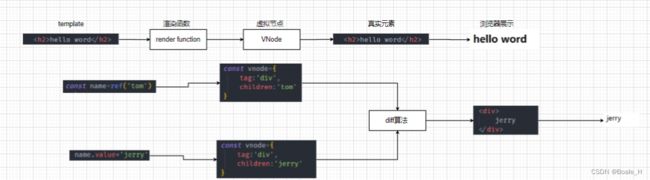
vue如何通过VNode渲染节点
vue如何通过VNode渲染节点
-
- vue的源码包含三大核心
- 实现一个Mini-Vue
-
- 渲染系统的实现
- vue2和vue3写法上的区别
vue的源码包含三大核心
Compiler模块:编译模板系统
Runtime模块:也可以称之为Renderer模块,真正的渲染的模块
Reactivity模块:响应式系统
实现一个Mini-Vue
包含三个模块:
渲染系统模块
可响应式系统模块
应用程序入口模块
渲染系统的实现
该模块主要包含三个功能:
功能一:h函数,用于返回一个VNode对象;
功能二:mount函数,用于将VNode挂载到DOM
功能三:patch函数,用于对两个VNode进行对比,决定如何处理新的VNode
第一步,创建一个renderer.js文件,定义一个h函数
const h = (tag, props, children) => {
// vnode就是一个JavaScript对象
return {
tag,
props,
children
}
}
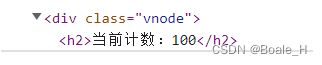
在html文件中,引入文件,并创建一个虚拟节点,可以输出打印一下这个vnode
<div id="app">div>
<script src="./renderer.js">script>
<script>
// 1、 通过h函数来创建一个vnode
const vnode = h('div', {
class: 'vnode'
}, [
h('h2', null, '当前计数:100'),
h('button', null, "+1")
])
console.log(vnode)
script>

第二步,实现挂载功能
在renderer.js文件中定义mount方法
const mount = (vnode, container) => {
//1、 将vnode变为elemnt,创建出真实的dom,并且在vnode上保存一份el
const el = vnode.el = document.createElement(vnode.tag)
// 2、处理props
if (vnode.props) {
for (const key in vnode.props) {
const value = vnode.props[key]
// 判断传递过来的是否是方法,比如onClick
if (key.startsWith("on")) {
el.addEventListener(key.slice(2).toLowerCase(), value)
}
// 设置属性
el.setAttribute(key, value)
}
}
// 3、处理children
if (vnode.children) {
// 如果子节点存在并且子节点是字符串,说明是其中的内容
if (typeof vnode.children === 'string') {
// 将内容放进去
el.textContent = vnode.children
} else {
// 说明子节点中是一个数组,其内部还有子节点
vnode.children.forEach((item) => {
// 再次调用挂载到el上
mount(item,el)
})
}
}
// 4、将el挂载到container上
container.appendChild(el)
}
在html文件中调用该mount方法
// 2、通过mount函数,将vnode挂载到#app上
mount(vnode,document.getElementById('app'))
再次刷新页面的时候就可以看到界面已经加载出来了vnode

第三步实现diff算法
第一种情况:节点不相同
新建一个vnode
// 3、创建一个新的vnode
const vnode1 = h('h2', {
class: 'vnode'
}, 'jerry')
将新的vnode替换旧的vnode,两个vnode之间进行一个diff算法,根据diff算法找到需要修改真实dom的那个地方,找到之后在进行修改
在renderer.js文件中定义一个patch方法
const patch=(n1,n2)=>{
// 判断两个vnode的类型是否一样,比如说n1为div,n2为h2
if(n1.tag!==n2.tag){
// 拿到n1节点的父元素
const n1ElementParent=n1.el.parentElement;
// 移除n1节点
n1ElementParent.removeChild(n1.el)
// 将n2节点添加上去
mount(n2,n1ElementParent)
}else{
}
}
在html文件中使用patch方法
patch(vnode,vnode1)
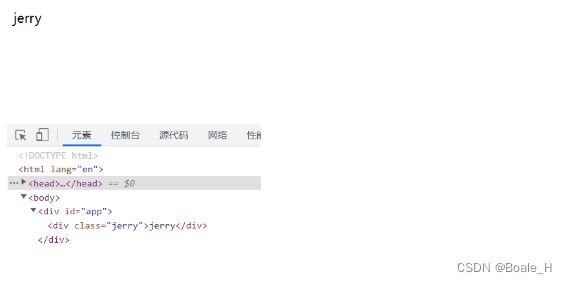
再次刷新页面可以看到已经替换

