图论02-【无权无向】-图的深度优先遍历
文章目录
- 1. 代码仓库
- 2. 深度优先遍历图解
- 3. 主要代码
-
- 3.1 dfs递归的主要代码 - 先序遍历和后序遍历
- 3.2 dfs非递归的主要代码 - 使用栈
- 3.3 递归与非递归遍历出来的顺序不一致
- 3.4 标记不同的联通分量
- 4. 完整代码
-
- 4.1 CC.java
- 4.2 Graph.java
1. 代码仓库
https://github.com/Chufeng-Jiang/Graph-Theory
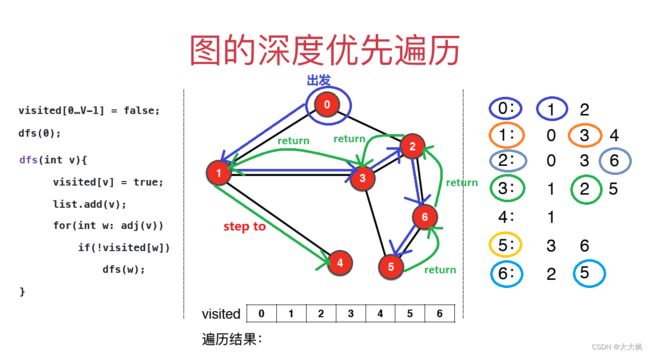
2. 深度优先遍历图解
复杂度分析:O( V+E )
3. 主要代码
数据输入
7 6
0 1
0 2
1 3
1 4
2 3
2 6
3.1 dfs递归的主要代码 - 先序遍历和后序遍历
private void dfs(int v){
visited[v] = true;
pre.add(v); // 先序遍历:先加入容器,再进行递归
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w])
dfs(w);
post.add(v); // 后序遍历:先进行递归,再加入容器
}
- 访问过的的顶点设置为True避免重复访问;
- 将访问过的顶点添加到order容器中,用于输出访问顺序
- 遍历与当前顶点相邻的
其中一个顶点,并且对这一个顶点再次进行dfs。
3.2 dfs非递归的主要代码 - 使用栈
private void dfs(int v){
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(v);
visited[v] = true;
while(!stack.empty()){
int cur = stack.pop();
pre.add(cur);
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w]){
stack.push(w);
visited[w] = true;
}
}
}
3.3 递归与非递归遍历出来的顺序不一致
因为非递归使用的是的栈,把0压栈之后,0出栈并进入pre容器进行记录。
随后是跟0相连的顶点都入栈,入栈的顺序是 |1<—2,但是出栈的顺序是反过来的,2先出栈进入pre容器,最后才是1出栈进入pre容器。
因此两种方法遍历出来的顺序会不一样。
3.4 标记不同的联通分量
for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i ++)
visited[i] = -1;
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(visited[v] == -1){
dfs(v, cccount);
cccount ++;
}
private void dfs(int v, int ccid){
visited[v] = ccid;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(visited[w] == -1)
dfs(w, ccid);
}
// 判断两个顶点是否属于同一连通分量
public boolean isConnected(int v, int w){
G.validateVertex(v);
G.validateVertex(w);
return visited[v] == visited[w];
}
// 输出每个联通分量
public ArrayList<Integer>[] components(){ // 每个联通分量设置成一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer>[] res = new ArrayList[cccount];
for(int i = 0; i < cccount; i ++) // 如果有3个连通分量,就设置3个ArrayList
res[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++) // 填充每个连通分量的ArrayList
res[visited[v]].add(v); // visited[v]的取值只有0、1.2.3等,是组名,表示是哪个连通分量
return res;
}
如果图中存在多个联通分量,使用循环进行DFS;
- 初始化visited数组,赋值都为 -1;
- 遍历顶点开始dfs,同一个连通分量使用相同的ccid进行标记;
- 同一个ccid的放到容一个ArrayList中进行输出
visited[v]得到v的ccid,res[visited[v]]== res[ccid],即数组首地址。
4. 完整代码
4.1 CC.java
package Chapt02_DFS._0205_Graph_DFS_ConnectedComponentsCount;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CC {
private Graph G;
private int[] visited;
private int cccount = 0;
public CC(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new int[G.V()];
for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i ++)
visited[i] = -1;
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(visited[v] == -1){
dfs(v, cccount);
cccount ++;
}
}
private void dfs(int v, int ccid){
visited[v] = ccid;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(visited[w] == -1)
dfs(w, ccid);
}
public int count(){
return cccount;
}
// 判断两个顶点是否属于同一连通分量
public boolean isConnected(int v, int w){
G.validateVertex(v);
G.validateVertex(w);
return visited[v] == visited[w];
}
/************************************************************
* ArrayList[] arraylist1 = new ArrayList[3];
* List[] arraylist1 = new ArrayList[3];
* 输出:[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
***********************************************************/
public ArrayList<Integer>[] components(){ // 每个联通分量设置成一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer>[] res = new ArrayList[cccount];
for(int i = 0; i < cccount; i ++) // 如果有3个连通分量,就设置3个ArrayList
res[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++) // 填充每个连通分量的ArrayList
res[visited[v]].add(v); // visited[v]的取值只有0、1.2.3等,是组名,表示是哪个连通分量
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g3.txt");
CC cc = new CC(g);
System.out.println(cc.count());
System.out.println(cc.isConnected(0, 6));
System.out.println(cc.isConnected(5, 6));
ArrayList<Integer>[] comp = cc.components();
for(int ccid = 0; ccid < comp.length; ccid ++){
System.out.print(ccid + " : ");
for(int w: comp[ccid])
System.out.print(w + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
4.2 Graph.java
package Chapt02_DFS._0205_Graph_DFS_ConnectedComponentsCount;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
/// 暂时只支持无向无权图
public class Graph {
private int V;
private int E;
private TreeSet<Integer>[] adj;
public Graph(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();
if(V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
adj = new TreeSet[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i ++)
adj[i] = new TreeSet<Integer>();
E = scanner.nextInt();
if(E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
for(int i = 0; i < E; i ++){
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
if(a == b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected!");
if(adj[a].contains(b)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected!");
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void validateVertex(int v){
if(v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + "is invalid");
}
public int V(){
return V;
}
public int E(){
return E;
}
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].contains(w);
}
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
public int degree(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for(int v = 0; v < V; v ++){
sb.append(String.format("%d : ", v));
for(int w : adj[v])
sb.append(String.format("%d ", w));
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
System.out.print(g);
}
}