STM32F767 FatFs SD卡中断
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* © Copyright (c) 2021 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software component is licensed by ST under BSD 3-Clause license,
* the "License"; You may not use this file except in compliance with the
* License. You may obtain a copy of the License at:
* opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "main.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include "delay.h"
#include "bsp_printf.h"
#include "bsp_key.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "bsp_sdram.h"
#include "bsp_malloc.h"
#include "bsp_sdmmc.h"
#include "ff.h" /* Obtains integer types */
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro -------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
SD_HandleTypeDef hsd1;
UART_HandleTypeDef huart1;
SDRAM_HandleTypeDef hsdram1;
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
volatile uint8_t rx_done, tx_done;
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_USART1_UART_Init(void);
static void MX_SDMMC1_SD_Init(void);
static void MX_FMC_Init(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
//通过串口打印SD卡相关信息
void show_sdcard_info(void)
{
HAL_SD_CardCIDTypeDef cid;
switch(hsd1.SdCard.CardVersion)
{
case CARD_V1_X:printf("Card Version:CARD_V1_X\r\n");break;
case CARD_V2_X:printf("Card Version:CARD_V2_X\r\n");break;
}
switch(hsd1.SdCard.CardType)
{
case CARD_SDSC:printf("Card Type:CARD_SDSC\r\n");break;
case CARD_SDHC_SDXC:printf("Card Type:CARD_SDHC_SDXC\r\n");break;
case CARD_SECURED:printf("Card Type:CARD_SECURED\r\n");break;
}
if(HAL_OK != HAL_SD_GetCardCID(&hsd1, &cid))
{
Error_Handler();
}
printf("Card ManufacturerID:%d\r\n",cid.ManufacturerID); //制造商ID
printf("Card RCA:%d\r\n",hsd1.SdCard.RelCardAdd ); //卡相对地址
printf("Card Capacity:%d MB\r\n",(uint32_t)(((uint64_t)hsd1.SdCard.BlockNbr*hsd1.SdCard.BlockSize)>>20)); //显示容量
printf("Card BlockSize:%d\r\n\r\n",hsd1.SdCard.BlockSize); //显示块大小
printf("Card LogBlockNbr:%d\r\n\r\n",hsd1.SdCard.LogBlockNbr);
printf("Card LogBlockSize:%d\r\n\r\n",hsd1.SdCard.LogBlockSize);
}
static void Sdram_SendCommand(uint32_t CommandMode, uint32_t CommandTarget, uint32_t AutoRefreshNumber, uint32_t ModeRegisterDefinition)
{
FMC_SDRAM_CommandTypeDef Command;
Command.AutoRefreshNumber = AutoRefreshNumber;
Command.CommandMode = CommandMode;
Command.CommandTarget = CommandTarget;
Command.ModeRegisterDefinition = ModeRegisterDefinition;
HAL_SDRAM_SendCommand(&hsdram1, &Command, 0);
}
static void Sdram_Init_Sequence(void)
{
uint32_t ModeRegisterDefinition;
// uint16_t Mode_WB;
// uint16_t Mode_Op;
// uint16_t Mode_CasLatency;
// uint16_t Mode_Bt;
// uint16_t Mode_BurstLength;
Sdram_SendCommand(FMC_SDRAM_CMD_CLK_ENABLE, FMC_SDRAM_CMD_TARGET_BANK1, 0, 0);
delay_us(200);
Sdram_SendCommand(FMC_SDRAM_CMD_PALL, FMC_SDRAM_CMD_TARGET_BANK1, 0, 0);
Sdram_SendCommand(FMC_SDRAM_CMD_AUTOREFRESH_MODE, FMC_SDRAM_CMD_TARGET_BANK1, 1, 0);
//SDRAM????2?êy
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_BURST_LENGTH_1 ((uint16_t)0x0000)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_BURST_LENGTH_2 ((uint16_t)0x0001)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_BURST_LENGTH_4 ((uint16_t)0x0002)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_BURST_LENGTH_8 ((uint16_t)0x0004)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_BURST_TYPE_SEQUENTIAL ((uint16_t)0x0000)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_BURST_TYPE_INTERLEAVED ((uint16_t)0x0008)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_CAS_LATENCY_2 ((uint16_t)0x0020)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_CAS_LATENCY_3 ((uint16_t)0x0030)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_OPERATING_MODE_STANDARD ((uint16_t)0x0000)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_WRITEBURST_MODE_PROGRAMMED ((uint16_t)0x0000)
#define SDRAM_MODEREG_WRITEBURST_MODE_SINGLE ((uint16_t)0x0200)
ModeRegisterDefinition=(uint32_t)SDRAM_MODEREG_BURST_LENGTH_1 | //éè??í?·¢3¤?è:1(?éò?ê?1/2/4/8)
SDRAM_MODEREG_BURST_TYPE_SEQUENTIAL | //éè??í?·¢ààDí:á?D?(?éò?ê?á?D?/??′í)
SDRAM_MODEREG_CAS_LATENCY_3 | //éè??CAS?μ:3(?éò?ê?2/3)
SDRAM_MODEREG_OPERATING_MODE_STANDARD | //éè??2ù×÷?£ê?:0,±ê×??£ê?
