ArrayDeque 源码解析(JDK1.8)
目录
一. 前言
二. 源码解析
2.1. 概览
2.2. 属性
2.3. 构造方法
2.4. 入队
2.4.1. addFirst(E, e)
2.4.2. add(E e) & addLast(E e)
2.4.3. offer(E e)
2.5. 扩容
2.6. 出队
2.6.1. poll() & pollFirst()
2.6.2. pollLast()
2.7. 删除元素
2.8. 获取元素
2.9. 栈操作
一. 前言
ArrayDeque 和
LinkedList 是Deque的两个通用实现,由于官方更推荐使用ArrayDeque用作栈和队列,由于作者已经讲解过 LinkedList,本文将着重讲解ArrayDeque的具体实现。
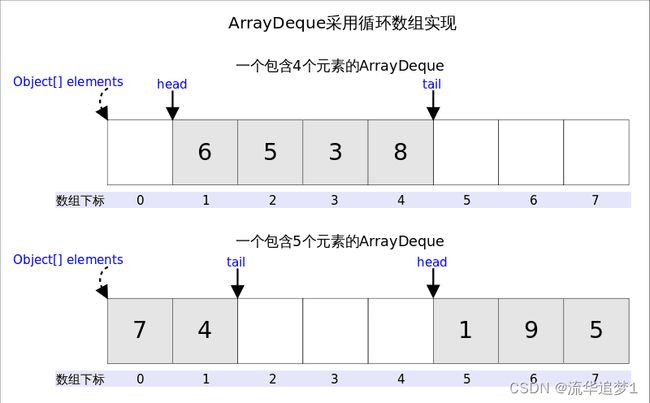
双端队列是一种特殊的队列,它的两端都可以进出元素,故而得名双端队列。ArrayDeque 是一种以数组方式实现的双端队列,它是非线程安全的。由其名字可以看出,其是一个由数组实现的双端队列,对比 LinkedList 是由链表实现的双端队列。
从名字可以看出ArrayDeque底层通过数组实现,为了满足可以同时在数组两端插入或删除元素的需求,该数组还必须是循环的,即循环数组(circular array),也就是说数组的任何一点都可能被看作起点或者终点。ArrayDeque是非线程安全的(not thread-safe),当多个线程同时使用的时候,需要程序员手动同步;另外,该容器不允许放入null元素。
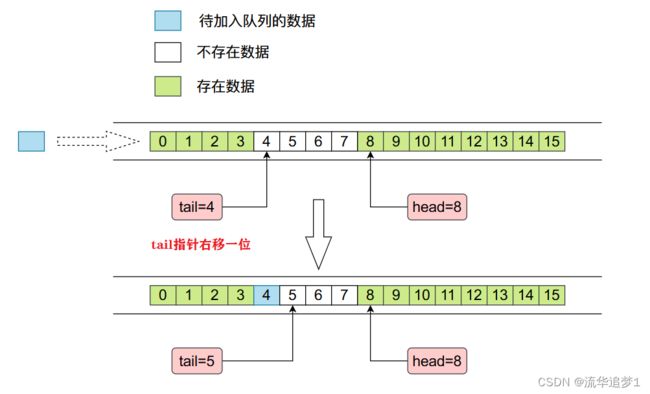
上图中我们看到,head指向首端第一个有效元素,tail指向尾端第一个可以插入元素的空位。因为是循环数组,所以head不一定总等于0,tail也不一定总是比head大。
二. 源码解析
2.1. 概览
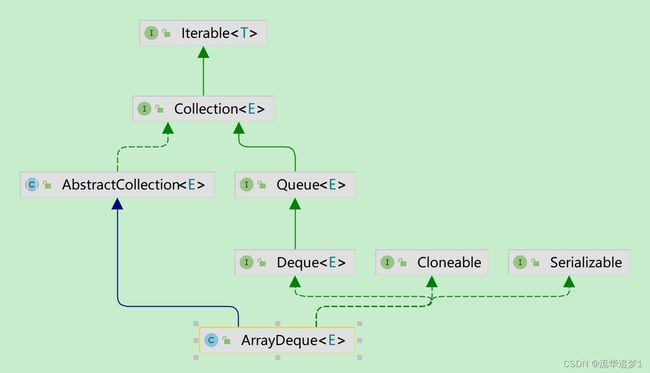
通过继承体系可以看到,ArrayDeque 实现了 Deque 接口,Deque 接口继承自 Queue 接口,它是对 Queue 的一种增强。
public interface Deque extends Queue {
// 添加元素到队列头
void addFirst(E e);
// 添加元素到队列尾
void addLast(E e);
// 添加元素到队列头
boolean offerFirst(E e);
// 添加元素到队列尾
boolean offerLast(E e);
// 从队列头移除元素
E removeFirst();
// 从队列尾移除元素
E removeLast();
// 从队列头移除元素
E pollFirst();
// 从队列尾移除元素
E pollLast();
// 查看队列头元素
E getFirst();
// 查看队列尾元素
E getLast();
// 查看队列头元素
E peekFirst();
// 查看队列尾元素
E peekLast();
// 从队列头向后遍历移除指定元素
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);
// 从队列尾向前遍历移除指定元素
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);
/*
* 队列中的方法
*/
// 添加元素,等于addLast(e)
boolean add(E e);
// 添加元素,等于offerLast(e)
boolean offer(E e);
// 移除元素,等于removeFirst()
E remove();
// 移除元素,等于pollFirst()
E poll();
// 查看元素,等于getFirst()
E element();
// 查看元素,等于peekFirst()
E peek();
/*
* 栈方法
*/
// 入栈,等于addFirst(e)
void push(E e);
// 出栈,等于removeFirst()
E pop();
/*
* Collection中的方法
*/
// 删除指定元素,等于removeFirstOccurrence(o)
boolean remove(Object o);
// 检查是否包含某个元素
boolean contains(Object o);
// 元素个数
public int size();
// 迭代器
Iterator iterator();
// 反向迭代器
Iterator descendingIterator();
} Deque 中新增了以下几类方法:
*First,表示从队列头操作元素;
*Last,表示从队列尾操作元素;
push(e),pop(),以栈的方式操作元素的方法。
2.2. 属性
// 存储元素的数组
transient Object[] elements;
// 头指针
transient int head;
// 尾指针
transient int tail;
// 默认最小容量(注意:elements的长度一定是2的次方幂)
private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;从属性我们可以看到,ArrayDeque 使用数组存储元素,并使用头尾指针标识队列的头和尾,其最小容量是 8。
