139.【JUC并发编程-04】
JUC-并发编程04
- (八)、共享模型之工具
-
- 1.线程池
-
-
- (1).自定义线程池_任务数小于队列容量
- (2).自定义线程池_任务数大于队列容量
- (3).自定义线程池_拒绝策略
-
- 2.ThreadPoolExecutor
-
-
- (1).线程池状态
- (2).构造方法
- (3).newFixedThreadPool (固定大小线程池)
- (4).newCachedThreadPool (缓存线程池)
- (5). newSingleThreadExecutor (单线程线程池)
- (6).提交任务
- (7).关闭线程池
-
- 3.异步模式之工作线程
-
-
- (1). 定义
- (2).饥饿线程
- (3).饥饿线程_解决
- (4).创建多少线程池合适
-
- 4.任务调度线程池
-
-
- (1).Timer 实现定时任务
- (2).newScheduledThreadPool (延迟线程池)
- (3).newScheduledThreadPool (定时线程池)
- (4).正确处理线程池异常
- (5).定时任务测试
-
- 5. Tomcat 线程池
-
-
- (1).Tomcat 在哪里用到了线程池呢
- (2).Tomcat 配置
-
- 6.Fork/join
-
-
- (1).任务拆分概念
- (2).任务拆分举例
- (3).任务拆分优化
-
- (九)、JUC
-
- 1.AQS原理
-
-
- (1).aqs概述
- (2).自定义锁
-
- (十)、 ReentrantLock 原理
-
- 1.非公平锁实现原理
-
-
- (1).加锁解锁流程
-
- (十一)、线程安全集合类概述
-
- 1.概述
(八)、共享模型之工具
1.线程池
线程是十分消耗资源的,假如说线程数大于CPU核定的线程数的话。那么性能将会受到严重的影响,建立线程池可以解决这个问题!!!
(1).自定义线程池_任务数小于队列容量
步骤1: 阻塞队列
// 阻塞队列
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列:
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 5.容量
private int capacity;
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 6.带超时的阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock(); // 1.获取元素的时候先进行加锁的操作
try {
// 将超时时间统一转换为纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) { // 2.假如说任务队列是空的
// ⭐⭐ 假如时间超了的话,那么我们就返回null
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); // 3.消费者进行阻塞等待,切记这里一定进行重赋值一下
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();//4.不为空的话,就进行消费
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞获取
public T tack() {
lock.lock(); // 1.获取元素的时候先进行加锁的操作
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) { // 2.假如说任务队列是空的
try {
emptyWaitSet.await(); // 3.消费者进行等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();//4.不为空的话,就进行消费
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞添加
public void put(T element) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capacity) { // 队列长度是否等于容量,假如说满的话
fullWaitSet.await(); // 服务者唤醒
}
queue.add(element); // 向队列中添加
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 获取队列大小
public int size() {
lock.lock();
try {
return queue.size();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
步骤二:线程池类
//线程池类
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 1.任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 2.线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 3.核心线程数
private int coreSize;
// 4.获取任务的超时时间
private long timeout;
// 5.时间单位
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
// 6.执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// 当任务数没有超过 cpu的核心线程数的时候,直接交给 worker 执行。
// 如果任务数超过 cpu的核心线程数的时候, 加入任务队列暂存。
synchronized (workers) {
if (workers.size() < coreSize) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增 worker{},任务队列为{}",worker,task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}",task);
taskQueue.put(task);
}
}
}
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapacity) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapacity);
}
class Worker extends Thread {
// 任务线程
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// (1).当 task 不为空,执行任务
// (2).当 task 执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.tack()) != null) {
try {
log.debug("正在执行.... {}",task);
task.run();
} finally {
task = null;
}
}
synchronized (workers){
log.debug("worker 被移除{}",this);
workers.remove(this); // 假如说执行完毕的话,需要移除
}
}
}
}
步骤三: 测试执行
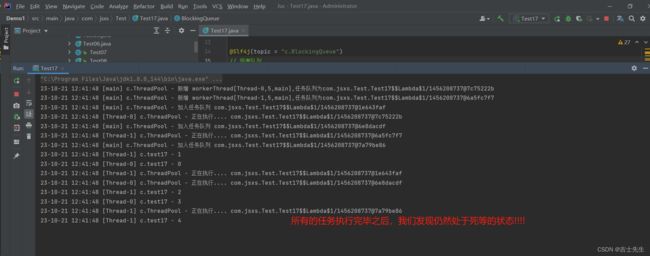
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test17")
public class Test17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(()->{
log.debug("{}",j);
});
}
}
}
线程执行完毕之后,我们仍然处于死等的状态!!!
设置有时限的线程池
设置有时间限制的线程池:
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/20 17:19
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test17
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test17")
public class Test17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
// ****************************阻塞队列
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
// 阻塞队列
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列:
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 5.容量
private int capacity;
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 6.带超时的阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock(); // 1.获取元素的时候先进行加锁的操作
try {
// 将超时时间统一转换为纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) { // 2.假如说任务队列是空的
// ⭐⭐ 假如时间超了的话,那么我们就返回null
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
try {
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); // 3.消费者进行阻塞等待,切记这里一定进行重赋值一下
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();//4.不为空的话,就进行消费
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞获取
public T tack() {
lock.lock(); // 1.获取元素的时候先进行加锁的操作
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) { // 2.假如说任务队列是空的
try {
emptyWaitSet.await(); // 3.消费者进行等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();//4.不为空的话,就进行消费
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞添加
public void put(T element) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capacity) { // 队列长度是否等于容量,假如说满的话
fullWaitSet.await(); // 服务者唤醒
}
queue.add(element); // 向队列中添加
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 获取队列大小
public int size() {
lock.lock();
try {
return queue.size();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
// ****************************线程池
//线程池类
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 1.任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 2.线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 3.核心线程数
private int coreSize;
// 4.获取任务的超时时间
private long timeout;
// 5.时间单位
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
// 6.执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// 当任务数没有超过 cpu的核心线程数的时候,直接交给 worker 执行。
// 如果任务数超过 cpu的核心线程数的时候, 加入任务队列暂存。
synchronized (workers) {
if (workers.size() < coreSize) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增 worker{},任务队列为{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", task);
taskQueue.put(task);
}
}
}
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapacity) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapacity);
}
class Worker extends Thread {
// 任务线程
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// (1).当 task 不为空,执行任务
// (2).当 task 执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
// while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.tack()) != null) {
// ⭐⭐⭐ 设置有时限的线程池
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) != null) {
try {
log.debug("正在执行.... {}", task);
task.run();
} finally {
task = null;
}
}
synchronized (workers) {
log.debug("worker 被移除{}", this);
workers.remove(this); // 假如说执行完毕的话,需要移除
}
}
}
}
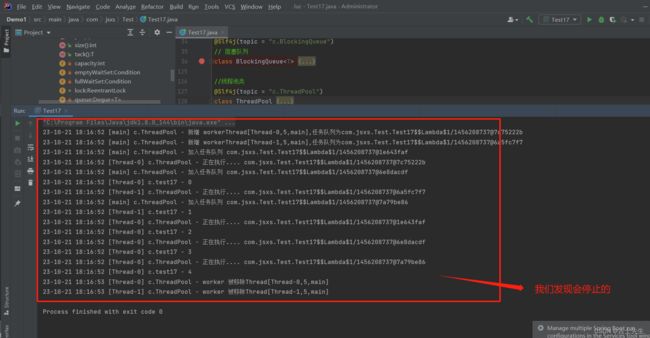
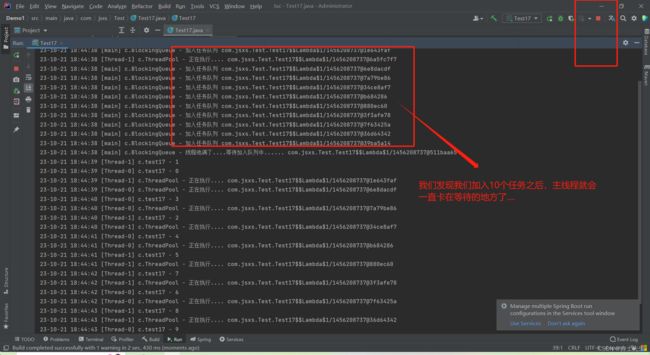
(2).自定义线程池_任务数大于队列容量
线程数为15,而队列的长度只有10个!!!