SDRAM_MODEREG_WRITEBURST_MODE_SINGLE; //éè??í?·¢D′?£ê?:1,μ¥μ?·??ê
Sdram_SendCommand(FMC_SDRAM_CMD_LOAD_MODE, FMC_SDRAM_CMD_TARGET_BANK1, 1, ModeRegisterDefinition);
HAL_SDRAM_ProgramRefreshRate(&hsdram1, 824);
}
char QSPIPath[4]; /* QSPI flash logical drive path */
FATFS fs; /* FatFs文件系统对象 */
FIL fnew; /* 文件对象 */
FRESULT res_flash; /* 文件操作结果 */
UINT fnum; /* 文件成功读写数量 */
char fpath[100]; /* 保存当前扫描路径 */
char readbuffer[512]; /* */
/* FatFs多项功能测试 */
DIR dir;
FATFS *pfs;
DWORD fre_clust, fre_sect, tot_sect;
static FRESULT miscellaneous(void)
{
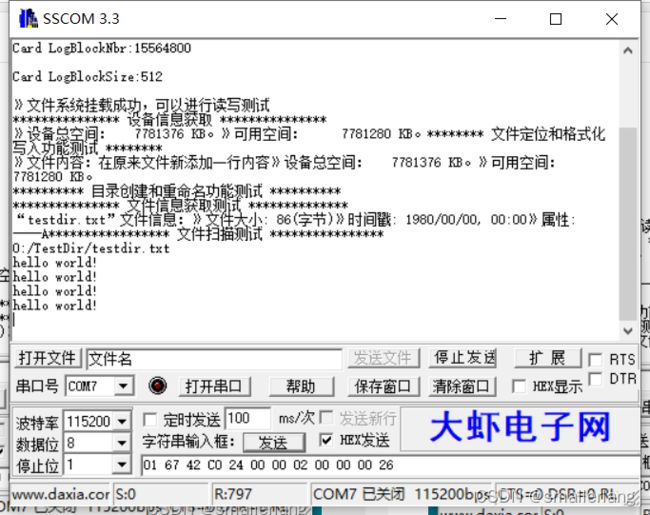
printf("\n*************** 设备信息获取 ***************\r\n");
/* 获取设备信息和空簇大小 */
res_flash = f_getfree("0:", &fre_clust, &pfs);
/* 计算得到总的扇区个数和空扇区个数 */
tot_sect = (pfs->n_fatent - 2) * pfs->csize;
fre_sect = fre_clust * pfs->csize;
/* 打印信息(4096 字节/扇区) */
printf("》设备总空间:%10lu KB。\n》可用空间: %10lu KB。\n", tot_sect /2, fre_sect /2);
printf("\n******** 文件定位和格式化写入功能测试 ********\r\n");
res_flash = f_open(&fnew, "0:FatFs读写测试文件.txt",
FA_OPEN_ALWAYS|FA_WRITE|FA_READ );
if ( res_flash == FR_OK )
{
/* 文件定位 */
res_flash = f_lseek(&fnew,f_size(&fnew));
if (res_flash == FR_OK)
{
/* 格式化写入,参数格式类似printf函数 */
f_printf(&fnew,"\n在原来文件新添加一行内容\n");
f_printf(&fnew,"》设备总空间:%10lu KB。\n》可用空间: %10lu KB。\n", tot_sect /2, fre_sect /2);
/* 文件定位到文件起始位置 */
res_flash = f_lseek(&fnew,0);
/* 读取文件所有内容到缓存区 */
res_flash = f_read(&fnew,readbuffer,f_size(&fnew),&fnum);
if(res_flash == FR_OK)
{
printf("》文件内容:\n%s\n",readbuffer);
}
}
f_close(&fnew);
printf("\n********** 目录创建和重命名功能测试 **********\r\n");
/* 尝试打开目录 */
res_flash=f_opendir(&dir,"0:TestDir");
if(res_flash!=FR_OK)
{
/* 打开目录失败,就创建目录 */
res_flash=f_mkdir("0:TestDir");
}
else
{
/* 如果目录已经存在,关闭它 */
res_flash=f_closedir(&dir);
/* 删除文件 */
f_unlink("0:TestDir/testdir.txt");
}
if(res_flash==FR_OK)
{
/* 重命名并移动文件 */
res_flash=f_rename("0:FatFs读写测试文件.txt","0:TestDir/testdir.txt");
}
}
else
{
printf("!! 打开文件失败:%d\n",res_flash);
printf("!! 或许需要再次运行“FatFs移植与读写测试”工程\n");
}
return res_flash;
}
/**
* 文件信息获取
*/
static FRESULT file_check(void)
{
FILINFO fno;
/* 获取文件信息 */
res_flash=f_stat("0:TestDir/testdir.txt",&fno);
if(res_flash==FR_OK)
{
printf("“testdir.txt”文件信息:\n");
printf("》文件大小: %ld(字节)\n", fno.fsize);
printf("》时间戳: %u/%02u/%02u, %02u:%02u\n",
(fno.fdate >> 9) + 1980, fno.fdate >> 5 & 15, fno.fdate & 31,fno.ftime >> 11, fno.ftime >> 5 & 63);
printf("》属性: %c%c%c%c%c\n\n",
(fno.fattrib & AM_DIR) ? 'D' : '-', // 是一个目录
(fno.fattrib & AM_RDO) ? 'R' : '-', // 只读文件
(fno.fattrib & AM_HID) ? 'H' : '-', // 隐藏文件
(fno.fattrib & AM_SYS) ? 'S' : '-', // 系统文件
(fno.fattrib & AM_ARC) ? 'A' : '-'); // 档案文件
}
return res_flash;
}
/**
* @brief scan_files 递归扫描FatFs内的文件
* @param path:初始扫描路径
* @retval result:文件系统的返回值
*/
static FRESULT scan_files (char* path)
{
FRESULT res; //部分在递归过程被修改的变量,不用全局变量
FILINFO fno;
DIR dir;
int i;
char *fn; // 文件名
#if _USE_LFN
/* 长文件名支持 */
/* 简体中文需要2个字节保存一个“字”*/
static char lfn[_MAX_LFN*2 + 1];
fno.lfname = lfn;
fno.lfsize = sizeof(lfn);
#endif
//打开目录
res = f_opendir(&dir, path);
if (res == FR_OK)
{
i = strlen(path);
for (;;)
{
//读取目录下的内容,再读会自动读下一个文件
res = f_readdir(&dir, &fno);
//为空时表示所有项目读取完毕,跳出
if (res != FR_OK || fno.fname[0] == 0) break;
#if _USE_LFN
fn = *fno.lfname ? fno.lfname : fno.fname;
#else
fn = fno.fname;
#endif
//点表示当前目录,跳过
if (*fn == '.') continue;
//目录,递归读取
if (fno.fattrib & AM_DIR)
{
//合成完整目录名
sprintf(&path[i], "/%s", fn);
//递归遍历
res = scan_files(path);
path[i] = 0;
//打开失败,跳出循环
if (res != FR_OK)
break;
}
else
{
printf("%s/%s\r\n", path, fn); //输出文件名
/* 可以在这里提取特定格式的文件路径 */
}//else
} //for
}
return res;
}
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
SCB_EnableICache();//使能I-Cache
SCB_EnableDCache();//使能D-Cache
SCB->CACR|=1<<2; //强制D-Cache透写,如不开启,实际使用中可能遇到各种问题
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USART1_UART_Init();
MX_SDMMC1_SD_Init();
MX_FMC_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
delay_init(216);
delay_ms(5000);
Sdram_Init_Sequence();
my_mem_init(SRAMIN); //初始化内部内存池
my_mem_init(SRAMEX); //初始化外部SDRAM内存池
show_sdcard_info(); //打印SD卡相关信息
uint8_t key;
uint8_t buf[512];
