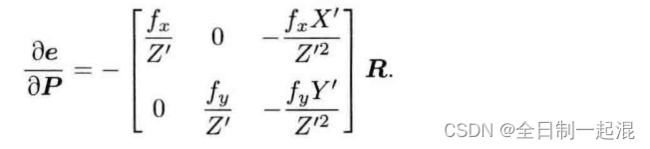手撕 视觉slam14讲 ch13 代码(7)后端优化 Backend::Optimize()
在上一篇 手撕(6)中的InsertKeyframe()插入关键帧的函数里,有一个 Backend::UpdateMap() 函数 ,从这里通过条件变量 map_update_ 来激活后端优化。
backend.h:
// * 有单独优化线程,在Map更新时启动优化
// * Map更新由前端触发
#ifndef MYSLAM_BACKEND_H
#define MYSLAM_BACKEND_H
#include "MYSLAM/common_include.h"
#include "MYSLAM/frame.h"
#include "MYSLAM/map.h"
namespace MYSLAM{
class Map;
// 后端
class Backend {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
typedef std::shared_ptr Ptr;//智能指针
/// 构造函数中启动优化线程并挂起
Backend();
// 设置左右目的相机,用于获得内外参
void SetCameras(Camera::Ptr left , Camera::Ptr right){
cam_left_=left;
cam_right_=right;
}
// 设置地图,让backend自己的地图指针指向当前的地图,而不是对当前地图进行修改,不需要锁
void SetMap(std::shared_ptr 后端在构造时,就构建了一个启动优化线程Backend::BackendLoop,并上锁,等待前端唤醒
// 构造函数 启动优化线程并挂起
Backend::Backend(){
// 创建一个线程,线程执行的函数是BackendLoop,并将this绑定到函数,
// 即这是this指向的类的成员函数
backend_running_.store(true);// 设置原子类型值
backend_thread_ = std::thread(std::bind(&Backend::BackendLoop, this));//上锁,唤醒一个wait的线程
}然后在前端的InsertKeyframe()插入关键帧的函数里,通过 Backend::UpdateMap() 函数 ,触发地图更新,启动优化:
// 触发地图更新,启动优化
void Backend::UpdateMap(){
std::unique_lock lock(data_mutex_);
map_update_.notify_one(); // 唤醒一个正在等待的线程
} 其中的条件变量 map_update_ 被激活,使得Backend::BackendLoop()函数解锁开始运行,分别获取激活关键帧和激活地图点,之后调用执行Optimize()函数执行优化:
// 后端线程
void Backend::BackendLoop(){
// load读取backend_running的值
// 实际上当后端在运行时,这是一个死循环函数,但是会等待前端的激活,即前端激活一次,就运行此函数,进行一次后端优化
while (backend_running_.load())// 读取原子类型值
{
std::unique_locklock(data_mutex_);
map_update_.wait(lock);//锁住当前线程
}
// 后端仅优化激活的Frames和mappoints
Map::KeyframesType active_kfs = map_->GetActiveKeyFrames(); // 获取激活关键帧
Map::LandmarksType active_landmarks =map_->GetActiveMapPoints(); // 获取激活地图点
Optimize(active_kfs,active_landmarks); //执行优化
} 优化函数:Backend::Optimize():
这里的优化流程 和前端的 EstimateCurrentPose() 函数有点类似,不同的地方是,在前端做这个优化的时候,只有一个顶点,也就是仅有化当前帧位姿这一个变量,因此边也都是一元边。
而在后端优化里面,局部地图中的所有关键帧位姿和地图点都是顶点,边也是二元边,在 g2o_types.h 文件中 class EdgeProjection 的 linearizeOplus()函数中,新增了一项 重投影误差对地图点的雅克比矩阵,见《视觉slam14讲》第二版 187页,公式(7.48)
优化流程依然:
- 步骤一: 创建线性方程求解器,确定分解方法
- 步骤二: 构造线性方程的矩阵块,并用上面定义的线性求解器初始化
- 步骤三: 创建总求解器 solver,并从 GN, LM, DogLeg 中选一个,再用上述块求解器 BlockSolver 初始化
- 步骤四: 创建稀疏优化器(SparseOptimizer)
- 步骤五: 自定义图的顶点和边,并添加到 SparseOptimizer 优化器中
- 步骤六: 设置优化参数,开始执行优化
- 步骤七: 使用卡方检查来剔除外点,同时调整阈值
- 步骤八:迭代优化完成之后,我们把优化估计的pose和地图点给关键帧,并把关键帧对应的异常特征去除,最后返回内点个数。
//后端优化函数
void Backend::Optimize(Map::KeyframesType &keyframes, Map::LandmarksType &landmarks){
// 设定g2o
typedef::g2o::BlockSolver_6_3 BlockSolverType;
typedef::g2o::LinearSolverCSparseLinearSolverType; //线性求解器类型
// 块求解器BlockSolver
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg (
g2o::make_unique( g2o::make_unique())); // 选择梯度下降法
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; //稀疏求解
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); //设置求解器
// vertex(优化量 顶点)
// pose 顶点 使用Keyframe id
std::mapvertices; // 定义了一个名为vertices的std::map,它的键是unsigned long类型,值是指向位姿VertexPose对象的指针。
unsigned long max_kf_id = 0;
// 遍历关键帧,确定第一个顶点