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/20 17:19
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test17
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test17")
public class Test17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) { // ⭐开启的线程为15个,而容量只有10个
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
// **************************** 阻塞队列
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
// 阻塞队列
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列:
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 5.容量
private int capacity;
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 6.带超时的阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock(); // 1.获取元素的时候先进行加锁的操作
try {
// 将超时时间统一转换为纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) { // 2.假如说任务队列是空的
// 假如时间超了的话,那么我们就返回null
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
try {
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); // 3.消费者进行阻塞等待,切记这里一定进行重赋值一下
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();//4.不为空的话,就进行消费
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞获取
public T tack() {
lock.lock(); // 1.获取元素的时候先进行加锁的操作
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) { // 2.假如说任务队列是空的
try {
emptyWaitSet.await(); // 3.消费者进行等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();//4.不为空的话,就进行消费
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞添加
public void put(T element) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capacity) { // 队列长度是否等于容量,假如说满的话
log.debug("线程池满了....等待加入队列中...... {}", element);
fullWaitSet.await(); // 服务者唤醒
}
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", element);
queue.add(element); // 向队列中添加
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 获取队列大小
public int size() {
lock.lock();
try {
return queue.size();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
// **************************** 线程池
//线程池类
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 1.任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 2.线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 3.核心线程数
private int coreSize;
// 4.获取任务的超时时间
private long timeout;
// 5.时间单位
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
// 6.执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// 当任务数没有超过 cpu的核心线程数的时候,直接交给 worker 执行。
// 如果任务数超过 cpu的核心线程数的时候, 加入任务队列暂存。
synchronized (workers) {
if (workers.size() < coreSize) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增 worker{},任务队列为{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
taskQueue.put(task);
}
}
}
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapacity) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapacity);
}
class Worker extends Thread {
// 任务线程
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// (1).当 task 不为空,执行任务
// (2).当 task 执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
// while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.tack()) != null) {
//
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) != null) {
try {
log.debug("正在执行.... {}", task);
task.run();
} finally {
task = null;
}
}
synchronized (workers) {
log.debug("worker 被移除{}", this);
workers.remove(this); // 假如说执行完毕的话,需要移除
}
}
}
}
(3).自定义线程池_拒绝策略
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.RunnerException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/20 17:19
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test17
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test17")
public class Test17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(1, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 1,(queue,element)->{
// (1).死等 ⭐
// queue.put(element);
// (2).带超时等待 ⭐⭐
// queue.offer(element,500,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// (3).放弃任务的执行 ⭐⭐⭐
// log.debug("放弃{}",element);
// (4).抛出异常 ⭐⭐⭐⭐
// try {
// throw new RunnerException("任务执行失败"+element);
// } catch (RunnerException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// (5).让调用者自己执行任务 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
// element.run();
});
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { // 开启的线程为15个,而容量只有10个
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
// **************************** 阻塞队列
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
// 阻塞队列
class BlockingQueue<T> {
// 1. 任务队列:
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 2. 锁
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
// 5.容量
private int capacity;
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 6.带超时的阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock(); // 1.获取元素的时候先进行加锁的操作
try {
// 将超时时间统一转换为纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) { // 2.假如说任务队列是空的
// ⭐⭐ 假如时间超了的话,那么我们就返回null
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
try {
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); // 3.消费者进行阻塞等待,切记这里一定进行重赋值一下
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();//4.不为空的话,就进行消费
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞获取
public T tack() {
lock.lock(); // 1.获取元素的时候先进行加锁的操作
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) { // 2.假如说任务队列是空的
try {
emptyWaitSet.await(); // 3.消费者进行等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();//4.不为空的话,就进行消费
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 阻塞添加
public void put(T element) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capacity) { // 队列长度是否等于容量,假如说满的话
log.debug("线程池满了....等待加入队列中...... {}", element);
fullWaitSet.await(); // 服务者唤醒
}
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", element);
queue.add(element); // 向队列中添加
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 获取队列大小
public int size() {
lock.lock();
try {
return queue.size();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// ⭐⭐带超时时间阻塞添加
public boolean offer(T element, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
lock.lock();
try {
long nanos = timeUnit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.size() == capacity) { // 队列长度是否等于容量,假如说满的话
log.debug("线程池满了....等待加入队列中...... {}", element);
if (nanos <= 0) {
return false;
}
nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); // 服务者设置等待时间
}
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", element);
queue.add(element); // 向队列中添加
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
public void tryPut(RejectPolicy<T> rejectPolicy, T element) {
lock.lock();
try {
// 判断队列是否满了?
