队列(Queue)概念+通过单、双链表来模拟队列+环形队列+OJ面试题(用队列实现栈、用栈实现队列、设计环形队列)
文章目录
- 队列(Queue)
-
- 一、 概念
-
- 1.尾进头出
- 二、模拟队列
-
- 1.单链表实现队列
-
- 1.1 设置结点
- 1.2 入队offer
- 1.3出队 poll
- 1.4 empty方法,peek方法,getUsedSize方法
- 2.双链表实现队列
-
- 2.1 创建结点
- 2.2 入队列
- 2.3 出队列
- 2.4 peek、size、isEmpty方法
- 三、环形队列
-
- 1. 环形队列一般用数组实现
- 2.判断数组是否满了的方法:
- 3.下标循环
- 4、双端队列(Deque)
- 四、队列的使用
- 五、OJ题
-
- 1.设计循环队列
-
- 1.1 思路
- 1.2 代码
- 2.用队列实现栈
-
- 2.1 思路
- 2.2 图解
- 2.1 代码
- 3.用栈实现队列
-
- 3.1 思路
- 3.2 图解
- 3.3 代码
队列(Queue)
一、 概念
- 与栈相反,队列就像食堂排队买饭一样,排好队后,第一个来的人,先买饭,后来的人后买,依次从队尾排到队头,离开的时候,买好饭的人从队头离开
- 或者可以这么理解:队列就是挤牙膏,出去的都是前面的,后面的挤向前面
- 队列和栈一样,可以使用数组实现也可以使用链表实现
1.尾进头出
- 队列只能在一段进行插入数据,在另一端进行删除的特殊线性表。
- 尾进头出 :先进先出,后进后出。
- 插入的一端叫队尾,删除的一端叫队头。
二、模拟队列
1.单链表实现队列
普通单链表:
加last结点
- 入队列: 头插法 o(1)
- 出队列:删除链表中的最后一个结点 o(n)
- 用last记录尾结点来改进:
- 入队:从尾结点插入 o(1)
- 出队:从头结点删除 o(1)
局限:只能从尾部插入,头部删除,但是双链表没有限制
1.1 设置结点
public class MyQueue {//单链表实现队列
static class Node {
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public int usedSize;
public Node Last;
public Node Head;
设置头尾结点,使用大小
1.2 入队offer
public void offer(int val) {//入队
Node node = new Node(val);
if (Head == null) {//当头结点为空时
Head = node;
Last = node;
} else {
Last.next = node;//尾插
Last = node;//Last后移
}
usedSize++;
}
当头结点为空时,头尾结点都是node
否则进行尾插法,List结点后移
1.3出队 poll
public int poll() {//出队
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
int val = Head.val;
Head = Head.next;
if (Head==null){
Last = null;//只剩一个结点
}
usedSize--;
return val;
}
1.判断是否为空
2.记录头结点的值
3.头结点后移一位,如果移位后的头结点为空,则Last也要置为空
4.返回记录的val
1.4 empty方法,peek方法,getUsedSize方法
public boolean empty() {
return usedSize == 0;
}
public int peek(){
if (empty()){
return -1;
}
return Head.val;
}
public int getUsedSize(){
return usedSize;
}
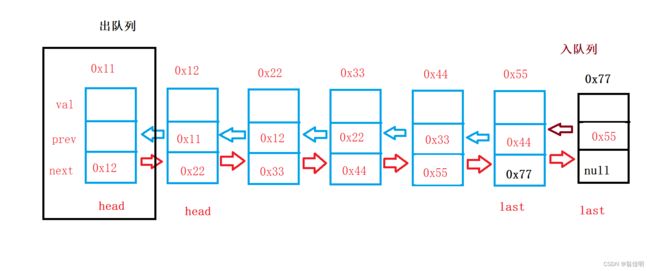
2.双链表实现队列
2.1 创建结点
public class MyQueue1 {
public static class ListNode {
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
int val;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
ListNode head;
ListNode last;
int size = 0;
创建头尾结点,构造方法,长度大小
2.2 入队列
public void offer(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
} else {
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
}
last = node;
size++;
}
当头结点为空的时候,头尾结点都是node
不为空,在尾部插入,尾结点后移,长度加一
2.3 出队列
public int poll() {
int val = 0;
if (head == null) {
return -1;
} else if (head == last) {
val = head.val;
head = null;
last = null;
} else {
val = head.val;
head = head.next;
head.prev.next = null;
head.prev = null;
}
size--;
return val;
}
val记录要返回的值
如果头结点为空,不能删除,返回-1
只有一个结点,取出val,头尾结点置空
否则,删除头结点,返回头结点的值,长度减一;
当然,也可以头结点入队,尾结点出队
2.4 peek、size、isEmpty方法
public int peek() {
if (head == null) {
return -1;
}
return head.val;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
同上
三、环形队列
1. 环形队列一般用数组实现
1.因为要循环的进入队列,我们把数组看成一个环形的结构
2.我们在进队时要考虑数组是否满了
2.判断数组是否满了的方法:
- 1.使用usedsize,每次进队出队改变usedsize的大小,当usedsize等于数组的长度时说明已经存满
- 2.使用标记,空的为false,判断要添加的位置是否为空,如果进队,标记为true,出队标记为false
- 3.牺牲一个空间,来表示已经存满,判断rear的下一个是不是front,是front证明满了
3.下标循环
- 牺牲一个空间,当rear的下一个是front时,来判断数组是否满了
- 如果此时头结点是元素出队,将89入队,此时rear应该移动到0下标,
- rear = (rear+1)%len :通过加一取余数组长度,完成数组索引的循环
- 当出队时,front从7下标移动到0小标:front = (front +1)%len
数组下标循环技巧
1.向后:下标 = (当前下标+要移动的距离)%数组长度
2.向前:小标 = (当前小标+数组长度-要移动的距离)%数组长度
4、双端队列(Deque)
双端队列:两端都能进出队列
deque 是 “double ended queue” 的简称
-
Deque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList对象
-
add和offer的区别:add在没有可用空间,无法插入元素时,会抛出一个异常
四、队列的使用
- Queue是一个接口,它的底层是通过链表实现的
- 方法:offer入队、poll出队、peek获取队头、size个数、isEmpty判断队列是否为空
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);//相当于尾插法
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
System.out.println(queue.size());
queue.poll();
System.out.println(queue.size());
System.out.println(queue);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();双链表实现双端队列
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();双链表实现普通队列
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>(); 链式栈
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();当链表使用
都是通过创建LinkedList对象实现,只不过实现了不同的接口
