优雅的接口防刷处理方案
为了防止恶意访问接口造成服务器和数据库压力增大导致瘫痪,接口防刷在工作中是必不可少的。给大家介绍几种设计方案。
验证码
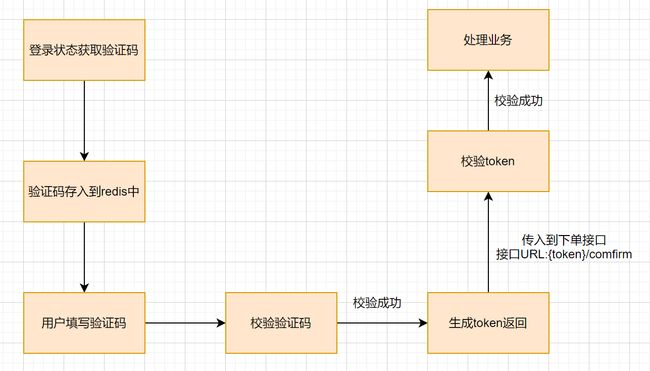
在登录状态下获取验证码,把验证码把保存在Redis(key是用户ID_商品ID)中,在提交的时候校验用户填写的验证码和Redis中验证码是否一样。
token
Token 机制,Token 一般都是用来做鉴权的。对于有先后顺序的接口调用,我们要求进入下个接口之前,要在上个接口获得令牌, 不然就认定为非法请求。
验证码和token结合:
拦截器+Redis
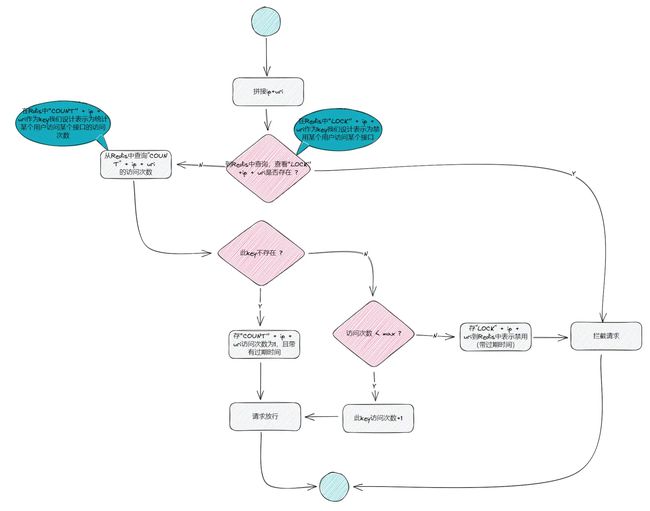
通过ip地址+uri拼接作为访问标识,在Interceptor中拦截请求,从Redis中统计用户访问接口次数从而达到接口防刷目的。
@Slf4j
public class BrowseLimitInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
//多长时间内
@Value("${browse.second}")
private Long second = 10L;
//访问次数
@Value("${browse.count}")
private Long count = 3L;
//禁用时长--单位/秒
@Value("${browse.lockTime}")
private Long lockTime = 60L;
//锁住时的key前缀
public static final String LOCK_PREFIX = "LOCK";
//统计次数时的key前缀
public static final String COUNT_PREFIX = "COUNT";
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
String ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
String lockKey = LOCK_PREFIX + ip + uri;
Object isLock = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(lockKey);
if(Objects.isNull(isLock)){
// 还未被禁用
String countKey = COUNT_PREFIX + ip + uri;
Object browseCount = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(countKey);
if(Objects.isNull(browseCount)){
// 首次访问
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(countKey,1,second, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}else{
// 没到限制访问次数
if((Integer)browseCount < count){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(countKey);
}else{
log.info("{}禁用访问{}",ip, uri);
// 禁用
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(lockKey, 1,lockTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
throw new CommonException(ResultCode.ACCESS_FREQUENT);
}
}
}else{
// 此用户访问此接口已被禁用
throw new CommonException(ResultCode.ACCESS_FREQUENT);
}
return true;
}
}
流程图如下:
这种方案最大的弊病是统一设置接口的访问防刷规则是x 秒内 y 次访问次数,禁用时长为 a 秒,在实际应用中可能每个接口的规则是不同的。
注解+拦截器
自定义注解
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target({METHOD, TYPE})
public @interface BrowserLimit {
/**
* 秒
* @return 多少秒内
*/
long second() default 5L;
/**
* 最大访问次数
* @return 最大访问次数
*/
long maxCount() default 3L;
/**
* 禁用时长,单位/秒
* @return 禁用时长
*/
long forbiddenTime() default 120L;
}
定义拦截器
@Slf4j
public class AccessLimintInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 锁住时的key前缀
*/
public static final String LOCK_PREFIX = "LOCK";
/**
* 统计次数时的key前缀
*/
public static final String COUNT_PREFIX = "COUNT";
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
HandlerMethod targetMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
// 获取目标接口方法所在类的注解@BrowserLimit
BrowserLimit targetClassAnnotation = targetMethod.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getAnnotation(BrowserLimit.class);
// 标记此类是否加了@BrowserLimit注解
boolean isBrushForAllInterface = false;
String ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
long second = 0L;
long mostCount = 0L;
long forbiddenTime = 0L;
