Springboot整合ShardingSphere实现分库分表
一、ShardingJDBC 简介
1.什么是ShardingJDBC
ShardingSphere是一套开源的分布式数据库中间件解决方案组成的生态圈,它由Sharding-JDBC、Sharding-Proxy和Sharding-Sidecar(计划中)这3款相互独立的产品组成,我们只关注 Sharding-JDBC即可.
官方地址:https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/current/cn/overview/
Sharding-JDBC定位为轻量级Java框架,在Java的JDBC层提供的额外服务。 它使用客户端直连数据库,以jar包形式提供服务,无需额外部署和依赖,可理解为增强版的JDBC驱动,完全兼容JDBC和各种ORM框架的使用。
- 适用于任何基于Java的ORM框架,如:JPA, Hibernate, Mybatis, Spring JDBC Template或直接使用JDBC。
- 基于任何第三方的数据库连接池,如:DBCP, C3P0, Druid等。
- 支持任意实现JDBC规范的数据库。目前支持MySQL,Oracle,SQLServer和PostgreSQL。

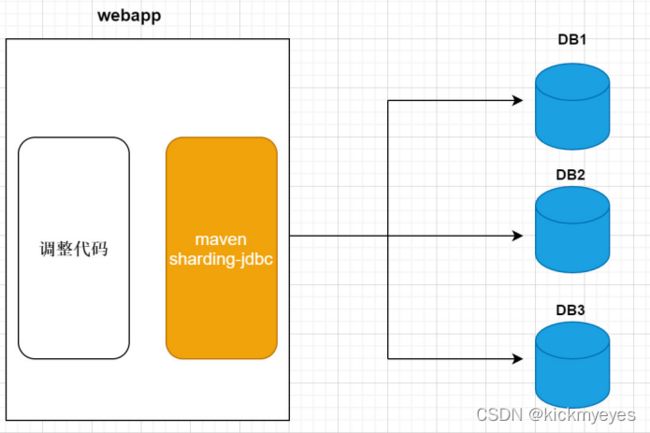
上图展示了Sharding-Jdbc的工作方式,使用Sharding-Jdbc前需要人工对数据库进行分库分表,在应用程序中加入Sharding-Jdbc的Jar包,应用程序通过Sharding-Jdbc操作分库分表后的数据库和数据表,由于Sharding-Jdbc是对Jdbc驱动的增强,使用Sharding-Jdbc就像使用Jdbc驱动一样,在应用程序中是无需指定具体要操作的分库和分表的。
2.Sharding-JDBC主要功能
- 数据分片
- 读写分离
通过Sharding-JDBC,应用可以透明的使用jdbc访问已经分库分表、读写分离的多个数据源,而不用关心数据源的数量以及数据如何分布。
3.Sharding-JDBC与MyCat的区别
- mycat是一个中间件的第三方应用,sharding-jdbc是一个jar包
- 使用mycat时不需要修改代码,而使用sharding-jdbc时需要修改代码
- Mycat 是基于 Proxy,它复写了 MySQL 协议,将 Mycat Server 伪装成一个 MySQL 数据库,而Sharding-JDBC 是基于 JDBC 的扩展,是以 jar 包的形式提供轻量级服务的。
二、Sharding-JDBC入门使用
1.搭建基础环境
- 需求说明
创建数据库lg_order, 模拟将订单表进行水平拆分, 创建两张表pay_order_1 与 pay_order_2,这两张表是订单表拆分后的表,我们通过Sharding-Jdbc向订单表插入数据,按照一定的分片规则,主键为偶数的落入pay_order_1表 ,为奇数的落入pay_order_2表, 再通过Sharding-Jdbc 进行查询. - 创建数据库
CREATE DATABASE lg_order CHARACTER SET 'utf8';
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS pay_order_1;
CREATE TABLE pay_order_1 (
order_id BIGINT(20) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT ,
user_id INT(11) ,
product_name VARCHAR(128),
COUNT INT(11)
);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS pay_order_2;
CREATE TABLE pay_order_2 (
order_id BIGINT(20) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT ,
user_id INT(11) ,
product_name VARCHAR(128),
COUNT INT(11)
);
- 创建SpringBoot项目引入maven依赖
sharding-jdbc以jar包形式提供服务,所以要先引入maven依赖。
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.6.7
com.example
shardingsphere
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
shardingsphere
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
com.alibaba
druid
1.1.21
org.apache.shardingsphere
sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter
4.0.0-RC1
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.3.1
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
org.projectlombok
lombok
2.分片规则配置(水平分表)
使用sharding-jdbc 对数据库中水平拆分的表进行操作,通过sharding-jdbc对分库分表的规则进行配置,配置内容包括:数据源、主键生成策略、分片策略等。
application.properties
- 基础配置
spring.application.name = sharding-jdbc-simple
server.servlet.context-path = /sharding-jdbc
spring.http.encoding.enabled = true
spring.http.encoding.charset = UTF-8
spring.http.encoding.force = true
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding = true
