C语言实现二叉树(二叉链表)
文章目录
- 定义结构体
- 初始化
- 先序遍历创建二叉树
-
- 方法一
-
- 测试
- 方法二:根据所给的字符串序列创建
- 其他方法
-
- 树的结点大小
- 树的高
- 判断树空
- 找某个结点的左孩子和右孩子
- 找某个结点的父节点
- 查找元素
- 拷贝树
- 清空树
定义结构体
#define ElemType char
typedef struct BinTreeNode {//树结点结构体,每一个数据结点对应于一个存储单元,一个数据结点包括3部分
ElemType data;
struct BinTreeNode* LeftChild;
struct BinTreeNode* RightChild;
}BinTreeNode;
typedef struct BinTree {//树结构体
BinTreeNode* root;//指向树的第一个结点——根结点
ElemType refvalue;//结束标记‘#’,是字符类型
};
初始化
void InitBinTree(BinTree *bt, ElemType ref){
bt->root = NULL;//一开始树中无结点
bt->refvalue = ref;
}
先序遍历创建二叉树
方法一
//1按照先序次序输入二叉树中结点的值,构造二叉链表表示的二叉树bt
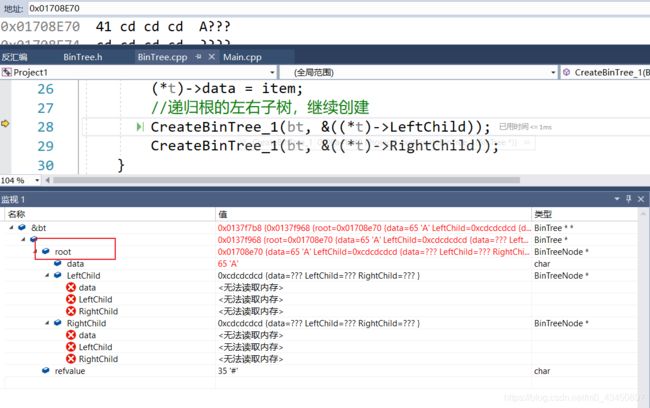
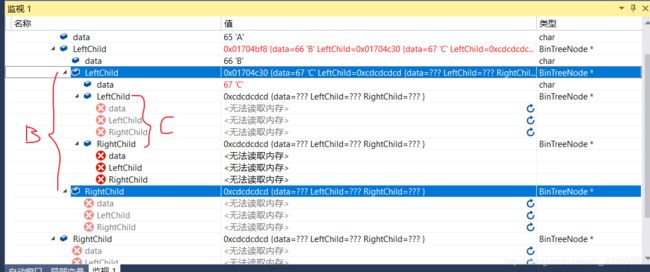
void CreateBinTree_1(BinTree *bt) {
CreateBinTree_1(bt, &(bt->root));//参数的传递都需要地址
}
void CreateBinTree_1(BinTree *bt, BinTreeNode **t) {//*t代表根节点的地址,这里参数的传递都需要地址,所以这里是指向根节点地址的地址
//先把根节点传进去
ElemType item;
printf("请输入输入二叉树的元素:");
scanf("%c", &item);
if (item == bt->refvalue) {
(*t) == NULL;//根节点为结束标记说明树为空
}
else {
//创建根节点(分配空间)
(*t) = (BinTreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(BinTreeNode));
assert((*t) != NULL);
(*t)->data = item;
//递归根的左右子树,继续创建
CreateBinTree_1(bt, &((*t)->LeftChild));
CreateBinTree_1(bt, &((*t)->RightChild));
}
}
//调用
void main() {
BinTree bt;
InitBinTree(&bt, '#');
CreateBinTree_1(&bt);//这样就不用在外面调用结构体的成员
}
测试
方法二:根据所给的字符串序列创建
注意参数char *&str,对字符采用引用
void CreateBinTree_4(BinTree *bt, char *str) {
CreateBinTree_4(bt, bt->root, str);
}
void CreateBinTree_4(BinTree *bt, BinTreeNode *&t, char *&str) {//BinTreeNode *&t 是根结点,BinTreeNode *类型
if (*str == bt->refvalue) {
t = NULL;
}
else {
t = (BinTreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(BinTreeNode));
t->data = *str;//*str代表指针指向字符串的第一个字符
CreateBinTree_4(bt, t->LeftChild, ++str);
CreateBinTree_4(bt, t->RightChild, ++str);
}
}
void main() {
BinTree bt;
InitBinTree(&bt, '#');
char *str = "ABC##D##G##";
CreateBinTree_4(&bt,str);
}
对字符串指针传递的分析
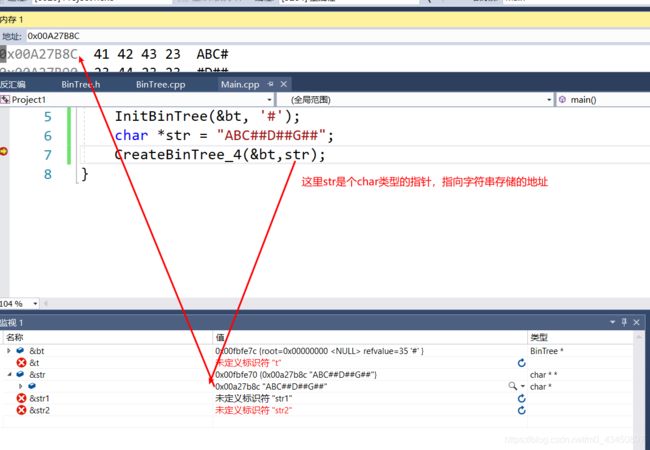

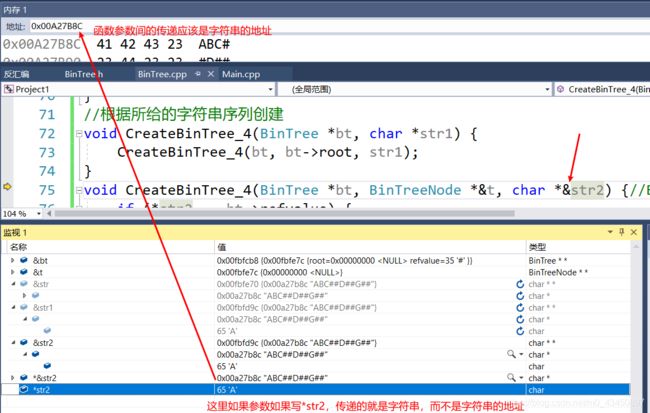
实际上str1与str2参数之间应该传递的是指向字符串地址的地址
其他方法
树的结点大小
