【文件系统】文件系统中的数据结构
目录
0.参考
1.文件系统的主要数据结构
2.超级块及其操作函数
3.inode及其操作函数
4.目录项数据结构定义及操作函数
5.文件结构体的定义及文件的操作函数
0.参考
推荐老师及视频:
西安邮电大学研究生导师陈莉君老师《高级操作系统》,可以上B站搜索教学视频,为防止被删,可以缓存.
推荐ups主:善不外来名不虚传
清华大学《高级操作系统》视频,陈渝老师在2020年2-5月录了这个视频
推荐书目:
《LINUX内核设计与实现》第二版,第三版
推荐链接:
内容摘选自
https://www.cnblogs.com/smartjourneys/p/7258226.html--文件系统1
https://www.cnblogs.com/smartjourneys/p/7260911.html--文件系统2
https://blog.csdn.net/yunsongice/article/details/5683859
https://blog.csdn.net/GerryLee93/article/details/106476030 --哈希链表
(以上感恩)
1.文件系统的主要数据结构
文件系统本身的数据结构
Linux内核采用VFS(Virtual Filesystem Switch)框架
每个文件系统都需要在VFS中注册,即填充一个struct file_system_type结构
此结构描述的是文件系统的名称以及一个指向对应VFS超级块读取例程的地址等信息
文件系统宏观上的两个数据结构:
(1)struct file_system_type
(2)struct vfsmount
文件系统的四个主要对象对应的数据结构
(1)超级块对象 存放系统中已安装文件系统的信息
(2)索引节点对象 存放关于具体文件的一般信息
(3)目录项对象 存放目录项与对应文件进行链接的信息
(4)文件对象 存放打开文件与进程之间进行交互的有关信息
文件系统宏观上的两个数据结构:
(1)
struct file_system_type {
const char *name;
int fs_flags;
struct super_block *(*read_super) (struct super_block *, void *, int);//ext2_read_super读取超级块,一般是第一个块
struct module *owner;
struct file_system_type * next;
struct list_head fs_supers;
};
5.8.13中这么定义:
struct file_system_type {
const char *name;
int fs_flags;
#define FS_REQUIRES_DEV 1
#define FS_BINARY_MOUNTDATA 2
#define FS_HAS_SUBTYPE 4
#define FS_USERNS_MOUNT 8 /* Can be mounted by userns root */
#define FS_DISALLOW_NOTIFY_PERM 16 /* Disable fanotify permission events */
#define FS_RENAME_DOES_D_MOVE 32768 /* FS will handle d_move() during rename() internally. */
int (*init_fs_context)(struct fs_context *);
const struct fs_parameter_spec *parameters;
struct dentry *(*mount) (struct file_system_type *, int,const char *, void *);
void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *);
struct module *owner;
struct file_system_type * next;
struct hlist_head fs_supers;
struct lock_class_key s_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key s_umount_key;
struct lock_class_key s_vfs_rename_key;
struct lock_class_key s_writers_key[SB_FREEZE_LEVELS];
struct lock_class_key i_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_dir_key;
};
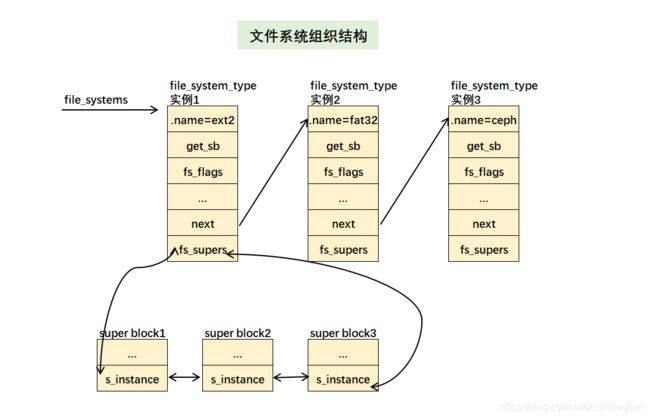
这相当于一个文件系统的类,比如会有各种文件系统,比如说ext2文件系统,xfs文件系统,drm文件系统
等系统.这样在去实例化的时候,相当于定义了一个类的一个对象,每一个文件系统都是一个对象,对象
与对象之间通过指针串起来.这里的链表是单向链表,可能是不经常添加或者删除文件系统吧.