if (queue.size() == capacity) { // 加入说队列满了
rejectPolicy.reject(this,element); // 权力
} else { // 有空闲
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}", element);
queue.add(element); // 向队列中添加
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
// **************************** 接口
@FunctionalInterface // ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ 拒绝策略
interface RejectPolicy<T> {
void reject(BlockingQueue<T> queue, T task);
}
// ****************************线程池
//线程池类
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool {
// 1.任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 2.线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
// 3.核心线程数
private int coreSize;
// 4.获取任务的超时时间
private long timeout;
// 5.时间单位
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy;
// 6.执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// 当任务数没有超过 cpu的核心线程数的时候,直接交给 worker 执行。
// 如果任务数超过 cpu的核心线程数的时候, 加入任务队列暂存。
synchronized (workers) {
if (workers.size() < coreSize) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增 worker{},任务队列为{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
// (1).死等 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
// (2).带超时等待
// (3).放弃任务的执行
// (4).抛出异常
// (5).让调用者自己执行任务
taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPolicy, task);
}
}
}
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapacity, RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapacity);
this.rejectPolicy = rejectPolicy;
}
class Worker extends Thread {
// 任务线程
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// (1).当 task 不为空,执行任务
// (2).当 task 执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
// while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.tack()) != null) {
//
while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) != null) {
try {
log.debug("正在执行.... {}", task);
task.run();
} finally {
task = null;
}
}
synchronized (workers) {
log.debug("worker 被移除{}", this);
workers.remove(this); // 假如说执行完毕的话,需要移除
}
}
}
}
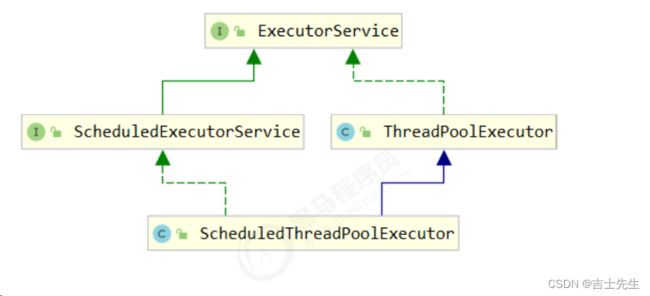
2.ThreadPoolExecutor
(1).线程池状态
ThreadPoolExecutor 使用 int 的高 3 位来表示线程池状态,低 29 位表示线程数量。
| 状态名 | 高 3 位 | 接收新任务 | 处理阻塞队列任务 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUNNING | 111 | Y | Y | 会接受新任务,会处理阻塞队列剩余任务 |
| SHUTDOWN | 000 | N | Y | 不会接收新任务,但会处理阻塞队列剩余任务 |
| STOP | 001 | N | N | 会中断正在执行的任务,并抛弃阻塞队列任务 |
| TIDYING | 010 | - | - | 任务全执行完毕,活动线程为 0 即将进入终结 |
| TERMINATED | 011 | - | - | 终结状态 |
从数字上比较,TERMINATED > TIDYING > STOP > SHUTDOWN > RUNNING
这些信息存储在一个原子变量 ctl 中,目的是将线程池状态与线程个数合二为一,这样就可以用一次 cas 原子操作进行赋值。
// c 为旧值, ctlOf 返回结果为新值
ctl.compareAndSet(c, ctlOf(targetState, workerCountOf(c))));
// rs 为高 3 位代表线程池状态, wc 为低 29 位代表线程个数,ctl 是合并它们
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
(2).构造方法
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
- corePoolSize CPU核心线程数目 (最多保留的线程数)
- maximumPoolSize 最大线程数目
- keepAliveTime 生存时间 - 针对救急线程
- unit 时间单位 - 针对救急线程
- workQueue 阻塞队列
- threadFactory 线程工厂 - 可以为线程创建时起个好名字
- handler 拒绝策略
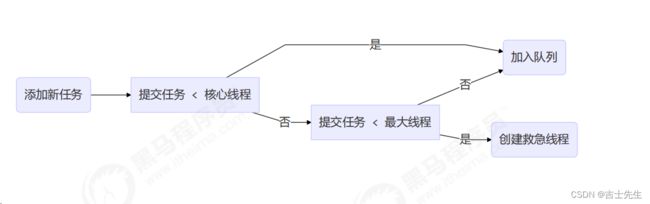
工作方式:

假如说核心线程数我们设置为2,最大线程数为3,阻塞队列长度为2。那么救急线程数为 maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize为1。假如说此时任务阻塞队列装不下了,任务5出现那么将会触发救急线程进行帮助我们处理任务5。任务5还没处理完毕,此时又加入一个任务6,那么因为线程已经要大于maximumPoolSize,那么需要进行执行拒绝策略!!!
-
线程池中
刚开始没有线程,当一个任务提交给线程池后,线程池会创建一个新线程来执行任务。 -
当线程数达到
corePoolSize并没有线程空闲,这时再加入任务,新加的任务会被加入workQueue队列排队,直到有空闲的线程。 -
如果队列选择了有界队列,那么
任务超过了队列大小时,会创建 maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize 数目的线程来救急 (也就是我们所说的救急线程),当我们的救急线程执行完毕任务之后,他就会被解雇也就是立即死亡,并不像核心线程数一样一直保留。 -
如果线程到达 maximumPoolSize 仍然有新任务 (也就是说救急线程也忙不过来了),这时会执行拒绝策略。拒绝策略 jdk 提供了 4 种实现,其它著名框架也提供了实现
- AbortPolicy 让调用者抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,这是
默认策略。 - CallerRunsPolicy 让调用者
运行任务 - DiscardPolicy
放弃本次任务 - DiscardOldestPolicy 放弃队列中最早的任务,
本任务取而代之 - Dubbo 的实现,在抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常之前会记录日志,并 dump 线程栈信息,方便定位问题
- Netty 的实现,是创建一个新线程来执行任务
- ActiveMQ 的实现,带超时等待(60s)尝试放入队列,类似我们之前自定义的拒绝策略。
- PinPoint 的实现,它使用了一个拒绝策略链,会逐一尝试策略链中每种拒绝策略。
- AbortPolicy 让调用者抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,这是
-
当高峰过去后,超过corePoolSize 的救急线程如果一段时间没有任务做,需要结束节省资源,这个时间由keepAliveTime 和 unit 来控制。

根据这个构造方法,JDK Executors 类中提供了众多工厂方法来创建各种用途的线程池
(3).newFixedThreadPool (固定大小线程池)
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
// 1.核心线程数为 nThreads 2. 最大线程数为 nThreads 3. 等待超时时间为 0 4.等待超时的单位是毫秒 5.线程阻塞队列
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); // 链表形式的阻塞队列
}
特点:
- 因为最大线程数和核心线程数相等,所以没有救急线程被创建,因此也无需超时时间。
- 阻塞队列是链表形式的,所以是无界的,可以放任意数量的任务。
评价: 适用于任务量已知,相对耗时的任务
1.使用默认的线程工厂
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/22 8:43
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test18
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("1");
});
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("2");
});
// 从这里开始进行阻塞队列,两个核心线程谁先执行完毕,谁就先去阻塞队列里面取
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("3");
});
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("4");
});
}
}
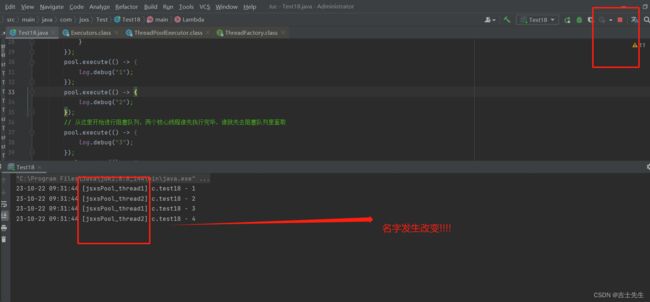
2.使用自定义的线程工厂
线程工厂主要影响的是: 线程的名字
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/22 8:43
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test18
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ⭐⭐ 线程工厂
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2, new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger t = new AtomicInteger(1);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable runnable) {
return new Thread(runnable, "jsxsPool_thread" + t.getAndIncrement());
}
});
pool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("1");
});
pool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("2");
});
// 从这里开始进行阻塞队列,两个核心线程谁先执行完毕,谁就先去阻塞队列里面取
pool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("3");
});
pool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("4");
});
}
}
(4).newCachedThreadPool (缓存线程池)
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
