线性代数-Python-02:矩阵的基本运算 - 手写Matrix及numpy中的用法
文章目录
- 一、代码仓库
- 二、矩阵的基本运算
-
- 2.1 矩阵的加法
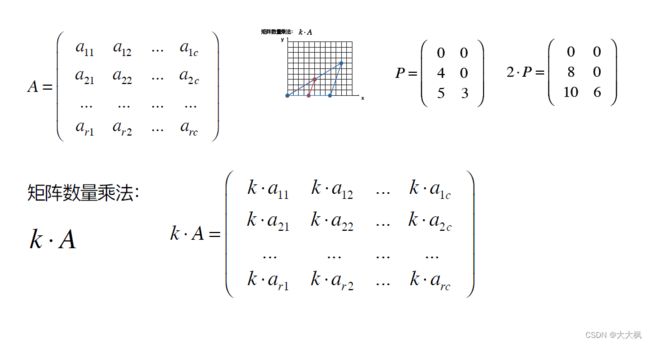
- 2.2 矩阵的数量乘法
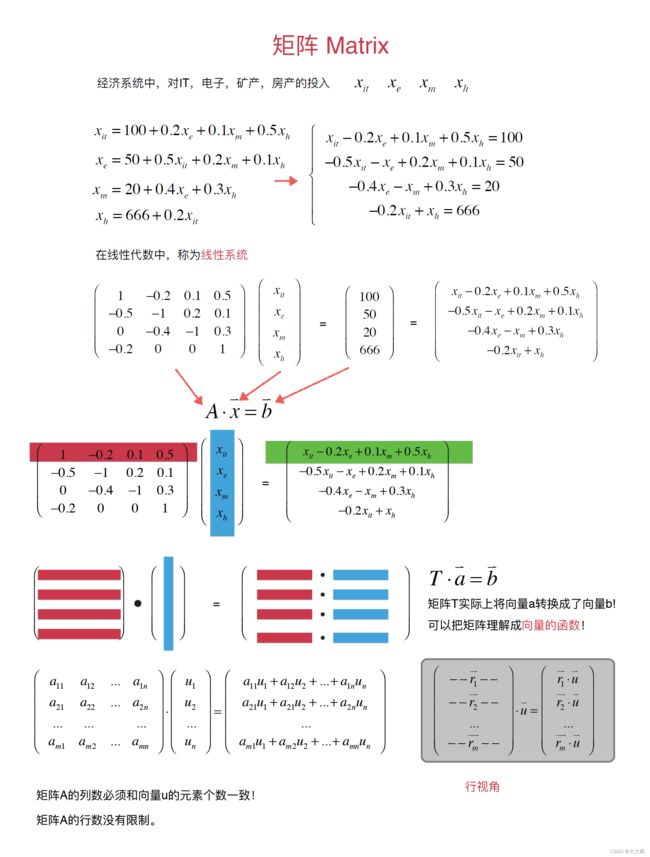
- 2.3 矩阵和向量的乘法
- 2.4 矩阵和矩阵的乘法
- 2.5 矩阵的转置
- 三、手写Matrix代码
-
- Matrix.py
- main_matrix.py
- main_numpy_matrix.py
一、代码仓库
https://github.com/Chufeng-Jiang/Python-Linear-Algebra-for-Beginner/tree/main
二、矩阵的基本运算
2.1 矩阵的加法
2.2 矩阵的数量乘法
2.3 矩阵和向量的乘法
2.4 矩阵和矩阵的乘法
2.5 矩阵的转置
三、手写Matrix代码
Matrix.py
from .Vector import Vector
class Matrix:
"""参数二:是一个二维列表"""
def __init__(self, list2d):
self._values = [row[:] for row in list2d]
@classmethod
def zero(cls, r, c):
"""返回一个r行c列的零矩阵"""
return cls([[0] * c for _ in range(r)])
def T(self):
"""返回矩阵的转置矩阵"""
return Matrix([[e for e in self.col_vector(i)]
for i in range(self.col_num())])
def __add__(self, another):
"""返回两个矩阵的加法结果"""
assert self.shape() == another.shape(), \
"Error in adding. Shape of matrix must be same."
return Matrix([[a + b for a, b in zip(self.row_vector(i), another.row_vector(i))]
for i in range(self.row_num())])
def __sub__(self, another):
"""返回两个矩阵的减法结果"""
assert self.shape() == another.shape(), \
"Error in subtracting. Shape of matrix must be same."
return Matrix([[a - b for a, b in zip(self.row_vector(i), another.row_vector(i))]
for i in range(self.row_num())])
def dot(self, another):
"""返回矩阵乘法的结果"""
if isinstance(another, Vector):
# 矩阵和向量的乘法
assert self.col_num() == len(another), \
"Error in Matrix-Vector Multiplication."