uint32_t sd_size;
uint32_t i;
BYTE work[FF_MAX_SS]; /* Work area (larger is better for processing time) */
//在外部SPI Flash挂载文件系统,文件系统挂载时会对SPI设备初始化
res_flash = f_mount(&fs,"0:",1);
if(res_flash == FR_NO_FILESYSTEM)
{
printf("》FLASH还没有文件系统,即将进行格式化...\r\n");
/* 格式化 */
res_flash=f_mkfs("0:",0, work, sizeof work);
if(res_flash == FR_OK)
{
printf("》FLASH已成功格式化文件系统。\r\n");
/* 格式化后,先取消挂载 */
res_flash = f_mount(NULL,"0:",1);
/* 重新挂载 */
res_flash = f_mount(&fs,"0:",1);
}
else
{
printf("《《格式化失败。》》\r\n");
while(1);
}
}
else if(res_flash!=FR_OK)
{
printf("!!外部Flash挂载文件系统失败。(%d)\r\n",res_flash);
printf("!!可能原因:SPI Flash初始化不成功。\r\n");
while(1);
}
else
{
printf("》文件系统挂载成功,可以进行读写测试\r\n");
}
/* FatFs多项功能测试 */
res_flash = miscellaneous();
printf("\n*************** 文件信息获取测试 **************\r\n");
res_flash = file_check();
printf("***************** 文件扫描测试 ****************\r\n");
strcpy(fpath,"0:");
scan_files(fpath);
/* 不再使用文件系统,取消挂载文件系统 */
f_mount(NULL,"0:",1);
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
delay_ms(1000);
printf("hello world!\r\n");
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
RCC_PeriphCLKInitTypeDef PeriphClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Configure LSE Drive Capability
*/
HAL_PWR_EnableBkUpAccess();
/** Configure the main internal regulator output voltage
*/
__HAL_RCC_PWR_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_PWR_VOLTAGESCALING_CONFIG(PWR_REGULATOR_VOLTAGE_SCALE1);
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSEState = RCC_HSE_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLM = 25;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLN = 432;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLP = RCC_PLLP_DIV2;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLQ = 9;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLR = 2;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Activate the Over-Drive mode
*/
if (HAL_PWREx_EnableOverDrive() != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV4;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV2;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_7) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
PeriphClkInitStruct.PeriphClockSelection = RCC_PERIPHCLK_USART1|RCC_PERIPHCLK_SDMMC1
|RCC_PERIPHCLK_CLK48;
PeriphClkInitStruct.Usart1ClockSelection = RCC_USART1CLKSOURCE_PCLK2;
PeriphClkInitStruct.Clk48ClockSelection = RCC_CLK48SOURCE_PLL;
PeriphClkInitStruct.Sdmmc1ClockSelection = RCC_SDMMC1CLKSOURCE_CLK48;
if (HAL_RCCEx_PeriphCLKConfig(&PeriphClkInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Enables the Clock Security System
*/
HAL_RCC_EnableCSS();
}
/**
* @brief SDMMC1 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_SDMMC1_SD_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN SDMMC1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END SDMMC1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN SDMMC1_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END SDMMC1_Init 1 */
hsd1.Instance = SDMMC1;
hsd1.Init.ClockEdge = SDMMC_CLOCK_EDGE_RISING;
hsd1.Init.ClockBypass = SDMMC_CLOCK_BYPASS_DISABLE;
hsd1.Init.ClockPowerSave = SDMMC_CLOCK_POWER_SAVE_DISABLE;
hsd1.Init.BusWide = SDMMC_BUS_WIDE_1B;
hsd1.Init.HardwareFlowControl = SDMMC_HARDWARE_FLOW_CONTROL_DISABLE;
hsd1.Init.ClockDiv = 0;
if (HAL_SD_Init(&hsd1) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
if (HAL_SD_ConfigWideBusOperation(&hsd1, SDMMC_BUS_WIDE_4B) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN SDMMC1_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END SDMMC1_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief USART1 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_USART1_UART_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END USART1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART1_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END USART1_Init 1 */
huart1.Instance = USART1;
huart1.Init.BaudRate = 115200;
huart1.Init.WordLength = UART_WORDLENGTH_8B;
huart1.Init.StopBits = UART_STOPBITS_1;
huart1.Init.Parity = UART_PARITY_NONE;
huart1.Init.Mode = UART_MODE_TX_RX;