// 1.核心线程数为0, 2.最大线程数为 2147483647 ,3.超时时间为 60 , 4.超时的单位是 秒 5.同步阻塞队列
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
特点
- 核心线程数是 0, 最大线程数是
Integer.MAX_VALUE,救急线程的空闲生存时间是 60s,意味着- 全部都是救急线程(60s 后可以回收)
- 救急线程可以无限创建
- 队列采用了
SynchronousQueue实现特点是,它没有容量,没有线程来取是放不进去的(一手交钱、一手交货)
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/22 8:43
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test18
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.创建我们的同步队列
SynchronousQueue<Integer> integers = new SynchronousQueue<>();
// 2.开启第一个线程
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 打印信息
log.debug("putting {} ", 1);
// 3. 向队列中添加数据 1
integers.put(1);
// 直到1被取走之后,我们这里才会往下继续允许 ⭐
log.debug("{} putted...", 1);
log.debug("putting...{} ", 2);
// 4.向队列中添加数据 2
integers.put(2);
log.debug("{} putted...", 2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "t1").start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 3. 开启第二个线程 取走我们的1
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("taking {}", 1);
integers.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "t2").start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 4.开启第三个线程 取走我们的2
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("taking {}", 2);
integers.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "t3").start();
}
}
评价 整个线程池表现为线程数会根据任务量不断增长,没有上限,当任务执行完毕,空闲 1分钟后释放线程。 适合任务数比较密集,但每个任务执行时间较短的情况。
(5). newSingleThreadExecutor (单线程线程池)
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
// 1.核心线程数为1 2.最大线程数为 1, 3.等待超时时间为0 4.时间单位为毫秒,5.链表阻塞队列
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
使用场景:
希望多个任务排队执行。线程数固定为 1,任务数多于 1 时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这唯一的线程也不会被释放。
区别:
-
自己创建一个单线程串行执行任务,如果任务执行失败而终止那么没有任何补救措施,而线程池还会新建一个线程,保证池的正常工作。
-
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() 线程个数始终为1,不能修改
- FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService 应用的是
装饰器模式,只对外暴露了ExecutorService接口,因此不能调用ThreadPoolExecutor 中特有的方法
- FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService 应用的是
-
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1) 初始时为1,以后还可以修改
- 对外暴露的是 ThreadPoolExecutor 对象,可以强转后调用 setCorePoolSize 等方法进行修改
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/22 8:43
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test18
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("1");
int i=1/0;
});
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("2");
});
pool.execute(()->{
log.debug("3");
});
}
}
(6).提交任务
// 执行任务 ⭐ lamda表达式无返回结果
void execute(Runnable command);
// 提交任务 task,用返回值 Future 获得任务执行结果 ⭐⭐ lamda表达式返回有结果
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,带超时时间
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消,带超时时间
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
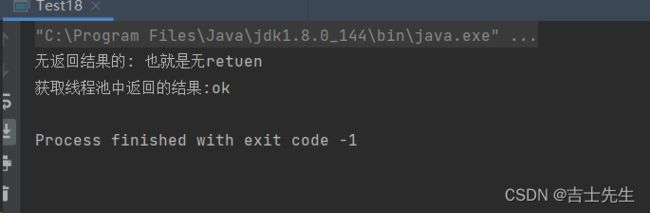
- execute 和 submit
package com.jsxs.Test;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 1.无返回值表达式
pool.execute(()->{
System.out.println("无返回结果的: 也就是无return");
});
// 2.存在返回值表达
Future<String> future = pool.submit(new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1);
return "ok";
}
});
System.out.println("获取线程池中返回的结果:"+future.get());
}
}
- 没有时限的invokeAll
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 这里是指提交 tasks 中所有任务,是一个集合
List<Future<String>> futures = pool.invokeAll(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin2");
Thread.sleep(500);
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin3");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "3";
}
));
for (Future<String> future : futures) {
log.debug("{}",future.get());
}
}
}
- 有时限的invokeAll
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,带超时时间 假如说超过时间报异常
List<Future<String>> futures = pool.invokeAll(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin2");
Thread.sleep(500);
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin3");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "3";
}
),600,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
for (Future<String> future : futures) {
log.debug("{}",future.get());
}
}
}
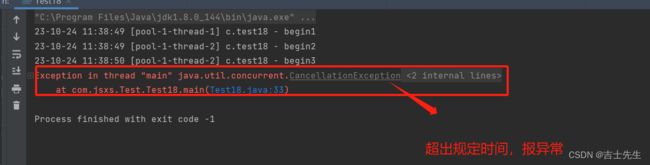
- invokeAny 返回最先执行完毕的
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消
String s = pool.invokeAny(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin2");
Thread.sleep(500); // 休眠的时间短,一定是他先完成
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin3");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "3";
}
));
System.out.println(s);
}
}
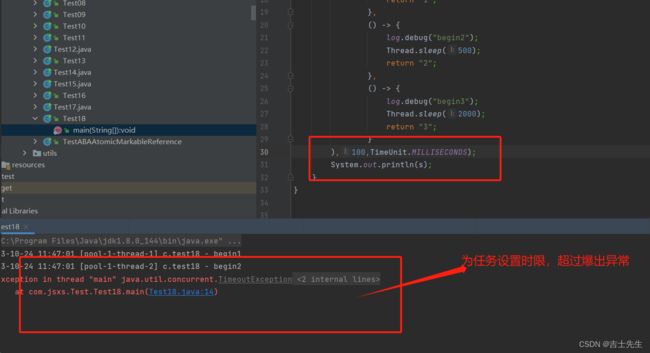
- invokeAny 返回最先执行完毕的 (有时间限制)
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
String s = pool.invokeAny(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin2");
Thread.sleep(500);
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin3");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "3";
}
),100,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // ⭐
System.out.println(s);
}
}
(7).关闭线程池
- shutdown
/*
线程池状态变为 SHUTDOWN
- 不会接收新任务
- 但已提交任务会执行完
- 此方法不会阻塞调用线程的执行
*/
void shutdown();
public void shutdown() {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
// 修改线程池状态
advanceRunState(SHUTDOWN);
// 仅会打断空闲线程
interruptIdleWorkers();
onShutdown(); // 扩展点 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 尝试终结(没有运行的线程可以立刻终结,如果还有运行的线程也不会等)
tryTerminate();
}
- shutdownNow
/*
线程池状态变为 STOP
- 不会接收新任务
- 会将队列中的任务返回
- 并用 interrupt 的方式中断正在执行的任务
*/
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {
List<Runnable> tasks;
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
// 修改线程池状态
advanceRunState(STOP);
// 打断所有线程
interruptWorkers();
// 获取队列中剩余任务
tasks = drainQueue();
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 尝试终结
tryTerminate();
return tasks;
}
- 其他方法
// 不在 RUNNING 状态的线程池,此方法就返回 true
boolean isShutdown();
// 线程池状态是否是 TERMINATED
boolean isTerminated();
// 调用 shutdown 后,由于调用线程并不会等待所有任务运行结束,因此如果它想在线程池 TERMINATED 后做些事
情,可以利用此方法等待
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
- 使用 shutdown 和 awaitTermination
shutdown 不会接受新任务,但是旧任务将会继续执行!!!
