Linux中Shell脚本总结
巩固一下Linux的知识时发现Shell脚本比较生疏了,于是在这里进行总结一下以便在后面的学习中方便查阅(当然文章部分参考了网上的讲解,就在这里声明了)。
一、Linux中Shell脚本有四种执行方法
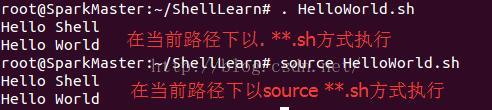
我在本机上的Home目录下新建了一个ShellLearn文件夹,利用vi编辑器写了一个HelloWorld.sh。路径为/root/ShellLearn,脚本内容为“Hello Shell Hello World”,如下所示:
方法一、以绝对路径执行bash shell脚本
/root/ShellLearn/HelloWorld.sh方法二、切换到shell脚本所在的目录执行shell脚本
cd /ShellLearn
./HelloWorld.sh方法三、直接使用bash或sh来执行bash shell脚本
cd /ShellLearn
bash HelloWorld.sh或
cd /ShellLearn
sh HelloWorld.sh方法四、在当前的shell环境中执行bash shell脚本
cd /ShellLearn
. HelloWorld.shcd /ShellLearn
source HelloWorld.sh二、变量的定义
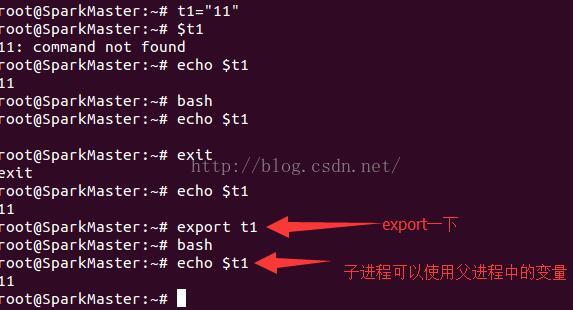
1、Shell脚本中定义的变量不论加不加引号均为String类型,定义变量时“=”两边不能有空格符,打印格式为“echo $变量名”;2、自己定义的变量具有一定的局部性,也就是说父进程中定义的变量只能在父进程中使用,子进程无法使用。若子进程需要使用父进程定义的变量,可采用export将父进程中定义的变量设置为环境变量,但这样定义的环境变量在命令窗口关闭或者系统重新启动就会丢失,所以要想使环境变量对所有用户都有效应该放置在/etc/profile文件中;
上述两种情况如下图所示:
三、Shell脚本常用的特殊变量
$# 是传给脚本的参数个数
$0 是脚本本身的名字
$1 是传递给该shell脚本的第一个参数
$2 是传递给该shell脚本的第二个参数
$@ 是传给脚本的所有参数的列表
$* 是以一个单字符串显示所有向脚本传递的参数,与位置变量不同,参数可超过9个
$$ 是脚本运行的当前进程ID号
$? 是显示最后命令的退出状态,0表示没有错误,其他表示有错误四、Shell函数
同C、C++编程语言一样,Shell函数的定义如下:
function fname()
{
shell脚本语句;
}vim functionDemo.sh
#定义一个函数fname
function fname(){
#输出第一个参数
echo $1
#输出函数所在文件名
echo $0
#输出所有参数
echo $@
}
#将函数中传入两个参数
fname "arg1" "args"
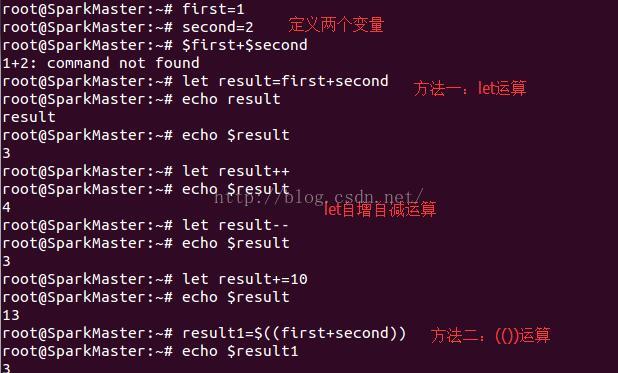
五、Shell命令中的基本运算
Linux Bash Shell命令行的变量都被解析成字符串,有三种方法可以进行基本的加减乘除运算:let、(())和[]
六、while、if、until和case控制语句的使用
1、while循环控制语句语法格式
while expression
do
command
command
done2、if判断语句语法格式
if 条件
then
Command
else
Command
#if条件判断的结束,用反拼表示
fi (1)判断字符串
1.if [ str1=str2 ];then fi ----当两个字符串相同时返回真
2.if [ str1!=str2 ];then fi ----当两个字符串不相等时返回真
3.if [ -n str1 ];then fi ----当字符串的长度大于0时返回真 (判断变量是否有值)
4.if [ -z str1 ];then fi ----当字符串的长度为0时返回真(2)判断数字
1.int1 -eq int2 --相等
2.int1 -ne int2 --不相等
3.int1 -gt int2 --大于
4.int1 -ge int2 --大于等于
5.int1 -lt int2 --小于
6.int1 -le int2 --小于等于1. -r file --用户可读为真
2. -w file --用户可写为真
3. -x file --用户可执行为真
4. -f file --文件存在且为正规文件为真
5. -d file --如果是存在目录为真
6. -c file --文件存在且为字符设备文件
7. -b file --文件存在且为块设备文件
8. -s file --文件大小为非0为真,可以判断文件是否为空
9. -e file --如果文件存在为真(4)判断逻辑
1. -a --与
2. -o --或
3. ! --非3、until循环控制语句语法格式
until condition
do
command
done应用举例,判断输入的数字与4的关系,如果不是4给出提示,相反如果是4则成功退出:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Please input the num (1-10): "
#接受用户输入
read num
while [[ $num != 4 ]]
do
#if语句,后面详细介绍,这里判断是否小于4
if [ $num -lt 4 ]
then
echo "Too small ,Try again.."
read num
#判断是否大于4
elif [ $num -gt 4 ]
then
echo "Too big ,Try again.. "
read num
else
exit 0
fi
done
echo ’Yes ,you are right !‘
应用举例,当变量i比2大时就退出循环:
#!/bin/bash
i=0
until [ $i -gt 2 ]
do
let i+=1
echo "i=$i"
done
4、case控制结构语法
case expression in
pattern1 )
statements ;;
pattern2 )
statements ;;
...
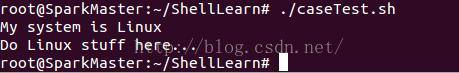
esac #!/bin/sh
#uname -s获取linux系统内核
SYSTEM=`uname -s`
case $SYSTEM in
Linux)
echo "My system is Linux"
echo "Do Linux stuff here..."
;;
FreeBSD)
echo "My system is FreeBSD"
echo "Do FreeBSD stuff here..."
;;
*)
echo "Unknown system : $SYSTEM"
echo "I don't what to do..."
;;
#case的反拼写法
esac
未完待续……