if (!Objects.isNull(targetClassAnnotation)) {
isBrushForAllInterface = true;
second = targetClassAnnotation.second();
mostCount = targetClassAnnotation.maxCount();
forbiddenTime = targetClassAnnotation.forbiddenTime();
}
// 目标方法中的 BrowserLimit注解
BrowserLimit accessLimit = targetMethod.getMethodAnnotation(BrowserLimit.class);
// 判断此方法接口是否要进行防刷处理
if (!Objects.isNull(accessLimit)) {
second = accessLimit.second();
mostCount = accessLimit.maxCount();
forbiddenTime = accessLimit.forbiddenTime();
if (isForbindden(second, mostCount, forbiddenTime, ip, uri)) {
throw new CommonException(ResultCode.ACCESS_FREQUENT);
}
} else {
// 判断类上是否加了防刷注解
if (isBrushForAllInterface && isForbindden(second, mostCount, forbiddenTime, ip, uri)) {
throw new CommonException(ResultCode.ACCESS_FREQUENT);
}
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 判断某用户访问某接口是否已经被禁用/是否需要禁用
*
* @param second 多长时间 单位/秒
* @param maxCount 最大访问次数
* @param forbiddenTime 禁用时长 单位/秒
* @param ip 访问者ip地址
* @param uri 访问的uri
* @return ture为需要禁用
*/
private boolean isForbindden(long second, long maxCount, long forbiddenTime, String ip, String uri) {
String lockKey = LOCK_PREFIX + ip + uri; //如果此ip访问此uri被禁用时的存在Redis中的 key
Object isLock = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(lockKey);
// 判断此ip用户访问此接口是否已经被禁用
if (Objects.isNull(isLock)) {
// 还未被禁用
String countKey = COUNT_PREFIX + ip + uri;
Object count = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(countKey);
if (Objects.isNull(count)) {
// 首次访问
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(countKey, 1, second, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} else {
// 此用户前一点时间就访问过该接口,且频率没超过设置
if ((Integer) count < maxCount) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(countKey);
} else {
log.info("{}禁用访问{}", ip, uri);
// 禁用
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(lockKey, 1, forbiddenTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return true;
}
}
} else {
// 此用户访问此接口已被禁用
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
这种方案有一个问题,就是接口请求路径中带有参数,例如:“/get/{id}",参数值不同,防刷就失效了。
可以用全类名+方法名作为key
String className = targetMethod.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getName();
String methodName = targetMethod.getMethod().getName();
在接口上添加注解
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
@BrowserLimit(second = 3, maxCount = 2, forbiddenTime = 40L)
public Result getOne(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
log.info("执行[pass]-getOne()方法,id为{}", id);
return Result.SUCCESS();
}
Nginx限流
安装ab测试
#ab运行需要依赖apr-util包,安装命令为:
yum install apr-util
#安装依赖 yum-utils中的yumdownload 工具,如果没有找到 yumdownload 命令可以
yum install yum-utils
cd /opt
mkdir abtmp
cd abtmp
yum install yum-utils.noarch
yumdownloader httpd-tools*
rpm2cpio httpd-*.rpm | cpio -idmv
cd /opt/abtmp/usr/bin
./ab -c 100 -n 10000 http://127.0.0.1/post #-c 100 即:每次并发100个 -n 10000 即: 共发送10000个请求
ngx_http_limit_conn_module
limit_conn_zone
