PAT (Basic Level) Practice (中文)题目集合
1001 害死人不偿命的(3n+1)猜想 (15 分)
#include1002 写出这个数 (20 分)
#include1003 我要通过! (20 分)
题解链接
1004 成绩排名 (20 分)
#include1005 继续(3n+1)猜想 (25 分)
#include1006 换个格式输出整数 (15 分)
#include1007 素数对猜想 (20 分)
#include1008 数组元素循环右移问题 (20 分)
#include1009 说反话 (20 分)
#include更新于2022.4.22
想到一个更简单的做法:
#include1010 一元多项式求导 (25 分)
#include1011 A+B 和 C (15 分)
#include1012 数字分类 (20 分)
#include1013 数素数 (20 分)
#include1014 福尔摩斯的约会 (20 分)
测试点太坑了!
测试点分析
#include1015 德才论 (25 分)
#include1016 部分A+B (15 分)
#include1017 A除以B (20 分)
高精度模板
#include1018 锤子剪刀布 (20 分)
#include1019 数字黑洞 (20 分)
#include1020 月饼 (25 分)
#include1021 个位数统计 (15 分)
#include1022 D进制的A+B (20 分)
#include更新于2022.4.22
更简单的写法:
#include1023 组个最小数 (20 分)
#include1024 科学计数法 (20 分)
分指数小于0和大于等于0两种情况,对于大于等于0的情况还要再细分是否输出.。
#include1025 反转链表 (25 分)
沃日,柳神太强了吧!!!
#include1026 程序运行时间 (15 分)
#include1027 打印沙漏 (20 分)
#include 1028 人口普查 (20 分)
注意,要比较年龄大小不是只比较年份,需要比较出生了多少天。
而且计算天数的时候不能从出生日期枚举到今天,会超时。
#include1029 旧键盘 (20 分)
千万不要把这个题理解成什么字符串匹配之类的问题,这就是个看第二行的字符串比第一行的字符串少了哪些种类的字符,而且要将字符串都转换为大写或小写来比较,最好是转换成大写因为最后让输出大写,否则还要再转换一次。
#include1030 完美数列 (25 分)
题解链接
1031 查验身份证 (15 分)
#include1032 挖掘机技术哪家强 (20 分)
#include1033 旧键盘打字 (20 分)
注意:
- 要使用 getline !
- +是上档键,其他符号均不是!
#include1034 有理数四则运算 (20 分)
这种给出分子和分母进行四则运算的题,想要计算结果不要一上来就对输入的四个数进行约分化简啥的,因为没意义,完全可以直接通过四个数的简单运算得到结果的分子和分母。
本题无论是结果部分,还是操作数部分,都具有相同的输出格式,所以我们采用同一函数处理。
#include1035 插入与归并 (25 分)
感觉这个题出的挺拉的。
有些情况既可以归为插入也可以归为归并;数据过于水,各种得到归并排序的合并区间的大小的方法都能过。
下面注释掉的方法是,取前两个不降序序列的长度中的较小者作为得到第二个序列时采用的合并区间的大小;没注释掉的方法是统计全部非最后一个不降序序列的长度的最小值作为得到第二个序列时采用的合并区间,之所以采用这个思路是因为前一个思路对于如下输入是不正确的(尽管可以过):
13
2 1 6 5 8 7 4 3 10 12 9 13 11
1 2 5 6 7 8 3 4 10 12 9 13 11
1 2 5 6 3 4 7 8 9 10 12 13 11
可以看出得到第二个序列采用的合并区间大小为2,即从第一个变为第二个是将相邻大小为1进行合并得到的,即每两个相邻的元素是有序的;所以下一步应该是保证每四个相邻元素是有序的;
但是要采用前一个思路,则会得到第二个序列采用的合并区间大小为4,下一步会将整个序列排列有序。
太坑了,判断是否为插入排序的时候不严格也可以。
#include1036 跟奥巴马一起编程 (15 分)
#include1037 在霍格沃茨找零钱 (20 分)
#include1038 统计同成绩学生 (20 分)
#include1039 到底买不买 (20 分)
#include1040 有几个PAT (25 分)
题解链接
1041 考试座位号 (15 分)
#include1042 字符统计 (20 分)
#include1043 输出PATest (20 分)
#include1044 火星数字 (20 分)
本题注意只有一种情况会输出tret,就是输入为0;tret总是单独一个字符串存在的。
#include 1045 快速排序 (25 分)
看正确率以为很难,其实不难,就是有点坑,测试点2要求0个的时候第二行要输出空行。
稍微用点思维吧,顺序遍历的时候更新遇到的最大值,逆序遍历的时候更新遇到的最小值,如果遇到的
#include1046 划拳 (15 分)
#include 1047 编程团体赛 (20 分)
#include1048 数字加密 (20 分)
#include1049 数列的片段和 (20 分)
柳神用的扩大一定的倍数来保证精度不丢失,我是直接使用了long double,注意longdouble在使用printf输出时要用Lf!
(一开始还想直接算组合数,仔细一看范围就不行了,所以换了思路)
#include更新于2022.4.22
看不懂自己之前写的代码了,重新写了个简单的:
#include1050 螺旋矩阵 (25 分)
首先说明一下题目的意思,就是需要自己去确定m和n,m和n满足:
- m * n = N;
- m不小于n;
- 二者的差值尽可能小.
