模拟退火算法求解TSP问题(python)
模拟退火算法求解TSP的步骤参考书籍《Matlab智能算法30个案例分析》。
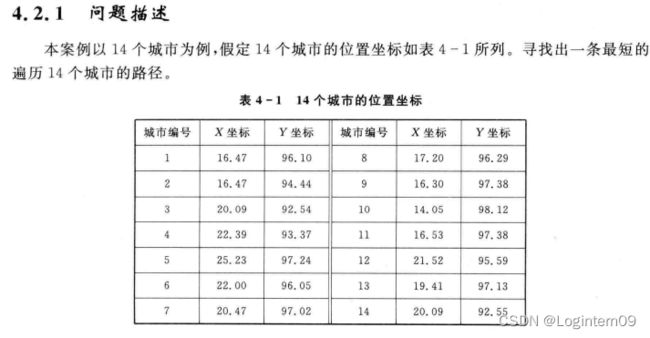
问题描述
TSP问题描述在该书籍的第4章
算法流程
部分实现代码片段
坐标轴转换成两点之间直线距离长度的代码
coordinates = np.array([(16.47, 96.10),
(16.47, 94.44),
(20.09, 92.54),
(22.39, 93.37),
(25.23, 97.24),
(22.00, 96.05),
(20.47, 97.02),
(17.20, 96.29),
(16.30, 97.38),
(14.05, 98.12),
(16.53, 97.38),
(21.52, 95.59),
(19.41, 97.13),
(20.09, 92.55),])
# 将距离坐标矩阵转换成两点之间实际的直线距离
city_num = coordinates.shape[0]
def get_distanceGraph(coordinates):
# 计算城市间的欧式距离
diatance_graph = np.zeros((city_num, city_num))
# 初始化生成矩阵
for i in range(city_num):
for j in range(i, city_num):
diatance_graph[i][j] = diatance_graph[j][i] = np.linalg.norm(coordinates[i] - coordinates[j])
print("diatance_graph", diatance_graph)
return diatance_graph
求解TSP问题路径长度的代码
def cal_length(cur_solution, distance_graph):
# 计算路线长度
total_length = 0
visited_city_list = [cur_solution[0]]
for i in range(city_num):
visited_city = visited_city_list[-1]
cur_city = cur_solution[i]
visited_city_id = visited_city - 1
cur_city_id = cur_city - 1
next_city_length = distance_graph[visited_city_id][cur_city_id]
total_length += next_city_length
visited_city_list.append(cur_city)
print("total_length", total_length)
return total_length
使用一个路径长度矩阵相对简单,可以进行笔算验证解结果的算例,验证计算TSP路径长度的代码是可行的
可以笔算验证的算例代码
# 各个节点之间的欧氏距离
distance_list = [[0, 4.0, 6.0, 7.5, 9.0, 20.0, 10.0, 16.0, 8.0],
[4.0, 0, 6.5, 4.0, 10.0, 5.0, 7.5, 11.0, 10.0],
[6.0, 6.5, 0, 7.5, 10.0, 10.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],
[7.5, 4.0, 7.5, 0, 10.0, 5.0, 9.0, 9.0, 15.0],
[9.0, 10.0, 10.0, 10.0, 0, 10.0, 7.5, 7.5, 10.0],
[20.0, 5.0, 10.0, 5.0, 10.0, 0, 7.0, 9.0, 7.5],
[10.0, 7.5, 7.5, 9.0, 7.5, 7.0, 0, 7.0, 10.0],
[15.0, 11.0, 7.5, 9.0, 7.5, 9.0, 7.0, 0, 10.0],
[8.0, 10.0, 7.5, 15.0, 10.0, 7.5, 10.0, 10.0, 0]]
demand_node_num = 9
supply_node_num = 0
city_num = 9
distance_graph = np.zeros((demand_node_num+supply_node_num, demand_node_num+supply_node_num))
for i in range(demand_node_num+supply_node_num):
distance_graph[i] = np.array(distance_list[i])
cur_solution = [3, 9, 6, 4, 7, 8, 1, 5, 2]
length = cal_length(cur_solution, distance_graph)
print("length", length)
Metropolis准则函数
# Metropolis准则函数
def Metropolis_func(cur_solution, new_solution, distance_graph, cur_temp):
# 计算新旧解之间的能量之差,如果能量降低:以概率1接受新解,如果能量升高,以一定概率接受劣化解
dC = cal_length(new_solution, distance_graph) - cal_length(cur_solution, distance_graph)
if dC < 0:
cur_solution = new_solution
cur_length = cal_length(cur_solution, distance_graph)
elif pow(math.e, -dC/cur_temp) >= np.random.rand(): # 大于一个随机生成的数:
cur_solution = new_solution
cur_length = cal_length(cur_solution, distance_graph)
else:
cur_length = cal_length(cur_solution, distance_graph)
return cur_solution, cur_length