ELK中Kibana6.2.3下Timelion使用
环境 :Ubuntu
介绍
Timelion是时间序列数据可视化工具,需要安装Metricbeat,使您可以在单个可视化文件中组合完全独立的数据源。它由一种简单的表达语言驱动,您可以使用该表达语言检索时间序列数据,执行计算以找出复杂问题的答案并可视化结果。
例如,Timelion使您可以轻松获得以下问题的答案:
用户空间中花费的CPU时间与结果相差一小时的实时百分比是多少?
我的入站和出站网络流量是什么样的?
我的系统实际使用多少内存?
1、 添加系统内存监控
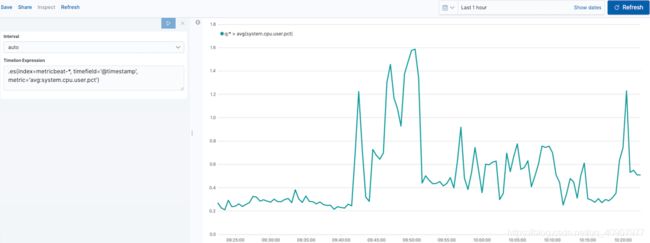
要开始跟踪CPU的实时百分比,请在Timelion Expression字段中输入以下内容:
.es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
比较数据
要比较这两个数据集,请添加另一个系列,其中包含前一个小时的数据,以逗号分隔:
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct'),
.es(offset=-1h,
index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
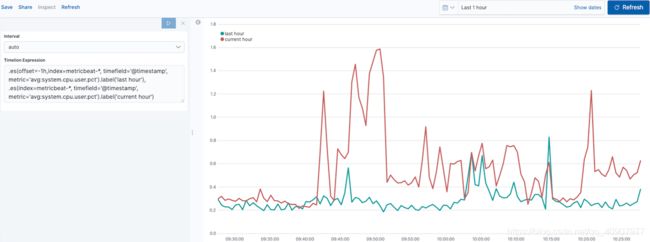
offset用日期表达式偏移数据检索。在此示例中,-1h将数据向后偏移一小时。

.es(offset=-1h,index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('last hour'), .es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('current hour')
添加标签名称
为了轻松地区分两个数据集,请添加标签名称:
label() 将自定义标签添加到可视化。
.es(offset=-1h,index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('last hour'), .es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('current hour')
添加标题
添加一个有意义的标题:
.es(offset=-1h,
index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
.label('last hour'),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
.label('current hour')
.title('CPU usage over time')
1.title()添加具有有意义名称的标题。标题使陌生的用户更容易理解可视化的目的。

更改图表类型编辑
要区分当前小时数据和最后一小时数据,请更改图表类
.es(offset=-1h,
index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
.label('last hour')
.lines(fill=1,width=0.5),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
.label('current hour')
.title('CPU usage over time')
1.lines()更改图表线的外观。在此示例中,.lines(fill=1,width=0.5)将填充级别设置为1,将边框宽度设置为0.5。
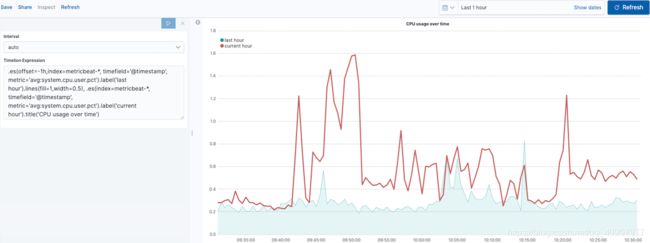
更改线条颜色编辑
为了突出当前小时数据,请更改线条颜色:
.es(offset=-1h,
index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
.label('last hour')
.lines(fill=1,width=0.5)
