基于Spring boot轻松实现一个多数据源框架
Spring Boot 提供了 Data JPA 的包,允许你使用类似 ORM 的接口连接到 RDMS。它很容易使用和实现,只需要在 pom.xml 中添加一个条目(如果使用的是 Maven,Gradle 则是在 build.gradle 文件中)。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
在Main Spring Application类中添加 2 个注释:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableJpaRepositories
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class SpringMainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringMainApplication.class, args);
}
}最后添加一个数据库连接包,配置数据库连接即可实现与数据库通信。
接下来,我们开始配置多数据源连接。
注意:多个数据库应该具有相同的驱动程序。无法连接到不同的数据库,如 MySql 和 Postgres SQL 数据库。数据库必须相同。此外,数据库模式必须相同,不同模式的 2 个数据库无法进行连接。
多数据源有哪些应用场景?
1.支持具有相同模式的同一应用程序内的多租户。
2.动态模拟多个环境数据库上的行为 ,而不需要重新启动应用程序。 例如,你可以动态连接到开发数据库或 QA 数据库,而无需重新启动应用程序。
3.支持多个数据库来模拟各种自动化测试场景。不同数据库可能具有不同的配置和静态信息,意味着你可以用一个自动化测试脚本覆盖多个测试用例。
4.在同一个应用程序中支持多个组织。根据用户登录,可以动态决定他们的数据应进入哪个组织的数据库。
5.一次性为多个数据库插入数据。例如,你有一个从脚本创建数据的批处理作业,你可以一次性连接到多个数据库,并对所有这些数据库运行脚本,而无需指向不同的应用程序或重新启动服务器来执行此操作。
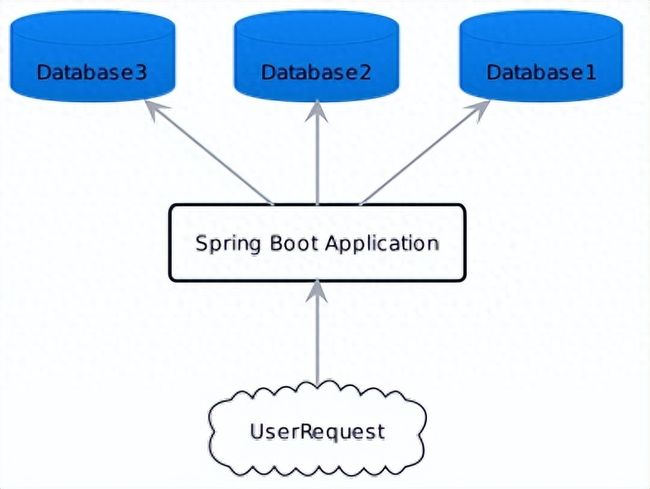
多数据源示意图如下:
第一步:添加 pom 依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
io.springfox
springfox-swagger2
2.9.2
io.springfox
springfox-swagger-ui
2.9.2
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.12
provided
org.postgresql
postgresql
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-parent
${spring-cloud-dependencies.version}
pom
import
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-gcp-dependencies
${project.version}
pom
import
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-surefire-plugin
第二步:添加数据库连接配置
app.datasource.db1.jdbc-url=jdbc:postgresql://db1.com:5432/dbname1
app.datasource.db1.username=postgres
app.datasource.db1.password=password
app.datasource.db2.jdbc-url=jdbc:postgresql://db2.com:5432/dbname2
app.datasource.db2.username=postgres
app.datasource.db2.password=password
app.datasource.db3.jdbc-url=jdbc:postgresql://db3.com:5432/dbname3
app.datasource.db3.username=postgres
app.datasource.db3.password=password这是 3 个独立的 PostgresSQL 实例,具有相同的模式但具有不同的数据。
第三步:添加多数据库配置。
首先,在 Spring 应用程序主文件中添加注解:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableJpaRepositories
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class MultidatabaseApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MultidatabaseApplication.class, args);
}
}添加配置类:
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(
entityManagerFactoryRef = "multiEntityManager",
transactionManagerRef = "multiTransactionManager")
@EntityScan("com.sample.client.repositories.dto.entity")
public class DatabaseConfiguration {
//添加 JPA 实体路径
private final String PACKAGE_SCAN = "com.sample.client.repositories.dto.entity";
// 将db1设置为主数据库
@Primary
@Bean(name = "db1DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties("app.datasource.db1")
public DataSource db1DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(HikariDataSource.class).build();
}
//db2连接数据源注入
@Bean(name = "db2DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties("app.datasource.db2")
public DataSource db2DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(HikariDataSource.class).build();
}
//db3连接数据源注入
@Bean(name = "db3DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties("app.datasource.db3")
public DataSource db3DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(HikariDataSource.class).build();
}
//多数据源配置
@Bean(name = "multiRoutingDataSource")
public DataSource multiRoutingDataSource() {
Map targetDataSources = new HashMap<>();
targetDataSources.put(ClientNames.DB1, db1DataSource());
targetDataSources.put(ClientNames.DB2, db2DataSource());
targetDataSources.put(ClientNames.DB3, db3DataSource());
MultiRoutingDataSource multiRoutingDataSource
= new MultiRoutingDataSource();
multiRoutingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(db1DataSource());
multiRoutingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
return multiRoutingDataSource;
}
//多实体配置代码
@Bean(name = "multiEntityManager")
