窥探-spring boot加载外部配置及其源码分析
窥探-spring boot加载外部配置及其源码分析
- 简单使用
-
- 使用@Value注解
- 使用@PropertySource注解加载属性
- 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
- 配置随机数
-
- 通过profiles进行多环境设置
- 分析配置加载
Spring Boot使开发者可以外部化配置,以便可以使用同一应用程序不同环境中的代码。 开发者可以使用属性文件,YAML文件,环境变量和命令行参数以外部化配置。属性值可以直接注入到开发者的通过使用@Value注释,可以通过Spring的Environment抽象访问来访问bean,或者通过@ConfigurationProperties绑定到结构化对象.
Spring Boot使用一个非常特殊的PropertySource顺序,该顺序旨在允许合理地覆盖值。 按以下顺序考虑属性:
- home目录下的devtools全局设置属性(~/.spring-boot-devtools.properties,如果devtools激活)。
- 测试用例上的@TestPropertySource注解。
- 测试用例上的@SpringBootTest#properties注解。
- 命令行参数
- 来自SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON的属性(环境变量或系统属性中内嵌的内联JSON)。
- ServletConfig初始化参数。
- ServletContext初始化参数。
- 来自于java:comp/env的JNDI属性。
- Java系统属性(System.getProperties())。
- 操作系统环境变量。
- RandomValuePropertySource,只包含random.*中的属性。
- 没有打进jar包的Profile-specific应用属性(application-{profile}.properties和YAML变量)。
- 打进jar包中的Profile-specific应用属性(application-{profile}.properties和YAML变量)。
- 没有打进jar包的应用配置(application.properties和YAML变量)。
- 打进jar包中的应用配置(application.properties和YAML变量)。
- @Configuration类上的@PropertySource注解。
- 默认属性(使用SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定)。
简单使用
使用@Value注解
在我们使用springboot的时候,我们有时候需要获取属性的值,使用@Value的方式是其中的一种形式。
创建项目,项目结构如下:
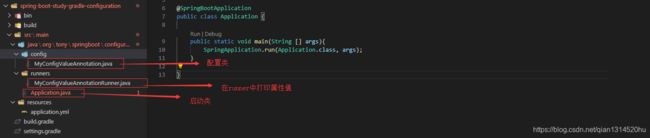
我们看看application.yml使用中的值:
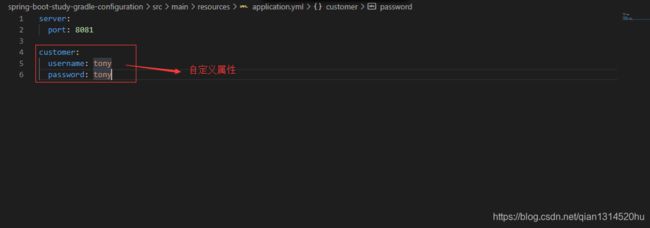
创建一个获取配置的类,使用@Value进行获取配置

进行启动的时候打印配置自定义属性:
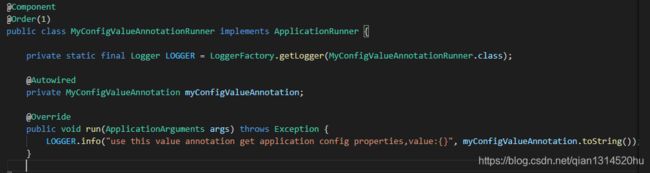
打印的日志如下:

获取到了自定义属性
使用@PropertySource注解加载属性
我们获取配置文件中的制定属性还可以通过@PropertySource或者@PropertySources注解进行实现
创建两个文件:MyConfigPropertySource.java和 MyConfigPropertySource2.java,代码如下:
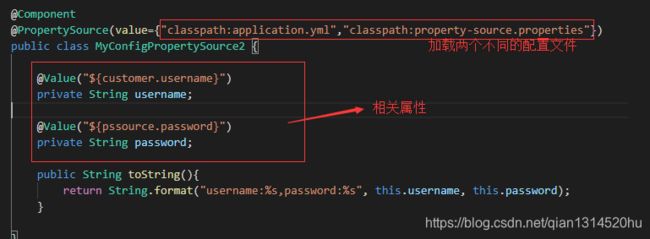
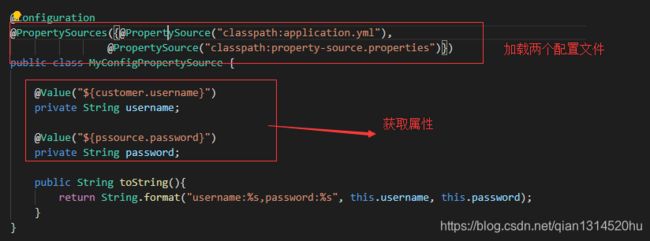
配置文件如下:property-source.properties