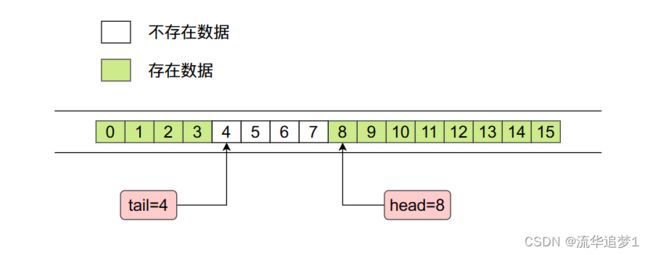
ArrayDeque底层是使用数组实现的,而且数组的长度必须是2的整数次幂,这么操作的原因是为了后面位运算好操作。在ArrayDeque当中有两个整形变量head和tail,分别指向右侧的第一个进入队列的数据和左侧第一个进入队列的数据,整个内存布局如下图所示:
其中 tail 指的位置没有数据,head 指的位置存在数据。
2.3. 构造方法
1. 调用无参构造器时,默认创建一个长度为16的数组。
2. 调用传入初始容量 n 的构造器,当 n 小于 8 时,会初始化一个长度为 8 的一个数组。
3. 当 n 大于等于 8 时,会初始化一个长度为 大于n的最小的2的幂 的数组(比如传入 3 算出来是 8,传入 9 算出来是 16,传入 16 算出来是 32)。
通过构造方法,我们知道默认初始容量是 16,最小容量是 8。
/*
* 空参构造器,底层初始化一个长度为16的数组
*/
public ArrayDeque() {
elements = new Object[16];
}
/*
* 指定元素个数初始化
* 传入初始容量,注意最终的容量是大于(没有等于)numElements的最大的2的幂
* 然后会创建出来。
*/
public ArrayDeque(int numElements) {
allocateElements(numElements);
}
/*
* 传入一个集合,将集合c中的元素初始化到数组中
* 创建一个长度为<小于等于c.size的最大的2的幂>的数组
* 然后将c中的元素添加到elements中。
*/
public ArrayDeque(Collection c) {
allocateElements(c.size());
addAll(c);
}// 构造一个长度为 严格大于numElements的最小的2的幂 的一个数组
private void allocateElements(int numElements) {
elements = new Object[calculateSize(numElements)];
}
// 返回严格大于numElements的最小的2的幂 (当numElements小于8时,返回8)
private static int calculateSize(int numElements) {
// MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8
int initialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
// 当numElements大于等于8时,计算出大于numElements的最小的2的幂
if (numElements >= initialCapacity) {
initialCapacity = numElements;
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 1);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 2);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 4);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 8);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 16);
initialCapacity++;
// 条件成立:说明爆int了,需要缩小数据,将initialCapacity无符号右移一位,相当于/2
if (initialCapacity < 0) // Too many elements, must back off
initialCapacity >>>= 1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 elements
}
// 这里如果numElements小于8时,直接返回8
return initialCapacity;
}2.4. 入队
2.4.1. addFirst(E, e)
// 从队头入队
public void addFirst(E e) {
// 不允许null元素
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
/*
* 将head指针减1并与数组长度减1取模
* 因为element.length一定是2的幂,2的幂-1的二进制从低位起是一串1,高位都是0
* 初始时head = 0,0 - 1 = -1 ,-1 & 15 = 15,此时head = 15
* 下一次 15 - 1 = 14,14 & 15 = 14,此时head = 14
* 再下一次 14 - 1 = 13,13 & 15 = 13,此时head = 13
* ...
* 这是为了防止数组到头了边界溢出。
* 最终如果到头了,且数组未满时,就从尾再向前,相当于循环利用数组。
* 即head指向的是当前队头元素。
*/
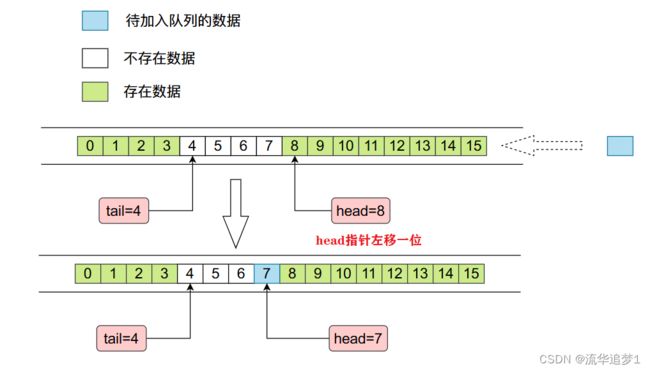
elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
// tail指向的是头元素的下一个位置。判断head == tail即判断数组是否满了,需要扩容。
if (head == tail)
// 从方法名可以看出,扩容为原数组长度2倍。
doubleCapacity();
}2.4.2. add(E e) & addLast(E e)
public boolean add(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
// 从队尾入队
public void addLast(E e) {
// 不允许null元素
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 初始时tail为0,直接入队,此时tail指向的是从队尾入队队列的头元素的下一个位置。
elements[tail] = e;
/*
* head指向的是队头元素的位置
* tail + 1指向队头的下一个元素,判断是否 == head,即判断数组是否满了。
* 即是否走扩容的逻辑。
*/
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}2.4.3. offer(E e)
public boolean offer(E e) {
return offerLast(e);
}
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}小结:
1. 入队有两种方式,从队列头或者从队列尾;
2. 如果容量不够了,直接扩大为两倍;
3. 通过取模的方式让头尾指针在数组范围内循环;
4. x & (len - 1) = x % len,使用 & 位运算的方式更快;
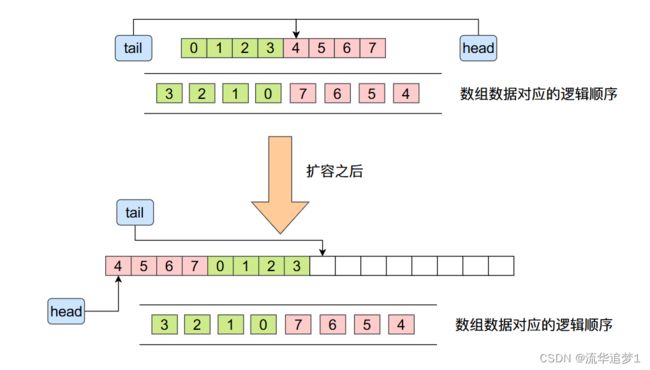
2.5. 扩容
private void doubleCapacity() {
// assert:断言,判断head是否等于tail
// 值为true时,程序从断言语句处继续执行
// 值为false时,程序从断言语句处停止执行
assert head == tail;
// 头指针的位置
int p = head;
// 数组长度
int n = elements.length;
// 头指针离数组尾的距离
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
// 新长度为旧长度的两倍
int newCapacity = n << 1;
// 判断是否溢出
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
// 新建新数组
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
// 将旧数组head之后的元素拷贝到新数组中
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
// 将旧数组下标0到head之间的元素拷贝到新数组中
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
// 赋值为新数组
elements = a;
// head指向0,tail指向旧数组长度表示的位置
head = 0;
tail = n;
}扩容这里迁移元素可能有点绕,请看下面这张图来理解:
2.6. 出队
2.6.1. poll() & pollFirst()
public E poll() {
return pollFirst();
}
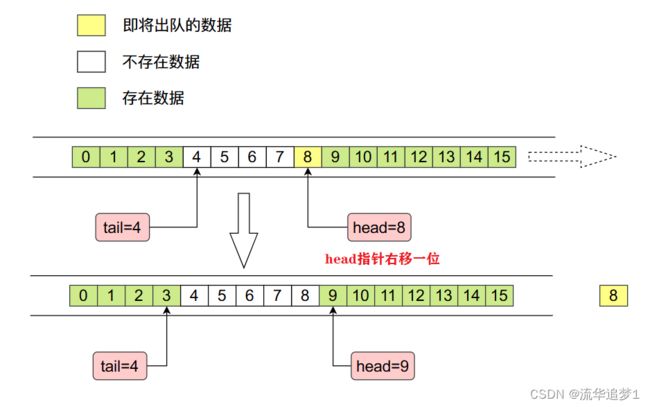
// 从队列头出队
public E pollFirst() {
int h = head;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 取队列头元素 (head指向的就是头元素)
E result = (E) elements[h];
// 如果队列为空,就返回null
if (result == null)
return null;
// 将队列头置为空
elements[h] = null;
// 队列头指针右移一位
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
// 返回出队的元素
return result;
}2.6.2. pollLast()
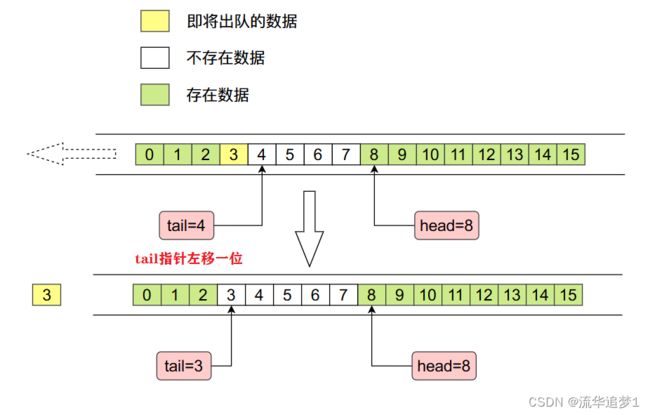
// 从队列尾出队
public E pollLast() {
// 尾指针左移一位 因为通过addLast()我们可以知道,tail指向的是头元素的下一个位置
int t = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 取当前尾指针处元素
E result = (E) elements[t];
// 如果队列为空返回null
if (result == null)
return null;
// 将当前尾指针处置为空
elements[t] = null;
// tail指向新的尾指针处
tail = t;
// 返回出队的元素
return result;
}2.7. 删除元素