.color(gray),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct')
.label('current hour')
.title('CPU usage over time')
.color(#1E90FF)
1.color()更改数据的颜色。支持的颜色类型包括标准颜色名称,十六进制值或用于分组数据的颜色架构。在此示例中,.color(gray)代表最后一个小时,.color(#1E90FF)代表当前小时。
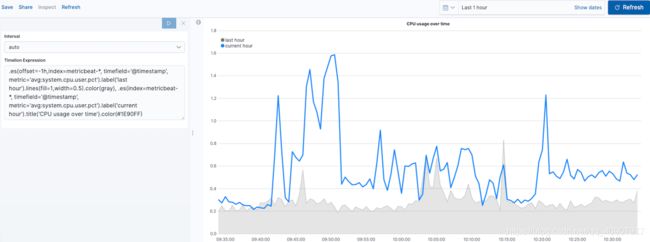
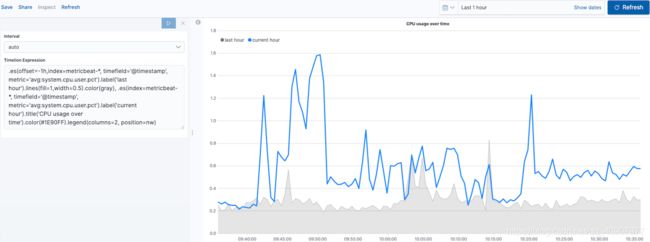
调整图例编辑
更改图例的位置和样式:
.es(offset=-1h,index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('last hour').lines(fill=1,width=0.5).color(gray), .es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='avg:system.cpu.user.pct').label('current hour').title('CPU usage over time').color(#1E90FF).legend(columns=2, position=nw)
1.legend()设置图例的位置和样式。在此示例中,.legend(columns=2, position=nw)将图例用两列放置在可视化的西北位置。
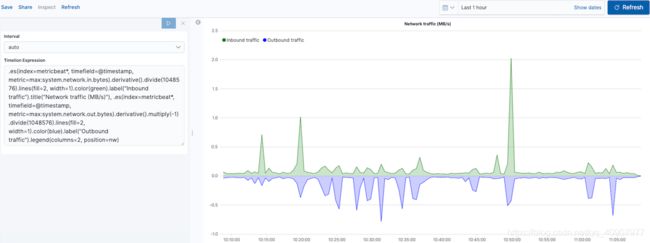
创建数学函数的可视化编辑
要创建入站和出站网络流量的可视化,请使用数学函数。
定义功能编辑
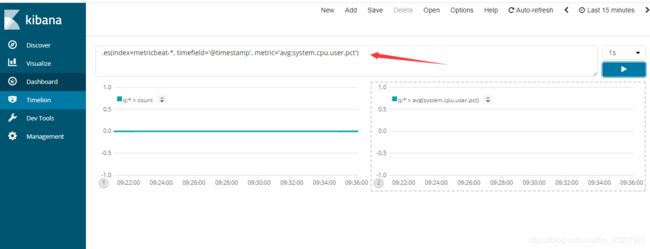
要开始跟踪入站和出站网络流量,请在“ Timelion表达式”字段中输入以下内容:
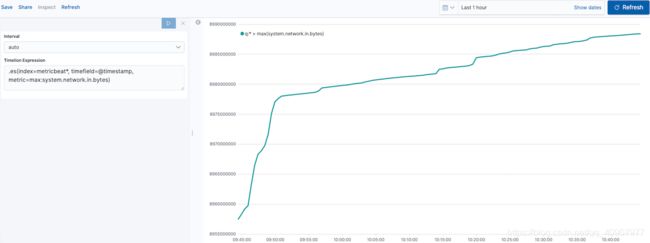
.es(index=metricbeat*, timefield=@timestamp, metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
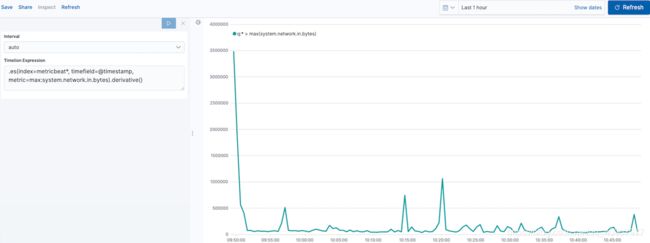
剧情变化率编辑
更改数据的显示方式,以便可以轻松监视入站流量:
.es(index=metricbeat*, timefield=@timestamp, metric=max:system.network.in.bytes).derivative()
1.derivative 绘制值随时间的变化。
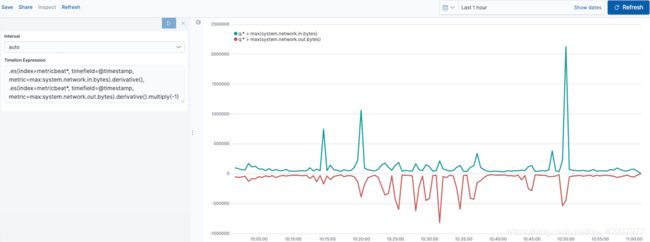
为出站流量添加类似的计算:
为出站流量添加类似的计算:
.es(index=metricbeat*, timefield=@timestamp, metric=max:system.network.in.bytes).derivative(), .es(index=metricbeat*, timefield=@timestamp, metric=max:system.network.out.bytes).derivative().multiply(-1)
1 .multiply()将数据系列乘以数字,数据系列的结果或数据系列列表。对于此示例,.multiply(-1)由于出站网络流量正在离开您的计算机,因此将出站网络流量转换为负值。
自定义可视化并设置其格式编辑
使用以下功能来自定义可视化并设置其格式:
.es(index=metricbeat*,
timefield=@timestamp,
metric=max:system.network.in.bytes)
.derivative()
.divide(1048576)
.lines(fill=2, width=1)
.color(green)
.label("Inbound traffic")
.title("Network traffic (MB/s)"),