huart1.Init.HwFlowCtl = UART_HWCONTROL_NONE;
huart1.Init.OverSampling = UART_OVERSAMPLING_16;
huart1.Init.OneBitSampling = UART_ONE_BIT_SAMPLE_DISABLE;
huart1.AdvancedInit.AdvFeatureInit = UART_ADVFEATURE_NO_INIT;
if (HAL_UART_Init(&huart1) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART1_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END USART1_Init 2 */
}
/* FMC initialization function */
static void MX_FMC_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN FMC_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END FMC_Init 0 */
FMC_SDRAM_TimingTypeDef SdramTiming = {0};
/* USER CODE BEGIN FMC_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END FMC_Init 1 */
/** Perform the SDRAM1 memory initialization sequence
*/
hsdram1.Instance = FMC_SDRAM_DEVICE;
/* hsdram1.Init */
hsdram1.Init.SDBank = FMC_SDRAM_BANK1;
hsdram1.Init.ColumnBitsNumber = FMC_SDRAM_COLUMN_BITS_NUM_9;
hsdram1.Init.RowBitsNumber = FMC_SDRAM_ROW_BITS_NUM_13;
hsdram1.Init.MemoryDataWidth = FMC_SDRAM_MEM_BUS_WIDTH_16;
hsdram1.Init.InternalBankNumber = FMC_SDRAM_INTERN_BANKS_NUM_4;
hsdram1.Init.CASLatency = FMC_SDRAM_CAS_LATENCY_3;
hsdram1.Init.WriteProtection = FMC_SDRAM_WRITE_PROTECTION_DISABLE;
hsdram1.Init.SDClockPeriod = FMC_SDRAM_CLOCK_PERIOD_2;
hsdram1.Init.ReadBurst = FMC_SDRAM_RBURST_ENABLE;
hsdram1.Init.ReadPipeDelay = FMC_SDRAM_RPIPE_DELAY_0;
/* SdramTiming */
SdramTiming.LoadToActiveDelay = 2;
SdramTiming.ExitSelfRefreshDelay = 7;
SdramTiming.SelfRefreshTime = 4;
SdramTiming.RowCycleDelay = 7;
SdramTiming.WriteRecoveryTime = 4;
SdramTiming.RPDelay = 2;
SdramTiming.RCDDelay = 2;
if (HAL_SDRAM_Init(&hsdram1, &SdramTiming) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler( );
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN FMC_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END FMC_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief GPIO Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOC_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOF_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOH_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOG_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOE_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOD_CLK_ENABLE();
/*Configure GPIO pin Output Level */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0|GPIO_PIN_1|GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
/*Configure GPIO pin : PC13 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_13;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_PULLUP;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOC, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/*Configure GPIO pin : PA0 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_0;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_PULLDOWN;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/*Configure GPIO pins : PH2 PH3 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_2|GPIO_PIN_3;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_PULLUP;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOH, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/*Configure GPIO pins : PB0 PB5 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_0|GPIO_PIN_5;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/*Configure GPIO pin : PB1 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_1;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_OD;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/*Configure GPIO pin : PD6 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_6;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_PULLUP;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOD, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
__disable_irq();
while (1)
{
}
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
ex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %d\r\n", file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
/************************ (C) COPYRIGHT STMicroelectronics *****END OF FILE****/
/**
* @brief This function handles SDMMC1 global interrupt.