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<Integer> result1 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end1");
return 1;
});
Future<Integer> result2 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin2");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end2");
return 2;
});
Future<Integer> result3 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin3");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end3");
return 3;
});
// ⭐不接受新的任务(如果接受到新的任务会报错),但接受旧的任务。
pool.shutdown();
// ⭐⭐ 这个线程池里面的所有任务都执行完毕了 或者 3秒之后主线程才放行
pool.awaitTermination(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
log.debug("111");
}
}
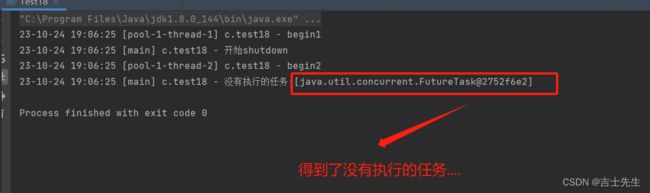
- shutdownNow
不接受新的任务,旧任务也不执行。
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test18")
public class Test18 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<Integer> result1 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end1");
return 1;
});
Future<Integer> result2 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin2");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end2");
return 2;
});
Future<Integer> result3 = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin3");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end3");
return 3;
});
log.debug("开始shutdown");
// ⭐ 直接关闭,包括正在运行的或者没运行的。
List<Runnable> runnables = pool.shutdownNow();
log.debug("没有执行的任务:{}",runnables);
}
}
3.异步模式之工作线程
(1). 定义
让有限的工作线程(Worker Thread)来轮流异步处理无限多的任务。也可以将其归类为分工模式,它的典型实现就是线程池,也体现了经典设计模式中的享元模式。
例如,海底捞的服务员(线程),轮流处理每位客人的点餐(任务),如果为每位客人都配一名专属的服务员,那么成本就太高了(对比另一种多线程设计模式:Thread-Per-Message)
注意,不同任务类型应该使用不同的线程池,这样能够避免饥饿,并能提升效率
例如,如果一个餐馆的工人既要招呼客人(任务类型A),又要到后厨做菜(任务类型B)显然效率不咋地,分成服务员(线程池A)与厨师(线程池B)更为合理,当然你能想到更细致的分工。
(2).饥饿线程
固定大小线程池会有饥饿现象
- 两个工人是同一个线程池中的两个线程
- 他们要做的事情是:为客人点餐和到后厨做菜,这是两个阶段的工作
- 客人点餐:必须先点完餐,等菜做好,上菜,在此期间处理点餐的工人必须等待
- 后厨做菜:没啥说的,做就是了
- 比如工人A 处理了点餐任务,接下来它要等着 工人B 把菜做好,然后上菜,他俩也配合的蛮好
- 但现在同时来了两个客人,这个时候工人A 和工人B 都去处理点餐了,这时没人做饭了,饥饿
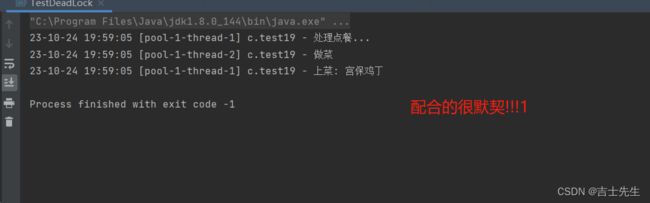
- 一个客人下: 配合的挺好的
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
static final List<String> MENU = Arrays.asList("地三鲜", "宫保鸡丁", "辣子鸡丁", "烤鸡翅");
static Random RANDOM = new Random();
static String cooking() {
return MENU.get(RANDOM.nextInt(MENU.size()));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.固定线程池: 工人的人数为2
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 2. 处理点餐业务
executorService.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
// 3.在线程池中再找一个工人进行做饭
Future<String> f = executorService.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
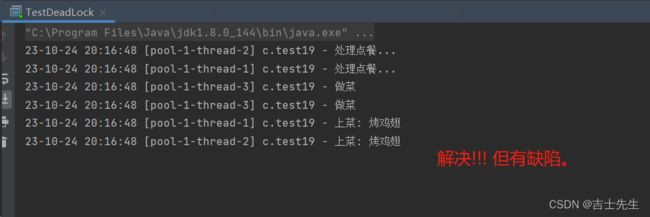
- 两个客人下: 会出现饥饿现象
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
static final List<String> MENU = Arrays.asList("地三鲜", "宫保鸡丁", "辣子鸡丁", "烤鸡翅");
static Random RANDOM = new Random();
static String cooking() {
return MENU.get(RANDOM.nextInt(MENU.size()));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.固定线程池: 工人的人数为2
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 2. ⭐处理第一个客人的点餐业务
executorService.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
// 3.在线程池中再找一个工人进行做饭
Future<String> f = executorService.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 3. ⭐⭐处理第二个客人的点餐业务
executorService.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
// 3.在线程池中再找一个工人进行做饭
Future<String> f = executorService.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
(3).饥饿线程_解决
- 保证拥有充足的工人
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
static final List<String> MENU = Arrays.asList("地三鲜", "宫保鸡丁", "辣子鸡丁", "烤鸡翅");
static Random RANDOM = new Random();
static String cooking() {
return MENU.get(RANDOM.nextInt(MENU.size()));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ⭐⭐1.固定线程池: 工人的人数为2
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 2. 处理第一个客人的点餐业务
executorService.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
// 3.在线程池中再找一个工人进行做饭
Future<String> f = executorService.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 3. 处理第二个客人的点餐业务
executorService.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
// 3.在线程池中再找一个工人进行做饭
Future<String> f = executorService.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
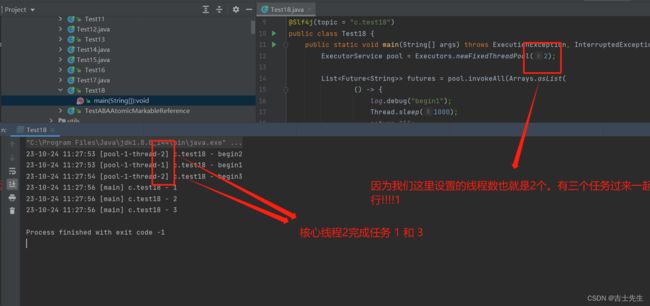
虽然能够解决我们的问题,但是有缺陷。因为我们未来可能不知道有多少任务量。
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
static final List<String> MENU = Arrays.asList("地三鲜", "宫保鸡丁", "辣子鸡丁", "烤鸡翅");
static Random RANDOM = new Random();
static String cooking() {
return MENU.get(RANDOM.nextInt(MENU.size()));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.固定服务员线程池: 1人
ExecutorService waiterPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
// 2.固定厨师线程池 1人
ExecutorService cookPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
// 2. 处理第一个客人的点餐业务
waiterPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
// 3.在线程池中再找一个工人进行做饭
Future<String> f = cookPool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 3. 处理第二个客人的点餐业务
waiterPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("处理点餐...");
// 3.在线程池中再找一个工人进行做饭
Future<String> f = cookPool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("做菜");
return cooking();
});
try {
log.debug("上菜: {}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
(4).创建多少线程池合适
- 过小会导致程序不能充分地利用系统资源、容易导致饥饿
- 过大会导致更多的线程上下文切换,占用更多内存
- CPU 密集型运算
通常采用 cpu 核数 + 1 能够实现最优的 CPU 利用率,+1 是保证当线程由于页缺失故障(操作系统)或其它原因导致暂停时,额外的这个线程就能顶上去,保证 CPU 时钟周期不被浪费。

- I/O 密集型运算 (WEB应用程序)
CPU 不总是处于繁忙状态,例如,当你执行业务计算时,这时候会使用 CPU 资源,但当你执行 I/O 操作时、远程RPC 调用时,包括进行数据库操作时,这时候 CPU 就闲下来了,你可以利用多线程提高它的利用率。
经验公式如下
线程数 = 核数 * 期望 CPU 利用率 * 总时间(CPU计算时间+等待时间) / CPU 计算时间
例如 4 核 CPU 计算时间是 50% ,其它等待时间是 50%,期望 cpu 被 100% 利用,套用公式
4 * 100% * 100% / 50% = 8
