【Linux后端服务器开发】线程创建/终止/等待/分离
目录
一、线程概念
二、线程创建
三、线程间共享全局变量
四、批量创建线程
五、多线程的局部变量
六、线程终止
七、线程等待
八、线程分离
一、线程概念
线程:线程是进程内的执行流
windows环境:线程有专门的数据结构,TCB
linux环境:线程与进程一样用PCB描述
进程是承担分配系统资源的基本实体,线程是cpu调用资源的基本单位
创建线程需要链接pthread动态库
线程间切换比进程间切换成本更低:cache在线程间上下文切换时不用再更新
线程的缺点:
性能损失:cpu的核数决定线程的个数,cpu的个数决定进程的个数
健壮性降低:一个线程挂掉会影响另一个线程
缺乏访问控制:进程是访问控制的基本粒度,在一个线程中调用某个os函数会对整个进程造成影响
编程难度提高:多线程的编程和调试难度提高
二、线程创建
makefile
mythread: mythread.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -lpthread
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf mythreadmythread.cc
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void* thread_routine(void* args)
{
while (true)
{
cout << "我是子线程, 我正在运行..." << endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
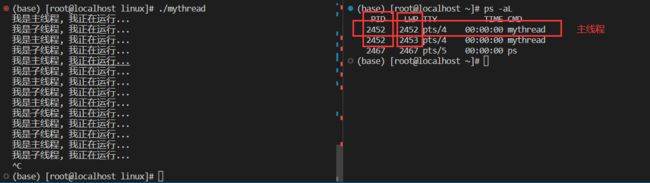
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_routine, (void*)"thread one");
//主线程
while (true)
{
cout << "我是主线程, 我正在运行..." << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
} 由运行结果可得,线程的LWP与PID有关,且主线程的LWP与PID相等
三、线程间共享全局变量
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
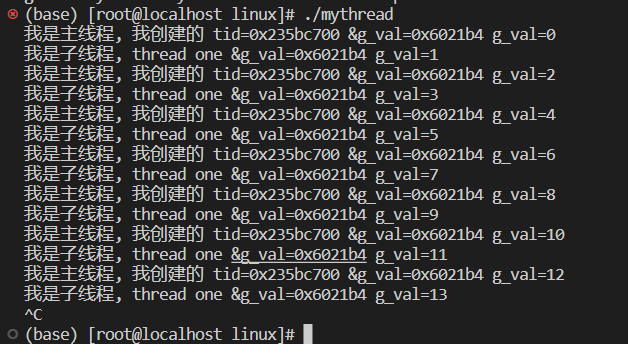
int g_val = 0;
void* thread_routine(void* args)
{
const char* name = (const char*)args;
while (true)
{
cout << "我是子线程, " << name << " &g_val=" << &g_val << " g_val=" << g_val << endl;
++g_val;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
int n = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_routine, (void*)"thread one");
assert(n == 0);
//主线程
while (true)
{
char buffer[64];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", tid);
cout << "我是主线程, 我创建的 tid=" << buffer << " &g_val=" << &g_val << " g_val=" << g_val << endl;
++g_val;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
} 线程私有的资源:
- PCB属性私有
- 私有上下文结构
- 私有栈结构
四、批量创建线程
// int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine)(void*), void arg)
// thread: 返回线程id
// attr: 设置线程的属性,attr为NULL表示使用默认值
// start_routine: 是个函数地址,线程启动后要执行的函数
// atg: 产给线程启动函数的参数#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class ThreadData
{
public:
pthread_t tid;
char namebuffer[64];
};
void* start_routine(void* args)
{
ThreadData* td = static_cast(args); //安全的进行强制类型转化
int cnt = 3;
while (cnt)
{
cout << "new thread create success, name : " << td->namebuffer << " cnt: " << cnt-- << endl;
sleep(1);
}
delete td;
return nullptr;
}
int main()
{
vector threads;
#define NUM 3
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; ++i)
{
ThreadData* td = new ThreadData();
snprintf(td->namebuffer, sizeof(td->namebuffer), "%s:%d", "thread", i + 1);
pthread_create(&td->tid, nullptr, start_routine, td);
threads.push_back(td);
}
for (auto& iter: threads)
cout << "create thread: " << iter->namebuffer << " : " << iter->tid << endl;
while (true) {
cout << "new thread create success, name : main thread" << endl;
sleep(1);
}
} 五、多线程的局部变量
每个线程都有独立的栈结构,线程内部定义的变量并不共享
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class ThreadData
{
public:
pthread_t tid;
char namebuffer[64];
};
void* start_routine(void* args)
{
sleep(1);
ThreadData* td = static_cast(args); //安全的进行强制类型转化
int cnt = 3;
while (cnt)
{
cout << "cnt: " << cnt << " &cnt: " << &cnt << endl;
cnt--;
sleep(1);
}
delete td;
return nullptr;
}
int main()
{
vector threads;
#define NUM 3
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; ++i)
{
ThreadData* td = new ThreadData();