.es(index=metricbeat*,
timefield=@timestamp,
metric=max:system.network.out.bytes)
.derivative()
.multiply(-1)
.divide(1048576)
.lines(fill=2, width=1)
.color(blue)
.label("Outbound traffic")
.legend(columns=2, position=nw)
使用条件逻辑创建可视化并跟踪趋势编辑
为了轻松检测异常值并发现随时间变化的模式,请使用条件逻辑修改时间序列数据,并使用移动平均值创建趋势。
使用Timelion条件逻辑,您可以使用以下运算符值比较数据:
eq #等于
ne #不相等
lt #少于
lte #小于或等于
gt #比...更棒
gte #大于或等于
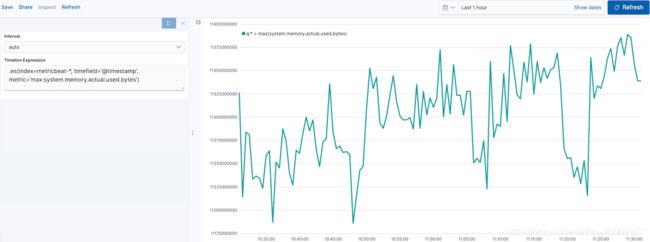
定义功能编辑
要绘制的最大值system.memory.actual.used.bytes,请在“ Timelion表达式”字段中输入以下内容:
.es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
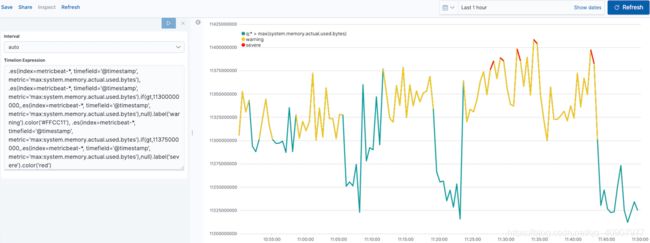
跟踪已用内存编辑
要跟踪使用的内存量,请创建两个阈值:
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.if(gt,
11300000000,
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
null)
.label('warning')
.color('#FFCC11'),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.if(gt,
11375000000,
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
null)
.label('severe')
.color('red')
1.Timelion条件逻辑大于运算符。在此示例中,警告阈值为11.3GB(11300000000),严重阈值为11.375GB(11375000000)。如果阈值对于您的机器而言太高或太低,请相应地调整这些值。
2.if()将每个点与一个数字进行比较。如果条件计算为true,则调整样式。如果条件的计算结果为false,则使用默认样式。
确定趋势编辑
要确定趋势,请创建一个新的数据系列:
.es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'), .es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes').if(gt,11300000000,.es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),null).label('warning').color('#FFCC11'), .es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes').if(gt,11375000000,.es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),null).label('severe').color('red'), .es(index=metricbeat-*, timefield='@timestamp', metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes').mvavg(10)
mvavg() calculates the moving average over a specified period of time. In this example, .mvavg(10) creates a moving average with a window of 10 data points.
