Autowired & Resource注解一站式彻底搞懂
注解Autowired有三种依赖注入的方式:属性注入、set方式注入、构造器注入。默认是通过bean类型注入,如果需要按照名称(byName)来装配,可以结合@Qualifier注解一起使用。
注解Resource有2种依赖注入的方式:属性注入、set方式注入。
- 如果没有指定name属性,当注解写在字段上时,默认取字段名,按照名称查找。
- 当注解标注在属性的setter方法上,即默认取属性名作为bean名称寻找依赖对象。
- 当找不到与名称匹配的bean时才按照类型进行装配。但是需要注意的是,如果name属性一旦指定,就只会按照名称进行装配。
public class BlogController {
@Autowired
private LtsClient ltsClient;
public BlogController(@Autowired LtsClient ltsClient){// 此处@Autowired注解可以省掉
this.ltsClient = ltsClient;
}
@Autowired
public void setLtsClient(LtsClient ltsClient) {
this.ltsClient = ltsClient;
}
}
1.Resource & Autowired注解触发时机
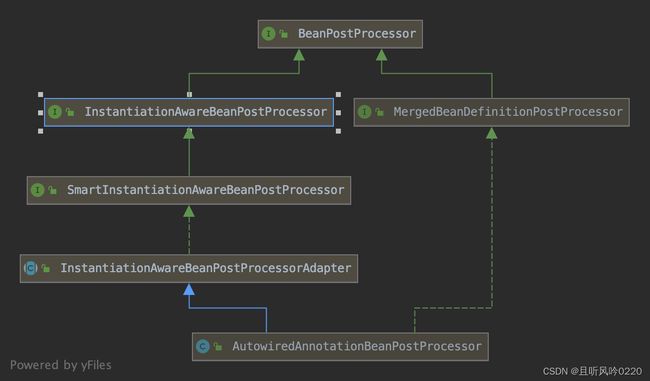
抽象类InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter存在的意义就是为了接口子类不需要实现的接口方法,由其空实现即可。
构造器依赖注入:利用 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 后置处理器解析目标类的构造器,根据参数个数确定构造器的类型,最终将目标类的构造器抽象成类Constructor,并做本地缓存处理。
属性注入、set方式注入:利用MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor后置处理器解析目标类存在的所有字段、方法,分别对应生成AutowiredFieldElement 、AutowiredMethodElement,并做本地缓存处理。
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory {
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args){
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {// ========================= 涉及构造器注入方式
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
...
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
// ========================= MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor后置处理器解析属性、方法set方式注入依赖
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
...
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
...
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
return exposedObject;
}
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
...
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
// 针对的是 构造方法 解决依赖注入
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// 普通的构造方法
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
protected Constructor<?>[] determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
if (beanClass != null && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 调用 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 后置处理器之determineCandidateConstructors方法
Constructor<?>[] ctors = ibp.determineCandidateConstructors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null) {
return ctors;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
...
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
...
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// =======================调用 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 后置处理器开始目标类的属性装配
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
...
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
...
}
}
2.获取符合Autowired&Resource条件的候选类
以下是注解Autowired三种依赖方式都会选择的bean装配方式:type or name 两种方式。
注入方式解决依赖问题的前提是在IOC容器中已经存在同class不同bean name的一个或者多个bean实例。
利用属性类在目标类的字段名跟众多候选类beanName对比,最终返回符合条件的实例bean。
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory{
// autowiredBeanNames集合元素为候选类中符合属性类条件的对应实例bean的beanName
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, String requestingBeanName,
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, TypeConverter typeConverter){
...// 代码简化
return doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);;
}
}
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor,String beanName,Set
autowiredBeanNames,TypeConverter typeConverter){
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
...
// 如果IOC容器中存在多个同Class的bean实例,则单独的Autowired注解导致返回全部的候选类,否则返回只满足注解Qualifier条件的候选类
//首先根据属性类的类型获取IOC容器中全部的候选类。如果提前初始化多个候选类实例,则实例Bean的名称一定不能相等
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {// 如果@Autowired其required属性为true则抛出异常
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;// 返回null时并不会抛出异常,最终目标类中的属性类装配失败,最终为null
}
...
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
// 利用 属性类的类信息descriptor 最终从候选类中确定出最终的bean实例之autowiredBeanName
// 其实也是利用属性类在目标类的字段名跟众多候选类beanName对比
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {// 候选类都不符合条件,则最终抛出异常
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);
}
}
...
// 最终找出autowiredBeanName对应的bean实例
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}else {
// 但是如果返回只有一个候选类,则即使其实例名对应的name属性非autowiredBeanName,也不会抛出异常,则返回唯一的实例
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
// 通过候选类的类信息,从IOC容器中获取或者创建其对应的bean实例
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
Object result = instanceCandidate;
return result;
}
protected Map findAutowireCandidates(String beanName, Class requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
boolean eager = descriptor.isEager();
// 针对属性类,获取当前IOC容器中存在的候选类的名称
String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this, requiredType, true,eager);
Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(candidateNames.length);
...