ngx_http_limit_conn_module 可以对于一些服务器流量异常、负载过大,甚至是大流量的恶意攻击访问等,进行并发数的限制;该模块可以根据定义的键来限制每个键值的连接数,只有那些正在被处理的请求(这些请求的头信息已被完全读入)所在的连接才会被计数。
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
-
limit_conn_zone只能够在http块中使用 -
limit_conn_zone:用来配置限流key及存放key对应信息的共享内存区域大小。此处的key是“ b i n a r y r e m o t e a d d r ”,表示 I P 地址,也可以使用 binary_remote_addr”,表示IP地址,也可以使用 binaryremoteaddr”,表示IP地址,也可以使用server_name作为key来限制域名级别的最大连接数。
-
limit_conn_status:配置被限流后返回的状态码,默认返回503。
·limit_conn_log_level:配置记录被限流后的日志级别,默认error级别。 -
客户端的IP地址作为键。
binary_remote_addr变量的长度是固定的4字节,存储状态在32位平台中占用32字节或64字节,在64位平台中占用64字节。
1M共享空间可以保存3.2万个32位的状态,1.6万个64位的状态。如果共享内存空间被耗尽,服务器将会对后续所有的请求返回 503 (Service Temporarily Unavailable) 错误。
limit_conn
server {
location /get/ {
# 指定每个给定键值的最大同时连接数,同一IP同一时间只允许有1个连接
limit_conn addr 1;
}
}
limit_conn:要配置存放key和计数器的共享内存区域和指定key的最大连接数。此处指定的最大连接数是1,表示Nginx最多同时并发处理1个连接。
ngx_http_limit_req_module
limit_req是漏桶算法实现,用于对指定key对应的请求进行限流。可以限制来自单个IP地址的请求处理频率。 限制的方法如同漏斗,每秒固定处理请求数,推迟过多请求。
# 限制请求数,大小为10m, 平均处理的频率不能超过每秒1次
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=1r/s;
server {
location /xxx/ {
# 桶容量5,默认会被延迟处理,如果不希望延迟处理,可以使用nodelay参数
limit_req zone=one burst=5 nodelay;
}
- limit_req_zone:配置限流key、存放key对应信息的共享内存区域大小、固定请求速率。此处指定的key是“$binary_remote_addr”,表示IP地址。固定请求速率使用rate参数配置,支持10r/s和60r/m,即每秒10个请求和每分钟60个请求。不过,最终都会转换为每秒的固定请求速率(10r/s为每100毫秒处理一个请求,60r/m为每1000毫秒处理一个请求)。
- limit_req:配置限流区域、桶容量(突发容量,默认为0)、是否延迟模式(默认延迟)。
lua-resty-limit-traffic
上面介绍的两个模块使用简单,对于复杂的场景很难实现,OpenResty提供了Lua限流模块lua-resty-limit-traffic,通过它可以按照更复杂的业务逻辑进行动态限流处理。
CentOS系统中安装openresty
sudo yum install yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://openresty.org/package/centos/openresty.repo
sudo yum install openresty
openresty安装后默认目录在/usr/local/openresty/,nginx目录在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/
定义lua脚本access_by_lua_block.lua
local limit_conn = require "resty.limit.conn"
local limit_req = require "resty.limit.req"
local limit_traffic = require "resty.limit.traffic"
# 300:固定平均速率 300r/s 200:桶容量
local lim1, err = limit_req.new("my_req_store", 300, 200)
assert(lim1, err)
local lim2, err = limit_req.new("my_req_store", 200, 100)
assert(lim2, err)
local lim3, err = limit_conn.new("my_conn_store", 1000, 1000, 0.5)
assert(lim3, err)
local limiters = {lim1, lim2, lim3}
local host = ngx.var.host
local client = ngx.var.binary_remote_addr
local keys = {host, client, client}
local states = {}
# 聚合限流器
local delay, err = limit_traffic.combine(limiters, keys, states)
if not delay then
if err == "rejected" then
return ngx.exit(503)
end
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "failed to limit traffic: ", err)
return ngx.exit(500)
end
if lim3:is_committed() then
local ctx = ngx.ctx
ctx.limit_conn = lim3
ctx.limit_conn_key = keys[3]
end
print("sleeping ", delay, " sec, states: ",
table.concat(states, ", "))
if delay >= 0.001 then
ngx.sleep(delay)
end
在 nginx.conf 的 server模块引入lua脚本:
server{
listen 8080;
server_name _;