第二种情况:节点相同,类名不同
patch方法
const patch = (n1, n2) => {
// 判断两个vnode的类型是否一样,比如说n1为div,n2为h2
if (n1.tag !== n2.tag) {
// 拿到n1节点的父元素
const n1ElementParent = n1.el.parentElement;
// 移除n1节点
n1ElementParent.removeChild(n1.el)
// 将n2节点添加上去
mount(n2, n1ElementParent)
} else {
// 1、拿出element对象,并在n2中保留一份
const el = n2.el = n1.el
// 2、处理props
const oldProps = n1.props || {}
const newProps = n2.props || {}
// 2、1获取所有的newProps添加到el中
for (const key in newProps) {
const oldValue = oldProps[key]
const newValue = newProps[key]
if (newValue !== oldValue) {
// 判断传递过来的是否是方法,比如onClick
if (key.startsWith("on")) {
el.addEventListener(key.slice(2).toLowerCase(), newValue)
} else {
el.setAttribute(key, newValue)
}
}
}
// 2、2删除旧的props
for(const key in oldProps){
if(!(key in newProps)){
if (key.startsWith("on")) {
const value=oldProps[key]
el.removeEventListener(key.slice(2).toLowerCase(), value)
} else {
el.removeAttribute(key)
}
}
}
// 3、处理children
}
}
在html中新建一个节点,调用patch方法
// 3、创建一个新的vnode
const vnode1 = h('div', {
class: 'jerry'
}, 'jerry')
patch(vnode,vnode1)
// 3、处理children
const oldChildren = n1.children || [];
const newChildren = n2.children || [];
// 情况一:newChildren是一个string类型
if (typeof newChildren === "string") {
if (typeof oldChildren === "string") {
if (newChildren !== oldChildren) {
el.textContent = newChildren
}
} else {
el.innerHTML = newChildren;
}
}else{
// 情况二:newChildren是一个数组
if(typeof oldChildren==='string'){
el.innerHTML=""
newChildren.forEach(item=>{
mount(item,el)
})
}else{
// oldChildren:[n1,n2,n3]
// newChildren:[n1,n2,n3,n4,n5]
// 前面有相同节点的元素进行patch操作
const commonLength=Math.min(oldChildren.length,newChildren.length)
for(let i=0;i<commonLength;i++){
patch(oldChildren[i],newChildren[i])
}
// 如果newChildren.length>oldChildren
// oldChildren:[n1,n2,n3]
// newChildren:[n1,n2,n3,n4,n5]
if(newChildren.length>oldChildren.length){
newChildren.slice(oldChildren.length).forEach(item=>{
mount(item,el)
})
}
// 如果newChildren.length
// oldChildren:[n1,n2,n3,n4,n5]
// newChildren:[n1,n2,n3]
if(newChildren.length<oldChildren.length){
oldChildren.slice(newChildren.length).forEach(item=>{
el.removeChild(item.el)
})
}
}
}
}
创建两个不同的节点,在进行patch操作
// 1、 通过h函数来创建一个vnode
const vnode = h('div', {
class: 'vnode'
}, [
h('h2', null, '当前计数:100'),
h('button',{onClick:function(){}}, "+1")
])
// 2、通过mount函数,将vnode挂载到#app上
mount(vnode,document.getElementById('app'))
// 3、创建一个新的vnode
const vnode1 = h('div', {
class: 'jerry'
}, 'jerry')
patch(vnode,vnode1)
vue2和vue3写法上的区别
主要是在获取h函数以及事件绑定上有区别
vue2
const h = this.$createElement;
const vnode = h('div', {
class: 'v-node-ele',
on: {
click: () => {
console.log('点击事件')
}
}
}, '虚拟节点内容')
vue3
import { h } from 'vue';
const vnode = h('div', {
class: 'v-node-ele',
onClick: () => {
console.log('点击事件')
}
}, h(
'span', null, 'children内容'
))
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/keyeking/p/16112165.html
https://blog.csdn.net/txf666/article/details/124755693
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42009005/article/details/122986362