// 遍历候选类,找到符合Autowired或者Autowired、Qualifier两个注解指明的对应候选类信息
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, descriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);//符合条件集合中添加候选类信息
}
}
...
return result;
}
protected boolean isAutowireCandidate(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd,
DependencyDescriptor descriptor, AutowireCandidateResolver resolver) {
String beanDefinitionName = BeanFactoryUtils.transformedBeanName(beanName);
...
String[] aliases = getAliases(beanDefinitionName));
// QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver#isAutowireCandidate
return resolver.isAutowireCandidate(new BeanDefinitionHolder(mbd, beanName, aliases), descriptor);
}
}
beanName:是指目标类的beanName。
descriptor:维护被注入的属性bean对应的Class值。
总结:不管是那种注解方式,都是根据注入类的类型从 IOC容器中获取候选类
2.1.利用注解Autowired & Qualifier 过滤候选类
存在两种情况:
- 如果只有注解Autowired则一直返回true,即可能存在多个候选类。
- 如果同时存在Autowired、Qualifier注解则只有符合注解Qualifier条件才能返回true。
- 条件就是候选类对应的bdHolder其bean实例名等于属性类注解Qualifier其属性value值。
public class QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver extends GenericTypeAwareAutowireCandidateResolver {
public boolean isAutowireCandidate(BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
// bdHolder 是ioc容器中某个候选类对应的BeanDefinition
// descriptor 是目标类通过依赖注入的属性的class信息
// 核心就是候选类对应的BeanDefinitionHolder中class信息是否与属性类的class信息一致
boolean match = super.isAutowireCandidate(bdHolder, descriptor);
if (match) {//不管是否@Qualifier注解都会返回true
match = checkQualifiers(bdHolder, descriptor.getAnnotations());
...
}
return match;
}
protected boolean checkQualifiers(BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder, Annotation[] annotationsToSearch) {
...
SimpleTypeConverter typeConverter = new SimpleTypeConverter();
for (Annotation annotation : annotationsToSearch) {// 遍历从属性类得到的全部注解信息
Class<? extends Annotation> type = annotation.annotationType();
boolean checkMeta = true;
boolean fallbackToMeta = false;
if (isQualifier(type)) {// 当前注解的类型type 是否为@Qualifier注解
if (!checkQualifier(bdHolder, annotation, typeConverter)) {
fallbackToMeta = true;
}
else {
checkMeta = false;
}
}
...
}
return true;
}
protected boolean checkQualifier(BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder, Annotation annotation,TypeConverter typeConverter){
Class<? extends Annotation> type = annotation.annotationType();
RootBeanDefinition bd = (RootBeanDefinition) bdHolder.getBeanDefinition();
AutowireCandidateQualifier qualifier = bd.getQualifier(type.getName());
...
Map<String, Object> attributes = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotationAttributes(annotation);
...
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : attributes.entrySet()) {//获取@Qualifier注解上全部属性值
String attributeName = entry.getKey();// 属性Key
Object expectedValue = entry.getValue();// 属性值 例如 @Qualifier 的属性key为 value = "ltsClient"
Object actualValue = null;
...
if (actualValue == null && attributeName.equals("value") &&
expectedValue instanceof String && bdHolder.matchesName((String) expectedValue)) {
continue;// 成立的核心条件为 候选类属性value值跟bdHolder中beanName值保持一样
}
...
if (!expectedValue.equals(actualValue)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
3.InjectionMetadata & InjectedElement

其中ResourceElement是指@Resource注解。AutowiredMethodElement & AutowiredFieldElement 均是实现了抽象类inject方法。
public class InjectionMetadata {
private final Class<?> targetClass;// 依赖注入的类信息
private final Collection<InjectedElement> injectedElements;// 依赖注入对应的注入方法,即属性、set方法两种方式
public InjectionMetadata(Class<?> targetClass, Collection<InjectedElement> elements) {
this.targetClass = targetClass;
this.injectedElements = elements;
}
public void inject(Object target, String beanName,PropertyValues pvs) {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate = (checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
// 调用具体的InjectedElement。AutowiredMethodElement or AutowiredFieldElement
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
public abstract static class InjectedElement {
// 子类ResourceElement注入依赖逻辑
protected void inject(Object target,String requestingBeanName, PropertyValues pvs) {
if (this.isField) {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}else {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
Method method = (Method) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
}
}
}
4.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- 如上述分析得知,针对三种不同的注入方式均存在预处理,即本地缓存。
- 被依赖的类【属性类】真正装配之时直接缓存提取相关注入方式对应的核心类即可。
public class AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor{
private final Map<Class<?>, Constructor<?>[]> candidateConstructorsCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
private final Map<String, InjectionMetadata> injectionMetadataCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
@Override// 实现接口SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 提前处理目标类的构造方法
public Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, final String beanName){
...
Constructor<?>[] candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
synchronized (this.candidateConstructorsCache) {
candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);
if (candidateConstructors == null) {
// 利用反射方法 获取目标类全部的构造方法
Constructor<?>[] rawCandidates = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
...
for (Constructor<?> candidate : rawCandidates) {
...