for(auto &keyframe : keyframes){
auto kf=keyframe.second;
VertexPose *vertex_pose=new VertexPose();
vertex_pose->setId(kf->keyframe_id_);// 定义节点编号
vertex_pose->setEstimate(kf->Pose());//设置初值
optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);//把节点添加到图中
if (kf->keyframe_id_>max_kf_id)
{
max_kf_id=kf->keyframe_id_;
}
vertices.insert({kf->keyframe_id_,vertex_pose});
}
// 路标顶点,使用路标id索引
std::map vertices_landmarks;
// 内参和左右外参
Mat33 K=cam_left_->K();
SE3 left_ext =cam_left_->pose();
SE3 right_ext =cam_right_->pose();
// edge边
int index =1 ;
double chi2_th = 5.991; // robust kernel 阈值
std::mapedges_and_features;
// 每一个landmark均需要建立一条边,所以landmark vertex的定义与edge的定义同步进行
// 遍历地图点,取出观测到该路标点的特征
for(auto &landmark : landmarks){
if (landmark.second->is_outlier_) //外点不优化
{
continue;
}
unsigned long landmark_id = landmark.second->id_; //路标点id
auto observations=landmark.second->GetObs();// 取出观测到该路标点的特征
// 再对特征进行遍历,得到该特征所处的帧
for(auto obs: observations){
if (obs.lock()=nullptr)
{
continue;
}
auto feat=obs.lock();
if (feat->is_outlier_ || feat->frame_.lock() ==nullptr)
{
continue;
}
auto frame=feat->frame_.lock();
EdgeProjection *edge=nullptr;
// 提供内参矩阵K,和初始化的初值
if (feat->is_on_left_image_)
{
edge=new EdgeProjection(K,left_ext);
}else
{
edge=new EdgeProjection(K,right_ext);
}
// 如果landmark还没有被加入优化,则新加一个顶点
if (vertices_landmarks.find(landmark_id) == vertices_landmarks.end())
{
VertexXYZ *v = new VertexXYZ;
v->setId(landmark_id + max_kf_id + 1);// 定义节点编号
v->setEstimate(landmark.second->Pos());//设置初值
v->setMarginalized(true); //边缘化
vertices_landmarks.insert({landmark_id, v});
optimizer.addVertex(v);//把节点添加到图中
}
// 设置edge的参数
edge->setId(index);
edge->setVertex(0,vertices.at(frame->keyframe_id_));// 设置连接的顶点:pose
edge->setVertex(1, vertices_landmarks.at(landmark_id)); // 设置连接的顶点:landmark
edge->setMeasurement(toVec2(feat->position_.pt));//传入观测值
edge->setInformation(Mat22::Identity());// 信息矩阵
//鲁棒核函数
auto rk =new g2o::RobustKernelHuber();
rk->setDelta(chi2_th);
edge->setRobustKernel(rk);
edges_and_features.insert({edge, feat});
optimizer.addEdge(edge);//把边添加到图中
index++;
}
}
// do optimization and eliminate the outliers
// 执行优化并去除外点
optimizer.initializeOptimization();// 设置优化初始值
optimizer.optimize(10);// 设置优化次数
//设置内点和外点数量
int cnt_outlier = 0, cnt_inlier = 0;
int iteration = 0;
while (iteration<5)
{
cnt_outlier = 0;
cnt_inlier = 0;
// 统计内点和外点
for(auto &ef : edges_and_features){
if (ef.first->chi2()>chi2_th)
{
cnt_outlier++;
}else{
cnt_inlier++;
}
}
//确保内点占1/2以上,否则调整阈值*2,直到迭代结束
double inlier_ratio = cnt_inlier/ double(cnt_inlier + cnt_outlier);
if (inlier_ratio>0.5)
{
break;
}else{
chi2_th *= 2;
iteration++;
}
}
// 记录是否为异常特征
for(auto &ef : edges_and_features){
if (ef.first->chi2()>chi2_th){
ef.second->is_outlier_=true; //记为为异常特征
// remove the observation
ef.second->map_point_.lock()->RemoveObservation(ef.second);
}else{
ef.second->is_outlier_=false;//记为为正常特征
}
}
LOG(INFO) << "Outlier/Inlier in optimization: " << cnt_outlier << "/"<< cnt_inlier;
// Set pose and lanrmark position
for(auto &v: vertices){