例如 4 核 CPU 计算时间是 10% ,其它等待时间是 90%,期望 cpu 被 100% 利用,套用公式
4 * 100% * 100% / 10% = 40
4.任务调度线程池
在『任务调度线程池』功能加入之前,可以使用 java.util.Timer 来实现定时功能,Timer 的优点在于简单易用,但由于所有任务都是由同一个线程来调度,因此所有任务都是串行执行的,同一时间只能有一个任务在执行,前一个任务的延迟或异常都将会影响到之后的任务。
(1).Timer 实现定时任务
假如说任务中出现了异常,就会停止运行了。
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
Timer timer = new Timer();
// 1.设置任务1
TimerTask task1 = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("task 1");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 2.设置任务2
TimerTask task2 = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("task 2");
}
};
log.debug("主线程启动....");
// 使用 timer 添加两个任务,希望它们都在 1s 后执行
// 但由于 timer 内只有一个线程来顺序执行队列中的任务,因此『任务1』的延时,影响了『任务2』的执行
timer.schedule(task1, 1000);
timer.schedule(task2, 1000);
}
}
我们发现是串行执行的,因为两个任务定时一样,但是没有一起打印出来。而是间隔了时间,所以我们得出是串行执行的。

(2).newScheduledThreadPool (延迟线程池)
- 未出现异常的情况下
这个是只执行一次
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 如何为1的话,那么仍然是线性运行的
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
log.debug("主线程开始...");
pool.schedule(()->{log.debug("两秒后执行第一个任务");},2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(()->{log.debug("两秒后执行第二个任务");},2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(()->{log.debug("两秒后执行第三个任务");},2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(()->{log.debug("两秒后执行第三个任务");},2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
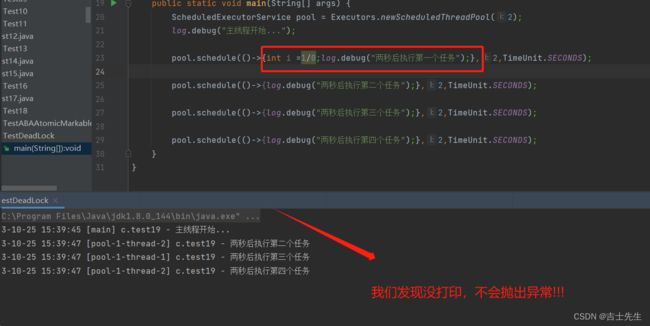
- 出现异常的情况下
这个是只执行一次
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
log.debug("主线程开始...");
// ⭐ schedule
pool.schedule(()->{int i =1/0;log.debug("两秒后执行第一个任务");},2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(()->{log.debug("两秒后执行第二个任务");},2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(()->{log.debug("两秒后执行第三个任务");},2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(()->{log.debug("两秒后执行第四个任务");},2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
出现异常,但不会抛出异常,也不会打印异常后的信息
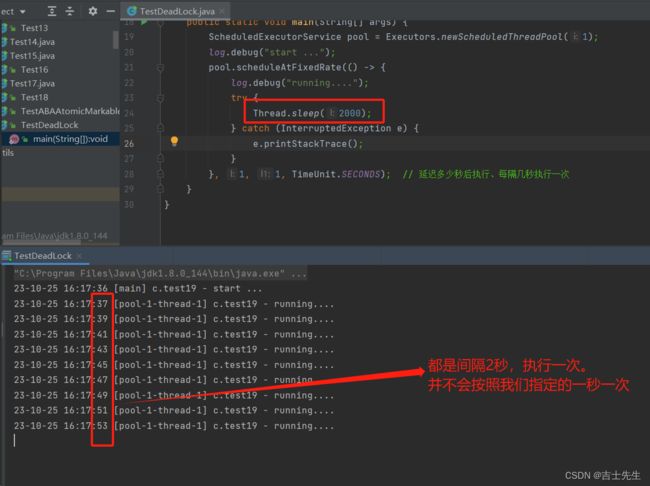
(3).newScheduledThreadPool (定时线程池)
- scheduleAtFixedRate() 方法
这个是执行多次
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
log.debug("start ...");
// ⭐scheduleAtFixedRate
pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
log.debug("running....");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000); //
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 延迟多少秒后执行、每隔几秒执行一次
}
}
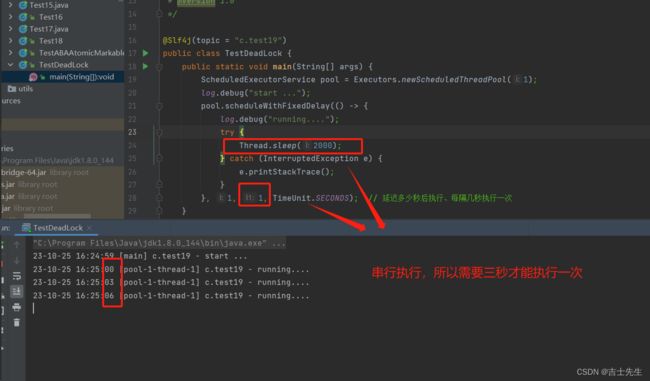
注意我们这里本来是1秒执行一次,重复执行的。但是因为里面有一个sleep()是两秒,scheduleAtFixedRate并行处理,所以是两秒运行一次。
- scheduleWithFixedDelay
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
log.debug("start ...");
// ⭐scheduleWithFixedDelay 串行
pool.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
log.debug("running....");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 延迟多少秒后执行、每隔几秒执行一次
}
}
(4).正确处理线程池异常
- 使用try catch
我们可以使用手动的 try catch 进行我们的手动抛出异常!!!
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
log.debug("主线程开始...");
// ⭐ try catch 抛出异常
pool.schedule(() -> {
try {
int i = 1 / 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("两秒后执行第一个任务");
}, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(() -> {
log.debug("两秒后执行第二个任务");
}, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(() -> {
log.debug("两秒后执行第三个任务");
}, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
pool.schedule(() -> {
log.debug("两秒后执行第四个任务");
}, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
(5).定时任务测试
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/24 19:52
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: TestDeadLock
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test19")
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int period = 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24 * 7;
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
// 当前时间
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// 周四的时间
LocalDateTime future = now.withHour(20).withMinute(4).withSecond(0).withNano(0).with(DayOfWeek.WEDNESDAY);
// 假如说当前时间大于本周的周四,必须要找到下周四
if (now.compareTo(future)>0){
future=future.plusWeeks(1); // 添加一周
}
// 做减法
long initDelay = Duration.between(now,future).toMillis();
pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {log.debug("1111");
}, initDelay, period, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
5. Tomcat 线程池
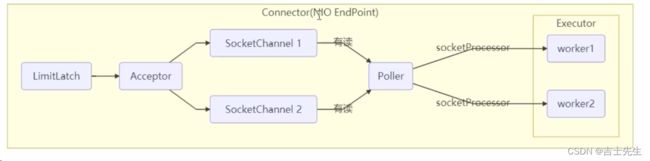
(1).Tomcat 在哪里用到了线程池呢
- LimitLatch 用来限流,可以
控制最大连接个数,类似 J.U.C 中的 Semaphore 后面再讲 - Acceptor 只负责【
接收新的 socket 连接】 - Poller 只负责监听
socket channel是否有【可读的 I/O 事件】 - 一旦可读,封装一个任务对象(socketProcessor),提交给 Executor 线程池处理
- Executor 线程池中的工作线程最终负责【处理请求】
Tomcat 线程池扩展了 ThreadPoolExecutor,行为稍有不同
- 如果总线程数达到 maximumPoolSize
- 这时不会立刻抛 RejectedExecutionException 异常
- 而是再次尝试将任务放入队列,如果还失败,才抛出RejectedExecutionException
异常源码 tomcat-7.0.42。
public void execute(Runnable command, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
submittedCount.incrementAndGet();
try {
super.execute(command);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException rx) {
if (super.getQueue() instanceof TaskQueue) {
final TaskQueue queue = (TaskQueue) super.getQueue();
try {
if (!queue.force(command, timeout, unit)) {
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Queue capacity is full.");
}
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
Thread.interrupted();
throw new RejectedExecutionException(x);
}
} else {
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
throw rx;
}
}
}
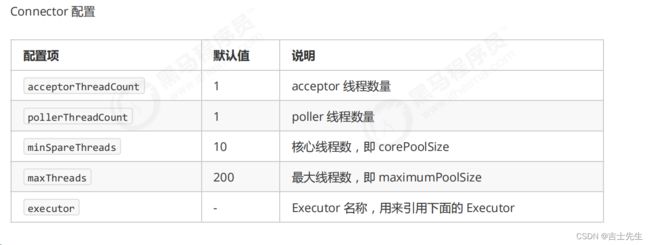
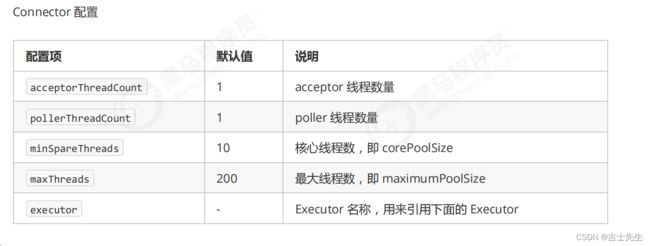
(2).Tomcat 配置
6.Fork/join
(1).任务拆分概念
Fork/Join 是 JDK 1.7 加入的新的线程池实现,它体现的是一种分治思想,适用于能够进行任务拆分的 cpu 密集型运算。
所谓的任务拆分,是将一个大任务拆分为算法上相同的小任务,直至不能拆分可以直接求解。跟递归相关的一些计算,如归并排序、斐波那契数列、都可以用分治思想进行求解.
