
exclude: [String, RegExp, Array],
max: [String, Number]
},
setup(props, {slots}) {
// ...
// setup 返回一个函数 就是 组件的render 函数
return () => {
// ...
}
}
每次 子组件改变 就会触发 render 函数
看下 render 函数的详情
const KeepAliveImpl = {
//...
// cache sub tree after render
let pendingCacheKey: CacheKey | null = null
const cacheSubtree = () => {
// fix #1621, the pendingCacheKey could be 0
if (pendingCacheKey != null) {
cache.set(pendingCacheKey, getInnerChild(instance.subTree))
}
}
onMounted(cacheSubtree)
onUpdated(cacheSubtree)
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
cache.forEach(cached => {
const { subTree, suspense } = instance
const vnode = getInnerChild(subTree)
if (cached.type === vnode.type && cached.key === vnode.key) {
// current instance will be unmounted as part of keep-alive's unmount
resetShapeFlag(vnode)
// but invoke its deactivated hook here
const da = vnode.component!.da
da && queuePostRenderEffect(da, suspense)
return
}
unmount(cached)
})
})
// ...
setup(props, { slot }) {
// ...
return () => {
// 记录需要被缓存的 key
pendingCacheKey = null
// ...
// 获取子节点
const children = slots.default()
const rawVNode = children[0]
if (children.length > 1) {
// 子节点数量大于 1 个,不会进行缓存,直接返回
current = null
return children
} else if (
!isVNode(rawVNode) ||
(!(rawVNode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT) &&
!(rawVNode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE))
) {
current = null
return rawVNode
}
// suspense 特殊处理,正常节点就是返回节点 vnode
let vnode = getInnerChild(rawVNode)
const comp = vnode.type
// 获取 Component.name 值
const name = getComponentName(isAsyncWrapper(vnode) ? vnode.type.__asyncResolved || {} : comp)
// 获取 props 中的属性
const { include, exclude, max } = props
// 如果组件 name 不在 include 中或者存在于 exclude 中,则直接返回
if (
(include && (!name || !matches(include, name))) ||
(exclude && name && matches(exclude, name))
) {
current = vnode
return rawVNode
}
// 缓存相关,定义缓存 key
const key = vnode.key == null ? comp : vnode.key
// 从缓存中取值
const cachedVNode = cache.get(key)
// clone vnode,因为需要重用
if (vnode.el) {
vnode = cloneVNode(vnode)
if (rawVNode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE) {
rawVNode.ssContent = vnode
}
}
// 给 pendingCacheKey 赋值,将在 beforeMount/beforeUpdate 中被使用
pendingCacheKey = key
// 如果存在缓存的 vnode 元素
if (cachedVNode) {
// 复制挂载状态
// 复制 DOM
vnode.el = cachedVNode.el
// 复制 component
vnode.component = cachedVNode.component
// 增加 shapeFlag 类型 COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE
// 把缓存的 key 移动到到队首
keys.delete(key)
keys.add(key)
} else {
// 如果缓存不存在,则添加缓存
keys.add(key)
// 如果超出了最大的限制,则移除最早被缓存的值
if (max && keys.size > parseInt(max as string, 10)) {
pruneCacheEntry(keys.values().next().value)
}
}
// 增加 shapeFlag 类型 COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE,避免被卸载
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE
current = vnode
// 返回 vnode 节点
return isSuspense(rawVNode.type) ? rawVNode : vnode
}
}
}
props.max 会确定 缓存组件的最大数量 默认没有上限,但是组件会占用内存 所以并不是 max越大越好
props.include 表示包含哪些组件可被缓存
props.exclude 表示排除那些组件