keyframes.at(v.first)->SetPose(v.second->estimate());
}
for (auto &v : vertices_landmarks) {
landmarks.at(v.first)->SetPos(v.second->estimate());
}
} 其中我们依然重点关注 步骤五 自定义的顶点和边
顶点(Vertex)
位姿顶点pose 和之前VertexPose的定义一样
// 位姿顶点
class VertexPose : public g2o::BaseVertex<6,SE3>{//优化量的参数模板
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
// 重置,设定被优化变量的原始值
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override
{
_estimate =SE3();
}
// 更新
virtual void oplusImpl(const double * update) override
{
Vec6 update_eigen;
update_eigen << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];
_estimate= SE3::exp(update_eigen) * _estimate; // 左乘更新 SE3 - 旋转矩阵R
}
// 存盘、读盘
virtual bool read(std::istream &in) override { return true; } //存盘
virtual bool write(std::ostream &out) const override { return true; } //读盘
};地图点顶点:
class VertexXYZ : public g2o::BaseVertex<3,Vec3>{//优化量的参数模板
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
// 重置,设定被优化变量的原始值
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override
{
_estimate =Vec3::Zero();
}
// 更新
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override
{
_estimate[0] += update[0];
_estimate[1] += update[1];
_estimate[2] += update[2];
}
// 存盘、读盘
virtual bool read(std::istream &in) override { return true; } //存盘
virtual bool write(std::ostream &out) const override { return true; } //读盘
};边(edge)
此时为包含地图的二元边,和一元边相比,新增了一项 重投影误差对地图点的雅克比矩阵_jacobianOplusXj,见《视觉slam14讲》第二版 187页,公式(7.48)
//包含地图的二元边
class EdgeProjection : public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<2,Vec2,VertexPose,VertexXYZ>{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
// 构造函数,构造时传入相机内外参
EdgeProjection(const SE3 &cam_ext, const Mat33 &K ): _cam_ext(cam_ext), _K(K) {}
// 计算雅克比矩阵
virtual void computeError() override {
const VertexPose *v0 = static_cast(_vertices[0]);
const VertexXYZ *v1 = static_cast(_vertices[1]);
SE3 T = v0->estimate();
Vec3 pos_pixel = _K * (_cam_ext * (T * v1->estimate())); //估计值:T*p,得到相机坐标系下坐标,然后在利用camera2pixel()函数得到像素坐标。
pos_pixel /= pos_pixel[2];
_error = _measurement - pos_pixel.head<2>();
}
// 计算雅克比矩阵
virtual void linearizeOplus() override{
const VertexPose *v0=static_cast(_vertices[0]);
const VertexXYZ *v1 = static_cast(_vertices[1]);
SE3 T = v0->estimate();
Vec3 pw=v1->estimate();
Vec3 pos_cam=_cam_ext*T*pw;
double fx = _K(0, 0);
double fy = _K(1, 1);
double X = pos_cam[0];
double Y = pos_cam[1];
double Z = pos_cam[2];
double Zinv = 1.0 / (Z + 1e-18);
double Zinv2 = Zinv * Zinv;
//2*6的雅克比矩阵
_jacobianOplusXi << -fx * Zinv, 0, fx * X * Zinv2, fx * X * Y * Zinv2,
-fx - fx * X * X * Zinv2, fx * Y * Zinv, 0, -fy * Zinv,
fy * Y * Zinv2, fy + fy * Y * Y * Zinv2, -fy * X * Y * Zinv2,
-fy * X * Zinv;
//P187 (7.48) 的雅克比矩阵
_jacobianOplusXj = _jacobianOplusXi.block<2, 3>(0, 0) *
_cam_ext.rotationMatrix() * T.rotationMatrix();
}
// 读操作
virtual bool read(std::istream &in) override { return true; }
// 写操作
virtual bool write(std::ostream &out) const override { return true; }
private:
SE3 _cam_ext;
Mat33 _K;
};