(2)还有一个与文件系统本身相关的数据结构:struct vfsmout,在5.8.13中是这么定义的:
struct vfsmount {
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* root of the mounted tree */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* pointer to superblock */
int mnt_flags;
} __randomize_layout;
D:\005-代码\001-开源项目源码\004-内核源码\linux-2.6.11.10\include\linux\mount.h中是这么定义的:
struct vfsmount
{
struct list_head mnt_hash;
struct vfsmount *mnt_parent; /* fs we are mounted on */
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint; /* dentry of mountpoint */
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* root of the mounted tree */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* pointer to superblock */
struct list_head mnt_mounts; /* list of children, anchored here */
struct list_head mnt_child; /* and going through their mnt_child */
atomic_t mnt_count;
int mnt_flags;
int mnt_expiry_mark; /* true if marked for expiry */
char *mnt_devname; /* Name of device e.g. /dev/dsk/hda1 */
struct list_head mnt_list;
struct list_head mnt_fslink; /* link in fs-specific expiry list */
struct namespace *mnt_namespace; /* containing namespace */
};
每个文件系统都有一个全局file_system_type类型的全局变量,例如:ext2_fs_type代表ext2文件系统
mount的时候会调用read_super.
2.超级块及其操作函数
超级块用来描述整个文件系统的信息
每个具体的文件系统都有自己的超级块
VFS超级块是各种文件系统在安装时建立的,并在卸载时被自动删除,其数据结构是super_block
所有超级块对象都以双向循环链表的形式链接在一起super_block的数据结构,摘自5.8.13版本的内核
D:\005-代码\001-开源项目源码\004-内核源码\linux-5.8.13\linux-5.8.13\include\linux\fs.h
struct super_block {
struct list_head s_list; /* Keep this first */
dev_t s_dev; /* search index; _not_ kdev_t */
unsigned char s_blocksize_bits;
unsigned long s_blocksize;
loff_t s_maxbytes; /* Max file size */
struct file_system_type *s_type;
const struct super_operations *s_op;
const struct dquot_operations *dq_op;
const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;
const struct export_operations *s_export_op;
unsigned long s_flags;
unsigned long s_iflags; /* internal SB_I_* flags */
unsigned long s_magic;
struct dentry *s_root;
struct rw_semaphore s_umount;
int s_count;
atomic_t s_active;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *s_security;
#endif
const struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_ENCRYPTION
const struct fscrypt_operations *s_cop;
struct key *s_master_keys; /* master crypto keys in use */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_VERITY
const struct fsverity_operations *s_vop;
#endif
struct hlist_bl_head s_roots; /* alternate root dentries for NFS */
struct list_head s_mounts; /* list of mounts; _not_ for fs use */
struct block_device *s_bdev;
struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi;
struct mtd_info *s_mtd;
struct hlist_node s_instances;
unsigned int s_quota_types; /* Bitmask of supported quota types */
struct quota_info s_dquot; /* Diskquota specific options */
struct sb_writers s_writers;
/*
* Keep s_fs_info, s_time_gran, s_fsnotify_mask, and
* s_fsnotify_marks together for cache efficiency. They are frequently
* accessed and rarely modified.
*/
void *s_fs_info; /* Filesystem private info */
/* Granularity of c/m/atime in ns (cannot be worse than a second) */
u32 s_time_gran;
/* Time limits for c/m/atime in seconds */
time64_t s_time_min;
time64_t s_time_max;
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
__u32 s_fsnotify_mask;
struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *s_fsnotify_marks;
#endif
char s_id[32]; /* Informational name */
uuid_t s_uuid; /* UUID */
unsigned int s_max_links;
fmode_t s_mode;
/*
* The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business
* even looking at it. You had been warned.
*/
struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex; /* Kludge */
/*
* Filesystem subtype. If non-empty the filesystem type field
* in /proc/mounts will be "type.subtype"
*/
const char *s_subtype;
const struct dentry_operations *s_d_op; /* default d_op for dentries */
/*
* Saved pool identifier for cleancache (-1 means none)
*/
int cleancache_poolid;
struct shrinker s_shrink; /* per-sb shrinker handle */
/* Number of inodes with nlink == 0 but still referenced */
atomic_long_t s_remove_count;
/* Pending fsnotify inode refs */
atomic_long_t s_fsnotify_inode_refs;
/* Being remounted read-only */
int s_readonly_remount;
/* per-sb errseq_t for reporting writeback errors via syncfs */
errseq_t s_wb_err;
/* AIO completions deferred from interrupt context */
struct workqueue_struct *s_dio_done_wq;
struct hlist_head s_pins;
/*
* Owning user namespace and default context in which to
* interpret filesystem uids, gids, quotas, device nodes,
* xattrs and security labels.