return Vector([self.row_vector(i).dot(another) for i in range(self.row_num())])
if isinstance(another, Matrix):
# 矩阵和矩阵的乘法
assert self.col_num() == another.row_num(), \
"Error in Matrix-Matrix Multiplication."
return Matrix([[self.row_vector(i).dot(another.col_vector(j)) for j in range(another.col_num())]
for i in range(self.row_num())])
def __mul__(self, k):
"""返回矩阵的数量乘结果: self * k"""
return Matrix([[e * k for e in self.row_vector(i)]
for i in range(self.row_num())])
def __rmul__(self, k):
"""返回矩阵的数量乘结果: k * self"""
return self * k
def __truediv__(self, k):
"""返回数量除法的结果矩阵:self / k"""
return (1 / k) * self
def __pos__(self):
"""返回矩阵取正的结果"""
return 1 * self
def __neg__(self):
"""返回矩阵取负的结果"""
return -1 * self
def row_vector(self, index):
"""返回矩阵的第index个行向量"""
return Vector(self._values[index])
def col_vector(self, index):
"""返回矩阵的第index个列向量"""
return Vector([row[index] for row in self._values])
def __getitem__(self, pos):
"""返回矩阵pos位置的元素"""
r, c = pos
return self._values[r][c]
def size(self):
"""返回矩阵的元素个数"""
r, c = self.shape()
return r * c
def row_num(self):
"""返回矩阵的行数"""
return self.shape()[0]
__len__ = row_num
def col_num(self):
"""返回矩阵的列数"""
return self.shape()[1]
def shape(self):
"""返回矩阵的形状: (行数, 列数)"""
return len(self._values), len(self._values[0])
def __repr__(self):
return "Matrix({})".format(self._values)
__str__ = __repr__
main_matrix.py
from playLA.Vector import Vector
from playLA.Matrix import Matrix
if __name__ == "__main__":
matrix = Matrix([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(matrix)
print("matrix.shape = {}".format(matrix.shape()))
print("matrix.size = {}".format(matrix.size()))
print("len(matrix) = {}".format(len(matrix)))
print("matrix[0][0] = {}".format(matrix[0, 0]))
matrix2 = Matrix([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
print(matrix2)
print("add: {}".format(matrix + matrix2))
print("subtract: {}".format(matrix - matrix2))
print("scalar-mul: {}".format(2 * matrix))
print("scalar-mul: {}".format(matrix * 2))
print("zero_2_3: {}".format(Matrix.zero(2, 3)))
T = Matrix([[1.5, 0], [0, 2]])
p = Vector([5, 3])
print("T.dot(p) = {}".format(T.dot(p)))
P = Matrix([[0, 4, 5], [0, 0, 3]])
print("T.dot(P) = {}".format(T.dot(P)))
print("A.dot(B) = {}".format(matrix.dot(matrix2)))
print("B.dot(A) = {}".format(matrix2.dot(matrix)))
print("P.T = {}".format(P.T()))
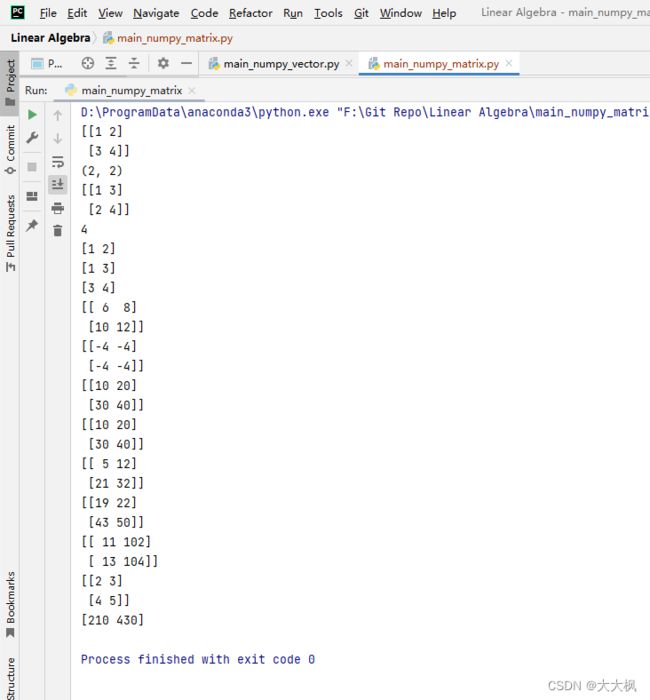
main_numpy_matrix.py
import numpy as np
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 矩阵的创建
A = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(A)
# 矩阵的属性
print(A.shape)
print(A.T)
# 获取矩阵的元素
print(A[1, 1])
print(A[0])
print(A[:, 0])
print(A[1, :])
# 矩阵的基本运算
B = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
print(A + B)
print(A - B)
print(10 * A)
print(A * 10)
print(A * B)
print(A.dot(B))
p = np.array([10, 100])
print(A + p)
print(A + 1)
print(A.dot(p))