*/
void SDMMC1_IRQHandler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN SDMMC1_IRQn 0 */
/* USER CODE END SDMMC1_IRQn 0 */
HAL_SD_IRQHandler(&hsd1);
/* USER CODE BEGIN SDMMC1_IRQn 1 */
/* USER CODE END SDMMC1_IRQn 1 */
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/**
* @brief Tx Transfer completed callbacks
* @param hsd: Pointer to SD handle
* @retval None
*/
void HAL_SD_TxCpltCallback(SD_HandleTypeDef *hsd)
{
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1);
tx_done = 1;
}
/**
* @brief Rx Transfer completed callbacks
* @param hsd: Pointer SD handle
* @retval None
*/
void HAL_SD_RxCpltCallback(SD_HandleTypeDef *hsd)
{
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1);
rx_done = 1;
}
/**
* @brief SD error callbacks
* @param hsd: Pointer SD handle
* @retval None
*/
void HAL_SD_ErrorCallback(SD_HandleTypeDef *hsd)
{
// rx_done = 1;
// tx_done = 1;
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0);
}
#include "bsp_sdmmc.h"
#include /*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Sample Code of OS Dependent Functions for FatFs */
/* (C)ChaN, 2018 */
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "ff.h"
#include "bsp_malloc.h"
#if FF_USE_LFN == 3 /* Dynamic memory allocation */
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Allocate a memory block */
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void* ff_memalloc ( /* Returns pointer to the allocated memory block (null if not enough core) */
UINT msize /* Number of bytes to allocate */
)
{
//return malloc(msize); /* Allocate a new memory block with POSIX API */
return (void*)mymalloc(SRAMIN,msize);
}
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Free a memory block */
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void ff_memfree (
void* mblock /* Pointer to the memory block to free (nothing to do if null) */
)
{
//free(mblock); /* Free the memory block with POSIX API */
myfree(SRAMIN,mblock);
}
#endif
#if FF_FS_REENTRANT /* Mutal exclusion */
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Create a Synchronization Object */
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* This function is called in f_mount() function to create a new
/ synchronization object for the volume, such as semaphore and mutex.
/ When a 0 is returned, the f_mount() function fails with FR_INT_ERR.
*/
//const osMutexDef_t Mutex[FF_VOLUMES]; /* Table of CMSIS-RTOS mutex */
int ff_cre_syncobj ( /* 1:Function succeeded, 0:Could not create the sync object */
BYTE vol, /* Corresponding volume (logical drive number) */
FF_SYNC_t* sobj /* Pointer to return the created sync object */
)
{
/* Win32 */
*sobj = CreateMutex(NULL, FALSE, NULL);
return (int)(*sobj != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE);
/* uITRON */
// T_CSEM csem = {TA_TPRI,1,1};
// *sobj = acre_sem(&csem);
// return (int)(*sobj > 0);
/* uC/OS-II */
// OS_ERR err;
// *sobj = OSMutexCreate(0, &err);
// return (int)(err == OS_NO_ERR);
/* FreeRTOS */
// *sobj = xSemaphoreCreateMutex();
// return (int)(*sobj != NULL);
/* CMSIS-RTOS */
// *sobj = osMutexCreate(&Mutex[vol]);
// return (int)(*sobj != NULL);
}
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Delete a Synchronization Object */
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* This function is called in f_mount() function to delete a synchronization
/ object that created with ff_cre_syncobj() function. When a 0 is returned,
/ the f_mount() function fails with FR_INT_ERR.
*/
int ff_del_syncobj ( /* 1:Function succeeded, 0:Could not delete due to an error */
FF_SYNC_t sobj /* Sync object tied to the logical drive to be deleted */
)
{
/* Win32 */
return (int)CloseHandle(sobj);
/* uITRON */
// return (int)(del_sem(sobj) == E_OK);
/* uC/OS-II */
// OS_ERR err;
// OSMutexDel(sobj, OS_DEL_ALWAYS, &err);
// return (int)(err == OS_NO_ERR);
/* FreeRTOS */
// vSemaphoreDelete(sobj);
// return 1;
/* CMSIS-RTOS */
// return (int)(osMutexDelete(sobj) == osOK);
}
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Request Grant to Access the Volume */
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* This function is called on entering file functions to lock the volume.
/ When a 0 is returned, the file function fails with FR_TIMEOUT.
*/
int ff_req_grant ( /* 1:Got a grant to access the volume, 0:Could not get a grant */
FF_SYNC_t sobj /* Sync object to wait */
)
{
/* Win32 */
return (int)(WaitForSingleObject(sobj, FF_FS_TIMEOUT) == WAIT_OBJECT_0);
/* uITRON */
// return (int)(wai_sem(sobj) == E_OK);
/* uC/OS-II */
// OS_ERR err;
// OSMutexPend(sobj, FF_FS_TIMEOUT, &err));
// return (int)(err == OS_NO_ERR);
/* FreeRTOS */
// return (int)(xSemaphoreTake(sobj, FF_FS_TIMEOUT) == pdTRUE);
/* CMSIS-RTOS */
// return (int)(osMutexWait(sobj, FF_FS_TIMEOUT) == osOK);
}
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Release Grant to Access the Volume */
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* This function is called on leaving file functions to unlock the volume.