*/
struct user_namespace *s_user_ns;
/*
* The list_lru structure is essentially just a pointer to a table
* of per-node lru lists, each of which has its own spinlock.
* There is no need to put them into separate cachelines.
*/
struct list_lru s_dentry_lru;
struct list_lru s_inode_lru;
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct work_struct destroy_work;
struct mutex s_sync_lock; /* sync serialisation lock */
/*
* Indicates how deep in a filesystem stack this SB is
*/
int s_stack_depth;
/* s_inode_list_lock protects s_inodes */
spinlock_t s_inode_list_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
struct list_head s_inodes; /* all inodes */
spinlock_t s_inode_wblist_lock;
struct list_head s_inodes_wb; /* writeback inodes */
} __randomize_layout;
struct super_operations {
struct inode *(*alloc_inode)(struct super_block *sb);
void (*destroy_inode)(struct inode *);
void (*free_inode)(struct inode *);
void (*dirty_inode) (struct inode *, int flags);
int (*write_inode) (struct inode *, struct writeback_control *wbc);
int (*drop_inode) (struct inode *);
void (*evict_inode) (struct inode *);
void (*put_super) (struct super_block *);
int (*sync_fs)(struct super_block *sb, int wait);
int (*freeze_super) (struct super_block *);
int (*freeze_fs) (struct super_block *);
int (*thaw_super) (struct super_block *);
int (*unfreeze_fs) (struct super_block *);
int (*statfs) (struct dentry *, struct kstatfs *);
int (*remount_fs) (struct super_block *, int *, char *);
void (*umount_begin) (struct super_block *);
int (*show_options)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
int (*show_devname)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
int (*show_path)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
int (*show_stats)(struct seq_file *, struct dentry *);
#ifdef CONFIG_QUOTA
ssize_t (*quota_read)(struct super_block *, int, char *, size_t, loff_t);
ssize_t (*quota_write)(struct super_block *, int, const char *, size_t, loff_t);
struct dquot **(*get_dquots)(struct inode *);
#endif
int (*bdev_try_to_free_page)(struct super_block*, struct page*, gfp_t);
long (*nr_cached_objects)(struct super_block *,
struct shrink_control *);
long (*free_cached_objects)(struct super_block *,
struct shrink_control *);
};
3.inode及其操作函数
struct inode_operations {
struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, unsigned int);
const char * (*get_link) (struct dentry *, struct inode *, struct delayed_call *);
int (*permission) (struct inode *, int);
struct posix_acl * (*get_acl)(struct inode *, int);
int (*readlink) (struct dentry *, char __user *,int);
int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, umode_t, bool);
int (*link) (struct dentry *,struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*unlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*symlink) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,const char *);
int (*mkdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,umode_t);
int (*rmdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
int (*mknod) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,umode_t,dev_t);
int (*rename) (struct inode *, struct dentry *,
struct inode *, struct dentry *, unsigned int);
int (*setattr) (struct dentry *, struct iattr *);
int (*getattr) (const struct path *, struct kstat *, u32, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*listxattr) (struct dentry *, char *, size_t);
int (*fiemap)(struct inode *, struct fiemap_extent_info *, u64 start,
u64 len);
int (*update_time)(struct inode *, struct timespec64 *, int);
int (*atomic_open)(struct inode *, struct dentry *,
struct file *, unsigned open_flag,
umode_t create_mode);
int (*tmpfile) (struct inode *, struct dentry *, umode_t);
int (*set_acl)(struct inode *, struct posix_acl *, int);
} ____cacheline_aligned;
4.目录项数据结构定义及操作函数
5.文件结构体的定义及文件的操作函数
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
int (*iopoll)(struct kiocb *kiocb, bool spin);
int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
int (*iterate_shared) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
__poll_t (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
unsigned long mmap_supported_flags;
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*fsync) (struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int datasync);
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
int (*check_flags)(int);
int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **, void **);
long (*fallocate)(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset,
loff_t len);
void (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f);
#ifndef CONFIG_MMU
unsigned (*mmap_capabilities)(struct file *);
#endif
ssize_t (*copy_file_range)(struct file *, loff_t, struct file *,
loff_t, size_t, unsigned int);
loff_t (*remap_file_range)(struct file *file_in, loff_t pos_in,
struct file *file_out, loff_t pos_out,
loff_t len, unsigned int remap_flags);
int (*fadvise)(struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int);
} __randomize_layout;