}
if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {
candidateConstructors = candidates.toArray(new Constructor<?>[0]);
// 利用反射方法rawCandidates[0].getParameterCount() 获取构造方法存在的参数个数
}else if (rawCandidates.length == 1 && rawCandidates[0].getParameterCount() > 0) {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {rawCandidates[0]};
} ... else {
candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[0];
}
this.candidateConstructorsCache.put(beanClass, candidateConstructors);
}
}
}
return (candidateConstructors.length > 0 ? candidateConstructors : null);
}
@Override// 实现接口MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class beanType, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
...
return buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);;
}
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
...
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
// 遍历目标类所有字段存在的注解
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {return;}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
@Override// 属性装配
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
// 获取上述解析得到的InjectedElement:AutowiredFieldElement or AutowiredMethodElement
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);// 调用InjectedElement对应的子类
return pvs;
}
private class AutowiredFieldElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
...
// 承继章节2
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
Object value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
...
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);// 反射方式给目标类设置属性值
}
}
}
private class AutowiredMethodElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Method method = (Method) this.member;
Object[] arguments;
int argumentCount = method.getParameterCount();
arguments = new Object[argumentCount];
...
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
MethodParameter methodParam = new MethodParameter(method, i);
DependencyDescriptor currDesc = new DependencyDescriptor(methodParam, this.required);
currDesc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
descriptors[i] = currDesc;
// 承继章节2
Object arg = beanFactory.resolveDependency(currDesc, beanName, autowiredBeans, typeConverter);
if (arg == null && !this.required) {
arguments = null;
break;
}
arguments[i] = arg;
}
...
if (arguments != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(bean, arguments);
}
}
}
}
以上分别对应注解Autowired三种依赖方式,其中属性注入即AutowiredFieldElement、方法set注入即AutowiredMethodElement。
5.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
@Resource注解对应的后置处理器,原理跟AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor基本一致。
public class CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor{
@Override
protected Object getResource(LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {
...
return autowireResource(this.resourceFactory, element, requestingBeanName);
}
protected Object autowireResource(BeanFactory factory, LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
Object resource;
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames;
// ResourceElement#name属性要不是注解@Resource属性name值,要不是属性类的字段名
String name = element.name;
if (factory instanceof AutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory = (AutowireCapableBeanFactory) factory;
DependencyDescriptor descriptor = element.getDependencyDescriptor();
// 如果检查到IOC容器中没有name属性对应的候选类,则尝试利用属性类的type重新创建候选类。过程参考章节2
if (this.fallbackToDefaultTypeMatch && element.isDefaultName && !factory.containsBean(name)) {
autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>();
resource = beanFactory.resolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, null);
if (resource == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.getLookupType(), "No resolvable resource object");
}
}else {// 如果IOC容器中已经存在name属性对应的候选类,则直接获取
resource = beanFactory.resolveBeanByName(name, descriptor);
autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);
}
}
else {
resource = factory.getBean(name, element.lookupType);
autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);
}
...
return resource;
}
public ResourceElement(Member member, AnnotatedElement ae, PropertyDescriptor pd) {
super(member, pd);// Member是指反射中Field、Method、Constructor等类的父类,此处是指Field
Resource resource = ae.getAnnotation(Resource.class);
String resourceName = resource.name();// 1、获取@Resource的name属性值
Class<?> resourceType = resource.type();
this.isDefaultName = !StringUtils.hasLength(resourceName);
if (this.isDefaultName) {// 2、一种情况是@Resource没有显式配置name属性,另一种情况是配置@Resource的type属性
resourceName = this.member.getName();//3、获取目标类中该属性类的字段名,称之为默认的属性类在IOC容器中的beanName
if (this.member instanceof Method && resourceName.startsWith("set") && resourceName.length() > 3) {
resourceName = Introspector.decapitalize(resourceName.substring(3));
}
}else if (embeddedValueResolver != null) {
resourceName = embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(resourceName);
}
...
this.name = (resourceName != null ? resourceName : "");
this.lazyLookup = (lazy != null && lazy.value());
}
@Override
protected Object getResourceToInject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {
return (this.lazyLookup ? buildLazyResourceProxy(this, requestingBeanName) :
getResource(this, requestingBeanName));
}
}
6.总结
- 不管是@Resource or @Autowired,只要是通过属性类即type进行匹配,则最终转化为属性类在目标类的字段名匹配。
- 单独@Autowired or @Autowired、@Qualifier组合使用的前提是应用中一定存在对应的bean,否则编译期存在异常提醒。
- @Resource利用type匹配,如果存在多个候选类则候选类中存在beanName与属性类在目标类的字段名匹配;如果只有一个候选类则不管匹配与否,都会返回该候选类作为属性类的bean实例。
- @Resource只要存在name 属性指明候选类的beanName,则必须存在对应的候选类,否则编译期存在异常提醒。
- @Resource没有显式指定name属性则不管是否存在候选类与属性类在目标类的字段名匹配,编译期均不会异常提醒。因为不管匹配与否,均有可能作为属性类的实例返回【候选类是多个则必须匹配,如果有且仅有一个候选类即使不匹配也可以正常返回】。