先按照题目说的顺序赋值到一个新的数组中,再输出。
由于如果直接开数组会爆,所以需要开二维vector,行是m列是n。(如果会用C里的分配空间的函数也可以,我忘记如何用了)
#include1051 复数乘法 (15 分)
无需控制实部为零不输出实部,虚部为零不输出虚部,没有这个测试点。
只需要注意精度小于一定程度的时候归为0,例如0.003-0.004i是要输出0.00+0.00i的,如果不归零则会出现输出-0.00i的情况。
#include1052 卖个萌 (20 分)
我眼瞎,没看见要输出括号,debug良久。
#include1053 住房空置率 (20 分)
如果是“空置”,那么就不是“可能空置”了。
#include1054 求平均值 (20 分)
看的柳神的!
有关 sscanf 和 sprintf 的用法
#include1055 集体照 (25 分)
题解链接
1056 组合数的和 (15 分)
请多一点这种题!
这数据量、空限、时限都非常感人~ ~ ~ ~
#include1057 数零壹 (20 分)
#include1058 选择题 (20 分)
#include1059 C语言竞赛 (20 分)
#include1060 爱丁顿数 (25 分)
我用的yxc模板进行的二分。
注意坑点:r要初始化为n,因为有可能全部天数都被选上
#include1061 判断题 (15 分)
#include1062 最简分数 (20 分)
#include1063 计算谱半径 (20 分)
#include1064 朋友数 (20 分)
#include1065 单身狗 (25 分)
#include1066 图像过滤 (15 分)
用sca
#include1067 试密码 (20 分)
不知道为什么这道题正确率这么低。
#include1068 万绿丛中一点红 (20 分)
#include1069 微博转发抽奖 (20 分)
#include1070 结绳 (25 分)
#include1071 小赌怡情 (15 分)
小赌也不怡情哦~
#include1072 开学寄语 (20 分)
一定注意输出编号的时候位数的控制。
#include1073 多选题常见计分法 (20 分)
真题真麻烦啊。
注意某个题的某个选项出错的次数是漏选之与多(错)选之之和。
#include1074 宇宙无敌加法器 (20 分)
#include1075 链表元素分类 (25 分)
题解链接
1076 Wifi密码 (15 分)
#include1077 互评成绩计算 (20 分)
#include1078 字符串压缩与解压 (20 分)
#include1079 延迟的回文数 (20 分)
高精度加法而已。
#include1080 MOOC期终成绩 (25 分)
题目写的我服了啊!
![]()
???;否则 ???
#include1081 检查密码 (15 分)
#include1082 射击比赛 (20 分)
#include1083 是否存在相等的差 (20 分)
#include1084 外观数列 (20 分)
#include1085 PAT单位排行 (25 分)
注意最后一个测试点要改double啥的。
#include1086 就不告诉你 (15 分)
我靠,怪不得正确率不是特别高,有些情况要考虑到:
- 1000,倒过来是1
- 2010,倒过来是102
还考虑到了负数,但是题目说了是正整数。
#include1087 有多少不同的值 (20 分)
#include1088 三人行 (20 分)
坑点:丙不一定是整数!
#include1089 狼人杀-简单版 (20 分)
卧槽,柳神水平确实牛皮!
题解链接
1090 危险品装箱 (25 分)
#include1091 N-自守数 (15 分)
#include1092 最好吃的月饼 (20 分)
#include1093 字符串A+B (20 分)
#include1094 谷歌的招聘 (20 分)
#include1095 解码PAT准考证 (25 分)
用STL不会超时,但是用cin和cout会超时,要用scanf和printf!!!
一开始我以为是因为我的每次询问都排序导致超时,所以将在线处理改为离线了,预处理排序,最后测试点3还是超时,其实应该不是这个原因,M才10不至于。
使用cin cout最多将最后一个测试点优化到190s,但是测试点3还是过不去,看了别人的博客发现其实根本原因在于使用scanf和printf,瞬间耗时降低到了两位数。
#include1096 大美数 (15 分)
这也太暴力了吧。
试除法求全部约数的模板
#include1097 矩阵行平移 (20 分)
(凭一己之力拉低正确率)
#include1098 岩洞施工 (20 分)
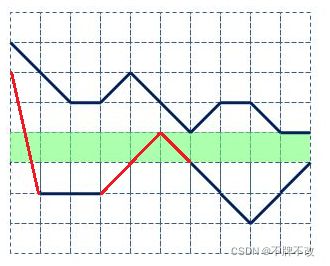
至少需要削掉的高度,不是指多个高出来的都要加起来,而是高出来的高度取max。
举个例子,两处红色部分都是高出的部分,要保证一个方格宽度的道路就必须把最高的那个去掉,而小的那么也会被同时去掉;当然不一定非要选绿色道路作为目标,也可以选其上面那行,原理一样结果一样。
#include1099 性感素数 (20 分)
#include1100 校庆 (25 分)
#include1101 B是A的多少倍 (15 分)
#include 1102 教超冠军卷 (20 分)
#include1103 缘分数 (20 分)
坑点:最后一个测试点“其中 a 和它的小弟 a−1 的立方差正好是另一个整数 c 的平方”。
#include1104 天长地久 (20 分)
题解链接
1105 链表合并 (25 分)
题解链接
1106 2019数列 (15 分)
有可能n<4
#include1107 老鼠爱大米 (20 分)
#include1108 String复读机 (20 分)
做过至少三次了吧。
#include1109 擅长C (20 分)
#include1110 区块反转 (25 分)
题解链接