access_by_lua_file "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/lua/access_by_lua_block.lua";
location /{
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8083;
}
}
OpenResty + Lua + Redis 实现 IP 限流
在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/lua目录下新建脚本access_by_redis.lua
local function close_redis(red)
if not red then
return
end
-- 释放连接(连接池实现),毫秒
local pool_max_idle_time = 10000
-- 连接池大小
local pool_size = 100
local ok, err = red:set_keepalive(pool_max_idle_time, pool_size)
local log = ngx_log
if not ok then
log(ngx_ERR, "set redis keepalive error : ", err)
end
end
-- 连接redis
local redis = require('resty.redis')
local red = redis.new()
red:set_timeout(1000)
local ip = "127.0.0.1"
local port = "6379"
local ok, err = red:connect(ip,port)
if not ok then
return close_redis(red)
end
#red:auth('123456')
red:select('0')
local clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"]
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"]
end
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.var.remote_addr
end
local incrKey = "user:"..clientIP..":freq"
local blockKey = "user:"..clientIP..":block"
local is_block,err = red:get(blockKey) -- check if ip is blocked
if tonumber(is_block) == 1 then
ngx.exit(403)
close_redis(red)
end
local inc = red:incr(incrKey)
if inc < 10 then
inc = red:expire(incrKey,1)
end
-- 每秒10次以上访问即视为非法,会阻止1分钟的访问
if inc > 10 then
--设置block 为 True 为1
red:set(blockKey,1)
red:expire(blockKey,60)
end
close_redis(red)
修改/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf目录下nginx.conf
server{
listen 8080;
server_name _;
access_by_lua_file "/usr/local/openresty/nginx/lua/access_by_redis.lua";
location /{
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8083;
}
}
OpenResty + Lua + Redis 实现防刷
-- access_by_lua_file '/opt/ops/lua/access_limit.lua'
local function close_redis(red)
if not red then
return
end
--释放连接(连接池实现)
local pool_max_idle_time = 10000 --毫秒
local pool_size = 100 --连接池大小
local ok, err = red:set_keepalive(pool_max_idle_time, pool_size)
if not ok then
ngx_log(ngx_ERR, "set redis keepalive error : ", err)
end
end
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeout(1000)
local ip = "redis-ip"
local port = redis-port
local ok, err = red:connect(ip,port)
if not ok then
return close_redis(red)
end
local clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"]
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"]
end
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.var.remote_addr
end
local incrKey = "user:"..clientIP..":freq"
local blockKey = "user:"..clientIP..":block"
local is_block,err = red:get(blockKey) -- check if ip is blocked
if tonumber(is_block) == 1 then
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN)
return close_redis(red)
end
local res, err = red:incr(incrKey)
if res == 1 then
res, err = red:expire(incrKey,1)
end
if res > 200 then
res, err = red:set(blockKey,1)
res, err = red:expire(blockKey,600)
end
close_redis(red)