这里将properties文件yml格式的话,是获取不到里面相关自定义属性。因为@PropertySource不支持yml文件。
使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
我们可以使用@ConfigurationProperties注解将相关的配置映射到实体类中,注解中有一个prefix,指定自定义配置的属性前缀
我们的配置文件application.yml中的username和password都是以customer为前缀,我们可以将代码编写如下:

这里我们定义的属性需要实现setter方法,我们就可以直接在runner中引用,打印就可以了

启动输入如下:
![]()
说明获取成功了
配置随机数
在springboot中,我们可以使用RandomValuePropertySource进行随机数的配置
修改application.yml
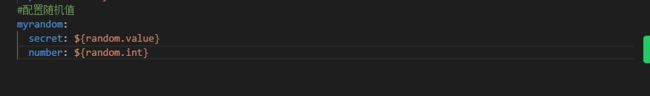
添加一个MyConfigRandomValue,进行配置属性的映射关系

创建一个runner,MyConfigRandomValueRunner.java

运行代码:
![]()
这样会打印相关的随机数
如果不喜欢application.properties作为配置文件名,则可以切换到另一个通过指定spring.config.name环境属性来指定文件名。还可以参考显式通过使用spring.config.location环境属性(以逗号分隔)
目录位置或文件路径的列表)。spring.config.name和spring.config.location很早就用于确定必须加载哪些文件,因此必须将其定义为环境属性(通常是操作系统环境变量,系统属性或命令行参数)。
通过profiles进行多环境设置
可以通过使用定义特定于配置文件的属性以下命名约定:application- {profile} .properties。如果没有设置活动配置文件,则环境具有一组默认配置文件(默认为[default])。 换句话说,如果未显式激活任何profile文件,那么将从应用程序default.properties中加载属性。
在之前的项目中,创建MyConfigProfile.java
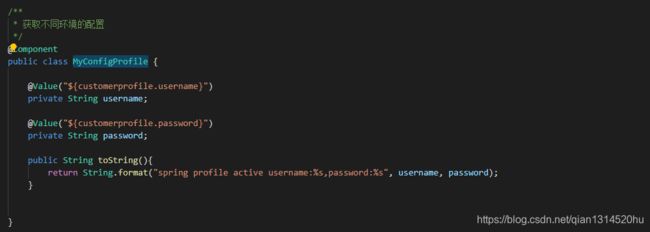
创建两个配置文件applcaition-dev.yml和applciation-test.yml


创建一个runner类MyConfigProfileRunner.java,进行启动打印相关信息
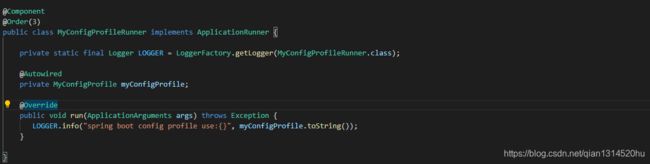
修改applciation.yml的配置:
![]()
运行项目我们可以看到日志打印出了test配置文件中相关的配置信息

启动端口是applciation-test.yml中的设置的端口号,同时username和password都是applciation-test.yml设置的
我们将application.yml改为dev
![]()
在运行
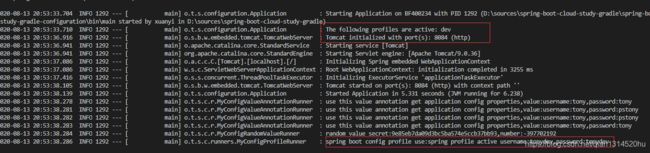
运行获得端口和username和password是application-dev.yml中设置的。此处就进行不同环境不同配置的切换了。
我们还可以在配置文件中使用占位符进行属性的设置
app.name=MyApp
app.description=${app.name} is a Spring Boot application
分析配置加载
springboot的启动是使用run方法,我们进入run方法,看加载配置的方法