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case = true
- 数据源
# 定义数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names = db1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.driver-class-name = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/lg_order?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.username = root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.password = XL00754123
- 配置数据节点
#配置数据节点,指定节点的信息
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.pay_order.actual-data-nodes = db1.pay_order_$->{1..2}
表达式 db1.pay_order_$->{1…2}
$ 会被 大括号中的 {1…2} 所替换
会有两种选择: db1.pay_order_1 和 db1.pay_order_2
- 配置主键生成策略
#指定pay_order表 (逻辑表)的主键生成策略为 SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.pay_order.keygenerator.column = order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.pay_order.key-generator.type = SNOWFLAKE
使用shardingJDBC提供的主键生成策略,全局主键
为避免主键重复, 生成主键采用SNOWFLAKE分布式ID生成算法
- 配置分片算法
#指定pay_order表的分片策略,分片策略包括分片键和分片算法
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.pay_order.tablestrategy.inline.sharding-column = order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.pay_order.tablestrategy.inline.algorithm-expression = pay_order_$->{order_id % 2 + 1}
分表策略表达式: pay_order_$-> {order_id % 2 + 1}
{order_id % 2 + 1} 结果是偶数 操作 pay_order_1表
{order_id % 2 + 1} 结果是奇数 操作 pay_order_2表
- 打开SQL日志
# 打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show = true
- 步骤总结
- 定义数据源
- 指定pay_order 表的数据分布情况, 分布在 pay_order_1 和 pay_order_2
- 指定pay_order 表的主键生成策略为SNOWFLAKE,是一种分布式自增算法,保证id全局唯一
- 定义pay_order分片策略,order_id为偶数的数据下沉到pay_order_1,为奇数下沉到在pay_order_2
3.编写程序
- 新增订单
@Mapper
public interface PayOrderDao {
/**
* 新增订单
*/
@Insert("insert into pay_order(user_id,product_name,COUNT) values(#{user_id},#{product_name},#{count})")
int insertPayOrder(@Param("user_id") int user_id, @Param("product_name") String product_name, @Param("count") int count);
}
- 测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = RunBoot.class)
public class PayOrderDaoTest {
@Autowired
PayOrderDao payOrderDao;
@Test
public void testInsertPayOrder(){
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
//插入数据
payOrderDao.insertPayOrder(1+i,"小米电视",1);
}
}
}
- 根据Id查询订单
@Mapper
public interface PayOrderDao {
/**
* 查询订单
*/
@Select({""})
List- 测试
@Test
public void testFindOrderByIds(){
List ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(517020734275452928L); //order_1表
ids.add(517020734380310529L); //order_2表
List 4.ShardingJDBC执行流程
当ShardingJDBC接收到发送的SQL之后,会执行下面的步骤,最终返回执行结果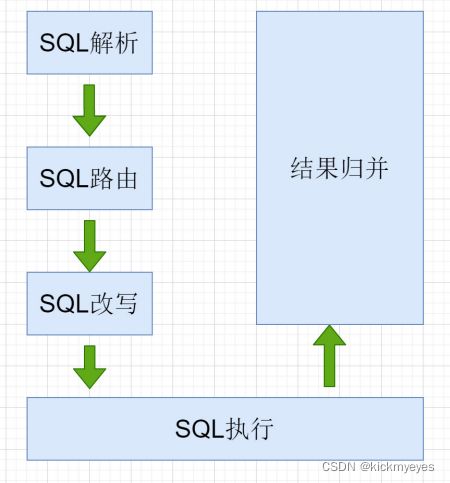
- SQL解析: 编写SQL查询的是逻辑表, 执行时 ShardingJDBC 要解析SQL ,解析的目的是为了找到需要改写的位置.
- SQL路由: SQL的路由是指 将对逻辑表的操作,映射到对应的数据节点的过程. ShardingJDBC会获取分片键判断是否正确,正确 就执行分片策略(算法) 来找到真实的表.
- SQL改写: 程序员面向的是逻辑表编写SQL, 并不能直接在真实的数据库中执行,SQL改写用于将逻辑SQL改为在真实的数据库中可以正确执行的SQL.