Deque<Integer> deque1 = new ArrayDeque<>();底层由数组实现的双端队列
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();双链表实现双端队列
Deque<Integer> stack1 = new ArrayDeque<>(); 双端队列实现顺序栈
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>(); 双链表实现链式栈
}
- Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkedList的对象,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
- 都是通过创建LinkedList对象实现,只不过实现了不同的接口
- ArrayDeque,数组实现的双端队列
五、OJ题
1.设计循环队列
1.1 思路
- 1.环形队列底层通过数组实现,设置队头和队尾
- 2.因为要牺牲一个数组的空间,来判断是否队列满了,所以在生成数组时+1
- 3.判断数组是否为满:看rear的下一个是不是front
- 4.入队:如果队列满了,返回false,否则存进当前队尾下标,队尾通过公式以循环的方式移动一位
- 5.出队:队尾=队头,说明队列为空,不能出队,否则让队头通过公式以循环的方式移动一位
1.2 代码
class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] elem;
private int front;//队头
private int rear;//队尾
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new int[k+1];
}
//入队
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
//1.检查队列是否已满
if (isFull()) {
return false;
} else {
elem[rear] = value;
rear = (1 + rear) % elem.length;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 出队
* @return
*/
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
} else {
front = (front + 1) % elem.length;
}
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}
public int Rear() {//获取队尾元素,rear前一个下标
if (isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
int index =(rear == 0)?elem.length-1:rear-1;//判断0->7的情况
return elem[index];
}
/**
* 判断是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
/**
* 判断队列是否为满
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
//判断队尾的下一个是不是队头
return (rear + 1) % elem.length == front;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/
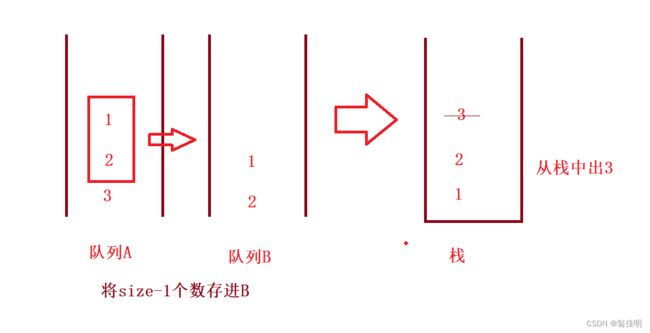
2.用队列实现栈
2.1 思路
- 栈是先进后出,队列是先进先出,一个队列无法实现,用两个队列实现
- 一个队列用来存储,一个队列为空
- 将size-1个数从不为空的队列取出,存到空队列中
- 原来队列中剩余的就相当于从栈中取出的,清空队列
- 存入的新队列的队尾,就相当于栈顶
- 如果继续从栈中出栈,再次size-1个数存进空队列
- 入栈:放进不为空的队列的队尾
2.2 图解
2.1 代码
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> qu1;
private Queue<Integer> qu2;
public MyStack() {
qu1 = new LinkedList<>();//初始化
qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if (!qu1.isEmpty()) {
qu1.offer(x);
} else if (!qu2.isEmpty()) {
qu2.offer(x);
} else {
qu1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
int data = 0;
if (empty()) {//两个队列都为空,当前栈为空,不能删元素
return -1;
}
if (!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int size = qu1.size();//size是不停变化的
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
int val = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(val);
}
return qu1.poll();//返回剩余的值
} else {
int size = qu2.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
int val = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(val);
}
return qu2.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int val = -1;
int size = qu1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
val = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(val);
}
return val;
} else {
int val = -1;
int size = qu2.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
val = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(val);
}
return val;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();
}
}
3.用栈实现队列
3.1 思路
- 一个栈实现不了,需要用两个栈实现队列
- 入队:存进第一个栈中
- 出队:如果第二个栈为空,将第一个栈的元素依次取出放进第二个栈,取出第二个栈的栈顶
- 如果第二个栈不为空,取出第二个栈的栈顶元素
3.2 图解
3.3 代码
class MyQueue2 {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue2() {//初始化
stack1 =new Stack<>();
stack2 =new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);//直接压入第一个栈
}
public int pop() {
if (empty()){//判断两个栈是否都为空
return -1;
}
int val = -1;
if (stack2.isEmpty()){//第二个栈为空时,将第一个栈依次取出存进第二个栈
int size = stack1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
val = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(val);
}
}
val = stack2.pop();//取出第二个栈的栈顶
return val;
}
public int peek() {//方法与pop一样,为简化写法、只是返回值不停
if (empty()){
return -1;
}
if (stack2.empty()){
while (!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {//返回两个栈都为空的情况
return stack2.isEmpty()&&stack1.isEmpty();
}
}
点击移步博客主页,欢迎光临~
![]()