递归根的左右孩子
int Size(BinTree *bt) {
return Size(bt->root);
}
int Size(BinTreeNode *t) {
if (t == NULL)return 0;
else {
return Size(t->LeftChild) + Size(t->RightChild)+1;
}
}
树的高
int Height(BinTree *bt) {
return Height(bt->root);
}
int Height(BinTreeNode *t) {
if (t == NULL)
return 0;
else {
int LeftHeight = Height(t->LeftChild);
int RightHeight = Height(t->RightChild);
return (LeftHeight > RightHeight? LeftHeight:RightHeight) + 1;
}
}
判断树空
bool BinTreeEmpty(BinTree *bt) {
return bt->root == NULL;
}
找某个结点的左孩子和右孩子
BinTreeNode* LeftChild(BinTreeNode *p) {
if (p == NULL)return NULL;
return p->LeftChild;
}
BinTreeNode* RightChild(BinTreeNode *p) {
if (p == NULL)return NULL;
return p->RightChild;
}
找某个结点的父节点
BinTreeNode* Parent(BinTree *bt, BinTreeNode *p) {//给出一个结点的地址找父节点
return Parent(bt, p);
}
BinTreeNode* Parent(BinTreeNode *t, BinTreeNode *p) {
if (t == NULL || p == NULL)return NULL;
if (t->LeftChild == p || t->RightChild == p) {//从根节点开始找
return t;
}
else {//看根节点的左右孩子是否是p的左右节点
BinTreeNode* q = Parent(t->LeftChild,p);
if (q != NULL) {
return q;
}
return Parent(t->RightChild,p);
}
}
查找元素
BinTreeNode* Search(BinTree *bt, ElemType key) {
return Search(bt->root, key);
}
BinTreeNode* Search(BinTreeNode *t, ElemType key) {
if (t == NULL)return NULL;
if (t->data == key) return t;
BinTreeNode* p = Search(t->LeftChild,key);
if (p != NULL) {
return p;
}
else {//左孩子找不到,再去找右孩子
return Search(t->RightChild, key);
}
}
拷贝树
void Copy(BinTree *bt1, BinTree *bt2) {
Copy(bt1->root, bt2->root);
}
void Copy(BinTreeNode *&t1, BinTreeNode *t2) {//需要用到指向 复制得到的树的根节点的 指针BinTreeNode *&t1
if (t2 == NULL)
t1 = NULL;
else {
t1 = (BinTreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(BinTreeNode));
assert(t1 != NULL);
t1->data = t2->data;
Copy(t1->LeftChild, t2->LeftChild);
Copy(t1->RightChild, t2->RightChild);
}
}
清空树
void BinTreeClear(BinTree *bt) {
return BinTreeClear(bt->root);
}
void BinTreeClear(BinTreeNode *&t) {//t就是一个指向各个结点的指针,因为是BinTreeNode *,所以要取这个指针的地址
if (t != NULL) {
BinTreeClear(t->LeftChild);
BinTreeClear(t->RightChild);
free(t);
t = NULL;
}
}