*/
void ff_rel_grant (
FF_SYNC_t sobj /* Sync object to be signaled */
)
{
/* Win32 */
ReleaseMutex(sobj);
/* uITRON */
// sig_sem(sobj);
/* uC/OS-II */
// OSMutexPost(sobj);
/* FreeRTOS */
// xSemaphoreGive(sobj);
/* CMSIS-RTOS */
// osMutexRelease(sobj);
}
#endif
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Low level disk I/O module SKELETON for FatFs (C)ChaN, 2019 */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* If a working storage control module is available, it should be */
/* attached to the FatFs via a glue function rather than modifying it. */
/* This is an example of glue functions to attach various exsisting */
/* storage control modules to the FatFs module with a defined API. */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "diskio.h" /* Declarations of disk functions */
#include "bsp_sdmmc.h"
/* Definitions of physical drive number for each drive */
#define DEV_RAM 0 /* Example: Map Ramdisk to physical drive 0 */
#define DEV_MMC 1 /* Example: Map MMC/SD card to physical drive 1 */
#define DEV_USB 2 /* Example: Map USB MSD to physical drive 2 */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Get Drive Status */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DSTATUS disk_status (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
int result;
return RES_OK;
// switch (pdrv) {
// case DEV_RAM :
// result = RAM_disk_status();
// // translate the reslut code here
// return stat;
// case DEV_MMC :
// result = MMC_disk_status();
// // translate the reslut code here
// return stat;
// case DEV_USB :
// result = USB_disk_status();
// // translate the reslut code here
// return stat;
// }
// return STA_NOINIT;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Inidialize a Drive */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DSTATUS disk_initialize (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
int result;
return RES_OK;
// switch (pdrv) {
// case DEV_RAM :
// result = RAM_disk_initialize();
// // translate the reslut code here
// return stat;
// case DEV_MMC :
// result = MMC_disk_initialize();
// // translate the reslut code here
// return stat;
// case DEV_USB :
// result = USB_disk_initialize();
// // translate the reslut code here
// return stat;
// }
// return STA_NOINIT;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Read Sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case 0 :
// translate the arguments here
res = SD_ReadDisk(buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
return res;
}
// switch (pdrv) {
// case DEV_RAM :
// // translate the arguments here
// result = RAM_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// // translate the reslut code here
// return res;
// case DEV_MMC :
// // translate the arguments here
// result = MMC_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// // translate the reslut code here
// return res;
// case DEV_USB :
// // translate the arguments here
// result = USB_disk_read(buff, sector, count);
// // translate the reslut code here
// return res;
// }
return RES_PARERR;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Write Sector(s) */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#if FF_FS_READONLY == 0
DRESULT disk_write (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */
LBA_t sector, /* Start sector in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to write */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case 0 :
// translate the arguments here
res = SD_WriteDisk((uint8_t *)buff, sector, count);
// translate the reslut code here
return res;
}
// switch (pdrv) {
// case DEV_RAM :
// // translate the arguments here
// result = RAM_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// // translate the reslut code here
// return res;
// case DEV_MMC :
// // translate the arguments here
// result = MMC_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// // translate the reslut code here
// return res;
// case DEV_USB :
// // translate the arguments here
// result = USB_disk_write(buff, sector, count);
// // translate the reslut code here
// return res;
// }
return RES_PARERR;
}
#endif
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Miscellaneous Functions */
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE cmd, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
DRESULT res;
int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case 0 :
// Process of the command for the RAM drive
switch(cmd)
{
case CTRL_SYNC:
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_SIZE:
*(DWORD*)buff = 512;
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE:
*(WORD*)buff = hsd1.SdCard.BlockSize;
res = RES_OK;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT:
*(DWORD*)buff = ((uint64_t)hsd1.SdCard.BlockNbr*hsd1.SdCard.BlockSize) / 512;
res = RES_OK;
break;
default:
res = RES_PARERR;
break;
}
return res;
}
// switch (pdrv) {
// case DEV_RAM :
// // Process of the command for the RAM drive
// return res;
// case DEV_MMC :
// // Process of the command for the MMC/SD card
// return res;
// case DEV_USB :
// // Process of the command the USB drive
// return res;
// }
return RES_PARERR;
}
DWORD get_fattime (void)
{
return 0;
// time_t t;
// struct tm *stm;
// t = time(0);
// stm = localtime(&t);
// return (DWORD)(stm->tm_year - 80) << 25 |
// (DWORD)(stm->tm_mon + 1) << 21 |
// (DWORD)stm->tm_mday << 16 |
// (DWORD)stm->tm_hour << 11 |
// (DWORD)stm->tm_min << 5 |
// (DWORD)stm->tm_sec >> 1;
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ FatFs Functional Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FFCONF_DEF 86631 /* Revision ID */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Function Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_READONLY 0
/* This option switches read-only configuration. (0:Read/Write or 1:Read-only)
/ Read-only configuration removes writing API functions, f_write(), f_sync(),
/ f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_chmod(), f_rename(), f_truncate(), f_getfree()
/ and optional writing functions as well. */
#define FF_FS_MINIMIZE 0
/* This option defines minimization level to remove some basic API functions.
/
/ 0: Basic functions are fully enabled.
/ 1: f_stat(), f_getfree(), f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_truncate() and f_rename()
/ are removed.
/ 2: f_opendir(), f_readdir() and f_closedir() are removed in addition to 1.
