Spring事务和事务传播机制
为什么需要事务
事务定义
将一组操作封装成一个执行单元(封装到一起),要么全部成功,要么全部失败。
为什么用到事务
比如 :A 给 B 转100¥,
B收到了100¥。
如果没有事务,第一步执行成功了,第二步执行失败了,那么A用户的钱就消失不见了。如果使用事务来解决,这组操作,要么都成功,要么都失败。
怎么实现事务
Spring(Spring Boot)实现事务两种方法:
1) 通过代码的方式手动实现事务(手动挡的车)
2) 通过注解的方式实现声明式事务(自动挡的车)
MySQL中的事务使用
MySQL 有 3 个重要的操作:开启事务、提交事务、回滚事务,它们对应的操作命令如下:
-- 开启事务
start transaction;
-- 业务执⾏
-- 提交事务
commit;
-- 回滚事务
rollback;Spring编程式事务(了解)
Spring ⼿动操作事务和上⾯ MySQL 操作事务类似,它也是有 3 个重要操作步骤:开启事务(获取事务)、提交事务、回滚事务。
SpringBoot 内置了两个对象,DataSourceTransactionManager ⽤来获取事务(开启事务)、提交或 回滚事务的,而TransactionDefinition 是事务的属性,在获取事务的时候需要将 TransactionDefinition 传递进去从而获得⼀个事务 TransactionStatus,实现代码如下:
1) 通过代码的方式手动实现事务
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager;
@Autowired
private TransactionDefinition transactionDefinition;
@RequestMapping("/add")
public int add(UserInfo userInfo) {
// 非空校验
if (userInfo == null || StringUtils.hasLength(userInfo.getUsername())
|| !StringUtils.hasLength(userInfo.getPassword())) {
return 0;
}
//1、开启事务
TransactionStatus transactionStatus =
transactionManager.getTransaction(transactionDefinition);
// 手动设置创建时间和修改时间的默认值
userInfo.setCreatetime(LocalDateTime.now().toString());
userInfo.setUpdatetime(LocalDateTime.now().toString());
int result = userService.add(userInfo);
System.out.println("添加:" + result);
// //2、回滚事务
// transactionManager.rollback(transactionStatus);
transactionManager.commit(transactionStatus);
return result;
}
}2) 通过注解的方式实现声明式事务
@Transactional 特点:
a. 可以添加在类上或方法上
b. 在方法执行前自动开启事务,在方法执行完(没有任何异常)自动提交事务,但是如果在方法执行期间出现异常,那么将自动回滚事务
@Transactional // 声明式事务(自动提交)
@RequestMapping("/insert")
public Integer insert(UserInfo userInfo) {
// 非空校验
if (userInfo==null || !StringUtils.hasLength(userInfo.getUsername())
|| !StringUtils.hasLength(userInfo.getPassword())) {
return 0;
}
int result = userService.add(userInfo);
System.out.println("添加 insert:" + result);
int num = 10/0;
return result;
}
@Transactional 注意事项:
@Transactional // 声明式事务(自动提交)
@RequestMapping("/insert")
public Integer insert(UserInfo userInfo) {
// 非空校验
if (userInfo==null || !StringUtils.hasLength(userInfo.getUsername())
|| !StringUtils.hasLength(userInfo.getPassword())) {
return 0;
}
int result = userService.add(userInfo);
System.out.println("添加 insert:" + result);
try {
int num = 10/0;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return result;
}问题:当程序中有 try-catch 之后,即使程序发生异常,那么事务也不会自动回滚~
解决:
1、将异常抛出去(不推荐)
try {
int num = 10/0;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 1、将异常继续抛出
throw e;
}2、使用代码
try {
int num = 10/0;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 1、将异常继续抛出
//throw e;
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
// 2、手动回滚事务
TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly();
}Spring 中设置事务隔离级别
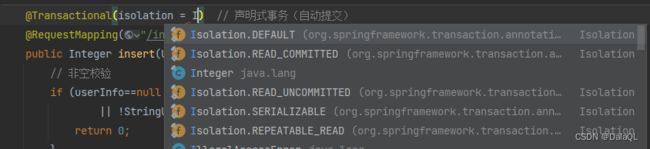
Spring 中事务隔离级别可以通过 @Transactional 中的 isolation 属性进⾏设置,具体操作如下图所 示:
MySQL 事务隔离级别有 4 种
Spring 中设置事务隔离级别
| 事务隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 读未提交 (READ UNCOMMITTED) | √ | √ | √ |
| 读已提交 (READ COMMITTED) | × | √ | √ |
| 可重复读 (REPEATABLE READ) | × | × | √ |
| 串行化 (SERIALIZABLE) | × | × | × |
脏读:⼀个事务读取到了另⼀个事务修改的数据之后,后⼀个事务⼜进⾏了回滚操作,从⽽导致 第⼀个事务读取的数据是错误的。
不可重复读:⼀个事务两次查询得到的结果不同,因为在两次查询中间,有另⼀个事务把数据修 改了。
幻读:⼀个事务两次查询中得到的结果集不同,因为在两次查询中另⼀个事务有新增了⼀部分数 据。
Spring 事务传播机制
Spring 事务传播机制定义了多个包含了事务的方法,相互调用时,事务是如何在这些方法间进行传递的。
Spring 事务传播机制分类
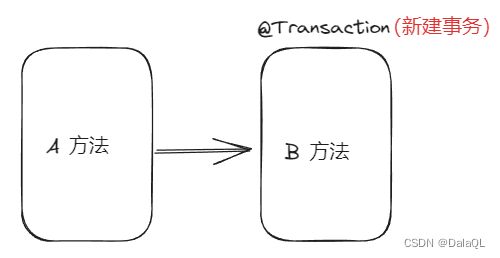
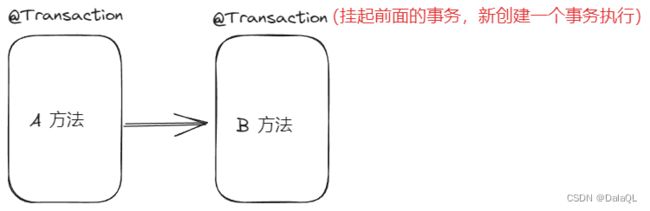
1、Propagation.REQUIRED 默认传播机制,如果调用链存在事务,则加入事务,如果不存在则创建事务。
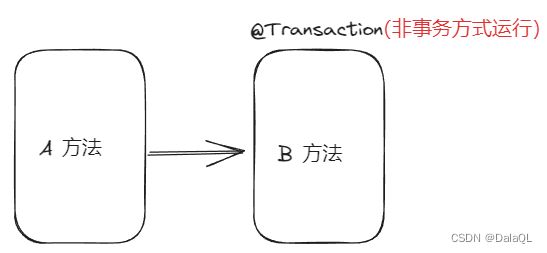
2、Propagation.SUPPORTS 默认传播机制,如果调用链存在事务,则加入事务;如果不存在则非事务方式运行。
3、 Propagation.MANDATORY 强制必须有事务。
4、Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW 创建⼀个新的事务,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂 起。也就是说不管外部⽅法是否开启事务,Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW 修饰的内部⽅法会新开 启自己的事务,且开启的事务相互独立,互不干扰。
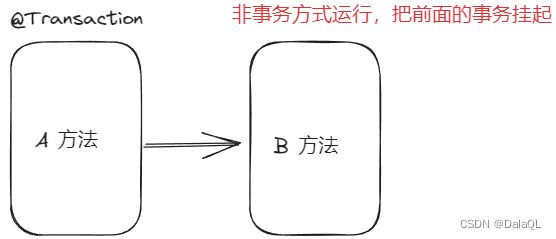
5、Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED 以⾮事务⽅式运⾏,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起。
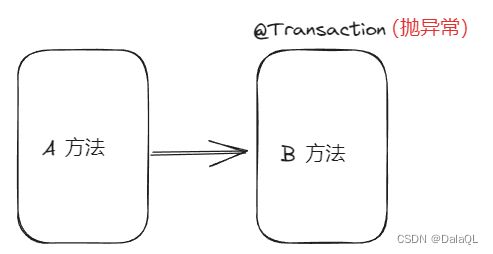
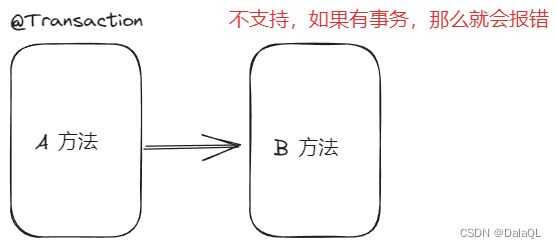
6、Propagation.NEVER 以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
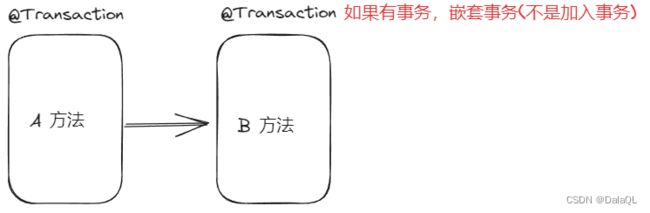
7、Propagation.NESTED 如果当前存在事务,则创建⼀个事务作为当前事务的嵌套事务来运行;如果当前没有事务,则该取值等价于 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED。
eg:
1、UserService
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public Integer add(UserInfo userInfo) {
int result = userMapper.add(userInfo);
System.out.println("用户添加:" + result);
return result;
}2、LogService
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public int add() {
try {
int num = 10/0;
} catch (Exception e) {
TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly();
}
return 1;
}3、UserController
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) // 声明式事务(自动提交)
@RequestMapping("/insert")
public Integer insert(UserInfo userInfo) {
// 非空校验
if (userInfo==null || !StringUtils.hasLength(userInfo.getUsername())
|| !StringUtils.hasLength(userInfo.getPassword())) {
return 0;
}
//添加用户
int result = userService.add(userInfo);
if (result > 0) {
logService.add();
}总结
1. 在 Spring 项目中使用事务,用两种方法手动操作和声明式自动提交,其中后者使用的最多,在方法上添加 @Transactional 就可以实现了。
2. 设置事务的隔离级别 @Transactional(isolation = Isolation.SERIALIZABLE),Spring 中的事务隔 离级别有 5 种。
3. 设置事务的传播机制 @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED),Spring 中的事务 传播级别有 7 种。