/**模板方法按该顺序委派给configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment,String [])
和configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment,String [])。
重写此方法以完全控制环境自定义,或者重写以上方法之一以对属性源或配置文件进行细粒度控制,分离。
configureEnvironment方法中配置属性的相关方法
*/
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
configureProfiles(environment, args);
- configurePropertySources方法
/***
* 在此应用程序的环境中添加,删除或重新排序任何PropertySource
*/
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
if (this.defaultProperties != null && !this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()) {
sources.addLast(new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", this.defaultProperties));
}
//添加命令行属性,判断命令行参数长度
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
//name = "commandLineArgs"
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (sources.contains(name)) {
PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite.addPropertySource(
new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
composite.addPropertySource(source);
sources.replace(name, composite);
}
else {
//添加PropertySource
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}
sources.contains(name):
通过PropertySource中的name
![]()
获取source方法

将相应的PropertySource保存到一个list中,之后通过name进行获取索引得到PropertySource
- configureProfiles(environment, args)方法配置profiles
/**
*配置该配置文件环境对于哪些应用程序是活动的(或默认情况下是活动的)。
配置文件期间可能会激活其他配置文件通过spring.profiles.active属性进行处理
*/
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
Set<String> profiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.additionalProfiles);
//获取profiles进行添加
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
environment.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.toStringArray(profiles));
}
获取environment.getActiveProfiles()获取activeProfiles
我们进入这个方法,environment是一个接口,我们查看当前接口的AbstractEnvironment类进行查看获取profiles
public abstract class AbstractEnvironment implements ConfigurableEnvironment {
//相关默认的属性值
public static final String IGNORE_GETENV_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.getenv.ignore";
public static final String ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.profiles.active";
public static final String DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.profiles.default";
protected static final String RESERVED_DEFAULT_PROFILE_NAME = "default";
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(this.getClass());
//获取默认的profiles
private final Set<String> defaultProfiles = new LinkedHashSet(this.getReservedDefaultProfiles());
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources;
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver;
//构造函数
public AbstractEnvironment() {
this.propertyResolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
this.customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Initialized " + this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " with PropertySources " + this.propertySources);
}
}
protected Set<String> getReservedDefaultProfiles() {
return Collections.singleton("default");
}
//获取active profiles
public String[] getActiveProfiles() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(this.doGetActiveProfiles());
}
//获取active profiles
protected Set<String> doGetActiveProfiles() {
Set var1 = this.activeProfiles;
synchronized(this.activeProfiles) {
if(this.activeProfiles.isEmpty()) {
//获取spring.profiles.active的属性值
String profiles = this.getProperty("spring.profiles.active");
if(StringUtils.hasText(profiles)) {
this.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(profiles)));
}
}
//返回activeprofiles
return this.activeProfiles;
}
}
//设置active profiles
public void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notNull(profiles, "Profile array must not be null");
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Activating profiles " + Arrays.asList(profiles));
}
Set var2 = this.activeProfiles;
synchronized(this.activeProfiles) {
//先清空active list
this.activeProfiles.clear();
String[] var3 = profiles;
int var4 = profiles.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String profile = var3[var5];
//验证profiles
this.validateProfile(profile);
//进行添加
this.activeProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
//添加active profiles
public void addActiveProfile(String profile) {
if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Activating profile '" + profile + "'");
}
this.validateProfile(profile);
this.doGetActiveProfiles();
Set var2 = this.activeProfiles;
synchronized(this.activeProfiles) {
this.activeProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
//获取默认的active profiles
public String[] getDefaultProfiles() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(this.doGetDefaultProfiles());
}
//获取默认的active profiles
protected Set<String> doGetDefaultProfiles() {
Set var1 = this.defaultProfiles;
synchronized(this.defaultProfiles) {
if(this.defaultProfiles.equals(this.getReservedDefaultProfiles())) {
String profiles = this.getProperty("spring.profiles.default");
if(StringUtils.hasText(profiles)) {
this.setDefaultProfiles(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(profiles)));
}
}
return this.defaultProfiles;
}
}
public void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notNull(profiles, "Profile array must not be null");
Set var2 = this.defaultProfiles;
synchronized(this.defaultProfiles) {
this.defaultProfiles.clear();
String[] var3 = profiles;
int var4 = profiles.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String profile = var3[var5];
this.validateProfile(profile);
this.defaultProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
public boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notEmpty(profiles, "Must specify at least one profile");
String[] var2 = profiles;
int var3 = profiles.length;
for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {
String profile = var2[var4];
if(StringUtils.hasLength(profile) && profile.charAt(0) == 33) {
if(!this.isProfileActive(profile.substring(1))) {
return true;
}
} else if(this.isProfileActive(profile)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
protected boolean isProfileActive(String profile) {
this.validateProfile(profile);
Set<String> currentActiveProfiles = this.doGetActiveProfiles();
return currentActiveProfiles.contains(profile) || currentActiveProfiles.isEmpty() && this.doGetDefaultProfiles().contains(profile);
}
protected void validateProfile(String profile) {
if(!StringUtils.hasText(profile)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid profile [" + profile + "]: must contain text");
} else if(profile.charAt(0) == 33) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid profile [" + profile + "]: must not begin with ! operator");
}
}
//获取系统属性
public MutablePropertySources getPropertySources() {
return this.propertySources;
}
public Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties() {
try {
return System.getProperties();
} catch (AccessControlException var2) {
return new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Nullable
protected String getSystemAttribute(String attributeName) {
try {
return System.getProperty(attributeName);
} catch (AccessControlException var3) {
if(AbstractEnvironment.this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
AbstractEnvironment.this.logger.info("Caught AccessControlException when accessing system property '" + attributeName + "'; its value will be returned [null]. Reason: " + var3.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
}
};
}
}
//获取系统环境
public Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment() {
if(this.suppressGetenvAccess()) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
} else {
try {
return System.getenv();
} catch (AccessControlException var2) {
return new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Nullable
protected String getSystemAttribute(String attributeName) {
try {
return System.getenv(attributeName);
} catch (AccessControlException var3) {
if(AbstractEnvironment.this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
AbstractEnvironment.this.logger.info("Caught AccessControlException when accessing system environment variable '" + attributeName + "'; its value will be returned [null]. Reason: " + var3.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
}
};
}
}
}
}
我们获取属性值,会校验相关的格式,分隔符什么的,会在AbstractPropertyResolver类中,当前类实现了ConfigurablePropertyResolver