/ 3: f_lseek() function is removed in addition to 2. */
#define FF_USE_FIND 0
/* This option switches filtered directory read functions, f_findfirst() and
/ f_findnext(). (0:Disable, 1:Enable 2:Enable with matching altname[] too) */
#define FF_USE_MKFS 1
/* This option switches f_mkfs() function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FASTSEEK 1
/* This option switches fast seek function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_EXPAND 0
/* This option switches f_expand function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_CHMOD 0
/* This option switches attribute manipulation functions, f_chmod() and f_utime().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) Also FF_FS_READONLY needs to be 0 to enable this option. */
#define FF_USE_LABEL 0
/* This option switches volume label functions, f_getlabel() and f_setlabel().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FORWARD 0
/* This option switches f_forward() function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_STRFUNC 1
#define FF_PRINT_LLI 0
#define FF_PRINT_FLOAT 0
#define FF_STRF_ENCODE 0
/* FF_USE_STRFUNC switches string functions, f_gets(), f_putc(), f_puts() and
/ f_printf().
/
/ 0: Disable. FF_PRINT_LLI, FF_PRINT_FLOAT and FF_STRF_ENCODE have no effect.
/ 1: Enable without LF-CRLF conversion.
/ 2: Enable with LF-CRLF conversion.
/
/ FF_PRINT_LLI = 1 makes f_printf() support long long argument and FF_PRINT_FLOAT = 1/2
makes f_printf() support floating point argument. These features want C99 or later.
/ When FF_LFN_UNICODE >= 1 with LFN enabled, string functions convert the character
/ encoding in it. FF_STRF_ENCODE selects assumption of character encoding ON THE FILE
/ to be read/written via those functions.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16LE
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-16BE
/ 3: Unicode in UTF-8
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Locale and Namespace Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_CODE_PAGE 936
/* This option specifies the OEM code page to be used on the target system.
/ Incorrect code page setting can cause a file open failure.
/
/ 437 - U.S.
/ 720 - Arabic
/ 737 - Greek
/ 771 - KBL
/ 775 - Baltic
/ 850 - Latin 1
/ 852 - Latin 2
/ 855 - Cyrillic
/ 857 - Turkish
/ 860 - Portuguese
/ 861 - Icelandic
/ 862 - Hebrew
/ 863 - Canadian French
/ 864 - Arabic
/ 865 - Nordic
/ 866 - Russian
/ 869 - Greek 2
/ 932 - Japanese (DBCS)
/ 936 - Simplified Chinese (DBCS)
/ 949 - Korean (DBCS)
/ 950 - Traditional Chinese (DBCS)
/ 0 - Include all code pages above and configured by f_setcp()
*/
#define FF_USE_LFN 3
#define FF_MAX_LFN 255
/* The FF_USE_LFN switches the support for LFN (long file name).
/
/ 0: Disable LFN. FF_MAX_LFN has no effect.
/ 1: Enable LFN with static working buffer on the BSS. Always NOT thread-safe.
/ 2: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the STACK.
/ 3: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the HEAP.
/
/ To enable the LFN, ffunicode.c needs to be added to the project. The LFN function
/ requiers certain internal working buffer occupies (FF_MAX_LFN + 1) * 2 bytes and
/ additional (FF_MAX_LFN + 44) / 15 * 32 bytes when exFAT is enabled.
/ The FF_MAX_LFN defines size of the working buffer in UTF-16 code unit and it can
/ be in range of 12 to 255. It is recommended to be set it 255 to fully support LFN
/ specification.
/ When use stack for the working buffer, take care on stack overflow. When use heap
/ memory for the working buffer, memory management functions, ff_memalloc() and
/ ff_memfree() exemplified in ffsystem.c, need to be added to the project. */
#define FF_LFN_UNICODE 0
/* This option switches the character encoding on the API when LFN is enabled.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP (TCHAR = char)
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16 (TCHAR = WCHAR)
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-8 (TCHAR = char)
/ 3: Unicode in UTF-32 (TCHAR = DWORD)
/
/ Also behavior of string I/O functions will be affected by this option.
/ When LFN is not enabled, this option has no effect. */
#define FF_LFN_BUF 255
#define FF_SFN_BUF 12
/* This set of options defines size of file name members in the FILINFO structure
/ which is used to read out directory items. These values should be suffcient for
/ the file names to read. The maximum possible length of the read file name depends
/ on character encoding. When LFN is not enabled, these options have no effect. */
#define FF_FS_RPATH 0
/* This option configures support for relative path.
/
/ 0: Disable relative path and remove related functions.
/ 1: Enable relative path. f_chdir() and f_chdrive() are available.
/ 2: f_getcwd() function is available in addition to 1.
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Drive/Volume Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_VOLUMES 1
/* Number of volumes (logical drives) to be used. (1-10) */
#define FF_STR_VOLUME_ID 0
#define FF_VOLUME_STRS "RAM","NAND","CF","SD","SD2","USB","USB2","USB3"
/* FF_STR_VOLUME_ID switches support for volume ID in arbitrary strings.
/ When FF_STR_VOLUME_ID is set to 1 or 2, arbitrary strings can be used as drive
/ number in the path name. FF_VOLUME_STRS defines the volume ID strings for each
/ logical drives. Number of items must not be less than FF_VOLUMES. Valid
/ characters for the volume ID strings are A-Z, a-z and 0-9, however, they are
/ compared in case-insensitive. If FF_STR_VOLUME_ID >= 1 and FF_VOLUME_STRS is
/ not defined, a user defined volume string table needs to be defined as:
/
/ const char* VolumeStr[FF_VOLUMES] = {"ram","flash","sd","usb",...