Fork/Join 在分治的基础上加入了多线程,可以把每个任务的分解和合并交给不同的线程来完成,进一步提升了运算效率.
Fork/Join 默认会创建与 cpu 核心数大小相同的线程池.
(2).任务拆分举例
这里我们进行递归1~5的和
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/25 21:00
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test19
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test")
public class Test19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(4);
// 调用方法
Integer invoke = pool.invoke(new MyTask(5));
System.out.println(invoke);
}
}
// 1~n 之间整数的和: 利用递归的方法
@Slf4j(topic = "c.MyTask")
class MyTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer> {
private int n;
public MyTask(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyTask{" +
"n=" + n +
'}';
}
@Override
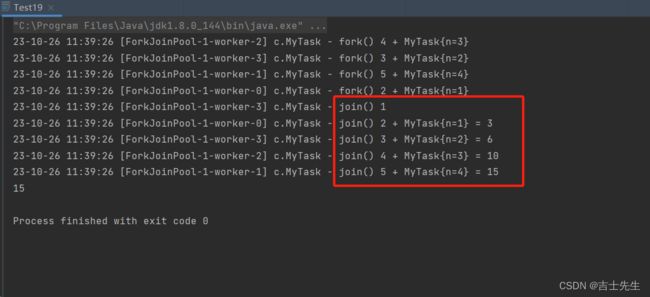
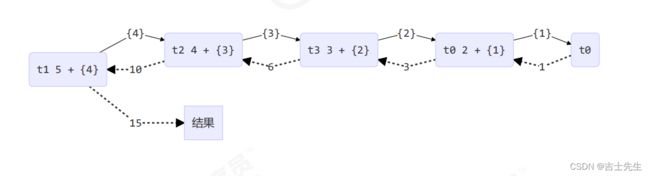
protected Integer compute() {
if (n == 1) { // 终止的条件
log.debug("join() {}", n);
return 1;
}
MyTask myTask = new MyTask(n - 1);
myTask.fork(); // ⭐让一个线程去执行任务
log.debug("fork() {} + {}", n, myTask);
Integer result = myTask.join() + n; // ⭐⭐执行后的结果 + n : 相当于 5+4+3+2+1
log.debug("join() {} + {} = {}", n, myTask, result.toString());
return result;
}
}
(3).任务拆分优化
利用我们二分的方法进行优化
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/25 21:00
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test19
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test")
public class Test19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(4);
Integer invoke = pool.invoke(new AddTask3(1,5));
System.out.println(invoke);
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.addTask3")
class AddTask3 extends RecursiveTask<Integer> {
// 起始的数 和 结束的数
int begin;
int end;
public AddTask3(int begin, int end) {
this.begin = begin;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" + begin + "," + end + '}';
}
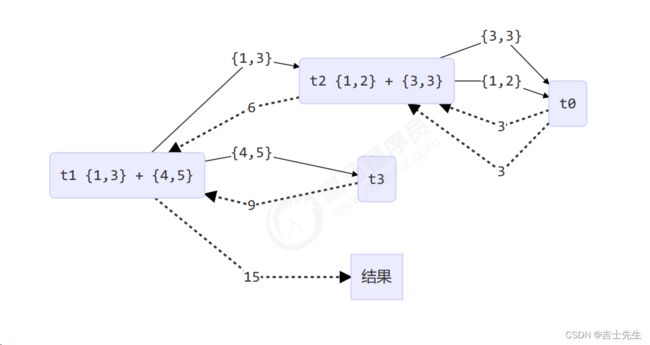
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
// 5, 5
if (begin == end) {
log.debug("join() {}", begin);
return begin;
}
// 4, 5
if (end - begin == 1) {
log.debug("join() {} + {} = {}", begin, end, end + begin);
return end + begin;
}
// 1 5 使用我们的二分操作
int mid = (end + begin) / 2; // 3
AddTask3 t1 = new AddTask3(begin, mid); // 1,3
t1.fork();
AddTask3 t2 = new AddTask3(mid + 1, end); // 4,5
t2.fork();
log.debug("fork() {} + {} = ?", t1, t2);
int result = t1.join() + t2.join();
log.debug("join() {} + {} = {}", t1, t2, result);
return result;
}
}
(九)、JUC
1.AQS原理
(1).aqs概述
全称是 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,是阻塞式锁和相关的同步器工具的框架。
特点:
- 用 state 属性来表示资源的状态(分
独占模式和共享模式),子类需要定义如何维护这个状态,控制如何获取锁和释放锁。getState- 获取 state 状态setState- 设置 state 状态compareAndSetState- cas 机制设置 state 状态- 独占模式是只有一个线程能够访问资源,而共享模式可以允许多个线程访问资源
- 提供了基于 FIFO 的等待队列,类似于 Monitor 的 EntryList
- 条件变量来实现等待、唤醒机制,支持多个条件变量,类似于 Monitor 的 WaitSet
子类主要实现这样一些方法(默认抛出 UnsupportedOperationException)
- tryAcquire
- tryRelease
- tryAcquireShared
- tryReleaseShared
- isHeldExclusively
- 获取锁的姿势
// 如果获取锁失败
if(!tryAcquire(arg)){
// 入队, 可以选择阻塞当前线程 park unpark
}
- 释放锁的姿势
// 如果释放锁成功
if(tryRelease(arg)){
// 让阻塞线程恢复运行
}
(2).自定义锁
自定义不可重入锁
package com.jsxs.Test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
/**
* @Author Jsxs
* @Date 2023/10/25 21:00
* @PackageName:com.jsxs.Test
* @ClassName: Test19
* @Description: TODO
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test")
public class Test19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLock myLock = new MyLock();
new Thread(() -> {
myLock.lock();
try {
log.debug("locking.....");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
log.debug("unlocking.....");
myLock.unlock();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
myLock.lock();
try {
log.debug("locking.....");
} finally {
log.debug("unlocking.....");