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean multiEntityManager() {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean em
= new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
em.setDataSource(multiRoutingDataSource());
em.setPackagesToScan(PACKAGE_SCAN);
HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter
= new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
em.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdapter);
em.setJpaProperties(hibernateProperties());
return em;
}
@Bean(name = "multiTransactionManager")
public PlatformTransactionManager multiTransactionManager() {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager
= new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(
multiEntityManager().getObject());
return transactionManager;
}
@Primary
@Bean(name="entityManagerFactory")
public LocalSessionFactoryBean dbSessionFactory() {
LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactoryBean = new LocalSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(multiRoutingDataSource());
sessionFactoryBean.setPackagesToScan(PACKAGE_SCAN);
sessionFactoryBean.setHibernateProperties(hibernateProperties());
return sessionFactoryBean;
}
//添加 hibernate 属性
private Properties hibernateProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("hibernate.show_sql", true);
properties.put("hibernate.format_sql", true);
properties.put("hibernate.dialect", "org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect");
properties.put("hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings", false);
properties.put("hibernate.jdbc.lob.non_contextual_creation", true);
return properties;
}
} 这样就完成了我们的多数据库配置。
com.sample.client.repositories.dto.entity — 此目录包含 3 个数据库通用的 JPA 实体。
MultiRoutingDataSource类是我们的实际实现,允许我们连接到多个数据库
接下来,我们还需要一个DBContextHolder类来保存数据库引用并在运行时动态更改数据库。
public class DBContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setCurrentDb(ClientNames dbType) {
contextHolder.set(dbType);
}
public static ClientNames getCurrentDb() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
public static void clear() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
} ClientNames枚举类如下:
public enum ClientNames {
DB1, DB2, DB3
}接下来我们需要对MultiRoutingDataSource进行重写:
public class MultiRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DBContextHolder.getCurrentDb();
}
}determineCurrentLookupKey 方法用于决定应用程序应该动态连接到哪个数据库。
好了,我们的配置就完成了。接下来,我们测试下多数据源是否生效:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/client")
public class ClientDataController {
@Autowired
private ClientMasterService clientMasterService;
@GetMapping("/{clientdb}")
public String findFromDatabase(@PathVariable String clientdbName) {
return clientMasterService.getClientNames(clientdbName);
}
}ClientMasterService实现如下:
@Service
public class ClientMasterService {
@Autowired
private ClientMasterRepository clientMasterRepository;
public String getClientNames(String client) {
switch (client) {
case "db1":
DBContextHolder.setCurrentDb(ClientNames.DB1);
break;
case "db2":
DBContextHolder.setCurrentDb(ClientNames.DB2);
break;
case "db3":
DBContextHolder.setCurrentDb(ClientNames.DB3);
break;
}
Entity1 e1 = clientMasterRepository.findByEntity1Name("John Doe");
if(e1 != null) {
return "found in database: " + client + " with id " + e1.getId();
}
return "found in " + client + " nada!";
}
}ClientMasterService使用DBContextHolder类根据从 Rest 端点传入的数据库名称(db1、db2 或 db3)设置要指向的数据库。
最后,编写 JPA Repository 基础代码:
@Repository
public interface ClientMasterRepository extends JpaRepository {
Entity1 findByEntity1Name(String name);
} Entity1 类如下:
@Entity
@Table(name = "entity1")
@Getter
@Setter
public class Entity1 implements Serializable {
@Id
@Column(name = "id", nullable = false)
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "entity1Name")
private String entity1Name;
}这样就完成了整个多数据源的配置!!!
总结
如果你有多租户需求,或者多环境测试需求等,可以自己尝试编写一个多数据源框架,也可以引入第三方库来解决此需求。