组件缓存的时机:
组件切换的时候 会保存 上一个组件的vnode 到 cache Map 中 key 是 vnode.key
组件卸载时机:
缓存组件数量超过max,会删除活跃度最低的缓存组件,或者 整个KeepAlive 组件被unmount的时候
对于KeepAlive 中组件 如何完成激活的
当 component 动态组件 is 参数发生改变时 ,
执行 KeepAlive组件 componentUpdateFn 就会执行 上一步的render 函数 会 生成 新的vnode (
然后再 走 patch
再走到 processComponent
再看下 processComponent中 针对 vnode.shapeFlag 为COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE(在keepalive render 函数中 组件类型 会被设置成COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE ) 有特殊处理
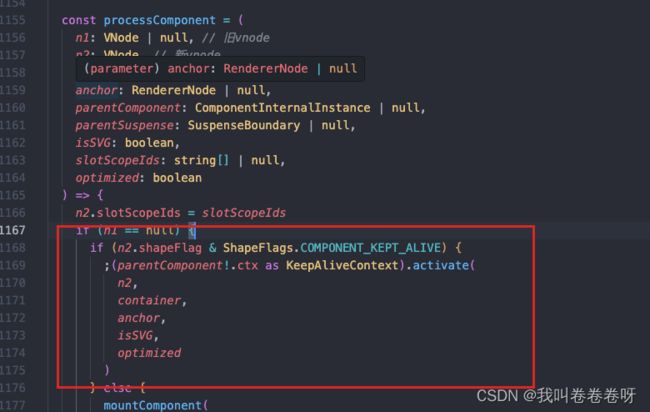
其中 parentComponent 其实指向的是 KeepAlive 组件, 得出 processComponent 实际调用的是 KeepAlive 组件上下文中的 activate 方法 去做挂载操作
sharedContext.activate = (vnode, container, anchor, isSVG, optimized) => {
const instance = vnode.component!
// 先直接将
move(vnode, container, anchor, MoveType.ENTER, parentSuspense)
// in case props have changed
patch(
instance.vnode,
vnode,
container,
anchor,
instance,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
vnode.slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
instance.isDeactivated = false
if (instance.a) {
invokeArrayFns(instance.a)
}
const vnodeHook = vnode.props && vnode.props.onVnodeMounted
if (vnodeHook) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, instance.parent, vnode)
}
}, parentSuspense)
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
// Update components tree
devtoolsComponentAdded(instance)
}
}
先直接将缓存的dom 先挂载到 container 下面(节约了 重新生成dom的 时间 ),在强制patch 一下 避免遗漏 有props 改变引发的更新。这时候 缓存的组件就被激活了。
对于KeepAlive 中组件 如何完成休眠的
<template>
<KeepAlive>
<component :is="xxx" />
</KeepAlive>
</template>
is 发生改变 会导致 上一次的组件执行unmount 操作
const unmount = (vnode, parentComponent, parentSuspense, doRemove = false) => {
// ...
const { shapeFlag } = vnode
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE) {
;(parentComponent!.ctx as KeepAliveContext).deactivate(vnode)
return
}
// ...
}
同理 也会走到。keepalive 上下文中的 deactivate 方法
sharedContext.deactivate = (vnode: VNode) => {
const instance = vnode.component!
move(vnode, storageContainer, null, MoveType.LEAVE, parentSuspense)
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
if (instance.da) {
invokeArrayFns(instance.da)
}
const vnodeHook = vnode.props && vnode.props.onVnodeUnmounted
if (vnodeHook) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, instance.parent, vnode)
}
instance.isDeactivated = true
}, parentSuspense)
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
// Update components tree
devtoolsComponentAdded(instance)
}
}
卸载态函数 deactivate 核心工作就是将页面中的 DOM 移动到一个隐藏不可见的容器 storageContainer 当中,这样页面中的元素就被移除了。当这一切都执行完成后,最后再通过 queuePostRenderEffect 函数,将用户定义的 onDeactivated 钩子放到状态更新流程后
总结
1.组件是通过类似于 LRU 的缓存机制来缓存的,并为缓存的组件 vnode 的 shapeFlag 属性打上 COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE 属性,当组件在 processComponent 挂载时,如果存在COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE 属性,则会执行激活函数,激活函数内执行具体的缓存节点挂载逻辑。
2.缓存不是越多越好,因为所有的缓存节点都会被存在 cache 中,如果过多,则会增加内存负担。
3.丢弃的方式就是在缓存重新被激活时,之前缓存的 key 会被重新添加到队首,标记为最近的一次缓存,如果缓存的实例数量即将超过指定的那个最大数量,则最久没有被访问的缓存实例将被丢弃。