myLock.unlock();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
/**
* 自定义锁 (不可重入锁)
*/
class MyLock implements Lock {
/**
* 创建我们的同步类
*/
class MySync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
@Override
protected boolean tryAcquire(int i) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
// 假如成功了,说明我们的锁是成功的
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
protected boolean tryRelease(int i) {
setState(0);
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
return true;
}
@Override // 是否持有独占锁
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState() == 1;
}
public Condition newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
}
private MySync sync = new MySync();
@Override // 加锁, (假如不成功就会进入等待队列)
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
@Override // 加锁,可打断 ()
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
@Override // 尝试加锁 (尝试一次)
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryAcquire(1);
}
@Override // 尝试加锁 (带超时时间)
public boolean tryLock(long l, TimeUnit timeUnit) throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, timeUnit.toNanos(l));
}
@Override // 解锁
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
@Override // 创建条件变量
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
}
(十)、 ReentrantLock 原理
1.非公平锁实现原理
(1).加锁解锁流程
先从构造器开始看,默认为非公平锁实现
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
NonfairSync 继承自 AQS
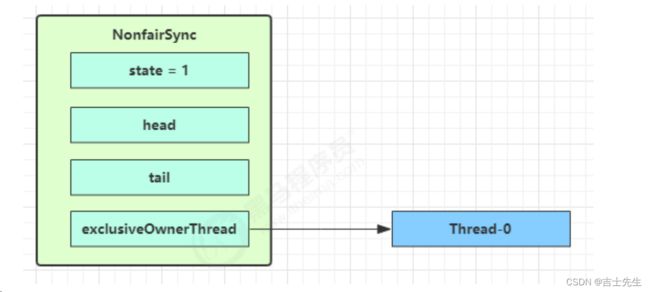
- 加锁成功流程⬇
- 加锁失败流程

Thread-1 执行了
1. CAS尝试将 state 由 0 改为 1,结果失败
2. 进入 tryAcquire(尝试加锁) 逻辑,这时 state 已经是1,结果仍然失败
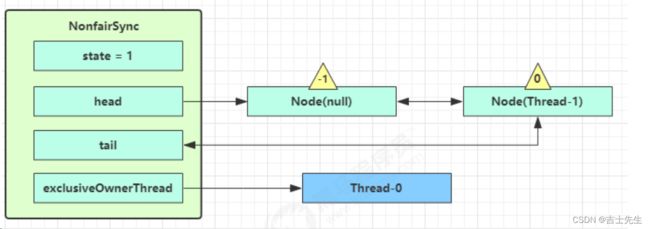
3. 接下来进入 addWaiter(添加到阻塞队列) 逻辑,构造 Node 队列
- 图中黄色三角表示该 Node 的 waitStatus 状态,其中 0 为默认正常状态
- Node 的创建是懒惰的
- 其中第一个 Node 称为 Dummy(哑元)或哨兵,用来占位,并不关联线程
- acquireQueued 会在一个死循环中不断尝试获得锁,失败后进入 park 阻塞
- 如果自己是紧邻着 head(排第二位),那么再次 tryAcquire 尝试获取锁,当然这时 state 仍为 1,失败
- 进入 shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 逻辑,将前驱 node,即 head 的 waitStatus 改为 -1,这次返回 false
-
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 执行完毕回到 acquireQueued ,再次 tryAcquire 尝试获取锁,当然这时 state 仍为 1,失败
-
当再次进入 shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 时,这时因为其前驱 node 的 waitStatus 已经是 -1,这次返回
true -
进入
parkAndCheckInterrupt, Thread-1 park(灰色表示)
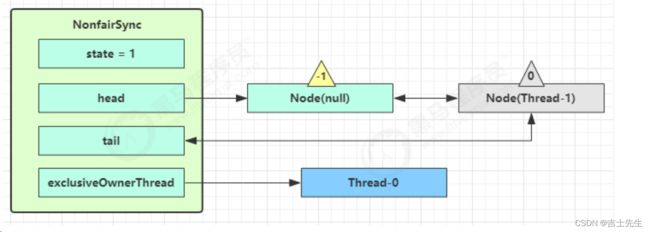
- 解锁竞争成功流程
再次有多个线程经历上述过程竞争失败,变成这个样子
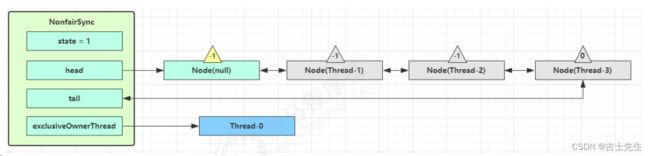
Thread-0 释放锁,进入 tryRelease 流程,如果成功
- 设置 exclusiveOwnerThread 为 null
- state = 0

当前队列不为 null,并且 head 的 waitStatus = -1,进入 unparkSuccessor 流程
找到队列中离 head 最近的一个 Node(没取消的),unpark 恢复其运行,本例中即为 Thread-1
回到 Thread-1 的 acquireQueued 流程
- exclusiveOwnerThread 为 Thread-1,state = 1
- head 指向刚刚 Thread-1 所在的 Node,该 Node 清空 Thread
- 原本的 head 因为从链表断开,而可被垃圾回收
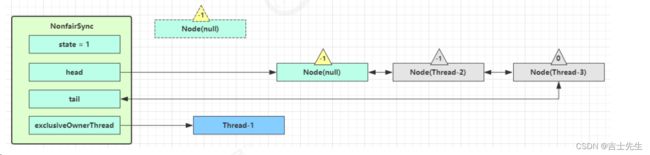
如果这时候有其它线程来竞争(非公平的体现),例如这时有 Thread-4 来了
如果不巧又被 Thread-4 占了先
- Thread-4 被设置为 exclusiveOwnerThread,state = 1
- Thread-1 再次进入 acquireQueued 流程,获取锁失败,重新进入 park 阻塞
(十一)、线程安全集合类概述
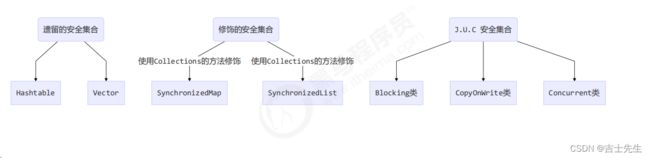
1.概述
-
遗留的线程安全集合如 Hashtable , Vector
-
使用 Collections 装饰的线程安全集合,如:
- Collections.synchronizedCollection
- Collections.synchronizedList
- Collections.synchronizedMap
- Collections.synchronizedSet
- Collections.synchronizedNavigableMap
- Collections.synchronizedNavigableSet
- Collections.synchronizedSortedMap
- Collections.synchronizedSortedSet
-
java.util.concurrent.*
重点介绍 java.util.concurrent.* 下的线程安全集合类,可以发现它们有规律,里面包含三类关键词:Blocking、CopyOnWrite、Concurrent
- Blocking 大部分实现基于锁,并提供用来阻塞的方法
- CopyOnWrite 之类容器修改开销相对较重
- Concurrent 类型的容器
- 内部很多操作使用
cas优化,一般可以提供较高吞吐量 - 弱一致性
- 遍历时弱一致性,例如,
当利用迭代器遍历时,如果容器发生修改,迭代器仍然可以继续进行遍历,这时内容是旧的 - 求大小弱一致性,
size 操作未必是 100% 准确 - 读取弱一致性
- 遍历时弱一致性,例如,
- 内部很多操作使用
遍历时如果发生了修改,对于非安全容器来讲,使用 fail-fast 机制也就是让遍历立刻失败,抛出 ConcurrentModificationException,不再继续遍历