- SQL执行: 通过配置规则 pay_order_$->{order_id % 2 + 1} ,可以知道当 order_id 为偶数时 ,应该向 pay_order_1表中插入数据, 为奇数时向 pay_order_2表插入数据.
- 将所有真正执行sql的结果进行汇总合并,然后返回。
三、Sharding-JDBC分库分表
1.水平分表
把一张表的数据按照一定规则,分配到同一个数据库的多张表中,每个表只有这个表的部分数据. 在Sharding-JDBC入门使用中, 我们已经完成了水平分表的操作.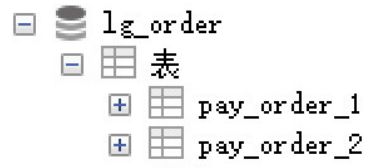
2.水平分库
水平分库是把同一个表的数据按一定规则拆到不同的数据库中,每个库可以放在不同的服务器上。
# 定义多个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names = db1,db2
# db1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.driver-class-name = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/lg_order_1?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.username = root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.password = 123456
# db2
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.driver-class-name = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/lg_order_2?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.username = root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.password = 123456
通过配置对数据库的分片策略,来指定数据库进行操作
# 分库策略,以user_id为分片键,分片策略为user_id % 2 + 1,user_id为偶数操作db1数据源,否则操作db2。
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.pay_order.databasestrategy.inline.sharding-column = user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.pay_order.databasestrategy.inline.algorithm-expression = db$->{user_id % 2 + 1}
- 分库分表的策略
分库策略 ,目的是将一个逻辑表 , 映射到多个数据源
# 分库找的是数据库 db$->{user_id % 2 + 1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.逻辑表名称.database-strategy.分片策略.分片策略属性名 = 分片策略表达式
分表策略, 如何将一个逻辑表 , 映射为多个 实际表
#分表 找的是具体的表 pay_order_$->{order_id % 2 + 1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.逻辑表名称.table-strategy.分片策略.algorithm-expression = 分片策略表达式
-
Sharding-JDBC支持以下几种分片策略:
○ standard:标准分片策略
○ complex:符合分片策略
○ inline:行表达式分片策略,使用Groovy的表达式.
○ hint:Hint分片策略,对应HintShardingStrategy。
○ none:不分片策略,对应NoneShardingStrategy。不分片的策略。
具体信息请查阅官方文档:https://shardingsphere.apache.org -
插入测试
@Test
public void testInsertPayOrder(){
//user_1 为奇数,插入到 lg_order_1 数据库
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//插入数据
payOrderDao.insertPayOrder(1,"海尔电视",1);
}
//user_2 为偶数,插入到 lg_order_2 数据库
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//插入数据
payOrderDao.insertPayOrder(4,"王牌电视",1);
}
}
首先会根据分库策略找到对应的数据库 db$->{user_id % 2 + 1}
然后再根据分表策略 找到要插入数据的表 pay_order_$->{order_id % 2 + 1}
6. 查询测试
@Test
public void testFindOrderByIds(){
List ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(517399941648220160L); //lg_order_1数据库的 order_1表
ids.add(517399941518196736L); //lg_order_2数据库的 order_1表
List 通过日志发现,sharding-jdbc将sql 路由到了 db1
原因在 配置上有问题,数据库只指定了 db1
7. 修改数据节点配置
#数据节点: db1.pay_order_1 , db1.pay_order_2, db2.pay_order_1,db2.pay_order_2
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.pay_order.actual-data-nodes = db$->{1..2}.pay_order_$->{1..2}
3.垂直分库
垂直分库是指按照业务将表进行分类,分布到不同的数据库上面,每个库可以放在不同的服务器上,它的核心理念是专库专用.