*/
#define FF_MULTI_PARTITION 0
/* This option switches support for multiple volumes on the physical drive.
/ By default (0), each logical drive number is bound to the same physical drive
/ number and only an FAT volume found on the physical drive will be mounted.
/ When this function is enabled (1), each logical drive number can be bound to
/ arbitrary physical drive and partition listed in the VolToPart[]. Also f_fdisk()
/ funciton will be available. */
#define FF_MIN_SS 512
#define FF_MAX_SS 512
/* This set of options configures the range of sector size to be supported. (512,
/ 1024, 2048 or 4096) Always set both 512 for most systems, generic memory card and
/ harddisk, but a larger value may be required for on-board flash memory and some
/ type of optical media. When FF_MAX_SS is larger than FF_MIN_SS, FatFs is configured
/ for variable sector size mode and disk_ioctl() function needs to implement
/ GET_SECTOR_SIZE command. */
#define FF_LBA64 0
/* This option switches support for 64-bit LBA. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable the 64-bit LBA, also exFAT needs to be enabled. (FF_FS_EXFAT == 1) */
#define FF_MIN_GPT 0x10000000
/* Minimum number of sectors to switch GPT as partitioning format in f_mkfs and
/ f_fdisk function. 0x100000000 max. This option has no effect when FF_LBA64 == 0. */
#define FF_USE_TRIM 0
/* This option switches support for ATA-TRIM. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable Trim function, also CTRL_TRIM command should be implemented to the
/ disk_ioctl() function. */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ System Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_TINY 0
/* This option switches tiny buffer configuration. (0:Normal or 1:Tiny)
/ At the tiny configuration, size of file object (FIL) is shrinked FF_MAX_SS bytes.
/ Instead of private sector buffer eliminated from the file object, common sector
/ buffer in the filesystem object (FATFS) is used for the file data transfer. */
#define FF_FS_EXFAT 0
/* This option switches support for exFAT filesystem. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable exFAT, also LFN needs to be enabled. (FF_USE_LFN >= 1)
/ Note that enabling exFAT discards ANSI C (C89) compatibility. */
#define FF_FS_NORTC 0
#define FF_NORTC_MON 1
#define FF_NORTC_MDAY 1
#define FF_NORTC_YEAR 2020
/* The option FF_FS_NORTC switches timestamp functiton. If the system does not have
/ any RTC function or valid timestamp is not needed, set FF_FS_NORTC = 1 to disable
/ the timestamp function. Every object modified by FatFs will have a fixed timestamp
/ defined by FF_NORTC_MON, FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR in local time.
/ To enable timestamp function (FF_FS_NORTC = 0), get_fattime() function need to be
/ added to the project to read current time form real-time clock. FF_NORTC_MON,
/ FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR have no effect.
/ These options have no effect in read-only configuration (FF_FS_READONLY = 1). */
#define FF_FS_NOFSINFO 0
/* If you need to know correct free space on the FAT32 volume, set bit 0 of this
/ option, and f_getfree() function at first time after volume mount will force
/ a full FAT scan. Bit 1 controls the use of last allocated cluster number.
/
/ bit0=0: Use free cluster count in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit0=1: Do not trust free cluster count in the FSINFO.
/ bit1=0: Use last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit1=1: Do not trust last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO.
*/
#define FF_FS_LOCK 0
/* The option FF_FS_LOCK switches file lock function to control duplicated file open
/ and illegal operation to open objects. This option must be 0 when FF_FS_READONLY
/ is 1.
/
/ 0: Disable file lock function. To avoid volume corruption, application program
/ should avoid illegal open, remove and rename to the open objects.
/ >0: Enable file lock function. The value defines how many files/sub-directories
/ can be opened simultaneously under file lock control. Note that the file
/ lock control is independent of re-entrancy. */
/* #include // O/S definitions */
#define FF_FS_REENTRANT 0
#define FF_FS_TIMEOUT 1000
#define FF_SYNC_t HANDLE
/* The option FF_FS_REENTRANT switches the re-entrancy (thread safe) of the FatFs
/ module itself. Note that regardless of this option, file access to different
/ volume is always re-entrant and volume control functions, f_mount(), f_mkfs()
/ and f_fdisk() function, are always not re-entrant. Only file/directory access
/ to the same volume is under control of this function.
/
/ 0: Disable re-entrancy. FF_FS_TIMEOUT and FF_SYNC_t have no effect.
/ 1: Enable re-entrancy. Also user provided synchronization handlers,
/ ff_req_grant(), ff_rel_grant(), ff_del_syncobj() and ff_cre_syncobj()
/ function, must be added to the project. Samples are available in
/ option/syscall.c.
/
/ The FF_FS_TIMEOUT defines timeout period in unit of time tick.
/ The FF_SYNC_t defines O/S dependent sync object type. e.g. HANDLE, ID, OS_EVENT*,
/ SemaphoreHandle_t and etc. A header file for O/S definitions needs to be
/ included somewhere in the scope of ff.h. */
/*--- End of configuration options ---*/
总结:
1、

2、
3、
#define FF_FS_NORTC 0
diskio.c中增加了DWORD get_fattime (void)函数