此处的 remove 和 poll,前者会抛出异常,后者不会。
public E remove() { // 当作队列时默认头部删除
return removeFirst();
}
public E poll() { // 默认头部删除
return pollFirst();
}
public E removeFirst() {
E x = pollFirst();
if (x == null) // 此时不存在会抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException(); // 没有此元素异常
return x;
}
public E removeLast() {
E x = pollLast();
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E pollFirst() {
int h = head; // 保存头部
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // 未选中 告诉编译器忽略 unchecked 警告信息,意思可以是null元素,编译期会通过,因为deque接口不允许有空值
E result = (E) elements[h]; // 保存这个元素
// Element is null if deque empty 如果deque为空,则元素为null
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot 垃圾回收
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1); // 头指向指向下一个
return result; // 返回这个值
}
public E pollLast() { // 尾部删除
int t = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1); // 因为tail指向的是最后一个元素的下一个空位置,所以得先找到最后一个元素
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // 可以是空
E result = (E) elements[t];
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[t] = null;
tail = t;
return result;
}
public E pop() { // 当作栈时默认头部出栈
return removeFirst();
}从队列头部开始和尾部开始删除指定元素
// 从队列头向后遍历移除指定元素
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null)
return false;
int mask = elements.length - 1; // 保存数组长度 mask即掩码
int i = head; // 保存头部
Object x; // x用于保存待删的元素
while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) { // 从前往后遍历数组
if (o.equals(x)) { // 如果相等
delete(i); // 删除i
return true;
}
i = (i + 1) & mask;
}
return false;
}
// 从队列尾向前遍历移除指定元素
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null)
return false;
int mask = elements.length - 1;
int i = (tail - 1) & mask;
Object x;
while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) { // 从后往前遍历数组
if (o.equals(x)) {
delete(i);
return true;
}
i = (i - 1) & mask;
}
return false;
}
private void checkInvariants() { // 有效性检查,
assert elements[tail] == null; // 判断是否尾部为空,tail位置没有元素
// 如果head == tail说明数组为空,令head位置为空,否则头部有元素,tail-1有元素
assert head == tail ? elements[head] == null :
(elements[head] != null &&
elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] != null);
// head-1位置没有元素
assert elements[(head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] == null;
}
private boolean delete(int i) { // 删除 i位置元素
checkInvariants(); // 校验不变量 有效性检查