timelion conditional03
Customize and format the visualizationedit
Customize and format the visualization using functions:
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.label('max memory')
.title('Memory consumption over time'),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.if(gt,
11300000000,
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
null)
.label('warning')
.color('#FFCC11')
.lines(width=5),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.if(gt,
11375000000,
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
null)
.label('severe')
.color('red')
.lines(width=5),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.mvavg(10)
.label('mvavg')
.lines(width=2)
.color(#5E5E5E)
.legend(columns=4, position=nw)
.label() adds custom labels to the visualization.
.title() adds a title with a meaningful name.
.color() changes the color of the data. Supported color types include standard color names, hexadecimal values, or a color schema for grouped data.
.lines() changes the appearance of the chart lines. In this example, .lines(width=5) sets border width to 5.
.legend() sets the position and style of the legend. For this example, (columns=4, position=nw) places the legend in the north west position of the visualization with four columns.
timelion conditional04
For additional information on Timelion conditional capabilities, go to I have but one .condition().
« TSVBMaps »
On this page
Before you begin
Create time series visualizations
Create visualizations with mathematical functions
Create visualizations with conditional logic and tracking trends
Most Popular
Intro to Kibana: Video
Deploy Hosted Elasticsearch & Kibana
Kibana Data Analyst - Virtual training
Kibana Guide:
What is Kibana?
Get started
Set Up Kibana
Discover
Visualize
Use rolled up data in a visualization
Supported aggregations
Lens
Most frequently used visualizations
TSVB
Timelion
Maps
Dashboard tools
Vega Graphs
Dashboard
Canvas
Graph data connections
Machine learning
Elastic Maps
Metrics
Logs
APM
Uptime
SIEM
Dev Tools
Stack Monitoring
Management
Reporting from Kibana
REST API
Kibana plugins
Limitations
Release Highlights
Breaking Changes
Release Notes
自定义可视化并设置其格式编辑
使用以下功能来自定义可视化并设置其格式:
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.label('max memory')
.title('Memory consumption over time'),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.if(gt,
11300000000,
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
null)
.label('warning')
.color('#FFCC11')
.lines(width=5),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.if(gt,
11375000000,
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes'),
null)
.label('severe')
.color('red')
.lines(width=5),
.es(index=metricbeat-*,
timefield='@timestamp',
metric='max:system.memory.actual.used.bytes')
.mvavg(10)
.label('mvavg')
.lines(width=2)
.color(#5E5E5E)
.legend(columns=4, position=nw)
1.label() 将自定义标签添加到可视化。
2.title() 添加具有有意义名称的标题。
3.color()更改数据的颜色。支持的颜色类型包括标准颜色名称,十六进制值或用于分组数据的颜色架构。
4.lines()更改图表线的外观。在此示例中,.lines(width = 5)将边框宽度设置为5。
5.legend()设置图例的位置和样式。对于此示例,(columns=4, position=nw)将图例放在具有四列的可视化的西北位置。

参考链接 :
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/timelion.html