snprintf(td->namebuffer, sizeof(td->namebuffer), "%s:%d", "thread", i + 1);
pthread_create(&td->tid, nullptr, start_routine, td);
threads.push_back(td);
}
for (auto& iter: threads)
cout << "create thread: " << iter->namebuffer << " : " << iter->tid << endl;
while (true)
{
cout << "new thread create success, name : main thread" << endl;
sleep(1);
}
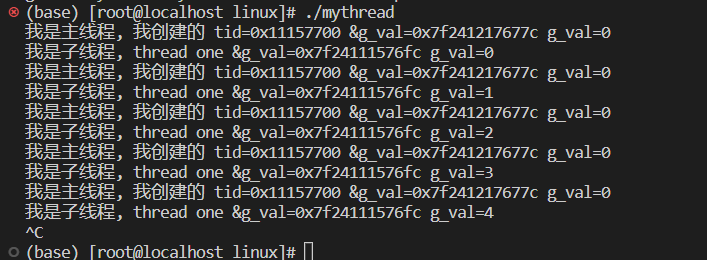
} __thread 内置类型
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// 添加 __thread ,可以将一个内置类型设置为线程局部存储
__thread int g_val = 0;
void* thread_routine(void* args)
{
const char* name = (const char*)args;
while (true)
{
cout << "我是子线程, " << name << " &g_val=" << &g_val << " g_val=" << g_val << endl;
++g_val;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
int n = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_routine, (void*)"thread one");
assert(n == 0);
//主线程
while (true)
{
char buffer[64];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", tid);
cout << "我是主线程, 我创建的 tid=" << buffer << " &g_val=" << &g_val << " g_val=" << g_val << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
} 六、线程终止
1. return :线程对应的函数返回了,线程也就终止了
2. pthread_exit() :线程终止信号,exit信号是进程终止信号
3. pthread_cance() :线程取消
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class ThreadData
{
public:
int number;
pthread_t tid;
char namebuffer[64];
};
class ThreadReturn
{
public:
int exit_code;
int exit_result;
};
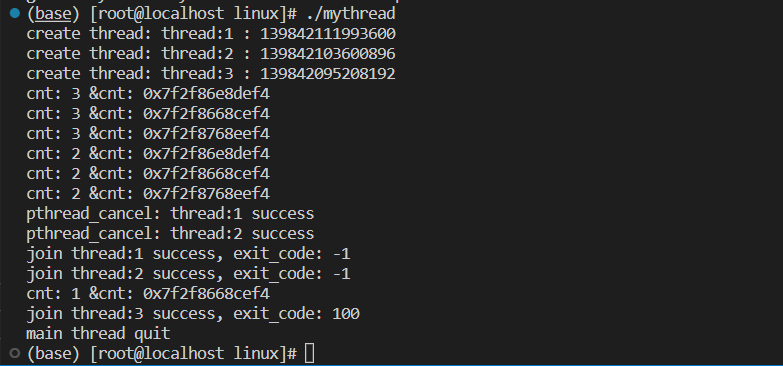
void* start_routine(void* args)
{
ThreadData* td = static_cast(args); //安全的进行强制类型转化
int cnt = 3;
while (cnt)
{
cout << "cnt: " << cnt << " &cnt: " << &cnt << endl;
cnt--;
sleep(1);
}
// delete td;
// return nullptr;
// pthread_exit(nullptr);
// return (void*)td->number;
// pthread_exit((void*)td->number);
// ThreadReturn* tr = new ThreadReturn();
// tr->exit_code = 1;
// tr->exit_result = td->number;
// return (void*)tr;
return (void*)100;
}
int main()
{
vector threads;
#define NUM 3
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; ++i)
{
ThreadData* td = new ThreadData();
td->number = i + 1;
snprintf(td->namebuffer, sizeof(td->namebuffer), "%s:%d", "thread", i + 1);
pthread_create(&td->tid, nullptr, start_routine, td);
threads.push_back(td);
}
for (auto& iter: threads)
cout << "create thread: " << iter->namebuffer << " : " << iter->tid << endl;
sleep(2);
for (int i = 0; i <= threads.size() / 2; ++i)
{
pthread_cancel(threads[i]->tid);
cout << "pthread_cancel: " << threads[i]->namebuffer << " success " << endl;
// 取消线程的线程的前提是线程还在运行
// 如果线程被取消,退出码为 -1
}
for (auto& iter: threads)
{
void* ret = nullptr;
// ThreadReturn* ret = nullptr;
// int n = pthread_join(iter->tid, nullptr);
int n = pthread_join(iter->tid, &ret); // void** pret;
assert(n == 0);
// cout << "join " << iter->namebuffer << " success, number: " << (long long)ret << endl;
cout << "join " << iter->namebuffer << " success, exit_code: " << (long long)ret << endl;
delete iter;
}
cout << "main thread quit" << endl;
return 0;
} 七、线程等待
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void** retval);
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class ThreadData
{
public:
pthread_t tid;
char namebuffer[64];
};
void* start_routine(void* args)
{
ThreadData* td = static_cast(args); //安全的进行强制类型转化
int cnt = 3;
while (cnt)
{
cout << "cnt: " << cnt << " &cnt: " << &cnt << endl;
cnt--;
sleep(1);
}
// delete td;
pthread_exit(nullptr);
}
int main()
{
vector threads;