在进行上面操作完了之后,会调用ConfigurationPropertySource.attach方法,如下:
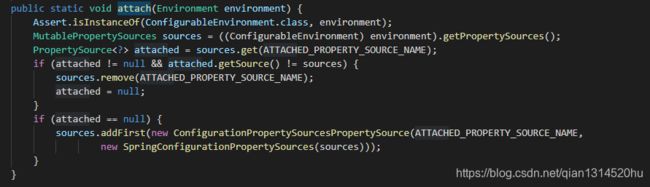
获取属性
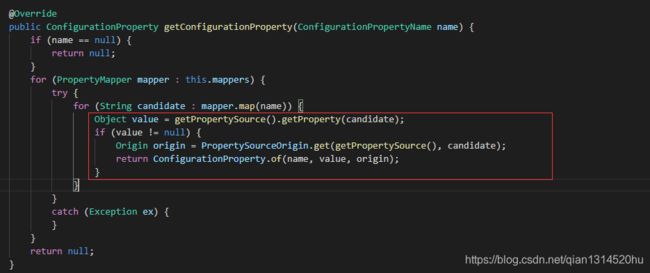
进行propertySource的检查:判断是否为random
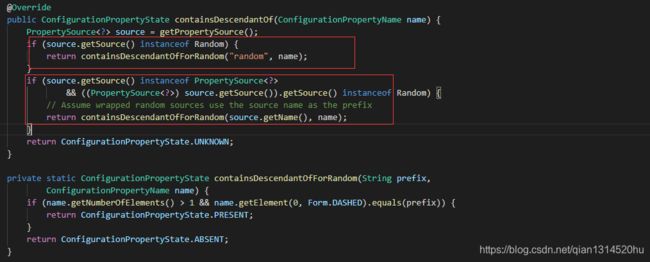
类SystemEnvironmentPropertyMapper进行相关的对系统变量的符号的转换,PropertyMapper用于系统环境变量。 通过删除来映射名称无效字符,转换为小写并用 _代替.。例如SERVER_PORT被映射到server.port。在另外,数字元素映射到索引(例如,HOST_0映射到host [0])