final Object[] elements = this.elements; // 定义一个新数组保存旧数组
final int mask = elements.length - 1;
final int h = head;//保存头部
final int t = tail;//保存尾部
final int front = (i - h) & mask; // i位置前的元素个数
final int back = (t - i) & mask; // i位置后的元素个数
// Invariant: head <= i < tail mod circularity
// 不变的是: 头小于i小于tail 保证循环性
// 再次检验,如果i到头部的距离大于等于尾部到头部的距离,表示当前队列已经被修改了,通过最开始检测,i是不应该满足该条件。
if (front >= ((t - h) & mask)) // 如果i不在head和tail之间
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// 判断i靠近头还是尾,尽量移动较少元素
// Optimize for least element motion
if (front < back) { // 如果i靠近head
if (h <= i) { // 在进行检测 h小于等于i 在i前面
// 直接覆盖 比如 0 1 2 3 3是待删元素,覆盖后 0 0 1 2
System.arraycopy(elements, h, elements, h + 1, front);
} else { // Wrap around h大于i 在i后面
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, elements, 1, i);
elements[0] = elements[mask];
System.arraycopy(elements, h, elements, h + 1, mask - h);
}
elements[h] = null;
head = (h + 1) & mask;
return false; // 返回false则是 从左往右移
} else { // i靠近tail
if (i < t) { // Copy the null tail as well i在tail前
System.arraycopy(elements, i + 1, elements, i, back);
tail = t - 1;
} else { // Wrap around i在tail后面
System.arraycopy(elements, i + 1, elements, i, mask - i);
elements[mask] = elements[0];
System.arraycopy(elements, 1, elements, 0, t);
tail = (t - 1) & mask;
}
return true; // 返回true则是从右往左
}
}2.8. 获取元素
peekFirst() 的作用是返回但不删除Deque首端元素,也即是head位置处的元素,直接返回elements[head]即可。
peekLast() 的作用是返回但不删除Deque尾端元素,也即是tail位置前面的那个元素。
public E element() { // 获取元素 默认获取队头
return getFirst();
}
public E getFirst() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[head];
if (result == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return result;
}
public E getLast() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
if (result == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return result;
}
public E peek() {
return peekFirst();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E peekFirst() {
// elements[head] is null if deque empty
return (E) elements[head];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E peekLast() {
return (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
}2.9. 栈操作
前面我们介绍 Deque 的时候说过,Deque 可以直接作为栈来使用,那么 ArrayDeque 是怎么实现的呢?非常简单,看如下代码:
// 入栈
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
// 出栈
public E pop() {
// 底层调用的还是pollFirst()
return removeFirst();
}