#define NUM 3
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; ++i)
{
ThreadData* td = new ThreadData();
snprintf(td->namebuffer, sizeof(td->namebuffer), "%s:%d", "thread", i + 1);
pthread_create(&td->tid, nullptr, start_routine, td);
threads.push_back(td);
}
for (auto& iter: threads)
cout << "create thread: " << iter->namebuffer << " : " << iter->tid << endl;
for (auto& iter: threads)
{
int n = pthread_join(iter->tid, nullptr);
assert(n == 0);
cout << "join " << iter->namebuffer << " success " << endl;
delete iter;
}
while (true)
{
cout << "new thread create success, name : main thread" << endl;
sleep(1);
}
} 线程等待返回值
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class ThreadData
{
public:
int number;
pthread_t tid;
char namebuffer[64];
};
class ThreadReturn
{
public:
int exit_code;
int exit_result;
};
void* start_routine(void* args)
{
ThreadData* td = static_cast(args); //安全的进行强制类型转化
int cnt = 3;
while (cnt)
{
cout << "cnt: " << cnt << " &cnt: " << &cnt << endl;
cnt--;
sleep(1);
}
// delete td;
// return nullptr;
// pthread_exit(nullptr);
// return (void*)td->number;
// pthread_exit((void*)td->number);
ThreadReturn* tr = new ThreadReturn();
tr->exit_code = 1;
tr->exit_result = td->number;
return (void*)tr;
}
int main()
{
vector threads;
#define NUM 3
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; ++i)
{
ThreadData* td = new ThreadData();
td->number = i + 1;
snprintf(td->namebuffer, sizeof(td->namebuffer), "%s:%d", "thread", i + 1);
pthread_create(&td->tid, nullptr, start_routine, td);
threads.push_back(td);
}
for (auto& iter: threads)
cout << "create thread: " << iter->namebuffer << " : " << iter->tid << endl;
// sleep(5);
// for (int i = 0; i < threads.size() / 2; ++i)
// {
// pthread_cancel(threads[i]->tid);
// cout << "pthread_cancel: " << threads[i]->namebuffer << " success " << endl;
// // 如果线程被取消,退出码为i-1
// }
for (auto& iter: threads)
{
// void* ret = nullptr;
ThreadReturn* ret = nullptr;
// int n = pthread_join(iter->tid, nullptr);
int n = pthread_join(iter->tid, (void**)&ret); // void** pret;
assert(n == 0);
// cout << "join " << iter->namebuffer << " success, number: " << (long long)ret << endl;
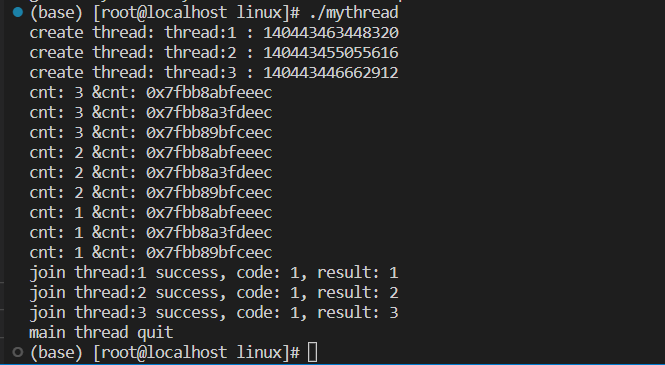
cout << "join " << iter->namebuffer << " success, code: " << ret->exit_code << ", result: " << ret->exit_result << endl;
delete iter;
}
cout << "main thread quit" << endl;
return 0;
} 八、线程分离
pthread_self() 获得线程ID
pthread_detach() 线程分离
线程分离状态,主线程无法等待
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
string changeID(const pthread_t& thread_id)
{
char tid[128];
snprintf(tid, sizeof(tid), "0x%x", thread_id);
return tid;
}
void* start_routine(void* args)
{
string name = static_cast(args);
// pthread_detach(pthread_self()); // 设置自己为分离状态
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
cout << name <<" running ... : " << changeID(pthread_self()) << endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, start_routine, (void*)"thread one");
string main_id = changeID(pthread_self());
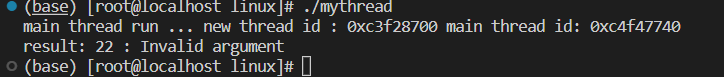
cout << "main thread run ... new thread id : " << changeID(tid) << " main thread id: " << main_id << endl;
// pthread_join(tid, nullptr);
pthread_detach(tid); // 主线程分离新线程
// sleep(1);
// 一个线程默认是joinable的,如果设置了分离状态,不能够再进行等待了
int n = pthread_join(tid, nullptr);
cout << "result: " << n << " : " << strerror(n) << endl;
return 0;
}