在使用微服务架构时,业务切割得足够独立,数据也会按照业务切分,保证业务数据隔离,大大提升了数据库的吞吐能力。
- 创建数据库
CREATE DATABASE lg_user CHARACTER SET 'utf8';
- 在lg_user 数据库中 users 创建表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS users;
CREATE TABLE users (
id BIGINT(20) PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(20) ,
phone VARCHAR(11),
STATUS VARCHAR(11)
);
- 规则配置
- 配置数据源信息
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names = db1,db2,db3
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db3.type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db3.driver-class-name = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db3.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/lg_user?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db3.username = root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db3.password = 123456
- 配置数据节点
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.users.actual-data-nodes = db$->{3}.users
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.users.table-strategy.inline.shardingcolumn = id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.users.table-strategy.inline.algorithmexpression = users
- 测试插入与查询
- UserDao
@Mapper
@Component
public interface UsersDao {
/**
* 新增用户
*/
@Insert("INSERT INTO users(id, username,phone,status) VALUE(#{id},#{username},#{phone},#{status})")
int insertUser(@Param("id")Long id, @Param("username")String username,@Param("phone")String phone,@Param("status")String status);
/**
* 查询用户
*/
@Select({
""})
List- UserDaoTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = RunBoot.class)
public class UserDaoTest {
@Autowired
UsersDao usersDao;
@Test
public void testInsert(){
for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) {
Long id = i + 100L;
usersDao.insertUser(id,"Timi"+i,"13511112222", "1");
}
}
@Test
public void testSelect(){
List ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(101L);
ids.add(105L);
List 四、Sharding-JDBC 操作公共表
1.什么是公共表
公共表属于系统中数据量较小,变动少,而且属于高频联合查询的依赖表。参数表、数据字典表等属于此类型。
可以将这类表在每个数据库都保存一份,所有更新操作都同时发送到所有分库执行。
2.公共表配置与测试
- 创建数据库
分别在 lg_order_1, lg_order_2 , lg_user都创建 district表
-- 区域表
CREATE TABLE district (
id BIGINT(20) PRIMARY KEY COMMENT '区域ID',
district_name VARCHAR(100) COMMENT '区域名称',
LEVEL INT COMMENT '等级'
);
# 指定district为公共表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.broadcast-tables=district
# 主键生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.district.key-generator.column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.district.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
- 编写代码, 操作公共表
- DistrictDao
@Mapper
@Component
public interface DistrictDao {
/**
* 插入数据
*/
@Insert("INSERT INTO district(district_name,level) VALUES(#{district_name},#{level})")
public void insertDist(@Param("district_name") String district_name,@Param("level") int level);
/**
* 删除数据
*/
@Delete("delete from district where id = #{id}")
int deleteDict(@Param("id") Long id);
}
- DistrictDaoTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = RunBoot.class)
public class DistrictDaoTest {
@Autowired
DistrictDao districtDao;
@Test
public void testInsert(){
districtDao.insertDist("昌平区",2);
districtDao.insertDist("朝阳区",2);
}
@Test
public void testDelete(){
districtDao.deleteDict(523944169266216961L);
}
}
五、Sharding-JDBC读写分离
Sharding-JDBC读写分离则是根据SQL语义的分析,将读操作和写操作分别路由至主库与从库。它提供透明化读写分离,让使用方尽量像使用一个数据库一样使用主从数据库集群。
1.MySQL主从同步
为了实现Sharding-JDBC的读写分离,首先,要进行mysql的主从同步配置。
我们直接使用MyCat讲解中,在虚拟机上搭建的主从数据库.
- 在主服务器中的 test数据库 创建商品表
CREATE TABLE products (
pid BIGINT(32) PRIMARY KEY ,
pname VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
price INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,
flag VARCHAR(2) DEFAULT NULL
);
2.sharding-jdbc实现读写分离
- 配置数据源
# 定义多个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names = db1,db2,db3,m1,s1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver-class-name = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url = jdbc:mysql://192.168.200.129:3306/test?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username = root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password = QiDian@666
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s1.type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s1.driver-class-name = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s1.url = jdbc:mysql://192.168.200.130:3306/test?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s1.username = root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.s1.password = QiDian@666
- 配置主库与从库的相关信息
- ms1 包含了 m1 和 s1
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.ms1.master-data-source-name=m1
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.master-slave-rules.ms1.slave-data-source-names=s1
- 配置数据节点
#配置数据节点
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.products.actual-data-nodes = ms1.products
- 编写测试代码
- ProductsDao
@Mapper
@Component
public interface ProductsDao {
/**
* 读写分离 插入
*/
@Insert("insert into products(pid,pname,price,flag) values(#{pid},#{pname},#{price},#{flag})")
int insertProduct(@Param("pid") Long pid, @Param("pname") String
pname,@Param("price") int price,@Param("flag") String flag);
/**
* 读写分离 查询
*/
@Select({"select * from products"})
List- 测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = RunBoot.class)
public class ProductsDaoTest {
@Autowired
ProductsDao productsDao;
/**
* 测试插入
*/
@Test
public void testInsert(){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
productsDao.insertProduct(100L+i,"小米手机",1888,"1");
}
}
/**
* 测试查询
*/
@Test
public void testSelect(){
List