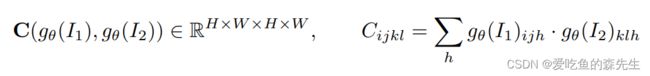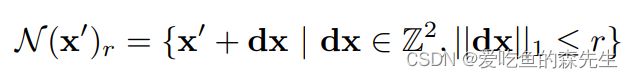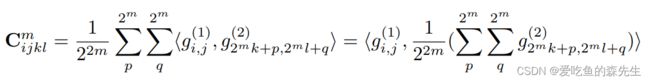论文|RAFT: Recurrent All-Pairs Field Transforms for Optical Flow
2022年8月13日
| 论文名称 | RAFT: Recurrent All-Pairs Field Transforms for Optical Flow |
|---|---|
| 作者 | Zachary Teed and Jia Deng |
| 发表期刊 | ECCV2020 |
| 主要思想 |
简述
优点
- 不像之前的coarse-to-fine类的方法,RAFT在计算时始终保持同一分辨率,而coarse-to-fine则是对多尺度预测,逐步细化的方式
- update operator是轻量的和循环的,而其他的算法则只能是循环几次,无法长时间循环。
- 一个新的update operator,由卷积GRU组成,可look up 生成的4D相关信息。
主要方法
RAFT的组成
RAFT的结构非常简洁,主要由三部分组成:
- feature encoder: 逐像素的提取特征;
- correlation layer:为所有的像素匹配对生成一个4D关联信息,还可以生成小分辨率的关联信息。(计算像素的相似)
- update operator:接收相关信息,不断更新光流场。
总体流程:
1. Feature Extraction
特征提取网络采用残差结构,最终输出为原图的1/8尺寸的特征图。
Context Encoder指对Frame1提取特征,结构和Feature Encoder类似。
2. Computing Visual Similarity
Step 1:
计算correlation volume C,Frame1和Frame2经过特征提取网络之后的特征相乘就是C。
Step 2: Correlation Pyramid
通过对C使用不同尺寸的池化,可以得到不同尺寸的Correlation volume,由此构成Correlation Pyramid结构。$HWH^K*W^K$
注意!C的前两个维度并没有变小,依旧可以保持一个大的分辨率,对于快速移动的物体更好。
Step 3 : Correlation Lookup
上一步构建了四层的Correlation Pyramid,这里要根据像素去查找这个Correlation Pyramid中的对应特征。如果对I1中的每个点的向量都要去I2中所有向量找对应点的话,需要的cost太大了,所以论文中设置了一个lookup的参数,即只对该位置附近位置的点做判断。将$Frame1$图像的点$(u,v)$根据确定的光流场$(f^1, f2)$映射到到$Frame2$,可以得到此时的坐标为$x'=(u+f^1(u), v+f^2(v))$。由此确定搜索区域:
其中,r为搜索半径,把四个层提取到的特征concat到一个特征。
out_pyramid = []
for i in range(self.num_levels):
corr = self.corr_pyramid[i]
dx = torch.linspace(-r, r, 2*r+1, device=coords.device)#返回一维Tensor,这个地方有问题吗
dy = torch.linspace(-r, r, 2*r+1, device=coords.device)#start->end->step
delta = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid(dy, dx), axis=-1)
centroid_lvl = coords.reshape(batch*h1*w1, 1, 1, 2) / 2**i
delta_lvl = delta.view(1, 2*r+1, 2*r+1, 2)
coords_lvl = centroid_lvl + delta_lvl
corr = bilinear_sampler(corr, coords_lvl)
corr = corr.view(batch, h1, w1, -1)#相关性查找
out_pyramid.append(corr)
out = torch.cat(out_pyramid, dim=-1)
Efficient Computation for High Resolution Images
4D correlation volume只需要计算一次,对于m层,correlation volume为
$(i,j), (k,l)$之间的相关信息为$2^m*2^m$网格中的相关信息的均值。(m=0,1,2,3)。所以$C^m_{ijkl}$
Iterative Update
该部分是在计算出相似度或计算出pooling后的feature map之后做的,用于得到最终的光流,该步骤并不只是执行一次,而是更新M次,但是feature map的计算只需要执行一次。
该部分的输入为:flow, correlation, and a latent hidden state,输出为the update ∆f and an updated hidden state。
初始化:初始化为全零,或者上一帧的光流
输入:当前光流,以及从金字塔中提取的对应的相关特征。所以输入是相关特征,光流以及上下文特征。
更新:采用ConvGRU不断更新。
def forward(self, net, inp, corr, flow, upsample=True):
motion_features = self.encoder(flow, corr)
inp = torch.cat([inp, motion_features], dim=1)
net = self.gru(net, inp)#这部分代码如下
delta_flow = self.flow_head(net)#两层卷积和一层ReLU函数
# scale mask to balence gradients
mask = .25 * self.mask(net)
return net, mask, delta_flow
class SepConvGRU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_dim=128, input_dim=192+128):
super(SepConvGRU, self).__init__()
self.convz1 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim+input_dim, hidden_dim, (1,5), padding=(0,2))
self.convr1 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim+input_dim, hidden_dim, (1,5), padding=(0,2))
self.convq1 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim+input_dim, hidden_dim, (1,5), padding=(0,2))
self.convz2 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim+input_dim, hidden_dim, (5,1), padding=(2,0))
self.convr2 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim+input_dim, hidden_dim, (5,1), padding=(2,0))
self.convq2 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim+input_dim, hidden_dim, (5,1), padding=(2,0))
def forward(self, h, x):
# horizontal
hx = torch.cat([h, x], dim=1)
z = torch.sigmoid(self.convz1(hx))
r = torch.sigmoid(self.convr1(hx))
q = torch.tanh(self.convq1(torch.cat([r*h, x], dim=1)))
h = (1-z) * h + z * q
# vertical
hx = torch.cat([h, x], dim=1)
z = torch.sigmoid(self.convz2(hx))
r = torch.sigmoid(self.convr2(hx))
q = torch.tanh(self.convq2(torch.cat([r*h, x], dim=1)))
h = (1-z) * h + z * q
return h
ConvGRU模块的hidden state经过两个卷积去预测光流的更新$\Delta f$,输出的光流为原图的1/8,通过上采样恢复到原始尺寸。这里的上采样方式是通过对每一个像素点的$3*3$邻域加权求和。
def upsample_flow(self, flow, mask):#mask输出通道为64*9,代表什么
""" Upsample flow field [H/8, W/8, 2] -> [H, W, 2] using convex combination """
N, _, H, W = flow.shape
mask = mask.view(N, 1, 9, 8, 8, H, W)
mask = torch.softmax(mask, dim=2)
up_flow = F.unfold(8 * flow, [3,3], padding=1)
up_flow = up_flow.view(N, 2, 9, 1, 1, H, W)
up_flow = torch.sum(mask * up_flow, dim=2)
up_flow = up_flow.permute(0, 1, 4, 2, 5, 3)
return up_flow.reshape(N, 2, 8*H, 8*W)